
- Factors Affecting Used Car Loan Interest Rates
- Comparison of Used Car Loan Options
- Impact of Market Conditions on Interest Rates
- Strategies for Lowering Used Car Loan Interest Rates
- Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
- Resources for Finding Used Car Loan Information
- Illustrative Examples of Used Car Loan Scenarios
Factors Affecting Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Used car loans, like new car loans, are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers to shop for the most favorable interest rates and avoid overpaying. These factors range from the borrower’s creditworthiness to the specific terms of the loan itself.
Obtaining a used car loan often involves a comprehensive evaluation of the borrower’s financial profile and the characteristics of the vehicle being financed. The interest rate reflects the lender’s assessment of the risk associated with the loan. Factors like credit score, loan amount, and down payment significantly influence this risk assessment. The length of the loan and the current market conditions also play a role.
Credit Score Impact
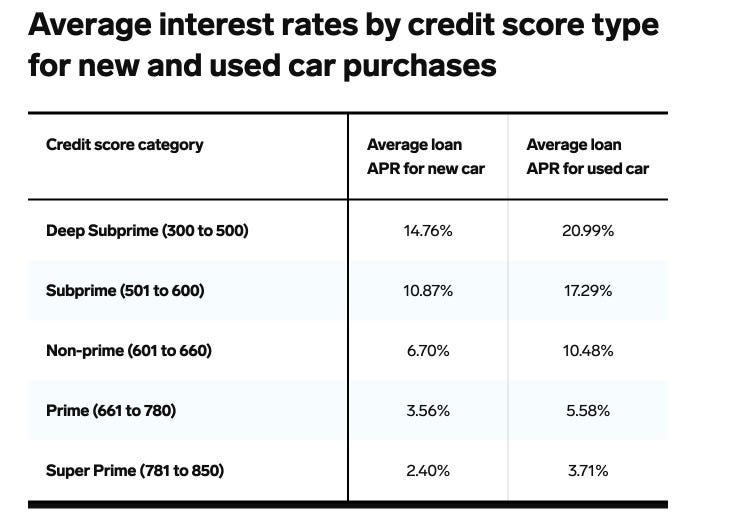
A borrower’s credit score is a key determinant of their interest rate. Lenders use credit scores to evaluate the borrower’s creditworthiness, estimating the likelihood of repayment. Higher credit scores generally translate to lower interest rates, as they indicate a lower risk of default. Conversely, lower credit scores lead to higher interest rates. This is because lenders perceive borrowers with lower credit scores as carrying a greater risk. A credit score in the excellent range (700 and above) typically results in a significantly lower interest rate compared to scores below 600.
Loan Amount and Down Payment
The loan amount and down payment directly impact the interest rate. A smaller loan amount often results in a lower interest rate, as the lender’s risk is reduced. A larger down payment similarly lowers the risk for the lender, leading to a potentially lower interest rate. The borrower’s ability to make a substantial down payment demonstrates a greater commitment to repaying the loan, which is attractive to lenders.
Length of Loan
The length of the loan, or loan term, also affects the interest rate. Shorter loan terms typically come with lower interest rates because the lender’s exposure to risk is reduced. A longer loan term exposes the lender to more risk over a longer period, thus often resulting in a higher interest rate. Borrowers should carefully consider the trade-offs between a shorter term with potentially higher monthly payments and a longer term with potentially lower monthly payments.
Interest Rate Range by Credit Score
| Credit Score Range | Typical Interest Rate Range (Example) |
|---|---|
| 700-850 (Excellent) | 3.50% – 6.00% |
| 680-699 (Good) | 4.50% – 7.50% |
| 600-679 (Fair) | 7.50% – 10.00% |
| Below 600 (Poor) | 10.00% – 15.00% + |
Note: These are illustrative examples, and actual interest rates can vary depending on the lender, the specific vehicle, and other factors.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, including prevailing interest rates for loans in general, play a role in used car loan interest rates. When overall interest rates are high, used car loan interest rates tend to be higher as well. Conversely, lower overall interest rates usually lead to lower used car loan interest rates. The current economic climate significantly influences the risk appetite of lenders, which, in turn, affects the interest rates they offer.
Vehicle Factors
The vehicle’s condition, year, make, model, and mileage also play a part in determining the interest rate. A higher-quality vehicle with low mileage and a recent model year is more likely to attract a lower interest rate. This is because lenders perceive such vehicles as having a lower risk of depreciation and mechanical issues.
Comparison of Used Car Loan Options

Navigating the used car loan market can feel overwhelming. Understanding the different types of loans available and their associated benefits and drawbacks is crucial for making an informed decision. This comparison will help you weigh the pros and cons of secured and unsecured loans, considering factors like interest rates, eligibility criteria, and repayment terms.
Choosing the right used car loan significantly impacts your financial well-being. A carefully considered approach ensures you secure the best possible terms and avoid potential pitfalls. A comprehensive understanding of the loan options allows you to select the most suitable choice for your specific needs and circumstances.
Secured vs. Unsecured Used Car Loans
Understanding the differences between secured and unsecured loans is paramount to selecting the most suitable financing option for your needs. Secured loans, often associated with lower interest rates, typically involve collateral, while unsecured loans rely solely on your creditworthiness.
- Secured Loans: These loans use the vehicle itself as collateral. If you default on the loan, the lender can repossess the car to recoup losses. This often results in lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans, especially for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit histories. A significant advantage is the potential for a lower interest rate, making it potentially more cost-effective. For example, a borrower with a less-than-stellar credit score might find a secured loan a more accessible path to car ownership than an unsecured loan.
- Unsecured Loans: These loans are based solely on your creditworthiness. The lender assesses your credit history, income, and other factors to determine your eligibility. Interest rates are generally higher than for secured loans, reflecting the higher risk for the lender. A key advantage is the absence of collateral requirements. However, borrowers with a strong credit history may find unsecured loans offer lower interest rates compared to secured loans. For example, an individual with a strong credit score might find an unsecured loan to be a more advantageous choice due to the lower interest rates and the lack of collateral requirements.
Key Differences in Interest Rates, Eligibility, and Repayment Terms
Comparing the key aspects of secured and unsecured loans is essential to selecting the appropriate loan for your financial situation. Interest rates, eligibility requirements, and repayment terms vary significantly between the two types of loans.
- Interest Rates: Secured loans typically command lower interest rates due to the reduced risk for the lender. The lower risk associated with secured loans often translates to more favorable interest rates. This lower risk translates into potentially lower monthly payments. For example, a secured loan might have an interest rate of 6%, while an unsecured loan might have an interest rate of 8%.
- Eligibility Criteria: Secured loans might have more lenient eligibility criteria for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit histories. This accessibility is a key advantage, particularly for those who may not qualify for an unsecured loan. For example, an individual with a less-than-perfect credit score might be eligible for a secured loan but not an unsecured loan.
- Repayment Terms: Both secured and unsecured loans offer various repayment terms. Lenders often provide flexibility in terms of loan duration and monthly payments. Careful consideration of these terms is essential to avoid financial strain. For example, a longer repayment term might reduce monthly payments but increase the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Loan Provider Comparison Table
This table illustrates a comparison of used car loan providers and their interest rates. Note that these rates are examples and may vary based on individual circumstances and market conditions.
| Loan Provider | Interest Rate (Example) | Loan Term (Example) | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 6.5% | 60 months | Strong credit history required |
| Credit Union B | 7.0% | 72 months | Good credit history, income verification |
| Online Lender C | 7.5% | 60 months | Credit score above 660, income verification |
| Finance Company D | 8.0% | 72 months | Credit score above 600, income verification |
Impact of Market Conditions on Interest Rates
Used car loan interest rates are not static; they fluctuate based on the overall economic climate. Understanding these market forces is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions and potentially secure more favorable financing terms. Factors like inflation, supply and demand for used cars, and general economic health all play a significant role in shaping the cost of borrowing.
Market conditions exert a powerful influence on the interest rates for used car loans. A robust economy, characterized by low unemployment and strong consumer confidence, often translates to lower interest rates. Conversely, periods of economic uncertainty, high inflation, or decreased consumer spending can lead to higher interest rates as lenders adjust their risk assessments. This dynamic interplay between economic factors and lending practices directly impacts the average interest rate borrowers face.
Fluctuations in the Overall Economy
The overall state of the economy significantly impacts the interest rates charged for used car loans. During periods of economic expansion, lenders are typically more willing to offer lower interest rates because of reduced risk. This is due to increased consumer spending and higher employment rates, which signal a healthier economic environment. Conversely, during economic downturns, lenders often increase interest rates to compensate for the increased risk of default. This is because lower consumer spending and higher unemployment rates lead to a less predictable economic climate.
Influence of Inflation
Inflation, the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, directly impacts used car loan interest rates. When inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases. To maintain their profit margins and compensate for the eroding value of their investments, lenders typically increase interest rates. This adjustment reflects the increased cost of borrowing money over time. For example, during periods of high inflation, lenders may increase the interest rates for used car loans to match the rising prices of goods and services.
Supply and Demand for Used Cars
The supply and demand dynamics in the used car market significantly influence interest rates. A shortage of used cars can drive up prices, making it more expensive for buyers to acquire vehicles. In this scenario, lenders might increase interest rates to reflect the increased risk associated with lending to consumers in a market with high prices and limited availability. Conversely, a surplus of used cars can lead to lower prices and potentially lower interest rates, as lenders perceive less risk in making loans. This is because consumers have more choices and the market is more stable.
General Economic Conditions
General economic conditions, beyond inflation and supply/demand, play a crucial role in used car loan interest rates. Factors such as consumer confidence, unemployment rates, and government policies all contribute to the overall economic environment. Strong consumer confidence often leads to lower interest rates, while high unemployment and uncertainty often lead to higher interest rates. Government policies, such as tax cuts or increased spending, can also influence economic conditions and subsequently, used car loan interest rates.
Relationship Between Market Conditions and Interest Rates
There is a direct relationship between market conditions and average interest rates for used car loans. As economic conditions improve, lenders are often more inclined to offer lower interest rates. Conversely, economic downturns and market uncertainties typically result in higher interest rates. This is a fundamental aspect of the lending process, where risk assessment directly influences the cost of borrowing.
Table: Interest Rate Fluctuations Over Time
| Economic Trend | General Impact on Interest Rates | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Expansion | Lower interest rates | 2018-2019 saw low unemployment and strong consumer confidence, resulting in lower used car loan interest rates. |
| Economic Recession | Higher interest rates | The 2008 financial crisis resulted in increased interest rates for used car loans due to the increased risk of default. |
| High Inflation | Higher interest rates | Periods of high inflation, such as the 1970s, often correlate with higher used car loan interest rates. |
| Low Supply of Used Cars | Higher interest rates | When used car inventory is low, prices rise, and lenders often increase interest rates to reflect the increased risk. |
Strategies for Lowering Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Securing a favorable interest rate on a used car loan is crucial for minimizing the overall cost of the purchase. Understanding the factors influencing interest rates and implementing effective strategies can significantly impact the financial burden of your car loan. This section explores actionable steps to secure a lower interest rate.
Lowering your used car loan interest rate involves a combination of proactive steps, including improving your credit score, negotiating with lenders, and comparing offers. A strong financial profile and skillful negotiation can lead to substantial savings over the life of the loan.
Improving Credit Score and Financial Standing
A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate. Maintaining a healthy credit history, demonstrating responsible debt management, and avoiding late payments are essential. Regularly checking your credit report for inaccuracies and promptly addressing any issues will positively impact your creditworthiness. Paying down existing debts, if possible, and keeping credit utilization low are additional strategies to improve your credit score. Consistent on-time payments and a low credit utilization ratio are key indicators of responsible financial management, which lenders value highly.
Negotiating with Lenders
Effective negotiation is a valuable tool in securing a better interest rate. Researching prevailing interest rates and understanding the lender’s criteria for interest rate adjustments are crucial. Knowing the market conditions and the lender’s specific criteria will allow you to tailor your negotiation strategy. Highlighting any positive aspects of your financial profile, such as a stable income and a long history of on-time payments, can strengthen your negotiation position. Presenting a compelling case for a lower rate based on your creditworthiness and the current market conditions can yield a more favorable interest rate. For example, if you have a high credit score and a consistent history of on-time payments, you can use this information to request a lower interest rate from the lender.
Comparing Loan Offers from Different Lenders
Comparing offers from multiple lenders is vital for securing the best possible interest rate. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the available options and the ability to select the most advantageous terms. Different lenders have different lending criteria and interest rate structures. A comparison of loan offers from multiple lenders will help you identify the best fit for your specific needs. Using online tools or contacting multiple lenders directly will give you a comprehensive overview of available options. For instance, using online loan comparison websites, you can easily compare interest rates, loan terms, and fees from various lenders.
Negotiation Tactics for Lower Interest Rates
Several negotiation tactics can be employed to secure a better interest rate. A well-prepared negotiation strategy can significantly influence the final interest rate offered. For instance, clearly articulating your financial standing and highlighting any positive aspects of your credit history will strengthen your position. Demonstrating a strong understanding of the market interest rates will provide evidence of your knowledge and preparedness. Another tactic is presenting a compelling case for a lower interest rate, justifying your request based on market conditions and your credit profile. Providing evidence of your consistent financial responsibility, such as a stable income and on-time payments, can sway the lender in your favor. Knowing the lender’s pricing structure and any current promotional offers is crucial.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
Navigating the complexities of a used car loan requires a clear understanding of the terms and conditions Artikeld in the loan agreement. Knowing the specifics of loan terms like APR, loan amount, and loan duration empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid potential financial pitfalls. A comprehensive understanding of the fine print is crucial for securing the best possible deal.
Key Terms and Definitions
Understanding the terminology associated with used car loans is essential for effective comparison and negotiation. Precise definitions of key terms like Annual Percentage Rate (APR), loan amount, loan duration, and monthly payments are vital for making sound financial choices.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Annual Percentage Rate (APR) | The APR represents the total cost of borrowing, encompassing interest and any fees associated with the loan. It’s expressed as a yearly percentage and is a critical factor in comparing different loan options. A lower APR generally translates to lower monthly payments. |
| Loan Amount | This is the principal amount borrowed to purchase the used car. It’s determined by the agreed-upon purchase price and any down payment. |
| Loan Duration (or Loan Term) | The loan term specifies the period over which the loan is to be repaid. Common loan terms for used cars range from 24 to 72 months. A longer term typically results in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. |
| Monthly Payments | The monthly payment is the fixed amount due each month to repay the loan. It’s calculated based on the loan amount, interest rate (APR), and loan term. A detailed breakdown of the payment components, including principal and interest, is often included in the loan agreement. |
| Down Payment | The down payment is the upfront amount paid by the borrower towards the purchase price of the used car. A higher down payment typically reduces the loan amount, leading to potentially lower monthly payments and a smaller total interest paid. |
| Prepayment Penalty | This is a fee charged by the lender if the loan is paid off earlier than the agreed-upon term. It’s crucial to understand if a prepayment penalty exists and its associated amount, as it can impact the overall cost of the loan. |
Significance of Reading the Fine Print
Thorough examination of the loan agreement is crucial. The fine print contains vital details that can significantly impact the overall cost and terms of the loan. These details may include hidden fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment charges. Carefully reviewing these provisions is essential for avoiding unexpected costs and ensuring a transparent agreement. Ignoring the fine print can lead to unforeseen financial obligations.
“Understanding the fine print is critical for avoiding unpleasant surprises down the road.”
Resources for Finding Used Car Loan Information
Knowing where to find reliable information on used car loan interest rates is crucial for securing the best possible deal. Navigating the complexities of the lending market can be overwhelming, but utilizing the right resources empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes. Thorough research is key to finding a loan that meets your financial needs and minimizes your overall borrowing costs.
Reliable Sources for Researching Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Several resources provide valuable information on used car loan interest rates. Utilizing a combination of these sources allows for a comprehensive understanding of the current market conditions and available options. By comparing offers from multiple lenders, you gain a broader perspective and increase your chances of securing the most favorable loan terms.
- Online Comparison Tools: Websites specializing in comparing financial products, including car loans, offer invaluable assistance. These tools typically gather data from various lenders, presenting you with a concise overview of available interest rates, loan terms, and other relevant details. Examples include sites like Bankrate, NerdWallet, and LendingTree. These tools often allow you to refine your search by factors like loan amount, credit score, and desired loan term.
- Financial Institutions’ Websites: Directly visiting the websites of banks, credit unions, and online lenders provides access to specific loan programs and interest rates. This allows you to see the rates offered by individual institutions, sometimes revealing more competitive options than those available through comparison tools. Be sure to read through the terms and conditions of each loan to understand all associated fees.
- Independent Financial Advisors: Consultations with financial advisors can be beneficial, especially for individuals seeking personalized guidance. Advisors can provide tailored recommendations based on your unique financial situation, helping you understand the complexities of different loan options. This personalized approach can be particularly valuable if you have specific financial goals or require detailed explanations of different loan structures. While this approach may come with a fee, the guidance can be well worth the investment.
Importance of Comparing Offers from Multiple Lenders
Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders is essential to maximizing your chances of securing the best possible interest rate. Each lender operates with its own criteria for assessing loan applications and determining interest rates. By examining offers from several sources, you gain a clearer picture of the competitive landscape and can identify the most favorable terms.
| Lender | Interest Rate | Loan Term | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 5.5% | 60 months | $300 |
| Credit Union B | 5.2% | 60 months | $250 |
| Online Lender C | 5.8% | 72 months | $200 |
This table provides a simplified example illustrating the differences in interest rates, loan terms, and fees offered by various lenders. The key takeaway is that comprehensive comparison is vital for finding the most advantageous loan.
“Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders is crucial to maximizing your chances of securing the best interest rate and overall loan terms. Don’t settle for the first offer you see; explore various options to ensure you are getting the most favorable deal.”
Illustrative Examples of Used Car Loan Scenarios

Understanding the factors influencing used car loan interest rates is crucial for making informed decisions. Different scenarios, characterized by varying loan amounts, credit scores, and loan durations, will result in distinct interest rates. These examples highlight the practical application of the discussed factors and demonstrate how these variables interact to determine the final interest rate.
Scenarios with Varying Loan Amounts, Credit Scores, and Loan Durations
Different loan amounts, credit scores, and loan durations will influence the interest rate charged on a used car loan. The following scenarios illustrate this.
-
Scenario 1: A borrower with a good credit score (750) is seeking a used car loan for $15,000 with a loan duration of 48 months.
This borrower is likely to receive a lower interest rate compared to other borrowers with less favorable credit scores or longer loan terms. Based on current market conditions, a projected interest rate of 6.5% is plausible. The lower credit risk associated with a higher credit score typically results in more favorable loan terms, reducing the interest rate. -
Scenario 2: A borrower with a moderate credit score (680) is seeking a used car loan for $20,000 with a loan duration of 60 months.
This borrower will likely face a higher interest rate due to a longer loan term and a moderate credit score. The increased risk to the lender due to the longer loan term and the less favorable credit score may lead to an interest rate around 8%. -
Scenario 3: A borrower with a fair credit score (620) is seeking a used car loan for $10,000 with a loan duration of 36 months.
This borrower is likely to receive a higher interest rate due to a shorter loan term and a fair credit score. The risk of default is potentially higher for this borrower, and a projected interest rate of 9% is possible. -
Scenario 4: A borrower with an excellent credit score (800) is seeking a used car loan for $25,000 with a loan duration of 72 months.
While the loan amount is higher, the excellent credit score significantly mitigates the risk. This borrower will likely receive a lower interest rate than those with lower credit scores, potentially around 5.5%. A longer loan term may still increase the risk slightly.
Loan Terms and Conditions for Each Example
Loan terms and conditions play a significant role in determining the final cost of a used car loan. These terms vary based on the lender, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and market conditions. For example, prepayment penalties, late payment fees, and balloon payments can significantly impact the overall cost.
| Scenario | Loan Amount | Credit Score | Loan Duration | Projected Interest Rate | Loan Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $15,000 | 750 | 48 months | 6.5% | Competitive interest rate, likely no prepayment penalty, standard late payment fees. |
| 2 | $20,000 | 680 | 60 months | 8% | Higher interest rate due to moderate credit score and longer loan term, potential prepayment penalty. |
| 3 | $10,000 | 620 | 36 months | 9% | Higher interest rate due to shorter loan term and fair credit score, potential prepayment penalty, and more stringent late payment fees. |
| 4 | $25,000 | 800 | 72 months | 5.5% | Lower interest rate due to excellent credit score, likely no prepayment penalty, standard late payment fees. |