
Determining Factors of Used Car Value
Understanding the factors that influence a used car’s price is crucial for both buyers and sellers. Knowing what affects value allows for informed decisions, preventing overpaying or undervaluing a vehicle. This comprehensive analysis delves into the key determinants, from physical condition to market trends.
The value of a used car is a complex interplay of various factors. It’s not solely dependent on age or mileage; a multitude of elements contribute to its overall worth. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential for both buyers and sellers to make sound decisions.
Key Factors Influencing Used Car Value
Several key factors significantly impact the price of a used car. These factors encompass the vehicle’s condition, market trends, and specific features. Understanding these elements is essential for accurately assessing a vehicle’s worth.
- Vehicle Condition: The physical and mechanical state of the car is paramount. This includes the appearance of the exterior, interior, and the overall cleanliness. A well-maintained car with minimal wear and tear will command a higher price than one with significant damage or neglect.
- Market Trends: Supply and demand, and general economic conditions, play a substantial role. High demand for specific models or colors can inflate prices, while a saturated market can depress them. Recent economic downturns, for instance, often correlate with reduced demand and lower used car prices.
- Specific Features: Features like advanced safety systems, navigation, and entertainment features can influence the selling price. Luxury features, unique trims, or optional packages can add value to the vehicle, potentially increasing its selling price.
Evaluating Used Car Condition
Proper evaluation of a used car’s condition is critical to determining its true value. This involves a multi-faceted approach, considering visual inspection, mechanical checks, and a thorough review of the vehicle’s documentation.
- Visual Inspection: Start with a comprehensive visual inspection of the exterior and interior. Assess for damage, scratches, dents, and any signs of neglect. Inspect the interior for wear and tear, cleanliness, and the presence of any modifications. Examine the tires for wear and tear and check the overall condition of the vehicle’s body.
- Mechanical Checks: A qualified mechanic should perform a thorough mechanical inspection. This includes checking the engine, transmission, brakes, suspension, and other vital components. This is essential for identifying potential mechanical issues and their associated costs.
- Documentation Review: Examine the vehicle’s service records. A well-maintained service history provides valuable insights into the vehicle’s previous upkeep and potential future issues. Check for any outstanding recalls or repairs. Ensure that the vehicle’s title and registration are valid and clear.
Common Wear and Tear Issues
Understanding common wear and tear issues is crucial for evaluating a used car’s value. These issues can significantly impact the vehicle’s price.
- Exterior Damage: Scratches, dents, and paint imperfections can detract from the car’s overall appeal and resale value.
- Interior Wear: Torn upholstery, worn-out carpets, or broken interior components can negatively impact the car’s aesthetic and perceived condition.
- Mechanical Issues: Problems with the engine, transmission, brakes, or other mechanical components can greatly reduce the vehicle’s value.
- Tire Wear: Tires in poor condition are a safety hazard and can affect the car’s performance and value.
Impact of Make and Model
Different car makes and models command varying prices in the used car market. Factors such as reputation, reliability, and desirability influence the value.
| Make and Model | Impact on Value |
|---|---|
| Luxury brands (e.g., BMW, Mercedes-Benz) | Generally command higher prices due to brand prestige and perceived quality. |
| Popular models (e.g., Toyota Camry, Honda Civic) | Tend to hold their value well due to reliability and widespread demand. |
| Less-common models (e.g., niche sports cars) | Values may fluctuate significantly based on specific features and market demand. |
Role of Mileage, Age, and Maintenance History
Mileage, age, and maintenance history are crucial indicators of a used car’s value. A well-maintained car with low mileage and a comprehensive service history will likely command a higher price.
- Mileage: Higher mileage generally translates to lower value due to increased wear and tear on the vehicle’s components. However, the impact of mileage depends heavily on the vehicle’s make, model, and maintenance history.
- Age: Older vehicles often have lower values, especially if not well-maintained. However, some classic models can appreciate in value over time.
- Maintenance History: A well-documented service history is a strong indicator of the vehicle’s care and upkeep. This history can significantly affect the price, providing assurance of its current condition and future reliability.
Market Trends and Influences

The used car market is a dynamic landscape, constantly shaped by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for accurately assessing used car values and making informed purchasing decisions. From economic fluctuations to global events, various forces can significantly impact the price of a pre-owned vehicle.
Current market conditions are characterized by shifts in supply and demand, economic influences, and geographic variations. These factors often intertwine, creating a multifaceted environment where accurate value estimations require a nuanced approach. Seasonal patterns also play a role, influencing demand and, consequently, pricing. Furthermore, unexpected events can disrupt the market equilibrium, affecting used car values in unforeseen ways.
Current Trends in the Used Car Market
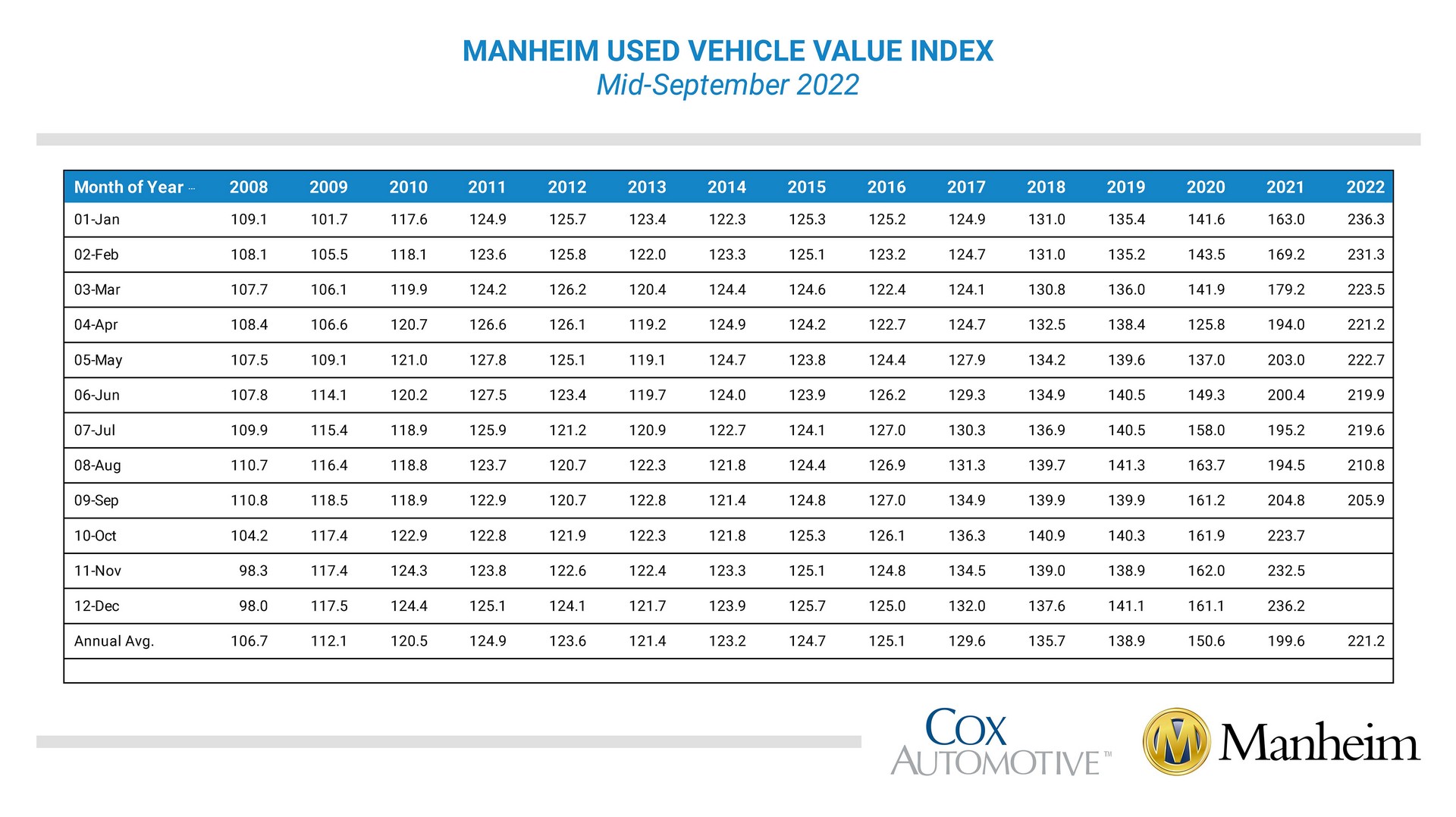
The used car market is experiencing a period of significant change. Supply chain disruptions and production limitations have led to shortages in some vehicle categories, while increased consumer demand has contributed to price increases. This imbalance between supply and demand has resulted in higher prices for used cars, particularly for models in high demand.
Effect of Economic Conditions on Used Car Values
Economic conditions exert a substantial influence on used car values. Recessions often lead to reduced consumer spending and decreased demand for vehicles, which can depress used car prices. Conversely, periods of economic growth typically see increased consumer confidence and demand, pushing used car values upward. For example, the 2008 recession significantly impacted used car prices, leading to a noticeable decline. Conversely, economic booms can lead to a substantial rise in used car values.
Comparison of Used Car Prices in Different Geographic Locations
Used car prices vary significantly across different geographic regions. Factors such as local economic conditions, taxes, and regulations can impact the cost of used vehicles. For example, a used car in a major metropolitan area with high living costs is likely to command a higher price than the same model in a rural area with lower living expenses. This difference is often attributed to variations in local demand and economic prosperity.
Influence of Seasonal Variations on Used Car Market Prices
Seasonal variations can influence the used car market. Certain times of the year, such as the summer months, might see a surge in demand for vehicles used for recreational purposes. This increased demand can result in higher prices for relevant models. Conversely, during other periods, such as the winter months, demand might decrease, leading to potentially lower prices. This pattern is closely linked to consumer behavior and the use cases for particular vehicles.
Impact of Recent Events on Used Car Values
Recent events, both natural and global, have also had a noticeable impact on used car values. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, can disrupt supply chains, affecting the availability of certain vehicles and leading to price increases. Global events, such as pandemics or geopolitical conflicts, can also influence used car prices, often through indirect effects on economic conditions. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted global supply chains, which directly affected used car prices.
Negotiation and Pricing Strategies
Mastering the art of negotiation is crucial when purchasing a used car. Understanding the market value, researching comparable vehicles, and employing effective tactics can significantly impact the final price. This section delves into various negotiation strategies, providing practical examples and demonstrating how to confidently secure a fair deal.
Strategies for Negotiating Used Car Prices
Knowing how to negotiate a fair price for a used car requires a multi-faceted approach. Preparation is key; thoroughly research the vehicle’s market value and identify comparable models. This groundwork allows for informed discussions and empowers you to confidently counter offers. Remember, the goal is to find a mutually agreeable price that reflects the vehicle’s condition and current market value.
Researching Comparable Used Cars
Thorough research is essential to establish a fair price. This involves identifying similar models with comparable mileage, features, and condition. Websites like Kelley Blue Book (KBB) and Edmunds provide valuable data for pricing comparisons. Analyzing these resources allows for a precise understanding of the used car’s value within the market.
Importance of Knowing the Market Value
Knowing the market value of a used car is paramount before entering negotiations. This knowledge provides a strong foundation for your negotiation strategy. By understanding the vehicle’s fair market value, you can confidently counter unrealistic offers and secure a price that aligns with the current market conditions. A clear understanding of the vehicle’s worth is essential for securing a beneficial transaction.
Effective Negotiation Tactics
A range of negotiation tactics can influence the outcome of a used car purchase. These techniques involve active listening, strategic questioning, and the ability to articulate your position clearly. Examples of effective tactics include highlighting the vehicle’s flaws and presenting counteroffers based on comparable market prices. Ultimately, the best strategy depends on the individual circumstances of the negotiation.
Negotiation Techniques and Effectiveness
| Negotiation Technique | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| The “Low Ball” Approach | Starting with a significantly lower offer than your desired price to gauge the seller’s willingness to negotiate. | Can be effective if the seller is open to negotiation. Can be perceived as aggressive if not used cautiously. |
| The “Counteroffer” Technique | Responding to an offer with a revised price, aiming for a compromise. | Highly effective when used strategically, showcasing a willingness to negotiate while maintaining your position. |
| The “Walk Away” Strategy | Expressing your willingness to leave the negotiation if the price is not satisfactory. | Effective when the seller values the sale and wants to avoid losing a potential customer. |
| The “Focus on Value” Approach | Highlighting the vehicle’s positive attributes and justifying the desired price. | Effective when used with a strong understanding of the vehicle’s value and the market’s pricing trends. |
| The “Bundle Deal” Strategy | Combining the used car purchase with other services or incentives. | Potentially effective if the seller is open to bundling. Can be challenging to negotiate effectively without market support. |
Types of Used Cars and Values
Understanding the diverse landscape of used car values is crucial for both buyers and sellers. Different types of vehicles, ranging from budget-friendly economy models to premium luxury cars, command varying price points. Factors like vehicle features, trims, and the year of manufacture significantly impact the final selling price. This section delves into these nuances, providing a comprehensive overview of used car valuations.
Used car values are not static; they fluctuate based on various factors, including market trends, manufacturer reputation, and demand. Understanding these dynamics is key to making informed decisions about buying or selling a used vehicle.
Different Vehicle Types and Value Ranges
Various categories of used cars exist, each with its own price range. Luxury vehicles, sports cars, and economy cars represent distinct market segments, each influencing the overall value proposition.
- Luxury Cars: High-end vehicles, often from established brands, feature premium materials, advanced technology, and a reputation for prestige. These used cars frequently command higher prices than their comparable economy or sports counterparts. For instance, a used BMW 7 Series, known for its luxury features and comfort, typically holds a higher value compared to a used Honda Civic, even if they are similar in age and mileage. The higher value stems from the prestige and quality associated with the BMW brand.
- Economy Cars: These vehicles prioritize affordability and fuel efficiency. Their used car values are generally lower compared to luxury or sports cars. Examples include models like the Toyota Corolla or Honda Civic. These cars tend to be popular choices for budget-conscious buyers, leading to higher demand and lower prices than luxury models.
- Sports Cars: Performance-oriented vehicles often feature enhanced engine capabilities and specialized handling features. Used sports cars typically exhibit a value range between economy and luxury cars. For instance, a used Porsche 911, renowned for its speed and performance, will generally hold a higher value than a used economy car like a Hyundai Accent but a lower value than a luxury car like a Mercedes-Benz S-Class.
Impact of Vehicle Features on Prices
The presence of advanced technology and safety features significantly influences used car prices. Buyers are often willing to pay a premium for vehicles equipped with these enhancements.
- Advanced Technology: Features like infotainment systems, navigation, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) increase the perceived value of a used car. A vehicle with a well-regarded infotainment system and advanced safety features might command a higher price than a similar model without these additions.
- Safety Features: Features like airbags, anti-lock brakes (ABS), and electronic stability control (ESC) enhance safety and appeal to buyers. Vehicles equipped with a comprehensive suite of safety features typically fetch higher prices compared to those with fewer safety provisions.
Role of Trims and Options
Different trims and options within a particular model year can significantly affect a used car’s value. Specific features and packages often contribute to the overall worth of the vehicle.
- Trim Levels: Various trim levels exist within a model, each offering a different combination of features and options. Higher trims often include more luxurious amenities and advanced technology, leading to higher prices.
- Specific Options: Options like leather interiors, sunroof, heated seats, and premium sound systems can significantly impact the perceived value of a used vehicle. A used car with desirable options like a panoramic sunroof or premium sound system may command a higher price compared to a similar model without these features.
Comparison of Used Cars Across Years
The year of manufacture plays a critical role in determining a used car’s value. Older models generally depreciate more than newer models.
- Model Year Impact: Used cars from more recent model years tend to hold their value better than older models. The depreciation rate often decreases with each year of a car’s model cycle. This means that a car from a newer model year may retain a higher percentage of its original value compared to a car from an older model year.
Price Variations Across Used Car Types
The following table provides a general overview of price variations across different used car types. Note that these are estimates and actual values may vary significantly based on specific model, year, mileage, condition, and market demand.
| Car Type | Typical Value Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Luxury Cars | $20,000 – $100,000+ |
| Sports Cars | $15,000 – $75,000+ |
| Economy Cars | $5,000 – $20,000 |
Financing and Insurance Considerations
Purchasing a used car involves more than just negotiating the price. Understanding financing options and securing appropriate insurance coverage are crucial steps to ensure a smooth and financially responsible ownership experience. These factors significantly impact the overall cost and affordability of the vehicle.
Careful consideration of financing and insurance options allows you to make informed decisions, preventing potential financial burdens down the road. A well-researched approach to financing and insurance can make the difference between a positive car-buying experience and a challenging one.
Financing a Used Car
Thorough research into financing options is essential for securing the best possible terms. Different lenders offer various interest rates and loan terms, affecting the overall cost of the car. Choosing the right financing option is crucial for managing your budget effectively.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates vary significantly depending on factors like your credit score, loan amount, and the lender. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate, making the loan more affordable. For example, a buyer with a strong credit history might secure a 4% interest rate, whereas someone with a lower credit score could face a rate of 8% or higher.
- Loan Terms: Loan terms dictate the repayment period. Shorter terms typically result in higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid. Longer terms lead to lower monthly payments but higher total interest. A 36-month loan might have higher monthly payments than a 60-month loan, but the 36-month option will result in less overall interest paid.
- Down Payments: A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, lowering the monthly payment and total interest paid. It also demonstrates financial responsibility to lenders, potentially improving loan terms.
- Credit Score: A strong credit history is often rewarded with lower interest rates and more favorable loan terms. Improving your credit score before applying for a loan can positively influence the financing process.
Insurance for Used Cars
Thoroughly researching insurance options is vital for securing adequate coverage at competitive rates. Different insurers offer varying coverage levels and premiums, so careful comparison is essential.
- Coverage Options: Comprehensive insurance covers damages beyond collisions, such as vandalism or theft. Collision insurance covers damages from accidents, regardless of fault. Liability insurance protects you from claims from others in the event of an accident. The right combination of coverage depends on your driving history and personal risk tolerance.
- Premiums: Insurance premiums depend on various factors including the car’s make, model, and year, your driving history, and your location. A vehicle with a higher repair cost or associated with higher accident rates might have a higher premium.
- Discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for safe drivers, good credit scores, or anti-theft devices. These discounts can significantly reduce insurance premiums.
Examples of Financing Options
Various financing options are available for used car purchases. These include traditional bank loans, online lenders, and dealer financing. Understanding the features and conditions of each option is critical for making an informed decision.
- Bank Loans: Traditional bank loans often require a credit check and may offer competitive interest rates for borrowers with good credit. However, the application process might be more complex than some online alternatives.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders can offer quick approvals and competitive interest rates, particularly for those with specific needs or circumstances. The application process is often streamlined and accessible.
- Dealer Financing: Dealer financing options are often available, and can be convenient for the buyer. However, interest rates may not always be the most competitive.
Relationship Between Financing Terms and Used Car Value
Financing terms directly impact the perceived value of a used car. A car with favorable financing options, such as low interest rates and flexible terms, might be more attractive to buyers.
Favorable financing terms can increase the perceived value of a used car, making it more appealing to potential buyers.
Insurance Providers and Coverage Options
A table illustrating various insurance providers and their coverage options for used cars can help buyers make informed decisions.
| Insurance Provider | Coverage Options | Premiums (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Collision, Comprehensive, Liability | $150-$250/month |
| Company B | Collision, Comprehensive, Liability, Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist | $175-$300/month |
| Company C | Collision, Comprehensive, Liability, GAP Insurance | $125-$225/month |
Note: Premiums are estimated and may vary based on individual circumstances.
Selling a Used Car

Selling a used car can be a straightforward process, but careful planning and execution are key to maximizing your return. Understanding the steps involved, effective advertising strategies, and accurate pricing is crucial to achieving a successful sale, whether you’re selling privately or through a dealership. A well-prepared car and a strategic negotiation approach will increase your chances of a smooth and profitable transaction.
Selling a used car involves a combination of meticulous preparation, strategic marketing, and adept negotiation. This process often requires a keen eye for detail and a practical approach to ensure a successful sale.
Private Sale Strategies
Thorough preparation is essential when selling a car privately. This involves more direct interaction with potential buyers, necessitating careful attention to presentation and clear communication. Prioritizing a clear, detailed description and competitive pricing will attract more qualified buyers.
- Thorough Inspection and Cleaning: A clean, well-maintained car commands a higher price and instills buyer confidence. This includes a comprehensive inspection of all mechanical components, interior, and exterior. Addressing any issues upfront builds trust and avoids potential complications during the negotiation process. A clean and well-maintained car, free of noticeable damage, increases the perceived value and attracts potential buyers. For instance, a car with a fresh paint job or minor repairs will attract more buyers.
- Comprehensive Advertising: Leveraging online platforms like classifieds and social media can reach a wide audience. High-quality photos are critical; they provide a realistic view of the car’s condition. Detailed descriptions, including specifications and any modifications, should be clear and concise. Consider using professional photography, highlighting the car’s best features. Using multiple platforms like Craigslist, Facebook Marketplace, and local classifieds can increase visibility.
- Negotiation and Closing: Be prepared to negotiate on price. Setting a realistic, yet firm, starting price, based on market research, is vital. Meeting potential buyers in a safe, public location is recommended. Ensure all aspects of the sale, including payment terms and ownership transfer, are clearly documented in a legally sound contract. Have a clear understanding of local regulations regarding vehicle transfers.
Dealership Sale Strategies
Selling through a dealership streamlines the process but often involves a lower sale price. Understanding the dealership’s valuation methods and procedures can optimize the outcome.
- Dealer Appraisal and Valuation: Dealers have established valuation methods. Provide complete documentation, including service records, maintenance history, and any relevant information. Understanding the factors considered by the dealership in assessing the car’s value can lead to a more favorable appraisal. This includes condition, mileage, and model year.
- Negotiating with the Dealer: Knowing the car’s market value is critical. Understand the dealership’s profit margin and be prepared to negotiate. A well-researched understanding of market prices for similar vehicles will enable a more informed negotiation process. Be aware of the dealer’s sales strategies and pricing tactics.
- Documentation and Paperwork: The dealership handles most paperwork, but understanding the sales contract is essential. Thorough review and comprehension of the contract details is important before signing. This includes warranties, if any, and details about the transfer of ownership. Confirm the accuracy of the paperwork to avoid future issues.
Pricing and Descriptions
Accurate pricing and clear descriptions are essential for attracting buyers and achieving a fair sale. Thorough market research and a realistic assessment of the car’s condition are critical.
- Market Research and Pricing: Utilize online resources and local listings to assess comparable vehicles. Consider factors like mileage, condition, model year, and features when setting a price. Use online tools to determine the value of similar used cars in the area.
- Comprehensive Descriptions: Include detailed information about the car’s condition, features, and any modifications. Highlight the car’s strengths and any potential drawbacks. High-quality photos, addressing any imperfections, can help attract buyers. Detailed descriptions, with specifics about features, paint conditions, and any maintenance, provide potential buyers with complete information.
Preparing the Car for Sale
Preparing a used car for sale enhances its appeal and increases the likelihood of a successful transaction. Investing in minor repairs and cosmetic improvements can significantly boost its perceived value.
- Exterior and Interior Cleaning: A clean exterior and interior create a positive first impression. Washing, detailing, and addressing any noticeable damage can enhance the car’s appearance. Thorough cleaning, including the interior, and addressing any obvious scratches or dents, is vital.
- Minor Repairs and Maintenance: Addressing any mechanical issues before listing the car is crucial. This includes ensuring that the car functions correctly. Fixing any minor issues will build trust and avoid potential problems during the sale. For instance, addressing minor mechanical issues, such as a leaky tire, is important to maintain the car’s appeal.
Negotiating the Sale
Effective negotiation strategies can help you achieve a mutually beneficial agreement. Knowing the car’s market value and being prepared to counter offers are crucial.
- Setting a Realistic Starting Price: Research comparable vehicles to determine a fair asking price. This ensures you’re not undervaluing or overvaluing the car. Be prepared to adjust your price based on negotiations and buyer interest.
- Responding to Offers: Be prepared to counter offers. Research the current market value for the car’s condition to support your negotiation position. Be open to negotiating and adjust your price if necessary.
- Closing the Deal: Finalize the agreement in a legally sound contract. Clearly Artikel all terms, including payment methods and ownership transfer. A clear, well-defined contract protects both parties involved in the transaction.
Used Car Inspection and Maintenance
A crucial aspect of purchasing a used car is thoroughly assessing its condition. A well-maintained vehicle will not only provide reliable transportation but also retain its value better over time. A pre-purchase inspection can uncover hidden problems and allow you to negotiate a fair price, saving you from costly repairs down the road.
A comprehensive understanding of potential maintenance issues and their associated costs is vital for making informed decisions. This section will delve into the importance of pre-purchase inspections, common maintenance problems, repair costs, and the significance of maintenance records in evaluating a used car’s value.
Importance of Pre-Purchase Inspections
Thorough pre-purchase inspections are paramount to identifying potential problems and negotiating a fair price. Inspections help uncover hidden issues that could significantly impact the car’s future value and reliability. A qualified mechanic or a trusted automotive inspection service can perform a comprehensive check, examining critical components like the engine, transmission, brakes, and electrical system. This proactive approach can prevent costly surprises after the purchase.
Common Maintenance Issues Affecting Used Car Value
Several maintenance issues can drastically affect a used car’s value. These include issues with the engine, transmission, brakes, electrical system, and suspension. Problems such as worn-out brakes, leaking fluids, or a failing transmission can significantly reduce the vehicle’s resale value. Engine misfires, damaged exhaust systems, or issues with the cooling system can also lead to costly repairs. Early detection and addressing these issues are key to maintaining a vehicle’s value.
Cost of Repairs and Impact on Resale Value
The cost of repairs directly impacts the resale value of a used car. Significant repairs can diminish the car’s perceived worth, especially if they involve major components like the engine or transmission. A car requiring extensive repairs will likely sell for a lower price than one in excellent mechanical condition. For example, a used car with a failing engine will have a significantly lower resale value compared to a car with a functioning engine.
Maintenance Records Enhancing Used Car Value
Well-documented maintenance records are a strong indicator of a car’s history and maintenance. A car with a comprehensive maintenance log, including service dates, parts replaced, and mileage, often commands a higher price. This transparency provides potential buyers with confidence in the car’s overall condition and reliability. This can translate into a higher sale price and a quicker sale. Examples include records showing timely oil changes, brake replacements, and other regular maintenance. Such records offer significant proof of the vehicle’s proper upkeep.
Typical Repair Costs for Various Car Parts and Systems
The following table provides an estimate of typical repair costs for various car parts and systems. These figures are approximate and can vary based on the make, model, and year of the vehicle.
| Car Part/System | Estimated Repair Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Engine Repair (Major) | $1,500 – $5,000+ |
| Transmission Repair | $800 – $3,000+ |
| Brake Repair (Major) | $500 – $1,500 |
| Suspension Repair | $300 – $1,000 |
| Electrical System Repair | $200 – $1,000 |
| Cooling System Repair | $200 – $800 |