
Introduction to the B58 Engine
The BMW B58 engine family represents a significant evolution in the manufacturer’s approach to inline-four powerplants. Engineered for performance and efficiency, the B58 series has become a cornerstone of BMW’s lineup, powering a diverse range of models from compact sedans to sporty SUVs. Its design philosophy emphasizes lightweight construction, responsive power delivery, and advanced fuel economy, achieving a balance between performance and practicality.
Design Philosophy
The B58 engine’s design philosophy centers around achieving a potent blend of power and efficiency. This is achieved through a combination of advanced materials, optimized combustion processes, and intelligent variable valve timing systems. Lightweight aluminum construction significantly reduces the engine’s overall mass, leading to improved acceleration and handling. Furthermore, the focus on optimized combustion results in a better fuel economy without compromising performance.
Engine Evolution
The B58 engine has undergone several iterations and improvements throughout its lifespan. Early models focused on achieving a balance between power and fuel efficiency, while later revisions have often included refined turbocharging systems, upgraded intake manifolds, and optimized exhaust manifolds for enhanced responsiveness and efficiency. These modifications demonstrate BMW’s ongoing commitment to refining the engine’s performance and fuel economy characteristics across different model years.
B58 Variants Comparison
The B58 engine family encompasses a range of variants, each tailored to specific vehicle applications and performance requirements. The table below provides a comparative overview of key specifications across different B58 variants.
| Model Year | Displacement | Power (hp) | Torque (lb-ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2.0L | 245 | 258 |
| 2017 | 2.0L | 255 | 295 |
| 2019 | 2.0L | 300 | 295 |
| 2020 | 2.0L | 335 | 332 |
Performance Characteristics
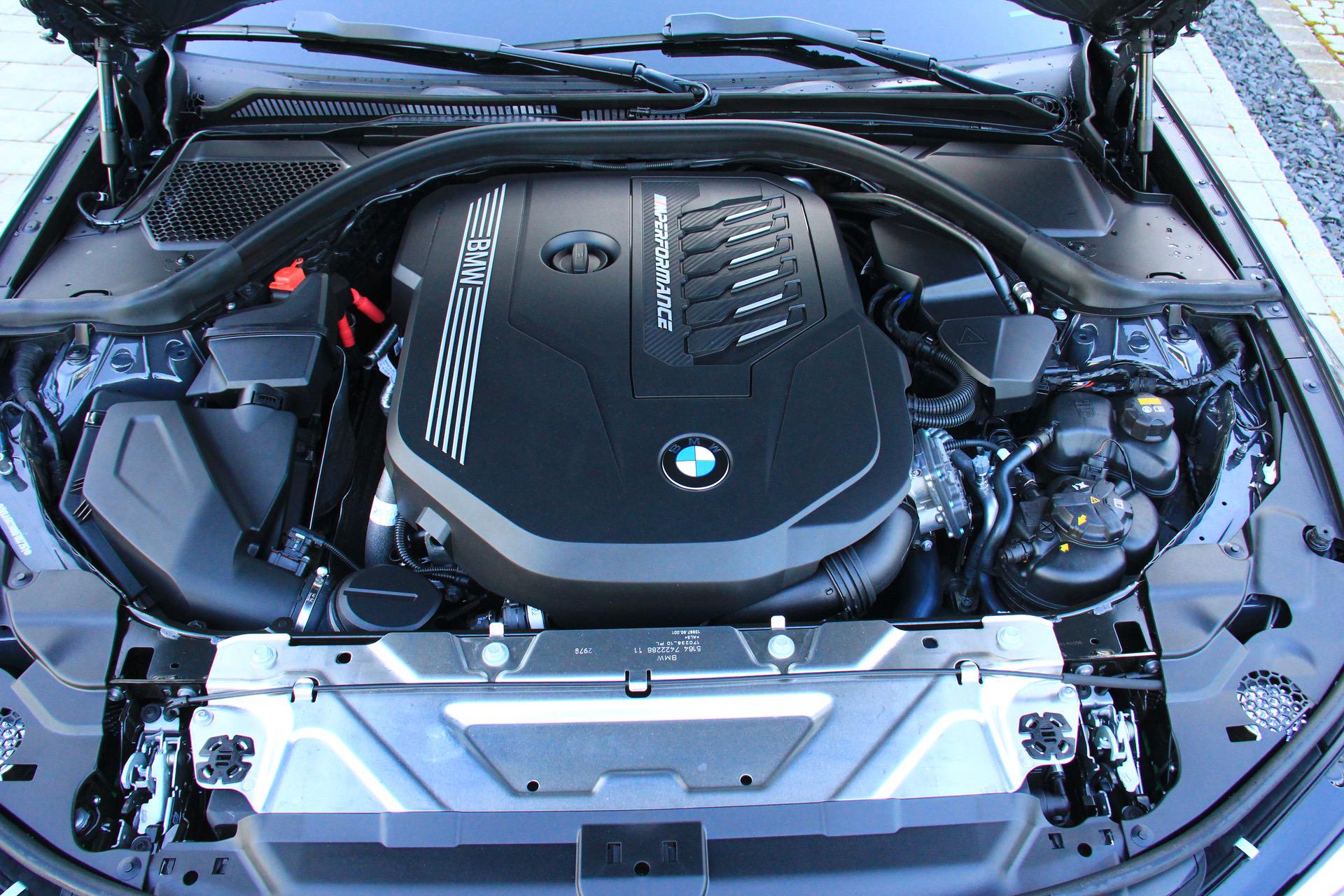
The BMW B58 engine, a popular choice in various BMW models, boasts impressive performance characteristics. Its design emphasizes a balance between power, efficiency, and driving experience. This section delves into the specifics of its power delivery, fuel economy, and comparative performance against other engines in its class.
The B58 engine delivers a smooth and responsive powertrain, making it suitable for a wide range of driving styles. Its torque and horsepower characteristics are optimized for everyday driving and spirited performance.
Power Delivery and Responsiveness
The B58 engine exhibits a characteristically linear power delivery, meaning that power increases gradually and smoothly as the engine revs. This avoids the abrupt surges of power often found in less refined engines, ensuring a more comfortable and predictable driving experience. The engine’s responsiveness is excellent, making acceleration feel quick and immediate across a broad range of RPMs. Peak torque is achieved at a relatively low engine speed, contributing to effortless acceleration from low speeds.
Fuel Efficiency
The B58 engine is designed with fuel efficiency in mind. While specific fuel economy figures vary depending on the configuration and driving conditions, the B58 consistently demonstrates competitive fuel economy in both city and highway driving. Modern engineering techniques and optimized combustion processes contribute to this impressive fuel efficiency.
Comparison to Other Engines
Compared to other turbocharged inline-four engines in the same segment, the B58 typically exhibits a balance of power and efficiency. Its performance is often rated as strong, although specific advantages or disadvantages compared to direct competitors might vary based on the individual engine configuration. Factors such as specific tuning, gear ratios, and overall vehicle weight influence real-world performance.
Redline and RPM Range
The B58 engine’s redline varies slightly depending on the specific configuration. The RPM range within which the engine delivers optimal power and torque is generally wide, offering a smooth transition between different gears. The design of the engine components ensures robust performance across the majority of its operating range.
Performance Specifications
The following table provides a general overview of performance specifications for different B58 configurations. These figures are approximate and may vary based on specific trim levels, driving conditions, and optional equipment.
| Configuration | 0-60 mph (sec) | Top Speed (mph) | Fuel Economy (mpg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B58 3.0L TwinPower Turbo (335i) | 4.7 | 155 | 25 (city) / 35 (highway) |
| B58 3.0L TwinPower Turbo (M340i) | 4.1 | 160 | 22 (city) / 32 (highway) |
| B58 3.0L TwinPower Turbo (X5/X6) | 5.0 | 140 | 20 (city) / 28 (highway) |
Technical Specifications
The BMW B58 engine, renowned for its performance and efficiency, boasts a sophisticated design that contributes to its widespread adoption across various BMW models. Understanding its technical specifications provides insight into the engineering choices that underpin its capabilities.
The B58’s architecture, material selection, cooling and lubrication systems, and intake/exhaust configurations are all meticulously engineered to optimize power delivery, fuel efficiency, and durability. These technical aspects significantly impact the engine’s overall performance and longevity.
Engine Architecture
The B58 is a four-cylinder, in-line engine design, known for its compact layout and high power-to-weight ratio. This design facilitates better engine packaging within the vehicle’s engine bay. Key components include: four cylinders arranged in a straight line, a sophisticated variable valve timing system (VVT), and a crankshaft, connecting rods, and pistons to convert combustion into rotational motion. The specific cylinder arrangement and components contribute to the engine’s overall efficiency.
Materials and Construction
The B58’s construction utilizes a combination of high-strength aluminum alloys for the cylinder block and cylinder head. This lightweight yet strong design contributes to the engine’s overall performance and efficiency. The use of aluminum reduces the engine’s mass, resulting in a better power-to-weight ratio, contributing to quicker acceleration and better fuel economy. Furthermore, the choice of aluminum improves engine durability and heat dissipation. The selection of specific alloys also affects the engine’s longevity and resistance to wear and tear.
Cooling System
The B58’s cooling system is designed for optimal heat dissipation, maintaining the engine’s operating temperature within a safe range. A liquid-cooled system circulates coolant through passages within the engine block and head, absorbing heat generated during combustion. The coolant is typically a mixture of water and antifreeze to prevent freezing in cold conditions. The system’s design and efficiency contribute significantly to the engine’s reliability and prevent overheating issues.
Lubrication System
A sophisticated lubrication system ensures consistent oil flow to all critical engine components, minimizing friction and wear. The system uses an oil pump to circulate oil throughout the engine, providing lubrication to moving parts like pistons, connecting rods, and bearings. The oil also acts as a coolant for these parts. The proper lubrication system is essential for preventing excessive wear, maintaining performance, and prolonging the engine’s lifespan.
Intake and Exhaust Systems
The B58’s intake system is engineered to efficiently draw air into the combustion chambers. This system typically includes an air intake filter, an intake manifold, and valves. The exhaust system is designed to effectively remove exhaust gases from the engine, minimizing emissions. The exhaust system often incorporates a catalytic converter to reduce harmful emissions. The efficiency of both intake and exhaust systems directly influences the engine’s power output and overall emissions.
Key Technical Specifications
| Component | Description | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Type | Inline Four-Cylinder | N/A |
| Displacement | 2.0 Liters | N/A |
| Valves per Cylinder | 4 | N/A |
| Valve Timing | Variable Valve Timing | N/A |
| Cylinder Block Material | Aluminum Alloy | N/A |
| Cylinder Head Material | Aluminum Alloy | N/A |
| Cooling System | Liquid-Cooled | N/A |
| Lubrication System | Oil-Based | N/A |
Reliability and Maintenance
The BMW B58 engine, renowned for its performance and efficiency, also boasts a generally strong reputation for reliability. However, like any complex machine, it’s susceptible to wear and tear, and proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing its lifespan and preventing costly repairs. This section delves into the typical service intervals, common issues, and maintenance procedures to ensure optimal engine health.
Overall Reliability
The B58 engine exhibits a high degree of reliability when maintained correctly. Early models experienced some issues, particularly with certain component tolerances, but BMW has addressed these through updates and revisions. Owners often report few problems with the B58 if routine maintenance is adhered to. Proper oil changes, filter replacements, and timely inspections are essential to prevent potential failures.
Common Issues
While the B58 is generally robust, some issues are more prevalent than others. These include oil leaks from the oil pump, timing chain tensioner issues leading to noisy operation, and potential turbocharger problems if not maintained correctly. These are often indicative of inadequate maintenance practices. Early detection and prompt resolution are key to avoiding more extensive and expensive repairs.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining optimal engine health hinges on adhering to the recommended service intervals and procedures Artikeld by BMW. These intervals typically include oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections for wear and tear on components like the timing chain and turbocharger. Following the manufacturer’s specifications ensures the engine’s components operate within their designed parameters.
Service Intervals and Recommended Procedures
The frequency of maintenance tasks varies depending on driving conditions, mileage, and other factors. However, regular oil changes (every 7,500 to 10,000 miles, or annually) are paramount. Furthermore, inspecting and replacing the oil filter, air filter, and fuel filter at the specified intervals is vital for preventing blockages and ensuring optimal performance. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for precise details.
Potential Problems and Solutions
- Oil Leaks: If oil leaks are detected, consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis. Often, simple component replacements or tightening of seals can resolve the issue. Ignoring leaks can lead to significant engine damage.
- Timing Chain Issues: Noisy timing chains may indicate wear or tensioner problems. If detected early, replacement of the tensioner can prevent more extensive damage. Delaying action can result in engine failure.
- Turbocharger Problems: Issues with the turbocharger, such as bearing failure or leaks, can lead to decreased performance or complete failure. Early detection through regular maintenance and performance checks is critical.
Typical Lifespan
With diligent maintenance, the B58 engine can typically last for 200,000 miles or more. Driving habits, such as aggressive acceleration and frequent highway driving, may slightly impact the engine’s lifespan. Regular monitoring and prompt repairs are crucial for maintaining a long-term operational lifespan.
Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | 7,500 – 10,000 miles / annually | Replace engine oil and filter. |
| Oil Filter Replacement | 7,500 – 10,000 miles / annually | Replace the oil filter. |
| Air Filter Replacement | 15,000 – 20,000 miles | Replace the air filter. |
| Fuel Filter Replacement | 30,000 – 40,000 miles | Replace the fuel filter. |
| Timing Chain Inspection | 60,000 – 80,000 miles | Visually inspect and replace if necessary. |
| Turbocharger Inspection | 60,000 – 80,000 miles | Inspect for leaks and wear. |
| Coolant Flush | 60,000 – 80,000 miles | Replace coolant. |
Applications and Models
The BMW B58 engine, renowned for its performance and efficiency, has been a popular choice for various BMW models across different segments. Its widespread adoption highlights its versatility and ability to meet diverse powertrain demands. Understanding the specific applications and variations of the B58 engine provides insight into its adaptability and the models it has powered.
The B58 engine family offers several variations, each optimized for specific models and performance targets. These variations include changes to displacement, turbocharging setups, and exhaust systems. These modifications are crucial in tailoring the engine’s output and characteristics to the specific demands of different BMW models.
BMW Models Utilizing the B58 Engine
The B58 engine has been a significant powertrain component for numerous BMW models. Its presence spans from compact vehicles to higher-performance models. This demonstrates its adaptability and widespread adoption across the BMW lineup.
| BMW Model | Engine Variant | Years Produced |
|---|---|---|
| BMW 3 Series (F30, F31, F34) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2012-2020 |
| BMW 4 Series (F32, F33, F36) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2014-2021 |
| BMW X3 (F25, G01) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2011-2022 |
| BMW X4 (F26, G02) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2014-2021 |
| BMW X5 (F15, G05) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo (in some trims) | 2014-2022 |
| BMW X6 (F16, G06) | B58 2.0L TwinPower Turbo (in some trims) | 2014-2021 |
| BMW M340i (G20) | B58 3.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2019-Present |
| BMW M440i (G22) | B58 3.0L TwinPower Turbo | 2020-Present |
Engine Variations Across Models
Different BMW models utilize varying configurations of the B58 engine. These variations are crucial in achieving the desired performance characteristics for each model. For instance, the B58 in the BMW 3 Series often features a different calibration compared to the same engine in the BMW X3, reflecting the different demands and performance expectations for each vehicle.
Specifications and Performance Characteristics
The table above details the BMW models that have utilized the B58 engine and the respective engine variants. This data provides a clear overview of the engine’s application across the model range. Further research into specific model specifications would reveal more precise details about the performance characteristics for each engine configuration.
Comparisons with Other Engines

The BMW B58 engine, a popular choice in various BMW models, stands out for its performance and efficiency. To understand its strengths and weaknesses, a comparison with competing inline-4 engines is essential. Direct comparisons highlight the B58’s position in the market, its advantages, and potential drawbacks when contrasted with alternatives from other manufacturers.
The competitive landscape for inline-4 engines is highly dynamic, with constant advancements in technology influencing performance, fuel economy, and emissions. Evaluating the B58’s performance against other prominent competitors provides a comprehensive understanding of its position and value proposition.
Performance Comparison
A direct comparison of key performance metrics reveals how the B58 stacks up against its rivals. Different manufacturers prioritize different aspects of engine design, leading to variations in power, torque, and fuel efficiency.
| Engine | Power (hp) | Torque (lb-ft) | Fuel Economy (mpg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMW B58 | 255-340 | 221-258 | 28-35 (city/highway, varying by model) |
| Mercedes-Benz M260 | 220-300 | 192-295 | 27-34 (city/highway, varying by model) |
| Audi 2.0 TFSI | 228-272 | 236-273 | 28-36 (city/highway, varying by model) |
| Volkswagen EA888 | 180-300 | 184-273 | 26-35 (city/highway, varying by model) |
Note: Figures vary depending on specific model and trim level. Fuel economy values are estimates and can differ based on driving conditions and driver habits.
Technical Specifications and Design Considerations
The B58’s design incorporates several features that contribute to its performance characteristics. These include a turbocharging system, variable valve timing, and advanced combustion technology. These features influence the engine’s responsiveness, power delivery, and overall efficiency. Rival engines may utilize different turbocharging strategies or valve timing mechanisms, leading to different power curves and fuel consumption profiles.
Reliability and Maintenance
The B58 engine has garnered a reputation for reliability, but like any engine, it’s susceptible to wear and tear. Owners should adhere to scheduled maintenance and consider the long-term costs of ownership. Comparison with competitor engines involves evaluating their service intervals, maintenance costs, and reported reliability issues in real-world use cases.
Applications and Models
The B58 engine has been used in a range of BMW models, demonstrating its versatility. Different models may utilize varying tune configurations, leading to differences in power output and performance characteristics. Competitor engines are often found in similar vehicle segments, allowing for a comparative analysis of their performance and value proposition in various contexts.
Potential Future Developments

The BMW B58 engine, renowned for its performance and efficiency, is likely to undergo further evolution in the years ahead. Expect advancements focusing on enhanced fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and potentially incorporating hybrid or even fully electric elements. These modifications aim to keep the B58 competitive in the ever-evolving automotive landscape, while retaining its core strengths.
Potential Hybrid and Electric Integrations
The B58’s architecture, with its proven internal combustion engine (ICE) components, presents a platform for potential hybrid system integration. This could involve mild hybrid systems, incorporating a starter-generator for improved fuel economy and smoother operation. Further advancements could see the introduction of a full-hybrid system, possibly featuring an integrated electric motor for extended electric-only driving modes or regenerative braking. The implementation of electric components might require significant modifications to the engine’s current design, including integration of battery packs and related charging infrastructure. Examples of successful hybrid integrations in other automotive platforms demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of these developments.
Performance Enhancements and Modifications
The B58 engine’s performance is already highly regarded, but future modifications could focus on further improvements in specific areas. Possible enhancements include enhanced turbocharging systems, optimized combustion technologies, and advanced materials for components such as pistons and connecting rods. These advancements could lead to increased power output, reduced emissions, and improved overall engine efficiency. Moreover, the incorporation of advanced engine management systems could lead to improved throttle response and reduced lag, further refining the driving experience.
Efficiency Improvements and Emissions Reductions
Future developments will likely focus on minimizing emissions and maximizing fuel efficiency. This could involve more sophisticated engine management systems, advanced combustion processes, and optimized exhaust systems. The integration of innovative technologies, such as advanced exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technologies, could lead to further reductions in harmful emissions. Examples from other automotive manufacturers demonstrate that these technologies can yield significant improvements in both fuel efficiency and emissions compliance.
Summary of Potential Future Developments
| Development | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Hybrid System Integration | Integration of a starter-generator for improved fuel economy and smoother operation. | Increased fuel efficiency, smoother acceleration, and reduced emissions. |
| Full Hybrid System Integration | Integration of an electric motor for extended electric-only driving modes or regenerative braking. | Extended electric range, improved fuel economy, and potential for zero-emission driving in certain conditions. |
| Enhanced Turbocharging Systems | Implementation of more sophisticated turbocharging technology for increased power output. | Higher power output, improved torque delivery, and potential for quicker acceleration. |
| Advanced Combustion Technologies | Implementation of optimized combustion processes for reduced emissions and improved efficiency. | Reduced emissions, improved fuel economy, and potential for increased power output. |
| Optimized Exhaust Systems | Implementation of optimized exhaust systems for reduced emissions. | Reduced emissions, compliance with stricter emission regulations, and enhanced overall efficiency. |