
Understanding Used Car Warranties
Used car warranties are a crucial consideration when purchasing a pre-owned vehicle. They offer varying levels of protection against mechanical failures, allowing buyers to make informed decisions and potentially mitigate financial risks. Understanding the different types of warranties, their coverage, and associated terms and conditions is essential for a smooth and transparent transaction.
Types of Used Car Warranties
Used car warranties come in various forms, each with unique coverage. Understanding these distinctions empowers buyers to select the best protection for their needs and budget.
- Manufacturer’s Warranty: This warranty is often part of the original vehicle’s purchase agreement and can transfer to a used car buyer. It typically covers specific components and defects related to the vehicle’s original manufacturer and design. The manufacturer’s warranty is often the most limited type of used car warranty, offering protection for specific components and not covering wear and tear issues. A good example is a manufacturer’s warranty that covers the engine and transmission for a specific period after the car is sold. This warranty is limited in its coverage and often does not transfer to the buyer in a used car transaction.
- Extended Warranty: This warranty is an add-on to a pre-existing warranty, either manufacturer’s or a previously purchased extended warranty. It extends coverage beyond the manufacturer’s warranty or a previously purchased extended warranty, offering protection for a specific duration and potentially for components not covered by the original warranty. Extended warranties can provide comprehensive coverage, potentially extending to several years. However, they often come with higher premiums and may have limitations based on the car’s age or mileage. A common example is an extended warranty that covers all mechanical components for three years or 50,000 miles, whichever comes first.
- Powertrain Warranty: This specific type of warranty focuses solely on the vehicle’s powertrain components, including the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. It’s a popular option for used car buyers, as it offers targeted protection for critical parts that can lead to substantial repair costs. This type of warranty is limited in its scope and does not include other components like the electrical system or bodywork.
Comparison of Warranty Coverage
Different warranty types offer varying levels of protection. Comparing their coverage is critical to making an informed choice.
| Warranty Type | Typical Coverage | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer’s Warranty | Covers defects in materials and workmanship, often for specific components. | Limited coverage, often not transferable, and may have mileage restrictions. |
| Extended Warranty | Covers a wider range of components and issues beyond the manufacturer’s warranty. | Higher premiums, often with exclusions and limitations. |
| Powertrain Warranty | Focuses on engine, transmission, and drivetrain components. | Excludes other vehicle systems like electrical or body components. |
Terms and Conditions of Used Car Warranties
Understanding the terms and conditions of a used car warranty is crucial. Thorough review of the fine print will clarify coverage specifics.
- Exclusions: Warranties often exclude certain types of damage, such as damage from accidents, neglect, or wear and tear. Careful review of the exclusions is essential.
- Limitations: Warranties may have limitations on the number of repairs covered or the total amount payable. Understanding these limits is essential for planning and budgeting.
- Repairs: Warranties often specify the conditions under which repairs will be covered. Understanding the procedures for initiating a claim is important.
Importance of Reading the Fine Print
Before purchasing a used car with a warranty, thoroughly review the fine print. This step ensures a clear understanding of the coverage and limitations. Carefully review the specific terms and conditions of the warranty. This meticulous approach will prevent potential disputes and ensure that the warranty aligns with your needs and expectations.
Factors Influencing Warranty Value
Used car warranties are not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Several crucial factors determine the scope and value of the coverage provided. Understanding these factors empowers buyers to make informed decisions and ensures they are getting the right level of protection for their investment.
Vehicle Age and Mileage
The age and mileage of a used vehicle are paramount considerations in determining warranty coverage. Older vehicles, with higher mileage, typically have shorter or less comprehensive warranties compared to newer, lower-mileage models. This is due to the increased likelihood of mechanical issues and wear and tear that accumulates over time and distance. Manufacturers often base their warranty coverage on expected lifespan and anticipated repair needs.
Vehicle Condition
A vehicle’s overall condition significantly impacts warranty eligibility. A well-maintained vehicle with minimal signs of damage or neglect is more likely to be covered by a warranty than one with extensive wear, visible damage, or a history of repairs. Warranties often exclude pre-existing conditions or issues not noted in the vehicle history report.
Vehicle History Report
A comprehensive vehicle history report is crucial in assessing warranty value. Reports detailing prior accidents, repairs, and maintenance provide a clear picture of the vehicle’s past. A history of frequent or extensive repairs might lead to limitations or exclusions in the warranty. A clean history, conversely, can often result in more comprehensive and valuable coverage.
Repair Cost Impact
Different repair costs can substantially influence warranty value. A warranty might cover repairs exceeding a certain threshold, or offer different levels of coverage depending on the type of repair. The warranty might also have limitations on the cost of labor or specific parts. For example, a warranty might cover engine repairs up to a certain dollar amount, but not the cost of replacing all worn components of a complex system. This is common in used vehicle warranties.
Warranty Value Comparison Table
| Vehicle Age (Years) | Mileage (Miles) | Vehicle Condition | Estimated Warranty Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 25,000 | Excellent | High – Comprehensive coverage for most parts |
| 5 | 50,000 | Good | Medium – Limited coverage for major components |
| 8 | 100,000 | Fair | Low – Coverage for critical systems only, or specific components |
| 10 | 150,000 | Fair to Poor | Very Low – Limited coverage for critical systems, or only for a short period. Potential exclusions. |
Note: The estimated warranty value in the table is a general guideline. Specific warranty terms and conditions will vary based on the individual dealership and warranty provider.
Navigating the Warranty Claim Process
Understanding the intricacies of a used car warranty claim process is crucial for both buyers and sellers. A clear understanding of the steps involved, the necessary documentation, and potential reasons for denial can help ensure a smooth and efficient resolution. This section provides a detailed guide to help you navigate the claim process successfully.
Steps Involved in Filing a Warranty Claim
Successfully navigating a warranty claim involves a structured approach. The process typically begins with identifying the covered issue and confirming its alignment with the warranty terms. This is followed by contacting the warranty provider and gathering the required documentation. The claim is then formally submitted and reviewed, and finally, a resolution is reached. The timeframes for each step vary depending on the specific warranty provider and the complexity of the issue.
Gathering Necessary Documentation
Thorough documentation is paramount for a successful warranty claim. Failure to provide all required documents can delay or even deny the claim. This section Artikels the essential documents needed for various warranty claims.
| Document Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Proof of Purchase | Original sales invoice or bill of sale. | Copies of the purchase agreement, registration documents, and any other proof of purchase |
| Warranty Information | Warranty certificate, policy details, and any relevant service records. | Copies of the warranty booklet, the specific warranty coverage terms, or a copy of the warranty registration form. |
| Proof of Defect | Photographs, videos, or detailed descriptions of the defect. | Clear pictures and videos of the damaged part, a written description of the issue, or mechanic’s report detailing the problem. |
| Service Records | Maintenance records and repair history. | Copies of previous repair orders, invoices, or service records from authorized dealerships. |
| Mechanic’s Report | Inspection report from a qualified mechanic, confirming the nature of the defect and its impact. | A detailed report from an independent mechanic stating the fault and the needed repair. |
Common Reasons for Warranty Claim Denial
Several factors can lead to a warranty claim being denied. A common reason is a failure to meet the warranty’s specific conditions, such as the vehicle not being properly maintained. Incorrect documentation or incomplete information can also contribute to claim rejection. Misuse of the vehicle or accidental damage, which are not covered under the warranty, are other potential causes. Claims based on issues that fall outside the warranty’s scope or time limits are also frequently denied.
Timeframe for Resolving Warranty Claims
Warranty claim resolution times vary greatly depending on factors such as the complexity of the issue, the warranty provider’s processing time, and the availability of parts. A simple claim might be resolved in a few weeks, while more intricate issues could take several months. Keep in mind that the warranty provider will typically Artikel the timeframe in their policy documents. Waiting periods are often dependent on the availability of parts, labor, and the provider’s backlog.
Step-by-Step Guide for Filing a Warranty Claim
This structured approach streamlines the warranty claim process.
- Identify the Covered Issue: Carefully review the warranty terms and conditions to ensure the issue is covered. Consult the warranty policy and the terms and conditions to verify the nature of the covered issue.
- Gather Required Documentation: Compile all necessary documents as detailed in the table above. Ensure all supporting documents are accurate and complete.
- Contact the Warranty Provider: Initiate contact with the warranty provider using the specified channels and request a claim form.
- Submit the Claim: Complete the claim form accurately and provide all supporting documents. Submit the claim and ensure all necessary documents are attached.
- Follow Up: Monitor the claim status and follow up with the warranty provider as needed. Regularly check the status of your claim.
Consumer Rights and Responsibilities
Understanding used car warranties involves not only the mechanics of coverage but also the legal rights and obligations of both buyers and sellers. Knowing these rights and responsibilities is crucial for ensuring a fair and transparent transaction, protecting your investment, and resolving disputes effectively. Buyers need to understand what they are entitled to, while sellers need to be aware of their duties to honor those rights.
Buyer Rights Regarding Warranties
Used car buyers have specific rights concerning warranties, stemming from consumer protection laws. These rights typically include the right to receive accurate information about the warranty’s terms, conditions, and limitations. This information should be presented clearly and concisely, avoiding ambiguity. Furthermore, buyers are entitled to have the warranty honored as Artikeld in the agreement. A clear understanding of the warranty’s scope is paramount. If the seller fails to uphold their warranty obligations, the buyer is entitled to recourse.
Seller Responsibilities Concerning Warranties
Used car sellers have a crucial responsibility to be transparent and accurate about warranties. They must provide detailed information regarding the warranty, including the duration, coverage, exclusions, and any limitations. Failure to disclose this information honestly and completely can violate consumer protection laws. Honoring the terms of the warranty is equally vital. The seller is obligated to fulfill the promises made under the warranty.
Examples of Warranty Violation
Several situations can illustrate violations of consumer rights. A seller might misrepresent the extent of a warranty’s coverage, failing to disclose pre-existing issues or omitting important exclusions. Another example involves a seller who refuses to honor a warranty claim despite the claim falling within the terms and conditions Artikeld. A third example involves a seller providing misleading information about the warranty’s duration or the specific components covered. These actions can lead to legal issues for the seller.
Legal Recourse for Consumers
If a used car warranty is not honored, consumers have recourse. This may involve filing a complaint with the relevant consumer protection agency. Small claims court procedures are available for resolving disputes involving a relatively small monetary value. Alternatively, a consumer can seek legal counsel to explore other avenues, such as filing a lawsuit for breach of contract, if the violation involves significant financial losses or if the situation cannot be resolved through other means.
Key Consumer Rights Related to Used Car Warranties
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Accurate Information | Sellers must provide precise and comprehensive details about the warranty, including coverage, exclusions, and limitations. |
| Warranty Honoring | Sellers must honor the terms of the warranty as Artikeld in the agreement. |
| Legal Recourse | Consumers have the right to pursue legal action if a warranty is not honored, including filing complaints or initiating lawsuits. |
Extended Warranties

Extended warranties for used cars can be a complex decision. While they promise added protection, they often come with a significant cost. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial before committing to one. The financial implications and the likelihood of actual use need careful consideration.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Determining the cost-effectiveness of an extended warranty requires a thorough evaluation of the potential repair costs against the premium paid. Researching average repair costs for common issues with the specific make and model of the used car is essential. Factors like the car’s age, mileage, and overall condition play a significant role in determining the potential need for repairs.
Potential Benefits of Extended Warranties
Extended warranties can provide peace of mind by covering unexpected repairs. This can protect buyers from substantial out-of-pocket expenses for costly mechanical issues. A well-structured extended warranty can potentially mitigate financial risks associated with major repairs. Some warranties offer comprehensive coverage, including parts and labor, for a specified period or mileage.
Potential Drawbacks of Extended Warranties
Extended warranties often come with high premiums. The cost may outweigh the potential savings if the car is relatively reliable or if the buyer prioritizes other financial needs. The actual value of the coverage depends on the specific terms and conditions of the warranty. It’s vital to thoroughly review the fine print and understand the exclusions and limitations before signing.
Scenarios Where Extended Warranties Might Be Beneficial
Extended warranties can be a wise investment in certain circumstances. For example, if a used car has a known history of expensive repairs or if the buyer anticipates significant use and travel, the warranty may be a prudent choice. Also, if the car is an older model or high-mileage, the probability of future repairs may be higher, making the warranty a worthwhile protection. Furthermore, if the buyer’s financial situation limits their ability to afford unexpected repairs, the warranty provides a safety net.
Summary Table: Pros and Cons of Extended Warranties
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Protection against unforeseen repair costs. | High upfront cost that may not be recouped. |
| Peace of mind knowing repairs are covered. | Potential for unnecessary coverage if the car is reliable. |
| Potential to mitigate financial risk associated with major repairs. | Complex terms and conditions that require careful review. |
| Comprehensive coverage may include parts and labor. | Exclusions and limitations can restrict coverage. |
Warranty Negotiation Strategies
Negotiating a used car warranty can significantly impact your financial commitment and peace of mind. A well-structured approach, understanding potential pitfalls, and leveraging your knowledge are crucial for securing favorable terms. This section explores effective strategies for negotiating used car warranties, ensuring you get the best possible deal.
Effective warranty negotiation requires a proactive and informed approach. Understanding the value of the warranty, the potential pitfalls, and having a solid plan are essential for securing the best possible terms. By employing successful tactics and carefully considering the pre-purchase inspection, you can maximize your chances of a favorable outcome.
Identifying Potential Warranty Pitfalls
Understanding potential warranty pitfalls is crucial to successful negotiation. These pitfalls can involve hidden exclusions, limited coverage, or unclear definitions of what constitutes a covered repair. A careful review of the warranty document is paramount. Pay close attention to the following:
- Exclusions: Warranties often exclude certain types of damage or repairs, such as damage caused by accidents, misuse, or wear and tear. Carefully scrutinize the exclusion clauses to ensure they align with your needs and expectations.
- Limitations on Coverage: Some warranties may limit the number of repairs covered or the maximum amount paid per repair. Understanding these limitations is essential to assess the warranty’s true value.
- Repair Standards: Scrutinize the warranty’s repair standards. Does it require specific repair shops or procedures? These conditions can impact your ability to access repairs under the warranty.
- Geographic Restrictions: Some warranties may have geographical limitations, restricting the services covered in certain areas. Assess the geographical coverage to ensure it aligns with your future needs.
- Time Limits: Warranties often have time limits for repairs or coverage. Consider the potential implications of these time constraints.
Successful Negotiation Tactics
Effective negotiation requires a combination of preparation, assertiveness, and a willingness to walk away. Here are some proven tactics:
- Thorough Research: Research the average warranty costs for similar used vehicles in your area. This gives you a baseline for negotiation.
- Pre-Purchase Inspection: A pre-purchase inspection conducted by a qualified mechanic can highlight potential mechanical issues and their impact on the warranty’s value. This inspection can be a powerful tool in negotiations.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the warranty offered with other potential warranties or options available.
- Conditional Acceptance: Consider a conditional acceptance of the warranty, linking the acceptance to a pre-purchase inspection or a detailed assessment of the vehicle’s condition.
- Alternative Offers: Be prepared to present alternative offers, such as a lower price or other add-ons, as a part of the negotiation process.
Role of Pre-Purchase Inspection in Warranty Negotiation
A pre-purchase inspection is invaluable during warranty negotiation. It provides a comprehensive assessment of the vehicle’s condition, uncovering potential mechanical issues that may impact the warranty’s value.
- Early Issue Detection: The inspection can detect potential issues before the purchase, reducing the likelihood of costly repairs later. This directly influences the warranty negotiation process.
- Warranty Modification: A pre-purchase inspection can highlight areas requiring further consideration or potentially necessitate modifications to the warranty terms.
- Negotiating Leverage: A detailed report from the pre-purchase inspection provides strong negotiating leverage, allowing you to demand better warranty terms or potentially decline the offer altogether.
Warranty Negotiation Flowchart
[Insert flowchart here, visually depicting the steps in the negotiation process. The flowchart should illustrate the process of gathering information, identifying potential pitfalls, formulating negotiation strategies, and the final decision-making process.]
Avoiding Common Warranty Pitfalls
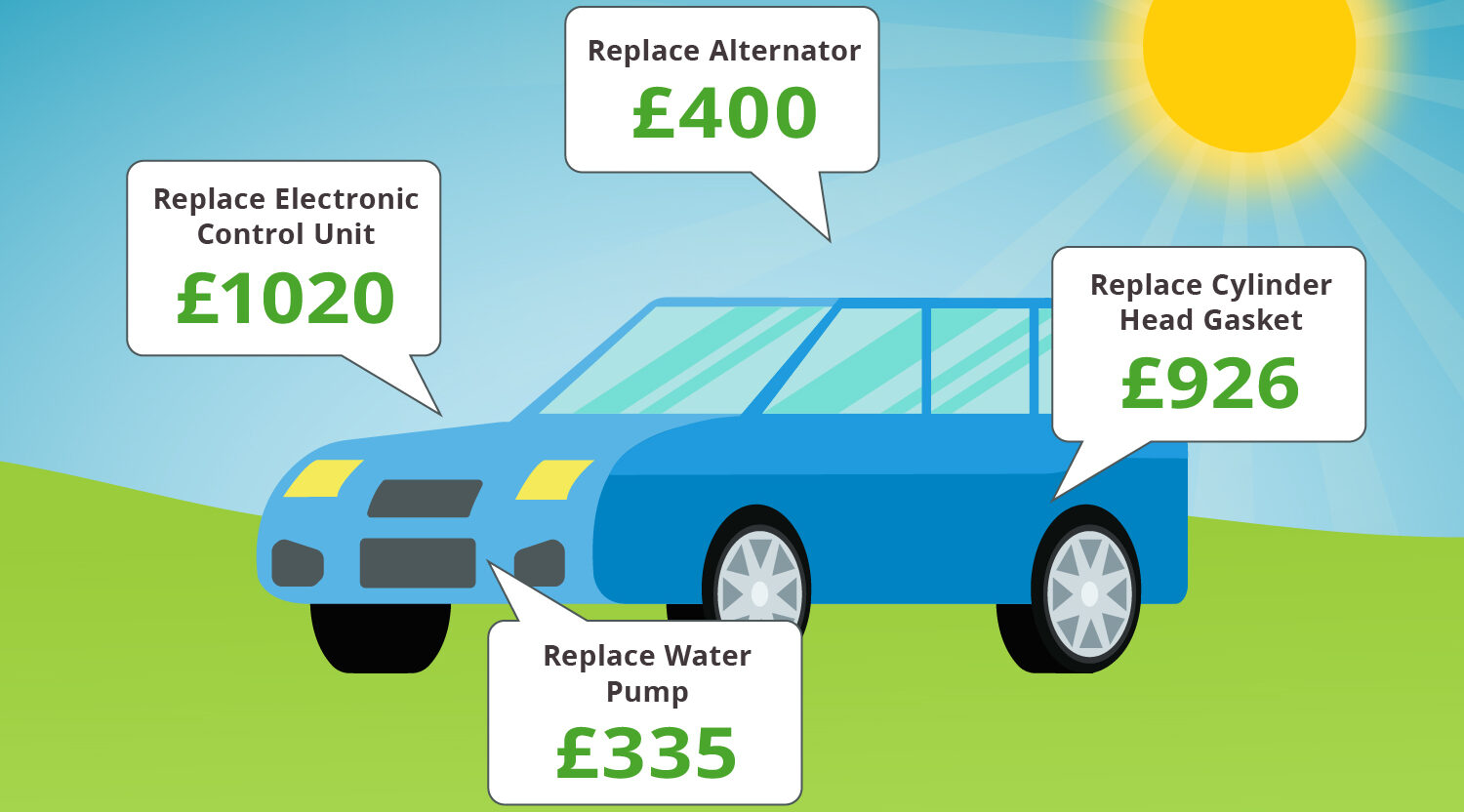
Purchasing a used car with a warranty can significantly protect your investment, but it’s crucial to understand potential pitfalls to avoid costly mistakes. Navigating the fine print and understanding the limitations of the warranty are essential for a smooth experience. Failing to thoroughly review the warranty documents can lead to unexpected issues when making a claim.
Understanding the warranty’s exclusions and limitations is critical to preventing future disappointments. A comprehensive understanding of these nuances is vital for maximizing the warranty’s benefits and avoiding situations where a claim is denied due to a lack of awareness.
Common Buyer Mistakes
Many buyers overlook crucial details when evaluating used car warranties. A lack of meticulous review can lead to missed opportunities to protect their investment and even prevent potential future issues. Understanding the potential for these errors is key to a positive experience.
- Neglecting to read the entire warranty document thoroughly. A cursory glance at the warranty document is often insufficient to grasp the full scope of coverage and exclusions.
- Failing to understand the warranty’s exclusions. Many warranties exclude specific repairs or components, such as wear-and-tear items or damage caused by accidents or neglect. It is important to understand these exclusions to avoid disappointment.
- Assuming the warranty covers all repairs. A warranty may only cover specific components or conditions, such as the engine or transmission, but not body panels or interior wear and tear.
- Ignoring the limitations of the warranty’s duration. Warranties have specific timeframes. Failure to recognize these limitations can lead to a claim being rejected if it is submitted after the expiration date.
Understanding Warranty Exclusions
Warranties often have specific exclusions that limit coverage. Knowing these limitations can help avoid future disputes and ensure that you understand the warranty’s scope. These exclusions are crucial to recognizing the limits of the warranty’s protection.
- Exclusions for wear-and-tear items. Many warranties exclude routine maintenance items or parts that naturally wear down over time, such as brakes, tires, and belts.
- Damage caused by accidents or neglect. If the vehicle sustains damage from an accident or misuse, the warranty may not cover repairs.
- Modifications or aftermarket parts. Warranties typically do not cover repairs or issues related to modifications or parts installed after the vehicle was purchased.
- Problems stemming from improper maintenance. A warranty might not cover repairs if the vehicle was not maintained according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Thorough Review of Warranty Documents
A comprehensive review of the warranty documents is paramount to understanding the specifics of the coverage. Careful examination of the terms and conditions will clarify the scope of the protection offered.
- Identify the specific components covered. Review the document to determine which parts or systems are covered under the warranty.
- Note the duration of the warranty. Pay close attention to the timeframe of coverage to avoid potential claim rejections.
- Understand the procedures for filing a claim. Review the warranty document for details on how to file a claim, including required documentation and steps involved.
- Examine the exclusions and limitations. Carefully identify any exceptions or exclusions that may apply to avoid potential disputes.
Examples of Avoidable Claims
Reviewing the warranty documents beforehand can prevent unnecessary disputes and wasted time. These examples highlight the importance of thorough scrutiny.
- A buyer filed a claim for a worn-out tire, despite the warranty explicitly excluding routine maintenance items.
- A buyer filed a claim for damage to the engine caused by a faulty fuel pump, but the warranty excluded problems related to aftermarket parts.
- A buyer filed a claim beyond the warranty’s expiration date, leading to the claim being denied.
- A buyer attempted to claim a repair for a cracked windshield due to an accident, but the warranty excluded damage from accidents.
Potential Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Careful planning and thorough review can help you avoid costly mistakes. Understanding these pitfalls can prevent potential problems and ensure a smooth process.
- Pitfall: Failing to read the entire warranty document. Solution: Take your time and carefully read every word of the warranty document, paying attention to the details, to ensure a complete understanding.
- Pitfall: Ignoring warranty exclusions. Solution: Identify and understand the warranty’s exclusions to avoid disappointment when a claim is denied.
- Pitfall: Assuming the warranty covers everything. Solution: Clarify the scope of the warranty with the seller or the manufacturer to ensure you understand what is covered.
- Pitfall: Missing the warranty’s expiration date. Solution: Keep track of the warranty’s expiration date to avoid submitting claims after the coverage period has ended.
Industry Trends in Used Car Warranties

The used car warranty market is dynamic, constantly adapting to shifting consumer expectations and technological advancements. Understanding these trends is crucial for both consumers and businesses to make informed decisions about purchasing, selling, and offering used car warranties. These evolving standards influence the value and longevity of these agreements.
Recent Trends in the Used Car Warranty Market
The used car warranty market is experiencing a surge in demand, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the value proposition. This trend is evident in the growing number of consumers actively seeking and evaluating warranty options when purchasing used vehicles. The heightened emphasis on transparency and clear communication regarding warranty terms and conditions further fuels this trend. A critical aspect is the rising consumer expectation for comprehensive coverage, pushing the industry to offer more robust and versatile warranty packages.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Warranty Offerings
Several technologies are transforming the way used car warranties are offered and managed. Advanced diagnostic tools and data analytics are providing dealerships with more accurate assessments of vehicle condition, allowing for more tailored and precise warranty coverage. Remote diagnostics and telematics are enabling real-time monitoring of vehicle performance, which is potentially revolutionizing preventative maintenance and predictive warranty claims. This data-driven approach can lead to more accurate assessments of potential future repair needs, enabling proactive warranty management.
Adaptation to Changing Consumer Demands
Dealerships and warranty providers are responding to evolving consumer preferences. Emphasis on digital platforms for warranty purchase and claim management is increasing, providing a more convenient and accessible experience for customers. The growing demand for flexible and customizable warranty options is being met by providers offering tailored packages to specific customer needs and budget constraints. These adaptable offerings are a key driver of customer satisfaction.
Environmental Factors and Evolving Warranties
Environmental considerations are influencing warranty offerings. For example, the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is prompting the development of unique warranty provisions tailored to the specific components and technologies of these vehicles. Warranty providers are adapting to the needs of EVs, recognizing the unique challenges and potential maintenance issues associated with these vehicles. The transition towards electric vehicles is creating a demand for a new approach to warranty coverage, recognizing the need for long-term maintenance and repair solutions.
Summary of Key Industry Trends
| Trend | Description | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Consumer Demand | Consumers are more actively seeking and evaluating warranty options. | More choices, potentially better coverage. |
| Technological Advancements | Diagnostic tools, data analytics, remote diagnostics, and telematics are transforming warranty management. | Potentially more accurate assessments of vehicle condition and proactive maintenance. |
| Adaptation to Consumer Needs | Customization and flexibility in warranty packages are increasing. | Tailored coverage to specific needs and budget. |
| Environmental Considerations | Warranty offerings are adapting to the growing adoption of EVs. | Unique coverage for electric vehicles. |