
Current Market Trends
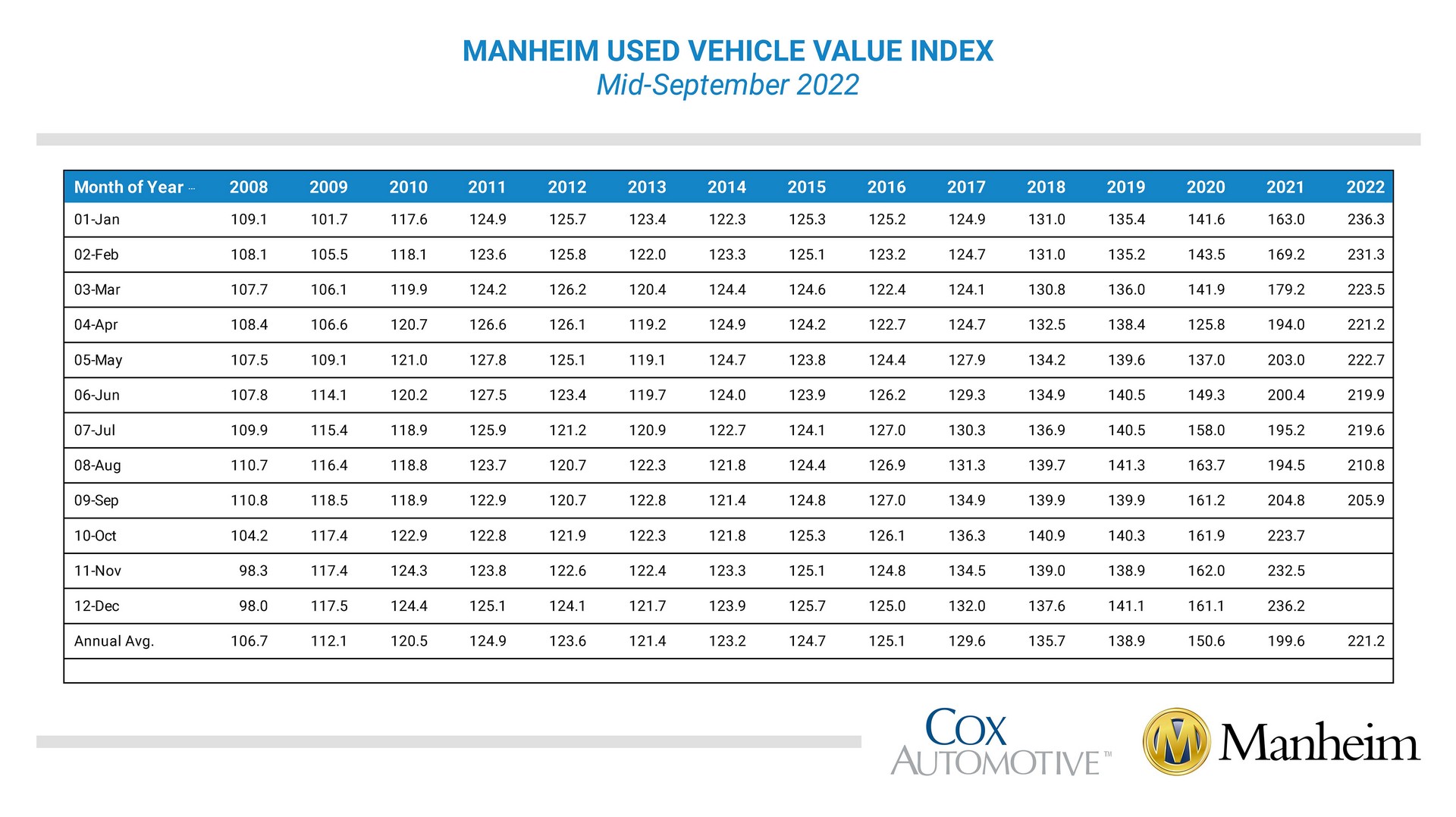
Used car prices in the USA have experienced significant fluctuations in recent years, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for both consumers and investors looking to navigate the market effectively. These shifts have impacted the affordability and accessibility of vehicles for various demographics.
Recent Trends in Used Car Prices
The used car market has been characterized by volatility, with prices rising sharply during the pandemic and subsequently declining, although still remaining above pre-pandemic levels. This dynamic environment requires careful consideration of the underlying forces shaping the market. Several key factors contribute to these shifts in pricing.
Factors Influencing Used Car Prices
Several factors have driven the recent trends in used car prices. Supply chain disruptions, particularly during the pandemic, limited new vehicle production, leading to a shortage of available used cars. Simultaneously, increased demand from consumers, coupled with reduced interest rates and a surge in demand for vehicles like SUVs and trucks, further fueled the price escalation.
Regional Variations in Used Car Prices
Used car prices exhibit regional disparities across the USA. Factors such as local demand, supply availability, and economic conditions in specific areas influence the price point. For example, coastal states often see higher prices compared to inland regions, reflecting higher incomes and demand in those areas.
Average Used Car Prices by Vehicle Type (Past Year)
The table below provides a snapshot of average used car prices for different vehicle types over the past year, offering a comparative view of the market trends. Data is aggregated from various sources to represent a broad picture. It’s important to note that these are averages and actual prices can vary based on specific vehicle conditions, mileage, and features.
| Vehicle Type | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| SUVs | $32,500 |
| Sedans | $25,000 |
| Trucks | $35,000 |
| Compact Cars | $20,000 |
Factors Affecting Prices
Used car prices in the USA are a complex reflection of numerous interacting economic forces. Fluctuations in manufacturing, global supply chains, fuel costs, interest rates, consumer confidence, and even comparisons with other markets all play significant roles in shaping the market. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting future trends and for consumers seeking to navigate the used car market.
Impact of Manufacturing Shortages
Manufacturing shortages, particularly the global semiconductor chip shortage, have had a profound impact on the used car market. The scarcity of crucial components for vehicle production led to decreased new car supply, pushing demand towards the used car market. This heightened demand, combined with limited supply, led to a significant increase in used car prices. The ripple effect extended beyond the immediate chip shortage, impacting related industries and exacerbating price pressures. For example, delays in manufacturing processes for parts like brakes or electrical systems could also contribute to a lack of availability in the used car market.
Global Chip Shortage’s Influence
The global chip shortage, a multifaceted crisis impacting numerous industries, profoundly affected the used car market. The reduced availability of semiconductors, critical for vehicle electronics and functionalities, directly curtailed new car production. This supply constraint, combined with persistent consumer demand, led to a surge in used car prices. The shortage’s impact was not limited to the direct components; it also indirectly influenced production of parts for cars. For example, a shortage of dashboard displays or infotainment systems would impact the used market for older models.
Influence of Rising Fuel Costs
Rising fuel costs, driven by global events and geopolitical factors, indirectly affect used car prices. Higher fuel costs often lead to increased demand for fuel-efficient vehicles, potentially boosting the prices of these models in the used market. Alternatively, if fuel prices rise sharply, consumers might opt for less fuel-efficient used cars, leading to a possible price correction for some models. The interplay between fuel efficiency and consumer preferences creates an interesting dynamic within the used car market.
Relationship Between Interest Rates and Affordability
Interest rates play a significant role in used car affordability. Higher interest rates typically make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer purchasing power and potentially impacting demand for used cars. Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and increase the affordability of used cars, leading to increased demand. This relationship is directly proportional; lower interest rates lead to more accessible financing, which can increase demand and consequently drive up prices.
Comparative Analysis of Used Car Prices
Comparing used car prices across different countries provides insights into market dynamics. Variations in supply and demand, economic conditions, and government regulations influence pricing differences. For example, a country with stricter emissions standards or higher taxes on imported vehicles could influence prices. Comparing these prices provides a broader context to understand the factors that influence the US used car market.
Impact of Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is a key factor affecting demand for used cars. During periods of high consumer confidence, consumers are more likely to purchase used cars, leading to increased demand and higher prices. Conversely, periods of low consumer confidence may decrease demand and cause prices to stabilize or potentially decrease.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Used Car Prices
| Economic Indicator | Correlation with Used Car Prices |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing Output | Positive |
| Interest Rates | Negative |
| Fuel Prices | Positive (for fuel-efficient models), or Negative (for less fuel-efficient models) |
| Consumer Confidence | Positive |
| Global Economic Conditions | Indirect; influenced by manufacturing, interest rates, and fuel prices |
The table above highlights the complex correlation between various economic indicators and used car prices. The positive or negative correlation is not always direct; instead, it is often influenced by indirect or compounded factors. For instance, a surge in global oil prices could impact both manufacturing output and fuel costs, which could in turn influence used car prices.
Vehicle-Specific Price Considerations
Used car prices aren’t a one-size-fits-all scenario. Various factors, specific to the make, model, and condition of the vehicle, significantly influence the final sale price. Understanding these nuances is crucial for both buyers and sellers to navigate the market effectively.
Make and Model Variations
Different makes and models of used cars exhibit considerable price disparities. Factors like brand reputation, perceived quality, and historical performance significantly impact resale values. For example, a used Honda Civic typically commands a lower price compared to a comparable-year, -mileage used Audi A4, reflecting the established reputation for reliability and value associated with Honda.
Resale Value of Specific Vehicle Types
Luxury cars often maintain higher resale values than similarly aged mainstream models. This is largely due to the premium associated with brand image and features. Electric vehicles (EVs) also show a complex pattern. Early adoption models may experience significant depreciation, but as EV technology matures and adoption increases, resale values are expected to stabilize or even improve.
Impact of Vehicle Mileage
Mileage is a primary determinant of used car pricing. A car with significantly lower mileage typically commands a higher price than a comparable model with higher mileage. This is because lower mileage often indicates better overall condition and fewer wear-and-tear issues. A used car with 25,000 miles is likely to fetch a higher price than a similar model with 75,000 miles, all other factors being equal.
Influence of Vehicle Condition
Vehicle condition plays a critical role in used car pricing. A meticulously maintained car with minimal damage, including cosmetic and mechanical issues, will generally fetch a better price than a car showing signs of wear and tear or prior accidents. Buyers are more likely to pay a premium for a car that looks and runs like new.
Effect of Features on Price
Features like sunroofs, navigation systems, and advanced safety technology can influence used car prices. These features can either attract buyers or simply not be a significant factor in the final sale price. The impact depends on the target market and the perceived value of the feature. A sunroof might increase the price of a basic model, but might not be a significant factor for a model already equipped with premium features.
Typical Depreciation Rates for Different Vehicle Types
| Vehicle Type | Typical Depreciation Rate (Estimated First 3 Years Post-Sale) |
|---|---|
| Luxury Cars (e.g., BMW, Mercedes-Benz) | 15-20% |
| Premium Cars (e.g., Acura, Audi) | 10-15% |
| Compact Cars (e.g., Honda Civic, Toyota Corolla) | 5-10% |
| SUVs/Crossovers | 8-12% |
| Trucks | 6-10% |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | 10-25% (depending on model year and features) |
Note: These are estimates and actual depreciation rates can vary based on several factors, including specific models, market conditions, and individual vehicle history.
Pricing Models and Resources

Understanding used car pricing requires a multifaceted approach, considering various factors and methodologies. Accurate price prediction models can help buyers and sellers navigate the market effectively, while access to reliable pricing data is crucial. This section explores different pricing models, resources for accessing data, and strategies for identifying deals.
Accurate used car pricing relies on a combination of market trends, vehicle specifics, and negotiation tactics. This includes evaluating the vehicle’s condition, mileage, and features alongside current market valuations.
Predicting Used Car Prices
Predictive models for used car prices leverage statistical methods to estimate future values. These models typically consider factors such as vehicle year, make, model, mileage, condition, and market trends. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify correlations between these factors and price fluctuations. For instance, a model might predict a 5% decrease in price for a 2015 Honda Civic with high mileage compared to a similar model in pristine condition. This prediction can be refined by incorporating factors like local market demand and regional economic conditions.
Resources for Pricing Data
Numerous resources provide current used car pricing data. Websites like Kelley Blue Book (KBB), Edmunds, and NADAguides offer detailed valuations based on various criteria. Mobile apps also provide similar functionalities, enabling quick access to price estimates on the go. These resources are often updated regularly to reflect changing market conditions.
Pricing Methodologies
Dealerships and private sellers employ diverse pricing strategies. Dealerships often use a combination of cost-plus pricing and market-based pricing, adjusting prices based on inventory levels, demand, and competition. Private sellers may rely on online marketplaces for guidance, or they may set prices based on perceived value, independent of market analysis.
Negotiating Used Car Prices
Negotiation is a crucial aspect of acquiring a used car at a fair price. Buyers should research comparable vehicles, understand the vehicle’s condition, and have a clear budget in mind. Understanding the dealer’s profit margin and market conditions can assist in developing a reasonable offer. Being prepared to walk away from a deal that doesn’t meet expectations is essential.
Role of Online Marketplaces
Online marketplaces like Carvana, Autotrader, and Craigslist significantly impact used car pricing. These platforms provide a vast selection of vehicles and facilitate price transparency, influencing pricing through aggregate data and competitive listings. Marketplaces often employ algorithms to analyze listings and suggest fair market values. This can streamline the process for both buyers and sellers.
Analyzing Used Car Listings for Deals
Analyzing listings involves checking for inconsistencies in pricing, evaluating the vehicle’s condition, and considering the seller’s reputation. Identifying a deal often involves comparing listings for similar vehicles, checking for discrepancies in pricing and features, and considering factors like location and seller type. Thorough research can help identify undervalued vehicles.
Comparison of Online Marketplace Pricing Models
| Marketplace | Pricing Model | Data Sources | Negotiation Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carvana | Algorithmic, based on market analysis and vehicle condition | Internal data, external market data | Limited |
| Autotrader | Market-based, with seller-determined prices | Market data, user-submitted data | Moderate |
| Craigslist | Seller-determined, with potential for significant negotiation | User-submitted data | High |
Note: This table provides a general overview and pricing models may vary.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses

Fluctuating used car prices have a significant impact on both consumers and businesses, creating challenges and opportunities across the market. These price swings influence purchasing decisions, profitability, and the overall health of the used car industry. Understanding these impacts is crucial for both individuals considering a used car purchase and businesses involved in vehicle sales.
Impact on Consumer Budgets
Used car prices directly affect consumer budgets, particularly those with limited disposable income. Increased prices make vehicle ownership more expensive, potentially forcing consumers to delay purchases, prioritize more affordable options, or even consider alternative transportation methods. For example, a significant rise in used SUV prices could lead to a consumer choosing a smaller, more economical vehicle, or even relying on public transport. This shift in consumer behavior can impact overall demand and influence future pricing trends.
Effect on Businesses
Price fluctuations in the used car market directly impact businesses that rely on vehicle sales. When prices rise, dealer profit margins can increase, but increased competition or reduced consumer demand can lead to reduced sales volume. Conversely, falling prices can erode profitability and make it difficult for businesses to maintain their operations, potentially impacting inventory management, staffing, and overall market position. For instance, a sustained period of falling prices might force some dealerships to cut staff or reduce their inventory, affecting their ability to meet future demand.
Consumer Challenges in Used Car Purchases
Consumers face numerous challenges when purchasing used cars. The complexity of negotiating prices, assessing vehicle condition, and navigating financing options can be daunting. Additionally, the sheer volume of choices and the lack of standardized information can make it difficult to make informed decisions. Unforeseen repairs or hidden mechanical issues can also lead to unexpected expenses, potentially creating financial strain. Finding a trustworthy seller and verifying the car’s history is another significant hurdle for consumers.
Business Strategies for Adapting to Price Changes
Businesses adapt to changing used car prices through various strategies. These include adjusting pricing models to reflect market fluctuations, optimizing inventory management to maintain profitability, and exploring alternative financing options to attract customers. Furthermore, providing transparent and detailed information about vehicle history and condition can build consumer trust. Implementing dynamic pricing strategies, based on real-time market data and vehicle specifications, is a significant step towards adapting to fluctuating prices. For instance, some dealers might offer attractive financing options during periods of low demand to stimulate sales.
Consumer Strategies for Buying Used Cars
Consumers can employ several strategies to navigate the used car market effectively. Thorough research and comparison shopping are crucial for identifying vehicles within their budget and in good condition. Seeking professional inspection and conducting independent research on vehicle history reports are essential steps. Negotiating prices, obtaining pre-approval for financing, and carefully reviewing the contract are all important for consumers to avoid costly mistakes. Knowing how to recognize potential red flags, such as inconsistent pricing or vague vehicle history, is also a vital skill for consumers.
Potential Consequences of Long-Term Price Trends
Long-term trends in used car prices can have profound consequences for the used car market. Sustained price increases can limit access to affordable vehicles, potentially exacerbating existing socioeconomic disparities. Conversely, prolonged periods of declining prices could negatively impact dealer profitability and overall market health. Changes in consumer preferences and adoption of electric vehicles could also alter the landscape of the used car market, leading to significant shifts in demand and pricing dynamics. For instance, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles might lead to a decline in demand for gasoline-powered used cars, impacting the prices of these vehicles.
Future Projections
Used car prices in the USA are highly dynamic, influenced by a complex interplay of supply, demand, and external factors. Predicting future trends requires careful consideration of various potential drivers, including technological advancements, government policies, and economic conditions. While precise forecasts are impossible, examining likely scenarios and potential impacts can offer valuable insights.
Potential Factors Influencing Future Trends
Several factors could significantly impact used car prices in the coming years. Changes in consumer demand, fluctuating fuel costs, and the emergence of new technologies are all relevant considerations. The economic climate, both domestically and internationally, plays a crucial role. Supply chain disruptions and geopolitical events can also influence the availability and cost of used vehicles.
Impact of New Technologies
The automotive industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity, while autonomous driving features are becoming increasingly common. The increasing adoption of EVs could affect used gasoline-powered vehicle values, potentially creating a market niche for certain models and leading to price variations. The availability and affordability of EV charging infrastructure will also be a critical factor.
Influence of Government Policies
Government policies can have a significant impact on the used car market. Regulations regarding emissions, fuel efficiency, and safety standards can influence the demand for certain types of vehicles. Incentives for electric vehicle adoption and tax policies affecting used car sales will play a crucial role in shaping future trends. For example, tax credits or subsidies for purchasing electric vehicles could drive demand and impact used gasoline-powered car values.
Comparison of Different Predictions
Various sources and analyses offer differing predictions for used car prices over the next five years. Some projections anticipate a gradual stabilization of prices, while others foresee continued volatility. Factors like the rate of EV adoption, the severity of potential economic downturns, and the effectiveness of government policies will all play a part in shaping the final outcome. For instance, a rapid increase in EV adoption could lead to a steeper decline in the price of gasoline-powered vehicles than currently anticipated by some analysts.
Expected Price Ranges (Illustrative Example)
| Source | Projected Average Price Change (2024-2029) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis A | -5% to +3% | Predicts a moderate price stabilization with slight fluctuations based on market conditions and technological shifts. |
| Analysis B | -8% to +2% | Forecasts a more significant decline in prices, driven by increasing EV adoption and potentially weaker demand for internal combustion engine vehicles. |
| Analysis C | +2% to +8% | Anticipates a potential rise in prices, especially for high-demand models, due to ongoing supply chain issues and continued high demand for specific vehicle types. |
Note: These are illustrative examples and do not represent specific, detailed predictions. Actual outcomes will depend on numerous interacting factors.