
Introduction

SUVs and vans, while both serving as vehicles for transportation, cater to vastly different needs and preferences. SUVs, often favored for their perceived ruggedness and elevated driving position, are typically associated with families, recreational activities, and individuals seeking a versatile, all-terrain option. Vans, on the other hand, are designed for practicality and space, prioritizing cargo capacity and accommodating large groups of passengers. This distinction in design and functionality often leads to misunderstandings and misinterpretations regarding their capabilities and applications. This exploration delves into the key differences between SUVs and vans, highlighting their primary uses, target demographics, and design characteristics, while also addressing common misconceptions. Furthermore, we will examine the evolution of these vehicles over time.
The fundamental difference between SUVs and vans lies in their primary design objectives. SUVs are engineered to prioritize driver visibility and handling, often with a focus on off-road capabilities, while vans are explicitly designed for maximizing interior space and cargo capacity. This results in distinct features such as higher ground clearance and all-wheel drive in SUVs, contrasted with the spacious interiors and customizable layouts of vans. This crucial difference shapes the experiences and intended use cases for each vehicle type.
Primary Uses and Target Demographics
SUVs cater to a broad range of users, from families needing ample space for children and gear to individuals seeking a stylish and capable vehicle for commuting and weekend adventures. The target demographic for SUVs is highly diverse, spanning various age groups and lifestyles. Vans, conversely, are more often chosen for specific needs, such as transporting multiple people or substantial cargo, or as part of a business or delivery operation. Their target demographics encompass families with multiple children, businesses, and organizations requiring significant cargo or passenger capacity. Consequently, the marketing strategies for each vehicle type reflect their differing applications.
Design and Functional Differences
SUVs typically feature a higher ground clearance, all-wheel drive systems, and robust suspension components. These attributes are designed to enhance off-road performance and maneuverability on uneven terrain. Vans, in contrast, prioritize interior space maximization, often incorporating adaptable seating configurations, flexible cargo areas, and robust loading systems. The unique designs of SUVs and vans directly impact their functionality, leading to variations in driving experience and cargo handling.
Common Misconceptions
A prevalent misconception is that SUVs are inherently more capable off-road than vans. While SUVs are often marketed with an emphasis on off-roading, a properly equipped and designed van can also be suitable for specific off-road conditions. Another common misunderstanding is that vans are solely for large families or commercial use. In reality, vans offer exceptional practicality for a variety of applications, including small businesses, individuals with particular needs, and those seeking space and convenience. Addressing these misconceptions helps to clarify the versatile applications of both vehicle types.
Evolution of SUVs and Vans
The evolution of SUVs reflects a gradual shift from basic off-road vehicles to more refined and sophisticated models, accommodating diverse needs and preferences. Initially designed for rugged terrain, SUVs have become more refined and integrated into mainstream lifestyles. Similarly, the development of vans demonstrates a trend toward increasing space, flexibility, and customization to meet evolving transportation demands. Early vans focused primarily on cargo capacity; modern designs incorporate advanced technologies and features to cater to a broader range of needs, including increased passenger comfort and safety.
Size and Dimensions
SUVs and vans offer vastly different interior and exterior dimensions, impacting passenger comfort, cargo capacity, and overall driving experience. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the vehicle best suited to individual needs. The size and dimensions directly influence the usability and practicality of each vehicle type.
The varying dimensions of SUVs and vans cater to diverse transportation requirements. Factors like passenger count, cargo volume, and intended use all contribute to the optimal size and configuration of each vehicle. This section details the typical dimensions of various SUV and van models, providing a comparative overview.
Typical Dimensions of SUV Models
SUVs come in a range of sizes, from compact to full-size. The dimensions vary considerably between models, influencing their handling, fuel efficiency, and interior space. A compact SUV, such as the Honda CR-V, generally measures around 170-180 inches in length, with a wheelbase of around 100-105 inches. Mid-size SUVs, like the Toyota Highlander, typically extend to around 190-200 inches in length and a wheelbase of 110-115 inches. Full-size SUVs, exemplified by the Ford Expedition, span over 200 inches in length and possess wheelbases exceeding 120 inches. These dimensions directly correlate with the vehicle’s cargo capacity and passenger space.
Typical Dimensions of Van Types
Passenger vans, categorized as cargo vans or passenger vans, also vary in size. Cargo vans are designed for maximum cargo space, with minimal passenger accommodations. Passenger vans prioritize passenger comfort and space, with cargo areas often less prominent. For example, a cargo van like the Ford Transit Connect can measure approximately 180 inches in length and 70 inches in width, with a wheelbase around 105 inches. Conversely, a passenger van such as the Chrysler Pacifica is typically longer, around 200 inches in length, and broader, potentially exceeding 75 inches in width, with a longer wheelbase. The size variations reflect the distinct purposes of each vehicle type.
Comparative Table of Dimensions
| Vehicle Model | Length (inches) | Width (inches) | Height (inches) | Wheelbase (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honda CR-V | 175 | 70 | 65 | 102 |
| Toyota Highlander | 195 | 75 | 68 | 112 |
| Ford Expedition | 210 | 78 | 72 | 125 |
| Ford Transit Connect | 180 | 72 | 70 | 105 |
| Chrysler Pacifica | 200 | 76 | 68 | 118 |
This table presents a concise comparison of various SUV and van models, showcasing their respective dimensions. The data allows for a direct comparison of length, width, height, and wheelbase, offering insights into the differences in size and structure.
Cargo and Passenger Capacity Comparison
Cargo capacity and passenger space differ significantly between SUVs and vans. SUVs generally offer a blend of cargo and passenger space, catering to families or individuals needing both. Vans, conversely, are designed for either substantial cargo capacity or a large number of passengers. The Ford Expedition, for instance, might accommodate up to 7 passengers with a significant cargo area. Conversely, a cargo van like the Ford Transit Connect is built primarily for transporting large quantities of goods, with limited passenger space. The Chrysler Pacifica, being a passenger van, maximizes passenger space, accommodating a larger number of passengers while having a more restricted cargo area.
Performance and Fuel Efficiency
SUVs and vans cater to diverse needs, and their performance and fuel efficiency characteristics significantly impact the ownership experience. Understanding the engine types, horsepower, torque, and fuel economy of each vehicle type is crucial for informed decision-making. Different driving conditions and terrains will also influence the performance and fuel economy of these vehicles.
Engine specifications, fuel efficiency, and handling vary substantially between SUVs and vans. These differences stem from design choices and target applications, influencing how well each vehicle type performs in various driving situations.
Engine Types and Specifications
Engine types, horsepower, and torque figures are crucial factors influencing performance. SUVs frequently feature powerful gasoline or diesel engines, optimized for robust performance. Vans, conversely, often use engines balanced for efficiency and towing capacity, resulting in a slightly different power profile. Horsepower and torque figures will vary greatly depending on the specific model and trim level. A more powerful engine in an SUV will offer quicker acceleration compared to a less powerful one.
Fuel Efficiency Considerations
Fuel efficiency is influenced by several factors including engine type, transmission, aerodynamic design, and driving style. A more fuel-efficient engine in a van will provide lower running costs compared to a less fuel-efficient one in an SUV. Modern advancements in engine technology are constantly improving fuel economy across both vehicle types. For instance, turbocharged engines in SUVs can offer impressive power output while maintaining acceptable fuel efficiency.
Driving Scenarios and Performance
Different driving scenarios demand different performance characteristics. City driving, highway cruising, and off-roading will impact the performance and fuel efficiency of both SUVs and vans differently. An SUV, designed for versatile use, might perform better on rough terrain but not as efficiently on the highway compared to a van designed for smooth highway driving. A van, optimized for cargo space and fuel efficiency, excels in highway driving, but its off-road capability might be limited compared to an SUV.
Acceleration and Handling
SUVs generally offer more acceleration due to their typically higher horsepower and torque output. However, vans often prioritize smooth acceleration and handling, which is better suited for carrying heavy loads. Vans, designed to prioritize comfort and spaciousness, tend to have a more controlled acceleration profile compared to an SUV, which often prioritizes a more responsive feel.
Fuel Economy Ratings
| Vehicle Type | Model | Trim | Fuel Economy (mpg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | Toyota RAV4 | LE | 28 city / 36 highway |
| SUV | Honda CR-V | EX | 27 city / 34 highway |
| Van | Toyota Sienna | LE | 24 city / 30 highway |
| Van | Mercedes-Benz Sprinter | Cargo | 21 city / 27 highway |
Note: Fuel economy ratings are estimates and may vary based on driving conditions and individual driving habits.
Safety Features
Safety features are paramount when considering any vehicle, especially those as large and potentially powerful as SUVs and vans. A thorough examination of standard safety equipment, safety ratings, and driver-assistance technologies is crucial for informed decision-making. Understanding the differences in occupant protection between these vehicle types ensures a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Safety features in vehicles are continually evolving to provide greater protection and aid in accident avoidance. Sophisticated driver-assistance technologies, enhanced occupant protection systems, and improved crash test ratings contribute to a safer driving experience. Different vehicle types may prioritize specific aspects of safety based on their intended use and design.
Standard Safety Features
The standard safety features offered in SUVs and vans vary significantly, with some commonalities and notable differences. Both vehicle types typically include anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and airbags. However, the sophistication and range of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) can differ considerably. Understanding the specific features available in each model is essential.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): This system prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, maintaining steering control and reducing stopping distances.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): ESC helps prevent skidding and loss of control by adjusting braking and engine power to maintain vehicle stability.
- Airbags: Airbags are designed to mitigate the impact forces on occupants during a collision, reducing the risk of injury. Different types of airbags, such as front, side, and curtain airbags, protect various parts of the body.
- Seatbelts: Seatbelts are essential for restraining occupants in the event of a collision. Three-point seatbelts are common in both vehicle types, providing superior restraint compared to lap belts alone.
Safety Ratings and Comparisons
Independent organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) provide valuable crash test data for vehicles. These ratings help consumers assess the relative safety of different models. Higher ratings generally indicate a greater likelihood of reduced injuries or fatalities in a collision. It’s crucial to check these ratings for specific models of SUVs and vans before making a purchase.
- NHTSA: The NHTSA provides ratings based on frontal, side, and rollover crash tests. These ratings help consumers understand how well a vehicle performs in various accident scenarios.
- IIHS: The IIHS provides more detailed crash test data, including ratings for various aspects of safety, such as headlight performance and crash avoidance systems.
Driver-Assistance Technologies
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are becoming increasingly common in both SUVs and vans. These systems can help prevent accidents and assist drivers in various situations. However, the specific features and sophistication of these systems can differ significantly between models.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: This system automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead.
- Lane Departure Warning: This system alerts the driver if the vehicle is drifting out of its lane.
- Automatic Emergency Braking: This system can automatically apply the brakes to help avoid collisions in certain situations.
Occupant Protection Features
Occupant protection features are critical for mitigating injuries in the event of a collision. Features like airbags, seatbelts, and advanced restraint systems contribute to the overall safety of occupants. The sophistication and effectiveness of these systems can vary significantly between models.
- Airbag Deployment: The deployment of airbags in a collision is a critical safety feature. Proper deployment and activation mechanisms minimize the impact forces on occupants.
- Seatbelt Retractors: The design and function of seatbelt retractors influence how well they restrain occupants in a collision.
Safety Rating Table (Example)
| Model | NHTSA Rating | IIHS Rating | Key Safety Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUV A | 5 Stars | Good | Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Departure Warning, Automatic Emergency Braking |
| SUV B | 4 Stars | Acceptable | ABS, ESC, Front Airbags |
| Van C | 5 Stars | Good | Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keeping Assist, Blind Spot Monitoring |
| Van D | 4 Stars | Marginal | ABS, ESC, Side Airbags |
Interior and Comfort
The interior experience significantly impacts a vehicle’s overall appeal and usability. Factors like space, comfort features, and material quality play a crucial role in determining passenger satisfaction and long-term ownership enjoyment. This section delves into the comparative interior design of SUVs and vans, highlighting key differences in passenger space, comfort, and storage.
The interior of a vehicle is often the first impression a driver or passenger has of the overall quality of the car. The design and comfort of the seats, the availability of amenities, and the amount of storage space are all significant considerations when choosing between an SUV and a van. The interior experience can be drastically different based on the model, manufacturer, and trim level.
Interior Space and Passenger Capacity
SUVs typically prioritize a comfortable and spacious interior for occupants. They offer a greater number of seating options compared to smaller cars but generally have fewer seats than vans. The interior space within SUVs is designed to accommodate a driver and a few passengers comfortably. Vans, conversely, are designed with a greater emphasis on carrying multiple passengers or a large amount of cargo. The interior design prioritizes passenger capacity and flexibility in seating arrangements.
Comfort Features and Materials
Different materials and features contribute to the overall comfort level of the vehicle’s interior. SUVs frequently incorporate high-quality leather or synthetic leather seating surfaces and advanced features like heated and ventilated seats, particularly in higher-end models. Vans often focus on durable, easily cleanable materials such as cloth or vinyl to meet the needs of families and those transporting large amounts of cargo.
Seat Design, Adjustability, and Comfort
The seat design and adjustability vary significantly between SUVs and vans. SUVs usually prioritize comfort and support, with seats that offer good posture and adjustability for individual needs. Vans often feature bench seats or modular seating arrangements to accommodate a greater number of passengers, sacrificing some individual seat adjustability in the process.
Storage and Cargo Space
Storage space is a critical consideration, especially for families or those who frequently transport goods. SUVs usually offer adequate storage space for personal items in the cabin, along with a cargo area that can accommodate larger items like luggage or sports equipment. Vans, however, are known for their impressive cargo capacity, often designed with modular storage solutions and spacious cargo areas for carrying large amounts of luggage, equipment, or supplies.
Comparison of Specific Models
| Feature | Example SUV (e.g., Toyota RAV4) | Example Van (e.g., Ford Transit) |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Capacity | 5-7 (depending on model) | 5-8+ (depending on model and configuration) |
| Cargo Space (cu ft) | 40-60 | 100-200+ (depending on model) |
| Seat Adjustability | Front seats: power adjustable, Rear seats: limited adjustability | Front seats: power adjustable, Rear seats: modular, customizable arrangements |
| Material Quality | High-quality synthetic or leather upholstery | Durable cloth or vinyl upholstery |
| Comfort Features | Heated/ventilated seats, advanced infotainment | Basic infotainment, cargo area security features |
Cost and Maintenance

Choosing between an SUV and a van often hinges on the budget. Understanding the varying purchase prices, maintenance costs, insurance premiums, and resale values is crucial for making an informed decision. Factors such as vehicle size, features, and the specific model significantly impact these costs.
Owning either an SUV or a van comes with a spectrum of financial responsibilities. The initial purchase price, along with ongoing maintenance and insurance, play a substantial role in the overall cost of ownership. Resale value also influences the long-term financial implications. Detailed analysis of these factors will provide a clear picture of the comparative costs.
Purchase Price
The initial investment in an SUV or van varies greatly depending on the make, model, and trim level. Luxury SUVs often command higher prices than comparable vans, reflecting the added features and materials. Entry-level models in both categories offer more affordable options.
Maintenance Costs
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and reliability of any vehicle. The frequency and expense of maintenance tasks can differ between SUVs and vans. Factors like the vehicle’s age, usage, and driving conditions also influence maintenance costs.
Repair Expenses
Average repair costs for SUVs and vans fluctuate. Some SUVs might have more specialized components, potentially leading to higher repair costs. However, vans, due to their often more robust construction, might have a lower frequency of certain repairs. Precise figures are difficult to provide without detailed specifications of the model and mileage.
Insurance Costs
Insurance premiums for SUVs and vans can vary based on factors like the vehicle’s size, safety features, and the driver’s history. Larger vehicles, like SUVs, often have higher insurance premiums than comparable smaller vans.
Resale Value
The resale value of a vehicle is influenced by factors such as demand, market trends, and the vehicle’s condition. SUVs generally maintain a higher resale value than vans, particularly in certain segments. However, specific model years and condition can significantly impact this difference.
Estimated Cost of Ownership
| Vehicle Model | Purchase Price (USD) | Estimated Annual Maintenance (USD) | Estimated Annual Insurance (USD) | Estimated Resale Value (USD) (after 5 years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota RAV4 | 25,000 | 1,500 | 1,800 | 15,000 |
| Honda Odyssey | 30,000 | 1,200 | 1,500 | 18,000 |
| Ford Explorer | 32,000 | 1,800 | 2,000 | 18,500 |
| Chevrolet Express Van | 28,000 | 1,000 | 1,200 | 16,000 |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary based on individual circumstances. Factors like specific trim levels, optional features, and usage patterns can significantly affect costs.
Practical Applications
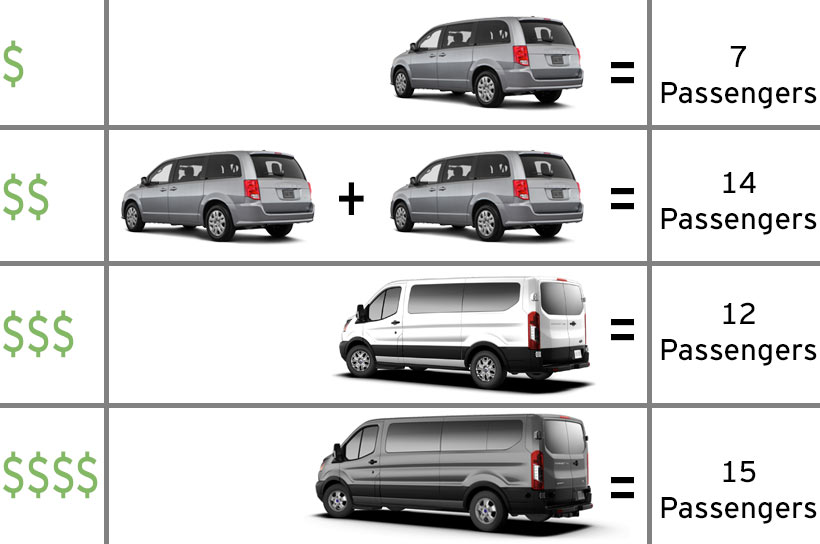
Choosing between an SUV and a van depends heavily on the intended use. Factors like passenger capacity, cargo space, and the specific needs of the user play a crucial role in making the right decision. Understanding the diverse applications of each vehicle type and considering various scenarios is key to selecting the best fit.
SUV Use Cases
SUVs offer a blend of passenger space and cargo capacity, making them suitable for a wide range of activities. Their elevated driving position and often all-wheel drive capability make them well-suited for various terrains and conditions.
- Family Adventures: SUVs excel at accommodating families with children and luggage. Their spacious interiors and versatility are ideal for transporting everyone and their gear for weekend trips, outings, or even daily commutes. The ability to navigate various road conditions makes them suitable for family vacations and exploring different environments.
- Commuting and Errands: SUVs offer comfortable seating for daily commutes, and their relatively spacious cargo areas make them practical for carrying groceries, sporting equipment, or other items. Their practicality makes them a solid choice for families with multiple needs.
- Recreational Activities: Their versatility extends to outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and fishing. The ability to handle rough terrain and carry equipment makes them a popular choice for these pursuits. Examples include transporting kayaks, camping gear, or equipment for outdoor adventures.
- Everyday Use: SUVs are often a great choice for drivers who require both passenger and cargo space for daily activities. Their versatility makes them ideal for a variety of daily tasks. Examples include driving to work, picking up children from school, or running errands.
Van Use Cases
Vans prioritize cargo space and passenger capacity, making them ideal for specific transportation needs. Their expansive interiors are well-suited for carrying large items or transporting multiple individuals.
- Commercial Use: Vans are frequently employed in commercial settings for transporting goods, delivering packages, or providing services that require a high capacity for carrying cargo. Their extensive cargo space makes them an excellent choice for businesses.
- Large Family Transportation: Families with multiple children or large amounts of luggage may find a van more practical than an SUV. Their spacious interiors can accommodate large groups of people and significant amounts of gear. The high passenger capacity makes them a preferred choice for transporting multiple individuals.
- Moving and Storage: Vans are excellent choices for moving furniture, appliances, or other large items. Their high cargo capacity makes them the preferred choice for moving large items and for storage purposes.
- Special Needs Transportation: Vans often come with specialized features such as wheelchair accessibility, making them ideal for transporting individuals with disabilities or special needs. The adaptability of van interiors makes them ideal for transporting people with various needs.
Factors to Consider
When choosing between an SUV and a van, consider factors like the number of passengers, the amount of cargo to be carried, and the type of terrain that will be regularly driven on.
| Factor | SUV | Van |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Capacity | Generally lower, but with increased passenger comfort | Higher, but may sacrifice individual passenger comfort for space |
| Cargo Space | Moderate, suitable for smaller loads | High, ideal for large or bulky items |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally lower than vans, but this depends on the specific model | Generally higher than SUVs, but this depends on the specific model |
| Cost | Generally higher than vans, but this depends on the specific model | Generally lower than SUVs, but this depends on the specific model |
| Maneuverability | Often better than vans in city environments | Less maneuverable in congested areas |
Recreational vs. Everyday Use
The choice between an SUV and a van also depends on whether the vehicle will primarily be used for recreational activities or daily commutes and errands.
- Recreational Use: SUVs are generally better suited for outdoor adventures due to their handling characteristics and ability to navigate varied terrain. Their versatility makes them suitable for weekend trips and outdoor activities. Examples include camping trips and hiking excursions.
- Everyday Use: Vans are ideal for daily transportation of people and goods, making them practical for families with multiple children, businesses needing cargo transport, or individuals who need high passenger capacity. Examples include daily commutes, transporting large items, and running errands.
Styling and Aesthetics
SUV and van designs often reflect their intended purpose and target audience. SUVs typically prioritize a rugged, adventurous aesthetic, while vans frequently lean towards practicality and versatility. The visual appeal of each vehicle type is influenced by factors such as perceived status, functionality, and contemporary design trends.
Exterior styling plays a crucial role in consumer perception and purchase decisions. A vehicle’s appearance communicates its character and functionality, influencing how potential buyers view its overall value proposition. Factors like size, shape, and the use of specific design elements contribute significantly to the aesthetic appeal.
SUV Design Aesthetics
SUV design often emphasizes a bold and robust appearance. This includes larger wheel sizes, high ground clearance, and a squared-off or angular design language. Many SUVs feature prominent, sculpted body lines, often with pronounced fenders and wheel arches.
Van Design Aesthetics
Van designs prioritize functionality and spaciousness over a flamboyant aesthetic. While some vans incorporate sleek modern lines, many focus on a simple, practical approach. Factors like a high roofline, large windows, and a boxy shape contribute to their visual identity. The design goal often prioritizes passenger or cargo space over an aggressive or sporty look.
Popular SUV Designs
The Toyota RAV4 exemplifies a popular compact SUV with a modern, yet practical design. The Jeep Wrangler, known for its off-road capability, features a rugged, angular design. The Tesla Model X, a premium SUV, showcases a sleek and futuristic design. These models demonstrate the diversity of SUV designs, ranging from compact and practical to large and premium.
Popular Van Designs
The Ford Transit, a popular commercial van, focuses on cargo space and durability. The Mercedes-Benz Sprinter, a full-size van, emphasizes comfort and versatility for both passengers and cargo. These examples highlight the functional nature of van designs.
Exterior Features
The size and shape of SUVs and vans vary greatly, impacting their visual presence. Headlights and taillights are designed to reflect the vehicle’s brand identity and aesthetic. For example, sleek headlights and taillights might be used in a modern SUV design, while rugged, square headlights and taillights might be present in a more rugged off-road SUV.
Gallery of SUV and Van Models
| Vehicle | Description |
|---|---|
| Toyota RAV4 | Compact SUV with a smooth and rounded design, highlighting its modern appeal. Rounded headlights and taillights complement the overall aesthetic. |
| Jeep Wrangler | Rugged SUV with a squared-off design, showcasing its off-road capabilities. Large, prominent wheel arches and a high ground clearance visually communicate its durability. |
| Tesla Model X | Premium SUV with a futuristic, sleek design. Aerodynamic lines and distinctive LED headlights are hallmarks of its futuristic appearance. |
| Ford Transit | Commercial van with a practical design. The high roofline and large windows are apparent features. The boxy shape maximizes cargo space. |
| Mercedes-Benz Sprinter | Full-size van emphasizing versatility. Large windows and ample interior space are highlighted, showcasing its functionality. |