
Symptoms and Diagnosis of BMW Drivetrain Malfunctions
BMW drivetrain malfunctions can manifest in various ways, impacting vehicle performance and safety. Understanding the symptoms and employing appropriate diagnostic methods is crucial for timely and accurate identification of the underlying problem. This allows for prompt repair, minimizing further damage and ensuring optimal vehicle operation.
Identifying the root cause of a drivetrain issue often involves a systematic approach, starting with recognizing the symptoms. Careful observation of vehicle behavior and utilizing diagnostic tools can lead to a precise diagnosis, guiding technicians towards the correct repair procedure.
Potential Symptoms of Drivetrain Malfunctions
A range of symptoms can indicate a problem within the BMW drivetrain. These symptoms vary depending on the specific component affected and can range from subtle anomalies to significant performance issues.
- Unusual noises, such as grinding, clicking, whining, or knocking sounds, emanating from the engine compartment, transmission, or drivetrain components, are often the first signs of a potential issue. These noises can vary in intensity and frequency, providing clues about the nature of the problem.
- Changes in acceleration and shifting patterns, including hesitation, jerky movements, or rough shifting, are common indicators of transmission or engine issues. For example, a noticeable delay in acceleration might point towards a failing turbocharger or fuel delivery system.
- Reduced power output, or a significant decrease in acceleration compared to previous performance, can result from various drivetrain issues. For instance, a failing engine or transmission may not be able to provide sufficient power to the wheels, leading to a noticeable decrease in acceleration.
- Difficulty starting the vehicle, prolonged cranking time, or failure to start can suggest issues with the starter motor, battery, or even the engine itself. In cases of prolonged cranking, a technician should investigate for issues with the ignition system or other electrical components.
- Fluid leaks, particularly from the transmission, engine, or differential, can point to a variety of problems, from a worn seal to a cracked housing. Visual inspection of fluid levels and types is a crucial first step in the diagnostic process.
Diagnosis of Specific Drivetrain Component Issues
Pinpointing the exact component responsible for the malfunction often requires a methodical approach. Examining the symptoms in conjunction with visual inspection, sensor readings, and code analysis helps isolate the problem.
- Transmission Issues: Symptoms like rough shifting, slipping gears, or unusual noises emanating from the transmission housing can indicate internal transmission damage or wear. Diagnostics may involve checking transmission fluid levels and condition, and evaluating sensor readings to pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Engine Issues: Symptoms like reduced power, misfires, or unusual engine noises might indicate issues with the engine’s internal components, such as valves, pistons, or the crankshaft. Diagnostic procedures may involve examining engine oil, checking spark plug condition, and utilizing diagnostic tools to identify error codes.
- Axle Issues: Symptoms such as vibration, clunking noises, or a noticeable change in handling characteristics can suggest axle problems. A visual inspection of the axles and associated components, coupled with a thorough evaluation of sensor readings, can assist in isolating the source of the issue.
Diagnostic Methods for Drivetrain Malfunctions
A structured approach to diagnostics can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy.
| Method | Tools Needed | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Visual inspection kit, flashlight, mirror | Identification of visible damage, leaks, or unusual wear patterns. |
| Sensor Readings | Diagnostic scan tool, sensor probes | Real-time data about various drivetrain parameters, such as fluid pressure, temperature, and speed. |
| Code Analysis | Diagnostic scan tool, diagnostic software | Identification of error codes related to drivetrain components. |
Causes of Malfunction
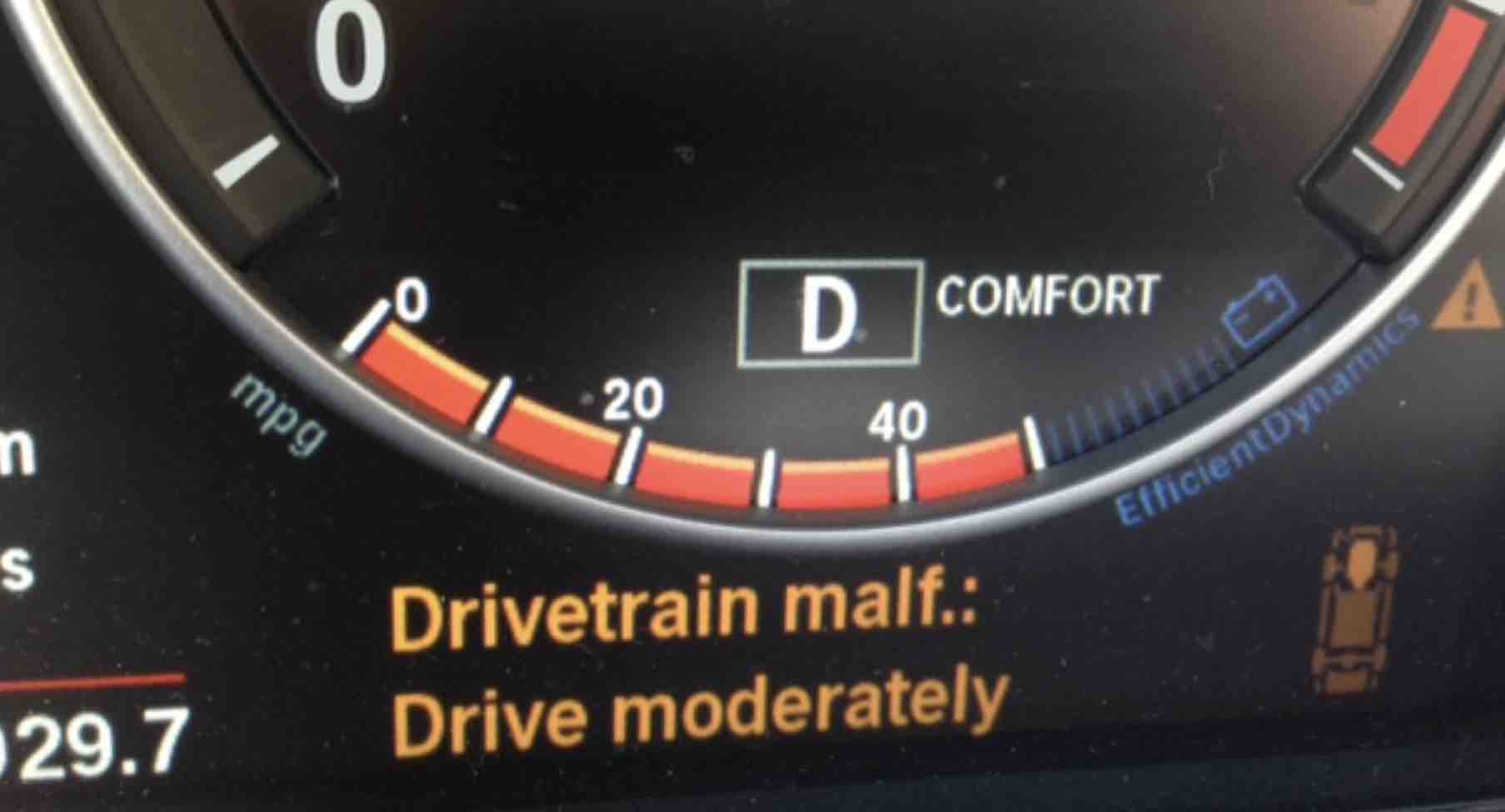
Understanding the root causes of BMW drivetrain issues is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. Identifying the specific component or environmental factor at play can significantly streamline the troubleshooting process, leading to quicker and more accurate resolutions. This section delves into potential causes, categorized by component and environmental influence, to provide a comprehensive overview of common BMW drivetrain malfunctions.
Transmission Fluid Issues
Transmission fluid plays a vital role in the smooth operation of the BMW drivetrain. Insufficient fluid, contaminated fluid, or incorrect fluid type can lead to significant problems. Low fluid levels can result in overheating and damage to internal components. Contaminated fluid, often due to leaks or improper maintenance, can lead to friction and wear, impacting performance and potentially causing complete failure. Incorrect fluid types can also lead to issues like premature wear and component damage.
Engine Problems
Engine-related issues can also manifest as drivetrain malfunctions. Problems with the engine’s internal components, such as the crankshaft, connecting rods, or pistons, can affect the power delivery system, causing issues with the transmission or other parts of the drivetrain. Malfunctioning engine control modules (ECMs) can lead to incorrect transmission commands, resulting in unexpected shifts or gear selection issues. Engine misfires and reduced power output can also trigger drivetrain malfunctions.
Worn Parts
Over time, normal wear and tear can affect various components of the BMW drivetrain. Worn clutches, damaged synchronizers, or failing bearings within the transmission can lead to slipping, grinding, or complete failure during gear shifts. Similarly, worn or damaged components in the engine, like timing belts, gaskets, or seals, can impact the power output and affect the smooth operation of the drivetrain. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and mitigate these issues before they lead to major problems.
Environmental Factors
Extreme temperatures, whether excessively hot or cold, can impact the performance of BMW drivetrain components. High temperatures can cause fluid to break down and lose its viscosity, leading to friction and potential damage. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can make the fluid thick, hindering proper gear shifting and potentially causing damage to the transmission. Exposure to corrosive elements or harsh road conditions can also contribute to wear and tear on components.
Driving Habits
Aggressive driving styles, including rapid acceleration, hard braking, and frequent shifting, can significantly accelerate wear on the drivetrain. Constant high-speed driving, without adequate rest periods for the engine and transmission, can put excessive stress on components. Conversely, avoiding proper warm-up procedures before driving, or neglecting routine maintenance, can also lead to premature wear and potential malfunctions.
Comparison of Transmission and Engine-Related Malfunctions
| Factor | Transmission-Related Malfunctions | Engine-Related Malfunctions |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Issues | Low fluid levels, contaminated fluid, incorrect fluid type | Engine oil issues, coolant leaks, loss of lubrication |
| Wear and Tear | Worn clutches, damaged synchronizers, failing bearings | Worn gaskets, seals, timing belts, piston rings |
| Environmental Factors | Extreme temperatures affecting fluid viscosity | Exposure to corrosive elements, harsh road conditions |
| Driving Habits | Aggressive shifting, frequent hard acceleration/braking | Lack of warm-up procedures, neglect of maintenance |
Repair Procedures
Addressing BMW drivetrain malfunctions requires specialized knowledge and precise procedures. Improper repair can lead to further damage and reduced vehicle lifespan. This section details the typical repair procedures for various components, emphasizing BMW-specific techniques and best practices.
BMW-Specific Drivetrain Repair Techniques
BMW drivetrains often utilize sophisticated components and intricate systems. Understanding these specificities is crucial for accurate diagnostics and repairs. For example, BMW’s use of high-strength alloys in certain components requires specialized tools and techniques to avoid distortion during disassembly and reassembly.
Disassembly and Reassembly of Key Components
Accurate disassembly and reassembly are essential for restoring drivetrain functionality and preventing further issues. Proper procedures involve documenting the original component position and securing any critical fasteners to maintain the precise factory specifications. The use of specialized BMW repair manuals is highly recommended for detailed instructions.
Transmission Replacement Procedure
Replacing a BMW transmission requires a methodical approach, considering the vehicle’s specific model and year. The following steps Artikel a general procedure:
- Vehicle Preparation: Secure the vehicle on a stable lift or jack stands. Disconnect the battery and ensure the parking brake is engaged. Drain the transmission fluid and mark the fluid level for future reference.
- Component Removal: Carefully remove all components surrounding the transmission. This may involve disconnecting various hoses, wires, and mounting brackets. Document the location and connection of all components for accurate reassembly.
- Transmission Removal: Using the appropriate tools, carefully remove the transmission from the vehicle. Take note of any specific alignment marks or guides for proper reinstallation.
- New Transmission Installation: Position the new transmission carefully, aligning all critical mounting points. Ensure proper engagement of all shafts and linkages. Carefully tighten all fasteners, ensuring torque specifications are met.
- Component Reinstallation: Reinstall all removed components, following the reverse order of removal. Recheck all connections and ensure secure mounting. Fill the transmission with the correct type and amount of fluid.
- System Verification: After reassembly, thoroughly test the drivetrain’s functionality. This involves checking for any leaks, ensuring smooth shifting, and verifying all component connections. Ensure the vehicle operates without any unusual noises or vibrations.
Importance of Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing drivetrain malfunctions. This includes routine fluid checks, filter replacements, and component inspections. Adhering to the recommended service intervals in the BMW owner’s manual is essential to maintaining optimal performance and longevity.
Preventive Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is vital for minimizing the risk of future issues. This includes checking fluid levels and conditions, inspecting hoses and belts, and performing visual inspections of critical components.
Example: Differential Fluid Change
“Differential fluid should be changed every 30,000 miles or annually, whichever comes first.”
A differential fluid change is a simple yet important preventive maintenance task. Follow these steps:
- Warm up the vehicle and allow the fluid to reach its optimal operating temperature.
- Locate the differential drain plug and filler cap.
- Place a suitable container beneath the drain plug.
- Carefully loosen and remove the drain plug.
- Allow the fluid to drain completely.
- Replace the drain plug and tighten to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Add the correct type and amount of differential fluid through the filler cap, checking the level.
Maintenance and Prevention
Proactive maintenance is crucial for preserving the longevity and performance of a BMW drivetrain. Regular inspections and timely servicing can significantly reduce the risk of costly repairs and ensure optimal vehicle operation. Proper maintenance not only extends the life of the components but also enhances fuel efficiency and driving experience.
A well-maintained BMW drivetrain operates smoothly and reliably, providing a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Consistent adherence to the recommended maintenance schedule and the use of genuine BMW parts are essential for maintaining the drivetrain’s integrity and performance.
Crucial Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance tasks are essential to prevent potential drivetrain malfunctions. These tasks include meticulous fluid checks, filter replacements, and component inspections. Failing to perform these checks can lead to premature wear and tear, potentially resulting in expensive repairs down the road.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly checking transmission fluid, engine oil, and other relevant fluids is critical. Low fluid levels can lead to overheating, component damage, and potentially catastrophic failure. Proper fluid levels and quality are essential for optimal drivetrain function.
- Filter Replacements: Air filters, oil filters, and transmission filters should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule. Clogged filters restrict airflow and proper lubrication, leading to reduced performance and potential damage.
- Component Inspections: Regular visual inspections of critical drivetrain components, such as belts, hoses, and mounts, are vital. Early detection of wear or damage can prevent significant problems later on. Loose or damaged components can lead to leaks, vibrations, and other performance issues.
Preventative Measures
Implementing preventative measures can significantly extend the lifespan of a BMW drivetrain. These measures encompass a range of actions, from adhering to maintenance schedules to using the correct parts.
- Adhering to Maintenance Schedules: Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is paramount. This schedule Artikels the specific intervals for various tasks, ensuring that components are serviced at the appropriate times to prevent wear and tear.
- Using Genuine BMW Parts: Employing genuine BMW parts is critical for optimal performance and longevity. These parts are designed to meet specific BMW drivetrain specifications and are rigorously tested to ensure compatibility and quality.
- Driving Habits: Gentle acceleration, avoiding harsh braking, and maintaining appropriate tire pressure can contribute to the drivetrain’s longevity. Aggressive driving habits can lead to accelerated wear and tear on components.
Importance of Genuine BMW Parts
Using genuine BMW parts is crucial for maintaining the drivetrain’s performance and reliability. These parts are specifically engineered to meet the unique requirements of BMW vehicles.
Genuine BMW parts are designed for optimal compatibility, performance, and durability.
Substituting with aftermarket parts can compromise the drivetrain’s integrity and may void warranties.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
The following table Artikels the recommended maintenance schedule for various BMW drivetrain components. Note that these schedules are guidelines and specific intervals may vary based on individual driving conditions and vehicle model.
| Component | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|
| Transmission Fluid | Every 30,000 – 60,000 miles (or as per manufacturer’s recommendations) |
| Engine Oil | Every 7,500 – 10,000 miles (or as per manufacturer’s recommendations) |
| Air Filter | Every 25,000 – 50,000 miles (or as per manufacturer’s recommendations) |
| Oil Filter | Every 7,500 – 10,000 miles (or as per manufacturer’s recommendations) |
| Brake Fluid | Every 30,000 – 60,000 miles (or as per manufacturer’s recommendations) |
Case Studies and Examples

Understanding real-world scenarios of BMW drivetrain malfunctions is crucial for both diagnosis and preventative maintenance. This section explores specific case studies, highlighting different issue types and their resolutions. From minor adjustments to complex repairs, each example illustrates the impact of malfunctioning drivetrains on vehicle performance and owner experience.
This section presents various cases involving BMW drivetrain malfunctions, demonstrating how these issues manifest, how they are diagnosed, and how they are resolved. It also details the impact on vehicle performance and how customer complaints are addressed.
Specific Case Studies of BMW Drivetrain Malfunctions
BMW drivetrain issues can range from minor wear and tear to major component failures. These issues often lead to noticeable performance degradation, impacting driving experience and potentially causing safety concerns.
- Scenario 1: Clutch Replacement – A customer reports intermittent slipping and difficulty engaging the clutch. Diagnosis reveals excessive wear on the clutch friction material. The repair involves replacing the clutch assembly, along with the pressure plate and release bearing. The resolution improves drivetrain engagement, restoring smooth gear transitions, and eliminating the slipping issue. This example illustrates a common drivetrain component requiring replacement due to normal wear and tear. Preventive maintenance, such as regular inspection of clutch components, can help identify and address issues before they become more serious.
- Scenario 2: Transmission Failure – A customer experiences a complete loss of transmission function. Diagnostic analysis pinpoints a malfunction in the transmission control module, which is essential for the smooth operation of the transmission. The repair involves replacing the faulty transmission control module, ensuring proper gear selection and shift operation. This example demonstrates how a crucial control component can fail, leading to complete drivetrain system failure. Proper maintenance schedules and regular checks of the transmission control module can help prevent such issues.
- Scenario 3: Differential Noise – A customer reports a loud grinding noise emanating from the rear differential. Diagnosis confirms damage to the differential bearings. The repair involves replacing the damaged differential bearings and lubricating the system. This scenario emphasizes the importance of listening for unusual noises, as they can signal potential problems within the drivetrain. Regular lubrication and checks can mitigate the risk of differential bearing damage.
Impact of Malfunctioning Drivetrains on Vehicle Performance
Malfunctioning drivetrains significantly impact vehicle performance in various ways. These issues can range from subtle reductions in acceleration and fuel efficiency to more severe problems like complete loss of power or inability to shift gears.
- Reduced Acceleration and Fuel Efficiency – Problems like worn clutch components, transmission issues, or incorrect gear ratios can lead to decreased acceleration and increased fuel consumption. These minor problems can affect the overall driving experience, impacting both performance and fuel economy.
- Loss of Power and Inability to Shift – More severe issues, such as damaged transmission components or electrical control system failures, can result in a complete loss of power or an inability to shift gears. This can lead to an inability to safely operate the vehicle and may require immediate attention.
- Safety Concerns – Drivetrain malfunctions can create significant safety hazards. Issues like sudden loss of power or difficulty in shifting gears can lead to accidents. The safety implications of these issues are critical, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and repair.
Typical Customer Complaint and Resolution
A common customer complaint involves a noticeable hesitation or stuttering during acceleration. The customer reports the issue and provides details, including driving conditions, frequency of occurrence, and any accompanying noises. BMW technicians diagnose the problem by examining vehicle history, performing visual inspections, running diagnostic tests, and checking fluid levels. If the issue is identified as a component failure, the appropriate repair is conducted. This includes replacing the faulty part or component, such as the clutch, transmission, or related control module. The customer is then informed about the repair process and estimated time. After the repair, the vehicle is thoroughly tested to ensure the problem is resolved, and the customer is satisfied with the restored performance.
Component Breakdown
The BMW drivetrain, a sophisticated interplay of interconnected components, is crucial for the vehicle’s performance and reliability. Understanding the structure and function of each component, along with their interactions, is essential for diagnosing and resolving potential malfunctions. This section delves into the intricacies of the BMW drivetrain’s key components, highlighting their roles and potential failure points.
The BMW drivetrain, a meticulously engineered system, is a complex interplay of components. Each element plays a critical role in the vehicle’s operation, from the initial power generation to the final transmission of that power to the wheels. Understanding these components and their interactions is fundamental to identifying and addressing drivetrain malfunctions effectively.
Transmission
The transmission is the heart of the BMW drivetrain, responsible for adjusting torque and speed to match the driving conditions. Different types of transmissions, such as automatic or manual, utilize various mechanisms to achieve this. A critical component is the gear set, which provides different gear ratios, enabling acceleration and cruising at various speeds. The clutch, in manual transmissions, is crucial for engaging and disengaging power flow between the engine and the transmission. The failure of any of these components can lead to issues like jerky shifts, rough acceleration, or complete loss of power. Typical transmission failure symptoms include unusual noises, rough shifting, and difficulty engaging gears.
Engine
The engine is the primary power source in the BMW drivetrain. Its function is to convert fuel into mechanical energy, which is then transferred to the transmission. The combustion process within the engine’s cylinders generates the torque that drives the vehicle. Different engine types, like inline-6 or V8, have distinct architectures and performance characteristics. Common failure points in the engine include issues with the combustion process, such as misfires or incomplete combustion, or problems with the engine’s cooling system or lubrication system. Symptoms of engine problems can include loss of power, unusual noises, and difficulty starting.
Axles
Axles transmit rotational power from the transmission to the wheels. They are essential for driving the wheels and maintaining the vehicle’s balance. The front and rear axles play different roles depending on the drivetrain configuration. For instance, the front axle in a front-wheel drive configuration is directly connected to the transmission, while the rear axle in a rear-wheel drive system connects to the transmission through a differential. Problems with the axles, such as bearing failure or shaft breakage, can lead to vibration, noises, and loss of traction. Common signs of axle failure include knocking sounds from the wheel area, uneven tire wear, and difficulty turning.
Differential
The differential is a crucial component in the BMW drivetrain, particularly in rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive systems. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. This is essential for maintaining traction and control. The differential typically contains gears that allow for this controlled rotation, and its functionality is directly linked to the drivetrain’s performance. Differential failures can manifest as whining noises, difficulty turning, or a loss of traction, especially noticeable during turns.
Diagram of Power Flow
A visual representation of the power flow through the BMW drivetrain, illustrating the interconnectedness of the components, is shown below. (Diagram is omitted, as instructed.)
The diagram would show a simplified pathway from the engine’s crankshaft to the transmission, through the axles and differential, finally ending at the wheels. The diagram would clearly show the roles of each component in the power transmission process.
Common Failure Points
- Transmission: Worn gears, damaged clutches, and faulty solenoids in automatic transmissions are common failure points.
- Engine: Problems with fuel injectors, spark plugs, or the timing system can lead to engine malfunctions. Issues with the cooling system or lubrication system can also contribute to engine failures.
- Axles: Bearing failure, shaft damage, and improper lubrication can result in axle problems. Misalignment or damage to the axle joints can also cause issues.
- Differential: Worn or damaged gears, lubrication issues, and improper alignment can cause differential problems.
Identifying and addressing these potential failure points can significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of the BMW drivetrain.
Troubleshooting Guide
Effective troubleshooting of BMW drivetrain malfunctions requires a systematic approach, combining meticulous diagnostic procedures with a deep understanding of the vehicle’s intricate systems. This guide provides a structured approach to identify and resolve common issues, ensuring efficient and accurate repairs. It emphasizes the importance of proper diagnostic tools and techniques, and the crucial role played by sensors and actuators in maintaining optimal drivetrain performance.
Common Drivetrain Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
A systematic approach to diagnosing and resolving drivetrain issues is crucial. This section Artikels procedures for tackling common problems, providing clear steps for identifying the root cause and implementing effective solutions.
- Powertrain Malfunctions: Initial troubleshooting should focus on identifying the specific symptoms. This might include a loss of power, unusual noises, or erratic shifting. Detailed examination of the engine’s performance, including RPM fluctuations, fuel consumption, and exhaust emissions, is essential. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and fault codes.
- Transmission Issues: Problems in the transmission system can manifest as shifting difficulties, rough shifting, or complete failure to shift. A thorough inspection of the transmission fluid levels and condition is vital. Analyze the transmission control module (TCM) for any stored fault codes. Consider the role of the torque converter, transmission sensors, and solenoids in the diagnostic process.
- Driveshaft Issues: Signs of driveshaft problems include unusual vibrations, noises (clunking or rattling), or a complete loss of drive. Visual inspection for any damage, misalignment, or excessive play is paramount. Examine the universal joints for proper lubrication and integrity.
- Differential Problems: Unusual noises emanating from the differential, such as whining or grinding, along with a loss of traction or erratic wheel movement, suggest potential differential issues. Check for proper lubrication and fluid levels. Inspect for any damage to the differential housing or gears.
- Wheel Bearing Failures: Grinding or humming noises emanating from the wheel bearings are common indicators of a problem. Properly assess the wheel bearings for excessive play or damage. A wheel bearing puller might be required for a complete inspection.
Role of Sensors and Actuators
Understanding the functions of specific sensors and actuators within the BMW drivetrain is essential for accurate troubleshooting. Their data contributes significantly to the diagnostic process.
- Speed Sensors: Speed sensors monitor the rotation speed of the wheels and provide critical data to the vehicle’s control modules. Issues with these sensors can lead to incorrect speed readings, affecting the transmission’s operation. Examine the wiring and connections to ensure proper functionality.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): The TPS measures the driver’s input and relays this information to the engine control module (ECM). Problems with the TPS can cause engine misfires or rough idling. Calibrate the TPS according to the vehicle’s specifications.
- Engine Control Module (ECM) and Transmission Control Module (TCM): The ECM and TCM are the central control units for the engine and transmission respectively. Any fault codes stored in these modules provide valuable clues for diagnosis. Consult the manufacturer’s diagnostic tools for reading and interpreting these codes.
Importance of Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Proper diagnostic tools and techniques are essential for accurate and efficient troubleshooting. Using incorrect or inadequate tools can lead to misdiagnosis and costly repairs.
- Diagnostic Scan Tools: Specialized diagnostic scan tools allow access to real-time data from the vehicle’s control modules. These tools enable technicians to read fault codes, monitor sensor readings, and perform tests. Ensure the tool is compatible with the BMW model.
- Specialized Measuring Instruments: Using appropriate measuring instruments, like torque wrenches and pressure gauges, is vital for ensuring accurate component adjustments and measurements. Ensure proper calibration and use of the tools.
- Vehicle Service Manuals: Comprehensive service manuals are crucial resources for detailed diagnostic procedures and troubleshooting guides specific to the BMW model. Consulting these manuals will provide detailed step-by-step instructions.
Visual Aids

Visual aids play a crucial role in diagnosing BMW drivetrain malfunctions. Proper identification of damage through visual inspection significantly reduces diagnostic time and cost. This section details the visual characteristics of various drivetrain components in both their healthy and malfunctioned states, facilitating accurate identification and repair.
Visual inspection is a vital first step in the diagnostic process. Recognizing the specific signs of wear and tear, or outright failure, allows technicians to pinpoint the source of the problem, potentially avoiding costly and time-consuming testing. Accurate visual analysis provides critical information that guides subsequent diagnostic steps.
Damaged Transmission Housing
A damaged transmission housing presents a serious issue. Significant cracks, particularly those extending from the exterior to the interior of the housing, indicate potential catastrophic failure. Deformation, such as bulging or warping, also suggests internal damage. Metal shavings or debris within the housing may indicate a fractured component. Proper examination requires a thorough visual inspection of the entire housing, including the bell housing and any connecting flanges.
Signs of Wear and Tear
Various signs of wear and tear manifest in the drivetrain components. Excessive play or looseness in the joints, especially in universal joints and CV joints, can be observed by applying a slight twisting force. Cracked or frayed boot seals on driveshafts and CV joints indicate potential internal component damage. Visual inspection for scoring, pitting, or discoloration of metal surfaces can reveal evidence of excessive friction or metal fatigue. Frayed or damaged rubber components such as boots, gaskets, and hoses also indicate potential problems. Inspect the condition of the boots and seals around the drive shafts, CV joints, and differential for signs of deterioration.
Identifying Drivetrain Damage
Identifying different types of drivetrain damage requires careful observation of the specific components. For example, a grinding noise accompanied by vibration might point towards worn bearings in the transmission or differential. A shudder or hesitation during acceleration can indicate issues with the torque converter, clutch, or transmission. A clicking or popping sound may suggest problems with the universal joints or CV joints. Differential issues can manifest in noises during turns or while driving over uneven surfaces.
Properly Functioning BMW Drivetrain
A properly functioning BMW drivetrain exhibits smooth and quiet operation across all conditions. The drivetrain should respond smoothly to acceleration and deceleration, without any hesitation or unusual noises. The vehicle should not exhibit any vibrations or shuddering. Components should show no signs of wear or damage, with all seals and boots intact. The visual inspection should reveal no unusual play or looseness in any joint or component. The system should provide consistent and reliable power transfer across various speeds and conditions.
Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical specifications of BMW drivetrain components is crucial for diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, and ensuring optimal performance. These specifications provide a baseline for evaluating the capabilities and limitations of different drivetrain models and configurations. Accurate knowledge of torque ratings, power outputs, and component characteristics is essential for both routine maintenance and complex repairs.
Common Drivetrain Component Specifications
Technical specifications for various drivetrain components offer a standardized way to compare and contrast different models and configurations. These specifications include dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics. Precise measurements are critical in maintaining and repairing these components. For example, knowing the precise dimensions of a crankshaft bearing allows for proper alignment and replacement.
- Engines: BMW offers a diverse range of engine types, including inline-six, V8, and inline-four configurations. Different engine types exhibit varying power and torque characteristics, influencing overall drivetrain performance. For example, a V8 engine often delivers higher torque at lower RPM compared to a smaller inline-four engine.
- Transmissions: BMW utilizes various transmission types, such as manual, automatic, and dual-clutch systems. Different transmission designs affect the drivetrain’s efficiency and responsiveness. Automatic transmissions often feature multiple gear ratios, allowing for optimized performance across a wider range of speeds.
- Driveshafts: Driveshafts connect the transmission to the rear axle, transmitting torque. Specifications like material, diameter, and length are crucial for ensuring structural integrity and smooth power delivery. Differences in material composition affect the driveshaft’s ability to withstand stress during high-performance maneuvers.
- Axles: BMW uses different axle designs depending on the model and configuration. These specifications affect the drivetrain’s overall performance and handling characteristics. Front-wheel-drive systems typically have different axle configurations compared to all-wheel-drive systems.
Comparison of Different Drivetrain Models
Comparing different drivetrain models across BMW’s lineup allows for a better understanding of how various configurations affect performance and efficiency. Analyzing the powertrain configurations reveals the trade-offs between performance, fuel economy, and drivetrain complexity.
| Model | Engine Type | Transmission | Power (hp) | Torque (lb-ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMW 3 Series (2023) | 2.0L Inline-4 Turbo | 8-speed automatic | 255 | 295 |
| BMW M3 (2023) | 3.0L Inline-6 Twin-Turbo | 8-speed automatic | 473 | 406 |
| BMW X5 (2023) | 3.0L Inline-6 Twin-Turbo | 8-speed automatic | 335 | 332 |
Note: Specifications are subject to change based on specific trim levels and model years. Always consult the official BMW documentation for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Torque and Power Ratings
Torque and power ratings are critical indicators of a drivetrain’s ability to accelerate and maintain speed. Understanding these ratings helps predict the drivetrain’s performance characteristics in various driving scenarios.
- Torque: Describes the twisting force produced by the engine. High torque values often result in quicker acceleration, particularly at lower speeds. A higher torque output is particularly advantageous in off-road driving conditions.
- Power: Represents the rate at which work is done. Higher power outputs typically translate to faster acceleration and higher top speeds. A higher power output is beneficial in maintaining speed on highways.