
Identifying Common Drivetrain Malfunctions in BMWs

BMWs are renowned for their powerful and sophisticated drivetrain systems, but like any complex mechanical assembly, they can experience malfunctions. Understanding these common issues and their symptoms is crucial for proactive maintenance and avoiding costly repairs. This information provides a comprehensive overview of potential drivetrain problems, categorized by vehicle type, to aid in diagnosis and preventative measures.
Common Drivetrain Issues in BMW Sports Cars
BMW sports cars, often featuring powerful engines and sophisticated transmissions, are prone to specific drivetrain issues. These issues often stem from the high performance demands and the intricate interplay of components.
| Malfunction Type | Symptoms | Potential Causes | Affected BMW Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission Problems (e.g., slipping, harsh shifts, rough engagement) | Difficulty shifting gears, hesitation or shuddering during acceleration, unusual noises from the transmission, and/or erratic performance. Potential error codes may indicate a malfunctioning torque converter, damaged clutches, or a faulty valve body. | Worn transmission fluid, damaged clutches, faulty solenoids, or issues with the valve body within the transmission. Overuse, inadequate maintenance, or aggressive driving can accelerate wear. Incorrect fluid type or improper fluid levels also contribute. | M3, M4, M5, Z4, and some 3-Series and 4-Series models. |
| Engine Misfires or Loss of Power | Intermittent or consistent loss of power, rough idling, and/or sputtering or surging during acceleration. Error codes related to oxygen sensors, fuel injectors, or spark plugs may be present. | Faulty spark plugs, misfiring cylinders, issues with the ignition system, or a malfunctioning fuel injector. Improper fuel quality or a clogged fuel filter can also contribute to engine misfires. | M3, M4, M5, M6, and many high-performance models. |
| Drivetrain Noise (e.g., whining, clicking, or knocking sounds) | Unusual noises emanating from the drivetrain, especially noticeable during acceleration, deceleration, or gear changes. The noise can be localized to the transmission, differential, or other components. | Worn or damaged bearings, seals, or bushings within the drivetrain components. Loose or damaged drive shafts, and/or worn universal joints can also contribute to drivetrain noise. | All high-performance models, including the M-series. |
Common Drivetrain Issues in BMW SUVs
BMW SUVs, while often robust, can also experience drivetrain problems, although these issues often differ from those in sports cars.
| Malfunction Type | Symptoms | Potential Causes | Affected BMW Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission Problems (e.g., slipping, harsh shifts, rough engagement) | Difficulty shifting gears, hesitation or shuddering during acceleration, unusual noises from the transmission, and/or erratic performance. Potential error codes may indicate a malfunctioning torque converter, damaged clutches, or a faulty valve body. | Worn transmission fluid, damaged clutches, faulty solenoids, or issues with the valve body within the transmission. Overuse, inadequate maintenance, or aggressive driving can accelerate wear. Incorrect fluid type or improper fluid levels also contribute. | X5, X6, X7, and some X3 and X4 models. |
| All-Wheel Drive System Malfunctions | Loss of all-wheel drive functionality, unusual noises from the all-wheel drive system, or erratic traction control. Error codes related to the all-wheel drive system components may be present. | Malfunctioning sensors, wiring issues, or damaged components within the all-wheel drive system. Improper maintenance or component wear can also contribute to malfunctions. | X5, X6, X7, and models with all-wheel drive systems. |
| Transfer Case Issues | Difficulty engaging or disengaging four-wheel drive, unusual noises, and/or loss of four-wheel drive functionality. | Worn or damaged components within the transfer case, including seals, bearings, and gears. Inadequate maintenance or excessive use of four-wheel drive can exacerbate these issues. | X5, X6, and X7 models. |
Troubleshooting BMW Drivetrain Problems
Diagnosing drivetrain issues in BMWs requires a systematic approach, combining technical knowledge with specialized tools and procedures. Proper diagnosis ensures accurate identification of the fault, minimizing unnecessary repairs and maximizing efficiency. This section details common diagnostic procedures, highlighting key steps and considerations for isolating and resolving drivetrain malfunctions.
Effective troubleshooting involves a deep understanding of BMW drivetrain systems and the specific components that can cause problems. This includes knowledge of how various sensors, actuators, and control modules interact to manage the vehicle’s powertrain. It also necessitates familiarity with the specific characteristics and symptoms associated with different drivetrain malfunctions.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
BMW drivetrain diagnostics often begin with a thorough inspection of the vehicle’s systems. This includes checking fluid levels, listening for unusual noises, and visually inspecting for any obvious damage or wear. A systematic approach is critical to isolating the source of the problem. Detailed records of observed symptoms, such as the nature of the malfunction (e.g., slipping, grinding, or jerking), are essential for accurate diagnosis. These records should include the specific conditions under which the issue occurs (e.g., temperature, load, speed).
Component Inspection and Testing
Thorough component inspection is a crucial step in isolating the problem area. This involves inspecting various components, including the transmission, differential, driveshaft, and related parts. Checking for wear, damage, and proper lubrication is essential. Testing involves utilizing specialized tools to evaluate the performance of sensors, actuators, and control modules. This can include checking sensor readings, testing actuator functionality, and reviewing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The inspection should cover electrical connections and wiring harnesses to identify potential issues with the control systems.
Diagnostic Tools
Various diagnostic tools are used in the process. Specialized BMW diagnostic tools provide access to the vehicle’s onboard computer systems, allowing technicians to retrieve DTCs, view sensor data, and perform tests. Basic diagnostic tools, such as multimeters and oscilloscopes, are also essential for checking voltage, current, and signal integrity in the electrical systems. Modern BMW vehicles often require specialized software and interfaces to access their complex electronic control units.
Troubleshooting Transmission Slipping
Troubleshooting a transmission slipping issue involves a systematic approach. The following steps provide a guide:
- Gather Information: Document the specific conditions under which the slipping occurs (e.g., speed, load, temperature). Note any associated symptoms (e.g., noise, vibration, harsh shifts). Recording DTCs is crucial.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the transmission fluid level and condition. Check for any obvious damage to the transmission housing or related components.
- Check Fluid Pressure: Measure transmission fluid pressure to ensure it’s within the specified range. Low or fluctuating pressure can indicate internal issues.
- Examine Transmission Control Module (TCM): Verify the TCM is functioning correctly by reviewing stored data and performing specific tests. A faulty TCM can cause slipping issues.
- Analyze Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Review any DTCs present in the vehicle’s computer system. DTCs can provide valuable clues about the source of the problem.
- Transmission Component Testing: Use specialized tools to test components such as solenoids, clutches, and gears. This may involve physical checks or electrical measurements.
- Check the Clutch Pack: Inspect the clutch pack for wear, damage, or debris that might be causing slipping. This often requires disassembly and inspection.
Diagnostic Procedures Overview
This table Artikels common diagnostic procedures, tools, and potential issues related to BMW drivetrain malfunctions.
| Diagnostic Procedure | Tools Used | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Visual inspection | Fluid leaks, damaged components, worn parts |
| Fluid Level Check | Dipstick, measuring tools | Low fluid level, contaminated fluid |
| DTC Retrieval | BMW diagnostic software | Malfunctioning sensors, control modules |
| Component Testing | Multimeter, oscilloscope, specialized BMW tools | Faulty actuators, sensors, or wiring |
Repair and Maintenance Recommendations
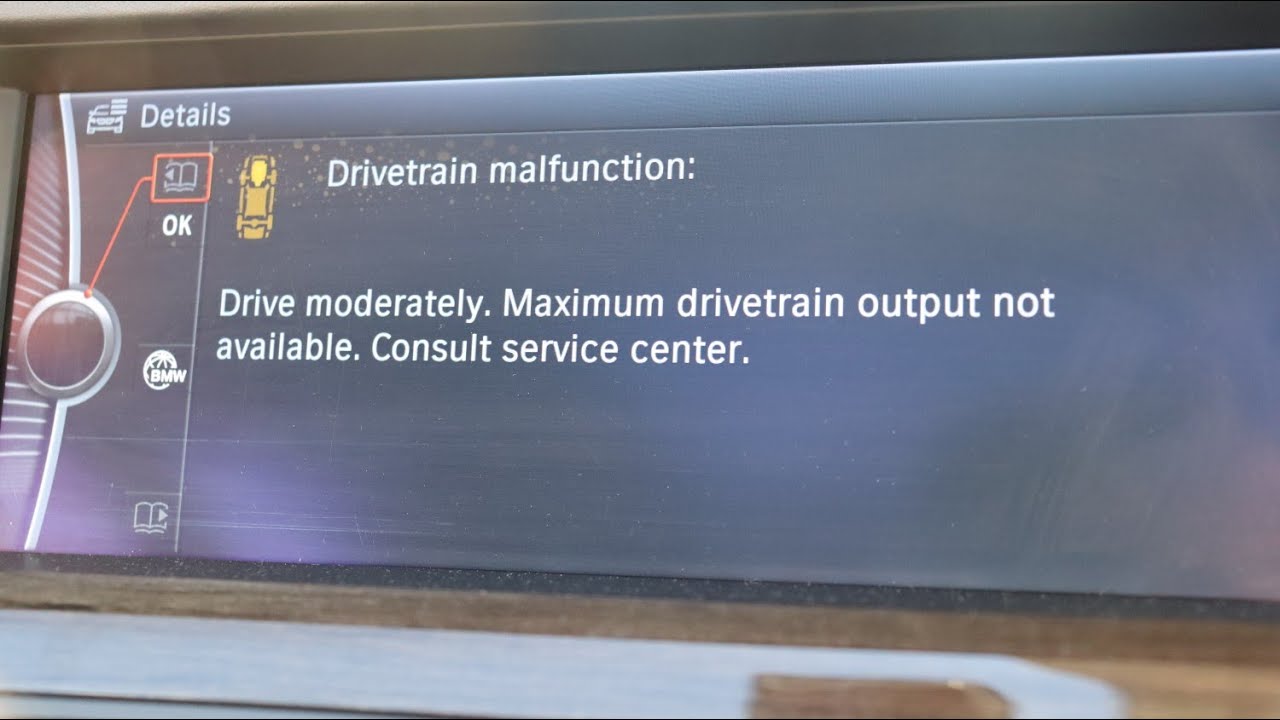
Proactive maintenance is crucial for preventing costly drivetrain repairs in BMWs. A well-maintained drivetrain not only extends the lifespan of your vehicle but also ensures optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Ignoring routine maintenance can lead to significant issues, potentially requiring extensive and expensive repairs down the line.
Proper maintenance is more than just keeping your BMW running; it’s about preserving its value and reliability. This section details preventative maintenance procedures, highlighting the importance of scheduled services and specific tasks to maintain a healthy drivetrain. By understanding and implementing these recommendations, you can avoid costly and time-consuming repairs.
Preventative Maintenance Strategies
A well-maintained drivetrain is a reliable drivetrain. Scheduled maintenance plays a critical role in preventing potential issues. This involves more than just checking fluids; it encompasses a range of tasks designed to ensure each component functions optimally.
Importance of Scheduled Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including scheduled services, is essential for maintaining the health and longevity of your BMW’s drivetrain. This proactive approach allows technicians to address minor issues before they escalate into major problems, saving you money and preventing potential breakdowns. Specific attention should be paid to critical drivetrain components during each scheduled service.
Specific Drivetrain Component Maintenance
Regular inspections and replacements of crucial components are paramount for maintaining optimal drivetrain function. This includes examining and replacing parts like the transmission fluid, differential fluid, and various filters. Maintaining proper fluid levels and cleanliness is vital for preventing premature wear and tear.
Preventative Maintenance Tasks
Preventative maintenance tasks are essential for preventing malfunctions. These tasks often involve checking fluid levels, inspecting hoses and belts, and replacing filters. These seemingly small tasks can significantly impact the long-term health of the drivetrain. Examples include:
- Fluid Checks: Regularly check transmission fluid, differential fluid, and engine oil levels. Use the manufacturer’s recommended specifications for correct levels and types. Low or contaminated fluids can cause significant damage.
- Filter Replacements: Replace air filters, fuel filters, and oil filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clogged filters restrict airflow and reduce fuel efficiency, impacting engine performance and potentially leading to drivetrain issues.
- Belt and Hose Inspections: Visually inspect drive belts and hoses for cracks, wear, or damage. Early detection and replacement of damaged components can prevent catastrophic failures.
- Component Inspections: Inspect drive shafts, universal joints, and other components for signs of wear or damage. This proactive approach helps prevent premature failure and potential accidents.
Repair Procedures for Common Problems
Addressing drivetrain issues promptly is crucial to minimize potential damage and repair costs. The repair procedures often vary based on the specific problem. Common repairs may involve replacing damaged components, repairing or replacing fluid lines, and adjusting or repairing sensors. Professional diagnostics are essential to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
A structured maintenance schedule is essential for proactively addressing potential issues. This schedule should be adhered to, ensuring that each critical component receives the necessary attention.
| Component | Frequency | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Fluid | Every 30,000-50,000 miles | Check level and condition. Replace as needed, following manufacturer specifications. |
| Differential Fluid | Every 60,000-80,000 miles | Check level and condition. Replace as needed, following manufacturer specifications. |
| Air Filter | Every 15,000-30,000 miles | Replace with a genuine BMW part. |
| Fuel Filter | Every 30,000-60,000 miles | Replace with a genuine BMW part. |
| Oil Filter | Every oil change | Replace with a genuine BMW part. |
Understanding the Impact of Driving Conditions

Driving a BMW, or any vehicle, is intrinsically linked to the environment. Different driving conditions can significantly affect drivetrain performance, longevity, and even the likelihood of malfunctions. Understanding these nuances is crucial for preventative maintenance and optimal vehicle operation. Factors such as extreme temperatures, aggressive driving styles, and specific road surfaces all contribute to the overall stress placed on the drivetrain components.
Extreme Temperatures
Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can significantly impact the performance and reliability of a BMW’s drivetrain. High temperatures can cause components like lubricants to thin out, reducing their protective qualities and leading to increased wear and tear. This is especially problematic in automatic transmissions, where heat buildup can impact fluid viscosity and cause overheating. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can lead to reduced engine efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and potential gear slippage in manual transmissions due to reduced lubrication and component stiffness. This can affect responsiveness and overall drivetrain performance.
Aggressive Driving
Aggressive driving styles place immense stress on the drivetrain components. Rapid acceleration, hard braking, and high-speed cornering all increase the load on the engine, transmission, and axles. Constant high-stress situations can accelerate wear and tear, potentially leading to premature failure of components like clutch plates, bearings, and even drive shafts. The constant strain from rapid acceleration and deceleration can lead to significant wear and tear on various parts of the drivetrain, potentially shortening its lifespan.
Road Surfaces and Weather Conditions
The type of road surface and weather conditions can also significantly impact drivetrain performance. Driving on poorly maintained roads, gravel, or uneven surfaces can increase stress on suspension components and the drivetrain itself, causing increased wear and tear on parts such as the axles and differential. Similarly, driving in heavy rain or snow can lead to reduced traction, requiring the drivetrain to work harder, increasing the load on the engine and transmission. This can result in potential overheating or damage. Potholes and other road imperfections can also lead to significant shock loads, causing stress and wear on the suspension and drivetrain components.
Influence of Driving Style on Drivetrain Longevity
Driving style directly correlates with the lifespan of a vehicle’s drivetrain. Consistent aggressive driving will significantly reduce drivetrain longevity compared to a smooth, controlled driving style. The table below illustrates the impact of different driving styles on drivetrain components.
| Driving Style | Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Gentle and Controlled | Minimizes wear and tear on drivetrain components, prolongs their lifespan. | Smooth acceleration and deceleration, avoiding sudden stops and starts. |
| Aggressive | Accelerates wear and tear, leading to potential premature failure of drivetrain components. | Rapid acceleration, hard braking, high-speed cornering, frequent use of high RPMs. |
| Routine Maintenance | Crucial for overall drivetrain health. Regular servicing ensures components operate optimally. | Oil changes, fluid checks, component inspections. |
Historical Context of Drivetrain Issues in BMW
BMW’s reputation for performance and engineering excellence often overshadows the historical challenges its drivetrain technologies have faced. While BMW has consistently pushed the boundaries of automotive innovation, a deeper understanding of past issues reveals valuable insights into the evolution of its systems and the ongoing pursuit of reliability. From early mechanical complexities to the complexities of modern electronics, the company’s journey reflects the continuous improvements and learning processes inherent in automotive development.
Early BMW models, particularly those relying on naturally aspirated engines, often experienced issues related to component wear and tear, especially under demanding driving conditions. The transition to turbocharging and more complex systems brought new challenges, including potential issues with turbocharger longevity, exhaust system failures, and intricate cooling systems. These issues, while not widespread, highlighted the increasing complexity of modern drivetrains and the need for robust engineering solutions.
Evolution of BMW Drivetrain Technologies
BMW’s evolution in drivetrain technology is marked by a progressive shift from traditional mechanical systems to increasingly sophisticated electronic controls. Early models focused on high-performance internal combustion engines, while later models integrated features like variable valve timing, advanced fuel injection systems, and sophisticated transmissions. This progression, while delivering improved performance, also introduced new potential points of failure and required increased attention to component integration and reliability.
Common Drivetrain Problems Across BMW Models
Several recurring drivetrain issues have been observed across various BMW models throughout their history. These issues often manifested as specific problems with particular components, such as transmission failures in certain models, clutch issues, or turbocharger failures. The nature and frequency of these problems varied depending on the model year, engine type, and driving conditions. This demonstrates the importance of accurate diagnostics and timely maintenance in mitigating these issues.
Factors Contributing to Historical Issues
Several factors contributed to the historical drivetrain problems in BMW models. Complex engineering designs, demanding performance targets, and tight manufacturing tolerances often resulted in heightened stress on components, leading to increased failure rates in some instances. Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological advancements sometimes outstripped the ability to thoroughly test and validate new systems. This highlights the ongoing tension between innovation and reliability in automotive engineering.
Timeline of BMW Drivetrain Advancements
The advancements in BMW drivetrain technology over time significantly influenced reliability and performance.
1970s-1980s: Early turbocharging and fuel injection systems. Increased complexity introduced challenges related to component durability and integration. 1990s: Advancements in transmission technology, including more sophisticated gear ratios and electronic controls. Reliability increased, but potential for electronic component failures emerged. 2000s-2010s: Increased use of electronic control units (ECUs) and sophisticated software controls. Drivetrains became highly integrated, leading to increased complexity but also enhanced performance and fuel efficiency. Early instances of software bugs and component failures emerged. 2010s-Present: Hybrid and electric vehicle technologies are increasingly integrated into BMW's lineup. Challenges related to battery technology, charging infrastructure, and integrating electric motors with existing systems.
Cost Estimation for Repair and Replacement
Estimating the cost of repairing or replacing drivetrain components in BMWs is complex, varying significantly based on the specific model, the component needing attention, and the extent of the damage. Factors like labor rates, part availability, and the complexity of the repair all play crucial roles in determining the final price tag. Understanding these variables is essential for making informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs.
Accurate cost estimations require careful consideration of individual circumstances. While general ranges can be provided, the actual cost for a particular BMW owner will depend on the specific vehicle, the exact issue, and the repair shop’s pricing structure. Detailed diagnostics and assessments are vital to determining the appropriate repair strategy.
General Cost Ranges for Drivetrain Repairs
BMW drivetrain repairs can span a wide price spectrum, influenced by factors such as the severity of the issue, the specific components involved, and the chosen repair facility. Minor repairs like a clutch replacement in a mid-range BMW model might cost between $1,500 and $3,000, including parts and labor. Major repairs, such as a transmission overhaul, can easily exceed $5,000 and could reach $10,000 or more, especially in higher-end models with complex systems.
Comparison of Repair Costs Across BMW Models
Different BMW models have varying complexities in their drivetrain systems. A basic repair on a 3 Series might be significantly less expensive than a comparable repair on an M3 due to the more advanced engineering and components used. Older models may have lower repair costs due to more readily available parts and less sophisticated systems. However, the labor hours needed for a repair on a vintage model could increase the overall cost.
Factors Influencing Repair Costs
Several key factors influence the overall cost of a drivetrain repair. Part availability is crucial. Rare or specialized parts can dramatically increase the cost. Labor rates at different repair shops also play a major role, with some facilities charging more than others for their services. The complexity of the repair itself is another major factor. A straightforward replacement might cost less than a complex repair involving multiple components.
Potential Cost of Replacing a Complete Drivetrain System
Replacing an entire drivetrain system is a significant undertaking and often comes with a substantial price tag. For example, replacing the complete transmission and drivetrain assembly in a high-performance BMW M model could exceed $20,000. This figure would likely include specialized parts, complex labor procedures, and the cost of any necessary diagnostic equipment. The cost can fluctuate significantly based on the particular model and the specific components involved.
Comparative Cost Analysis of Repair Options
| Repair Option | Estimated Cost (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Clutch Replacement | $1,500 – $3,000 | Replacing the clutch assembly in a mid-range model. |
| Transmission Fluid Change | $500 – $1,000 | Changing transmission fluid and filter. |
| Transmission Overhaul | $5,000 – $10,000+ | Repairing or replacing major transmission components. |
| Complete Drivetrain Replacement | $15,000 – $25,000+ | Replacing the entire drivetrain assembly. |
Note: These are estimated costs and may vary depending on specific vehicle models, repair shop locations, and individual circumstances.