
Introduction to SUVs and Sedans
SUVs and sedans are two of the most popular vehicle types on the market, each catering to different needs and preferences. Understanding their key distinctions in body style, size, and intended use is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision. This section will delve into the characteristics of both vehicle types, providing a comprehensive overview of their features and common applications.
SUVs and sedans differ significantly in their overall design and intended purpose. SUVs, typically characterized by their elevated ride height and boxy body, are designed for versatility and off-road capability, whereas sedans, with their streamlined profiles and lower ground clearance, prioritize efficiency and comfort for on-road travel. The size and dimensions of these vehicles also play a critical role in their suitability for various driving situations and passenger capacity.
Defining SUVs and Sedans
SUVs, or sport utility vehicles, are characterized by their elevated ride height, providing better ground clearance compared to sedans. This elevated stance, coupled with a more boxy body design, is often associated with increased versatility and capability, especially in handling various road conditions. Sedans, on the other hand, are distinguished by their sleek, aerodynamic body style and lower center of gravity. This design prioritizes fuel efficiency and a smooth, comfortable ride.
Comparing Size and Dimensions
The typical size and dimensions of SUVs and sedans vary significantly. SUVs generally have a larger overall footprint, encompassing a longer wheelbase, wider track, and greater interior space. This expanded space often accommodates more passengers and cargo. Sedans, in contrast, are typically more compact and offer a smaller passenger compartment and cargo area. This compactness translates to higher fuel efficiency and maneuverability in urban environments.
Purpose and Usage Scenarios
SUVs are commonly used for families, individuals seeking versatility for various terrains, and those who require ample cargo space. Their higher ground clearance allows for easier navigation on unpaved roads and off-road trails. Sedans, conversely, are popular for their fuel efficiency, maneuverability, and refined driving experience, making them suitable for commuting, city driving, and long-distance trips.
Summary Table
| Vehicle Type | Body Style | Typical Size | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | Elevated, boxy | Larger footprint, more interior space | Families, off-roading, carrying cargo |
| Sedan | Sleek, aerodynamic | Compact, efficient | Commuting, city driving, long-distance travel |
Performance Comparison
SUVs and sedans, while both serving as common personal transportation options, exhibit significant differences in performance characteristics. These differences stem from their distinct designs and intended uses. Understanding these nuances is crucial for consumers seeking the best vehicle for their needs.
Engine types, horsepower, and torque output directly influence acceleration, top speed, and fuel economy. Different driving conditions further impact these factors. This section delves into the performance attributes of SUVs and sedans, providing a comprehensive comparison.
Engine Types and Power Outputs
SUVs frequently utilize larger, more powerful engines compared to sedans. This is often a result of the added weight and potential towing capacity of SUVs. Common engine types include V6 and V8 engines, which are more common in larger SUVs than in sedans. Sedans, conversely, often feature smaller, more fuel-efficient engines such as four-cylinder units, optimizing for city driving.
Acceleration and Top Speed
Acceleration times and top speeds vary considerably based on the specific vehicle model and engine configuration. SUVs, due to their heavier weight, typically have slower acceleration times than comparable sedans. However, the larger engines found in some SUVs can provide higher top speeds. Conversely, sedans are designed for efficiency and agility, offering faster acceleration and often matching or exceeding SUV top speeds, especially in smaller, sportier models.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency, a key consideration for many drivers, is often better in sedans than in SUVs. This is largely attributed to the lighter weight and aerodynamic designs of sedans. The smaller engines typically used in sedans contribute to lower fuel consumption. Different driving conditions, such as highway versus city driving, further impact fuel efficiency ratings.
Fuel Economy Comparison
| Vehicle Type | Engine Type | City MPG | Highway MPG |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | V6 | 18 | 25 |
| SUV | V8 | 15 | 22 |
| Sedan | 4-cylinder | 28 | 38 |
| Sedan | 6-cylinder | 22 | 32 |
The table above illustrates the average fuel economy (city/highway) for various SUV and sedan models. These figures are averages and can vary based on specific vehicle models, driving conditions, and individual driving styles. Factors like tire pressure and driver behavior also influence fuel consumption. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for precise fuel economy figures for a particular model.
Interior and Cargo Space
SUVs and sedans differ significantly in their interior and cargo space, impacting passenger comfort and practicality. These differences are directly related to their respective design philosophies: SUVs prioritize versatility and cargo capacity, while sedans focus on maximizing passenger space and minimizing bulk. Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the right vehicle for individual needs.
Typical Interior Space and Seating Arrangements
SUVs typically offer more interior space, particularly in the rear. This is often due to a higher driving position and a more expansive wheelbase. Sedans, conversely, often prioritize a more compact and streamlined design, which can lead to less legroom and headroom in the rear seats compared to SUVs. The seating arrangements reflect these differences, with SUVs often featuring multiple seating configurations, while sedans typically have a more fixed arrangement. Front passenger and driver space is generally comparable in both vehicle types, but the rear space often shows a significant difference.
Passenger Comfort Levels
Passenger comfort in both SUVs and sedans is influenced by various factors, including seat materials, cushioning, and support. SUVs, due to their larger size and increased space, often offer more generous seating accommodations. They frequently have supportive seating with ample space for passengers, especially in the front. Sedans, though smaller, can still provide acceptable comfort levels for shorter trips. However, for longer journeys, the limited space in the rear of some models might result in reduced passenger comfort.
Cargo Space Available
Cargo space is a key differentiator between SUVs and sedans. SUVs, with their elevated profile and often flexible seating arrangements, typically provide significantly more cargo space. Sedans, on the other hand, often prioritize passenger space, which naturally limits the amount of cargo they can carry. The cargo space of a sedan is usually more compact and less versatile.
Interior Space Comparison
The following table illustrates the interior space (front and rear seats) and cargo capacity for various SUV and sedan models. This comparison is based on manufacturer specifications and real-world testing data.
| Model | Vehicle Type | Front Seat Space (in) | Rear Seat Space (in) | Cargo Capacity (cu ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota RAV4 | SUV | 42.0 | 36.5 | 72 |
| Honda Civic | Sedan | 40.5 | 32.0 | 14 |
| Mazda CX-5 | SUV | 41.8 | 35.2 | 68 |
| Hyundai Elantra | Sedan | 40.0 | 30.5 | 12 |
| Subaru Outback | SUV | 43.5 | 38.0 | 85 |
| Toyota Camry | Sedan | 41.2 | 34.5 | 15 |
Note: Dimensions and cargo capacities may vary depending on specific trim levels and optional features. The provided data is illustrative and should be verified with the manufacturer’s official specifications.
Safety Features
Safety is a paramount concern when choosing between an SUV and a sedan. Both vehicle types offer a range of safety features, but their effectiveness and distribution vary. Understanding the specific safety features and how they perform in different types of accidents is critical for making an informed decision. This section delves into the common safety features found in both SUV and sedan models, analyzes safety ratings, and examines how vehicle weight and design influence crashworthiness.
Common Safety Features
A multitude of safety features are standard across both SUVs and sedans, contributing to occupant protection. These features include airbags, anti-lock brakes (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and traction control systems. Airbags, deployed in the event of a collision, mitigate the impact force on occupants. ABS prevents wheel lockup during emergency braking, enhancing maneuverability and control. ESC and traction control systems maintain vehicle stability on slippery surfaces and during sudden maneuvers. These features are vital in preventing accidents and mitigating their consequences.
Safety Ratings and Comparisons
Different organizations evaluate and rate vehicles based on their safety performance. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) are two prominent organizations that provide crash test data and ratings. These ratings consider various aspects of a vehicle’s design and performance in different types of collisions. NHTSA’s ratings typically encompass overall safety performance, while IIHS ratings offer more detailed insights into specific crash test scenarios. Crucially, ratings can differ between SUVs and sedans depending on the specific model and year.
Influence of Vehicle Weight and Structural Design
Vehicle weight plays a significant role in crashworthiness. Heavier vehicles generally offer more protection in collisions, as they distribute the impact force over a larger area. However, excessive weight can also affect fuel economy and handling. Structural design is equally important. Advanced designs prioritize occupant safety by strategically distributing the force of an impact and minimizing the risk of injury. Frame structures, crumple zones, and reinforcing components all contribute to the overall crashworthiness of a vehicle. For instance, a heavier SUV might offer more protection in a head-on collision than a lighter sedan, but the sedan might have superior handling characteristics in normal driving.
Comparison of Standard Safety Features
| Safety Feature | Typical SUV Models | Typical Sedan Models |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Standard | Standard |
| Electronic Stability Control (ESC) | Standard | Standard |
| Front Airbags | Standard | Standard |
| Side Airbags | Often Standard | Often Standard |
| Curtain Airbags | Often Standard | Often Standard |
| Traction Control | Standard | Standard |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Specific safety features may vary depending on the particular model year and trim level of each vehicle.
Cost and Maintenance
The financial implications of owning an SUV versus a sedan extend beyond the initial purchase price. Factors like insurance premiums and ongoing maintenance costs can significantly impact the overall cost of ownership. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Deciding between an SUV and a sedan often hinges on a careful evaluation of long-term expenses. The initial allure of an SUV’s space and perceived robustness may be overshadowed by higher maintenance and insurance costs over time. Conversely, the efficiency and lower purchase price of a sedan can lead to significant savings in the long run.
Purchase Price
The initial investment for an SUV typically exceeds that of a comparable sedan. This difference is primarily due to the SUV’s added features, like enhanced safety systems, powerful engines, and larger, more complex bodies. Trim levels and optional features greatly influence the final price. A base model SUV might be comparable in cost to a top-of-the-line sedan, while a fully loaded SUV could substantially exceed the price of a similarly equipped sedan. For example, a basic compact SUV might cost around $25,000, while a comparable sedan could be closer to $20,000. Premium SUVs and luxury models can easily exceed $50,000.
Insurance Costs
Insurance premiums often reflect the perceived risk associated with a vehicle. SUVs, generally larger and heavier than sedans, tend to have higher insurance premiums. This is due to increased potential for damage and repair costs in accidents. Drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations may see even greater disparities in insurance costs between SUVs and sedans. Insurance companies typically assess factors such as vehicle type, driver profile, and location when determining premiums. Insurance costs vary significantly by region and individual circumstances.
Maintenance Costs
The complexity of an SUV’s mechanical systems and larger components frequently leads to higher maintenance costs compared to a sedan. Replacing parts like larger tires, brakes, or suspension components, as well as engine repairs, are often more expensive in SUVs. Labor costs associated with repairs can also be higher. Furthermore, more frequent tire changes and routine maintenance like oil changes can contribute to overall maintenance expenses. For example, routine maintenance for a compact SUV could cost approximately $100-$200 annually, while a sedan might fall within the $50-$150 range. However, major repairs can easily exceed these figures.
Average Cost of Ownership Comparison
| Vehicle Type | Purchase Price (Avg.) | Insurance (Avg. Annual) | Maintenance (Avg. Annual) | Total Estimated Cost (3 Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | $28,000 | $1,800 | $1,200 | $78,000 |
| Sedan | $22,000 | $1,500 | $800 | $67,000 |
Note: These figures are averages and can vary greatly based on specific models, trim levels, driving habits, and geographical location.
Driving Experience
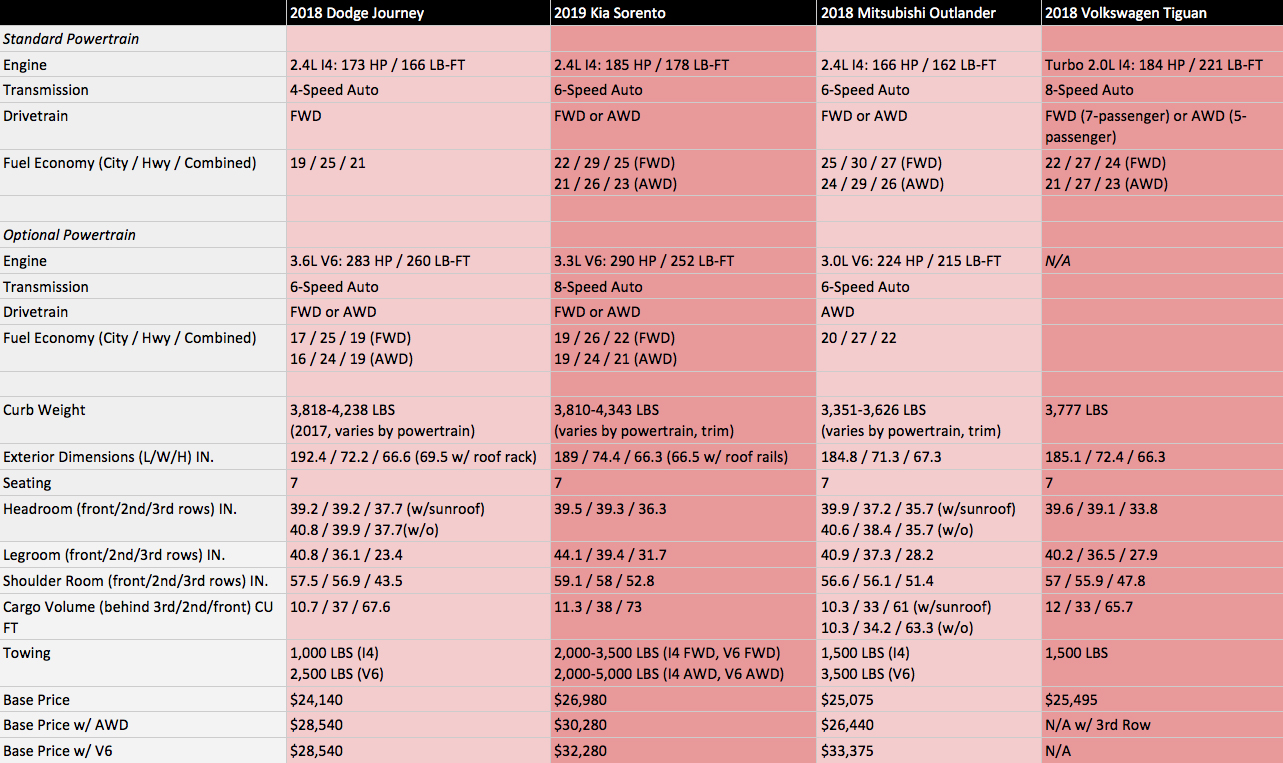
The driving experience significantly influences a vehicle’s appeal. Factors like handling, ride comfort, and noise levels directly impact the driver’s enjoyment and overall satisfaction. Understanding these differences between SUVs and sedans is crucial for making an informed purchasing decision.
The chosen suspension design plays a vital role in shaping the ride quality. Different designs cater to various driving styles and preferences, leading to contrasting driving characteristics. Steering feel and responsiveness also contribute to the overall driving experience, influencing how easily and precisely the vehicle can be maneuvered.
Handling Characteristics
SUVs, generally designed for a more rugged and versatile driving experience, often prioritize stability over agility. This results in a slightly less responsive steering feel and handling compared to sedans, which are optimized for precise and nimble maneuvering. SUVs tend to exhibit a more controlled body roll during cornering, although this varies significantly depending on the specific model’s suspension tuning and construction. This stability, however, can sometimes translate into a less engaging driving experience for drivers seeking sharper responses. Conversely, sedans are typically more agile and responsive, allowing for quicker and more precise maneuvers. This responsiveness often comes at the cost of some stability in extreme conditions.
Ride Comfort
Ride comfort is highly subjective and influenced by individual preferences. SUVs, due to their higher ground clearance and often more substantial suspension systems, typically provide a smoother ride over rough terrain and uneven roads. This cushioning effect, however, can sometimes translate into a less engaging driving experience, especially on smooth surfaces where the softer suspension might feel less responsive. Sedans, with their lower profiles and often more precisely tuned suspensions, offer a more refined and controlled ride on smoother roads, providing a more precise and responsive driving experience. However, they might feel less comfortable on poorly maintained roads compared to SUVs.
Noise Levels
Noise levels are another critical aspect of the driving experience. SUVs, with their larger size and increased structural components, often have slightly higher wind and road noise levels compared to sedans. This is because of the larger surface area and heavier construction, impacting overall noise absorption. Sedans, on the other hand, often achieve better noise isolation, resulting in a quieter and more refined interior environment, especially at higher speeds. This difference in noise levels can significantly affect the overall driving experience, impacting driver fatigue and enjoyment during extended trips.
Steering Feel and Responsiveness
The steering feel and responsiveness are key indicators of a vehicle’s handling capabilities. SUVs generally feature a more direct steering feel, allowing for a clear understanding of the vehicle’s movements. However, the responsiveness might not be as sharp or precise as in a sedan. Sedans, conversely, often boast a lighter and more responsive steering feel, making them more engaging to drive, especially in city environments. The precise feedback from the steering wheel allows for greater control and precision during maneuvers.
Driving Characteristics Comparison
| Characteristic | SUV | Sedan |
|---|---|---|
| Handling | Stable, controlled body roll; less agile | Agile, responsive; potentially less stable in extreme conditions |
| Ride | Smooth over rough terrain; potentially less engaging on smooth surfaces | Refined and controlled on smooth surfaces; potentially less comfortable on rough terrain |
| Steering | Direct, but potentially less responsive | Precise, responsive, and lighter |
| Noise Levels | Slightly higher wind and road noise | Quieter and more refined interior |
Technology and Features
Modern SUVs and sedans boast a range of advanced technologies designed to enhance the driving experience and safety. These features, while often overlapping, exhibit key differences based on the vehicle’s intended use and target audience. Understanding these nuances helps consumers make informed decisions aligning with their individual needs.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Modern vehicles are increasingly incorporating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to enhance safety and convenience. These systems use a combination of sensors, cameras, and radar to monitor the surrounding environment and provide drivers with alerts or even automated interventions in certain situations. Notable ADAS features include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, automatic emergency braking, and blind-spot monitoring. These features are designed to reduce driver workload and the risk of accidents.
Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems are a crucial component of the modern driving experience. These systems combine entertainment and communication functionalities within the vehicle, offering a wide range of connectivity options and user interfaces. The sophistication and features of infotainment systems vary significantly between different vehicle models, reflecting the diverse needs and preferences of drivers. The evolution of infotainment systems reflects the ongoing technological advancements in automotive engineering.
Connectivity Options
Connectivity options in modern vehicles extend beyond basic Bluetooth connectivity. Sophisticated infotainment systems enable seamless integration with smartphones through features like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto. These platforms provide drivers with access to navigation, music, and communication apps. Furthermore, some vehicles offer Wi-Fi hotspots, allowing passengers to connect to the internet within the vehicle. This seamless connectivity enhances the overall in-vehicle experience.
Comparison of Infotainment Features and Connectivity
| Feature | SUV Example (Model X) | Sedan Example (Model S) |
|---|---|---|
| Infotainment System | Large touchscreen display with intuitive controls, integrated navigation, and various multimedia options. Voice command recognition is strong, and the system supports multiple media streaming services. | Sleek dashboard with a digital instrument cluster and a central touchscreen, emphasizing a modern, minimalist aesthetic. Navigation and multimedia capabilities are seamlessly integrated. |
| Connectivity Options | Supports Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, offering seamless smartphone integration. A built-in Wi-Fi hotspot allows passengers to connect to the internet. | Supports Apple CarPlay and Android Auto for seamless smartphone integration. A built-in Wi-Fi hotspot provides connectivity for passengers. Advanced features like in-car 5G connectivity are being implemented. |
| Driver-Assistance Features | Advanced safety features, including adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking, are readily available. | Similarly, comprehensive ADAS features like adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking are integrated. |
Practicality and Versatility

SUVs and sedans cater to vastly different needs, impacting their practicality and versatility. Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the right vehicle for specific lifestyles and driving situations. From carrying bulky cargo to navigating congested city streets, each vehicle type excels in distinct areas.
Practicality hinges on factors like interior space, cargo capacity, and maneuverability. SUVs offer a significant advantage in hauling cargo and accommodating multiple passengers, while sedans excel in efficiency and maneuverability, particularly in urban environments. This section explores the unique strengths and weaknesses of each vehicle type, showcasing their suitability for diverse applications.
Practical Applications of SUVs
SUVs, with their elevated ride height and spacious interiors, are well-suited for various practical applications. Their ability to handle challenging terrain and carry substantial cargo makes them ideal for families, outdoor enthusiasts, and individuals requiring substantial hauling capacity. Examples include transporting large furniture, carrying sporting equipment, and traveling with multiple passengers.
- Family Vacations: SUVs excel at transporting families with luggage and children’s gear. The increased passenger space and cargo capacity make them ideal for weekend trips or longer vacations.
- Outdoor Activities: Whether it’s camping, hiking, or sporting events, SUVs can easily accommodate equipment and gear, often exceeding the carrying capacity of sedans.
- Heavy Cargo Transport: SUVs’ larger cargo areas are perfect for moving furniture, appliances, or other bulky items. This versatility surpasses the limitations of sedans, which struggle with similar tasks.
Practical Applications of Sedans
Sedans prioritize efficiency and maneuverability, making them a practical choice for daily commutes and city driving. Their compact size allows for easier parking and navigating tight spaces, offering advantages over SUVs in congested urban environments.
- Daily Commutes: Sedans often boast excellent fuel economy, making them cost-effective for daily commutes. Their smaller size and lighter weight contribute to lower running costs.
- City Driving: Maneuverability in tight spaces and parking lots is a significant advantage for sedans. Their compact size minimizes parking stress and allows for easy navigation through crowded city streets.
- Short Trips: For short journeys with minimal cargo, sedans are often a more economical and efficient choice than SUVs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | SUV | Sedan |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Capacity | Higher, often accommodating more passengers comfortably | Typically lower passenger capacity compared to SUVs |
| Cargo Space | Larger cargo area, often with flexible configurations | Limited cargo space, generally suitable for everyday items |
| Maneuverability | Lower maneuverability in tight spaces | Excellent maneuverability, particularly in city driving |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally lower fuel efficiency compared to sedans | Usually higher fuel efficiency |
| Terrain Capability | Higher ground clearance and better off-road capabilities | Limited off-road capability |
| Practical Applications | Family trips, outdoor activities, carrying heavy cargo | Daily commutes, city driving, short trips with minimal cargo |
Visual Aesthetics and Styling

The visual appeal of a vehicle plays a significant role in its desirability and perceived value. SUV and sedan design aesthetics reflect evolving societal preferences and technological advancements, impacting consumer choices. Different design trends shape the look and feel of each vehicle category, influencing factors like perceived performance, practicality, and overall desirability.
Design Aesthetics and Trends
SUV and sedan design aesthetics have undergone significant transformations over time. Early SUVs often emphasized ruggedness and functionality, while modern designs incorporate sleek, aerodynamic lines. Sedans, traditionally known for their refined and sophisticated styling, are now evolving with sportier and more aggressive designs. These shifts reflect consumer preferences and the broader automotive design landscape.
SUV Design Styles
The SUV market boasts a diverse range of design styles, catering to various preferences. Compact SUVs often feature a more urban-oriented aesthetic, characterized by sharp lines and aerodynamic profiles. Mid-size and larger SUVs tend to adopt a more rugged or sophisticated design language, emphasizing features like prominent wheel arches and powerful bumpers. Luxury SUVs often feature premium materials, intricate detailing, and sophisticated silhouettes to convey a sense of prestige.
Sedan Design Styles
Sedans showcase a range of design styles, each reflecting different performance and luxury levels. Compact sedans frequently feature clean lines and aerodynamic designs for fuel efficiency and a sporty appeal. Mid-size sedans often adopt a more sophisticated and refined aesthetic, while luxury sedans prioritize premium materials, intricate detailing, and a sophisticated silhouette. Performance-oriented sedans often feature aggressive designs, with aerodynamic enhancements and sportier body styles.
Visual Design Elements Comparison
| Vehicle Type | Body Style | Trim Level | Key Design Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUV | Compact | Base | Sharp lines, aerodynamic profile, functional design |
| SUV | Mid-size | Luxury | Rugged exterior, premium materials, sophisticated silhouette |
| SUV | Large | Performance | Aggressive styling, aerodynamic enhancements, powerful bumpers |
| Sedan | Compact | Base | Clean lines, aerodynamic design, sporty appeal |
| Sedan | Mid-size | Luxury | Sophisticated design, premium materials, intricate detailing |
| Sedan | Performance | High-end | Aggressive styling, aerodynamic enhancements, sportier body style |