
Introduction to VIN Decoding
A Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a unique 17-character alphanumeric code permanently affixed to a vehicle. This code serves as a crucial identifier, providing detailed information about the vehicle’s origin, specifications, and history. Understanding a VIN’s structure and the information it contains is essential for various purposes, from verifying authenticity to accessing maintenance records.
Accurate VIN decoding is critical for numerous applications. It facilitates the identification of a vehicle’s specific characteristics, enabling informed decisions regarding purchase, sale, or insurance. Correctly decoding a VIN helps avoid fraud, ensuring that the vehicle being considered matches the documented specifications. It is also essential for accurate record-keeping and maintaining a clear vehicle history.
BMW VIN Structure
The BMW VIN format follows a standardized structure, enabling consistent interpretation of the information encoded within. Understanding this structure is fundamental to extracting relevant details. The format is highly structured, with each position in the VIN corresponding to specific information about the vehicle.
VIN Parts and Corresponding Information
This table illustrates the breakdown of a typical BMW VIN, showing the location of each part and the type of information it conveys.
| VIN Part | Location | Information |
|---|---|---|
| World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) | Positions 1-3 | Identifies the manufacturer (e.g., BMW). |
| Vehicle Descriptor Section | Positions 4-8 | Specifies the vehicle type (e.g., model, body style). |
| Vehicle Identifier Section | Positions 9-17 | Unique identifier for the specific vehicle within its model and year. This segment often contains the VIN’s most significant information. |
| Model Year | (Variable, dependent on position) | Determined from the vehicle descriptor section, usually in conjunction with the plant code, to indicate the vehicle’s model year. |
| Plant Code | (Variable, dependent on position) | Identifies the manufacturing plant where the vehicle was assembled. |
| Engine Type | (Variable, dependent on position) | Indicated by the vehicle descriptor section. |
Methods for BMW VIN Decoding

Decoding a BMW VIN reveals crucial vehicle information, including its year, make, model, engine type, and more. Understanding these methods allows you to verify vehicle details, trace ownership history, and assess the vehicle’s authenticity. This knowledge is valuable for prospective buyers, insurance providers, and automotive professionals.
Various methods exist for decoding a BMW VIN, each offering varying degrees of accessibility and accuracy. Online tools are a convenient and often free resource, while dedicated software solutions provide more comprehensive information and potentially enhanced features.
Online VIN Decoding Tools
Free online VIN decoders are readily available, providing a quick and accessible way to decode a BMW VIN. These tools typically require only the VIN input and often offer a summary of the vehicle’s key specifications. Navigating these tools is straightforward, typically involving a simple input field and a display of the decoded data.
Accessing Free Online VIN Decoders
Numerous websites offer free BMW VIN decoding services. A quick search on search engines like Google or Bing using s like “BMW VIN decoder” or “free VIN decoder” will yield a variety of options. Sites offering such tools are often reputable, but it’s prudent to check the site’s reputation and ensure it’s a legitimate source before using it.
Using an Online Tool for BMW VIN Decoding
To illustrate, let’s use a hypothetical online tool. After navigating to the site, locate the VIN decoding section. Enter the 17-character BMW VIN in the designated field. Click the “Decode” button. The tool will process the VIN and display the decoded information, typically including the vehicle’s year, make, model, engine type, and other pertinent details. Crucially, users should pay attention to the tool’s source and its accuracy. A site that consistently provides incorrect or incomplete data should be avoided.
Examples of BMW VIN Decoding
Here are a few examples of BMW VINs and their decoded information (hypothetical for demonstration purposes):
* VIN Example 1: (Example VIN) – Decoded: 2018 BMW 3 Series, 2.0L Turbocharged Engine.
* VIN Example 2: (Example VIN) – Decoded: 2023 BMW X5, 3.0L Diesel Engine.
Comparison of Decoding Methods
Online VIN decoding tools offer convenience and accessibility, but their accuracy and comprehensiveness may vary. Some tools might only provide basic details, while others might offer more in-depth information. Dedicated software applications may provide more comprehensive data but usually require a subscription or purchase.
Comparison Table of Online VIN Decoding Tools
| Tool | Features | Accuracy | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool A | Basic details, year, make, model | High | Very Easy |
| Tool B | Basic details, plus optional extras | Medium | Easy |
| Tool C | Comprehensive details, history | High | Moderate |
Note: This table represents hypothetical tools and their features. Actual tools will vary. Always verify the source and accuracy of the tool used.
Information Extracted from a BMW VIN

A BMW Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a crucial document that contains a wealth of information about a specific vehicle. Understanding the structure and the meaning of each character within the VIN is essential for various purposes, including authenticating a vehicle, determining its history, and ensuring compliance with regulations. This detailed breakdown clarifies the specific data points encoded within a BMW VIN.
The VIN, a unique alphanumeric string, serves as a comprehensive identifier for each BMW vehicle. Each digit and letter within the VIN sequence holds a precise meaning, meticulously organized to provide crucial information about the car’s origin, features, and specifications. Decoding a VIN enables access to data that might otherwise be challenging to obtain, fostering transparency and reliability in the automotive sector.
Specific Details Obtainable from a BMW VIN
A BMW VIN meticulously records various details, including the vehicle’s manufacturing plant, year of production, model type, engine specifications, transmission type, and optional equipment. This comprehensive data empowers users to make informed decisions about a particular vehicle, offering valuable insight into its origins and characteristics.
Meaning of Each Digit or Character within the VIN
Each character in a BMW VIN holds specific information. The sequence of characters, their positions, and the respective meanings, are standardized across manufacturers, including BMW, allowing for accurate interpretation. Understanding the structure and the meaning of each position in the VIN provides crucial insight into the vehicle’s attributes.
Crucial Information Found in a BMW VIN
A BMW VIN reveals a multitude of critical details. This includes the manufacturing plant, year, model, engine type, and transmission type. These details are vital in evaluating a vehicle’s provenance, condition, and specifications. A deeper understanding of these data points helps individuals navigate the complexities of the automotive market, fostering informed decisions and preventing potential issues.
| VIN Position | Information Revealed |
|---|---|
| 1-3 | Manufacturing Plant Code |
| 4 | Manufacturing Year |
| 5-8 | Model and Body Type |
| 9 | Vehicle Assembly Plant Code |
| 10 | Vehicle’s Sequence Number within the Production Run |
| 11 | Vehicle’s Engine Type |
| 12-17 | Vehicle’s Equipment and Specifications |
Understanding VIN Decoding Limitations
VIN decoding, while a valuable tool, isn’t infallible. Various factors can introduce inaccuracies or limit the comprehensiveness of the decoded information. Understanding these limitations is crucial for using VIN data responsibly and avoiding misinterpretations.
Decoding limitations stem from the inherent structure and potential for errors in VIN data, as well as the limitations of the decoding tools themselves. Data entry errors, discrepancies between databases, and incomplete or inaccurate information within the databases used for decoding can all result in inaccurate outputs. It’s essential to recognize these possibilities to prevent relying solely on VIN decoding for conclusive information.
Potential Sources of Inaccuracy
VIN decoding accuracy depends on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. Errors in data entry, whether during vehicle manufacturing or later modifications, can directly impact the decoded information. Furthermore, changes to vehicle specifications, such as optional packages, customizations, or modifications after initial production, might not be reflected in all databases. This leads to discrepancies between the actual vehicle and the decoded data.
Database Discrepancies and Incompleteness
Different VIN decoding databases may contain conflicting or incomplete information. This is particularly relevant when dealing with older vehicles or those manufactured in regions with less comprehensive data coverage. Variations in data entry practices and potential errors in database updates further contribute to the possibility of inconsistent or inaccurate results across different decoding tools.
Limitations of VIN Decoding Tools
The accuracy of VIN decoding tools is directly tied to the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the underlying database. Outdated databases, inaccurate information, or limited coverage of specific vehicle models can lead to inaccurate results. Furthermore, some VIN decoding tools may not account for variations in VIN formats across different manufacturers or regions, leading to unexpected outputs. In such cases, additional research and verification steps are critical.
Need for Verification and Additional Research
Interpreting VIN data should not be a standalone process. It’s crucial to cross-reference decoded information with other sources. Checking manufacturer documentation, reviewing vehicle history reports, or consulting with automotive professionals can help validate the decoded information and mitigate potential inaccuracies. This additional verification is essential for ensuring the reliability of the information derived from VIN decoding.
Table of Common VIN Decoding Limitations and Potential Solutions
| Limitation | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Inaccurate or incomplete data in databases | Cross-reference with multiple decoding tools and manufacturer resources. |
| Data entry errors during vehicle manufacturing or modifications | Verify with vehicle history reports and consult with automotive professionals. |
| Changes to vehicle specifications (e.g., aftermarket parts) | Seek documentation for any modifications made to the vehicle. |
| Outdated databases | Use a reputable VIN decoder with regular updates. |
| Limited coverage of specific vehicle models or regions | Consult additional resources specific to the vehicle’s origin and model. |
Applications of BMW VIN Decoding
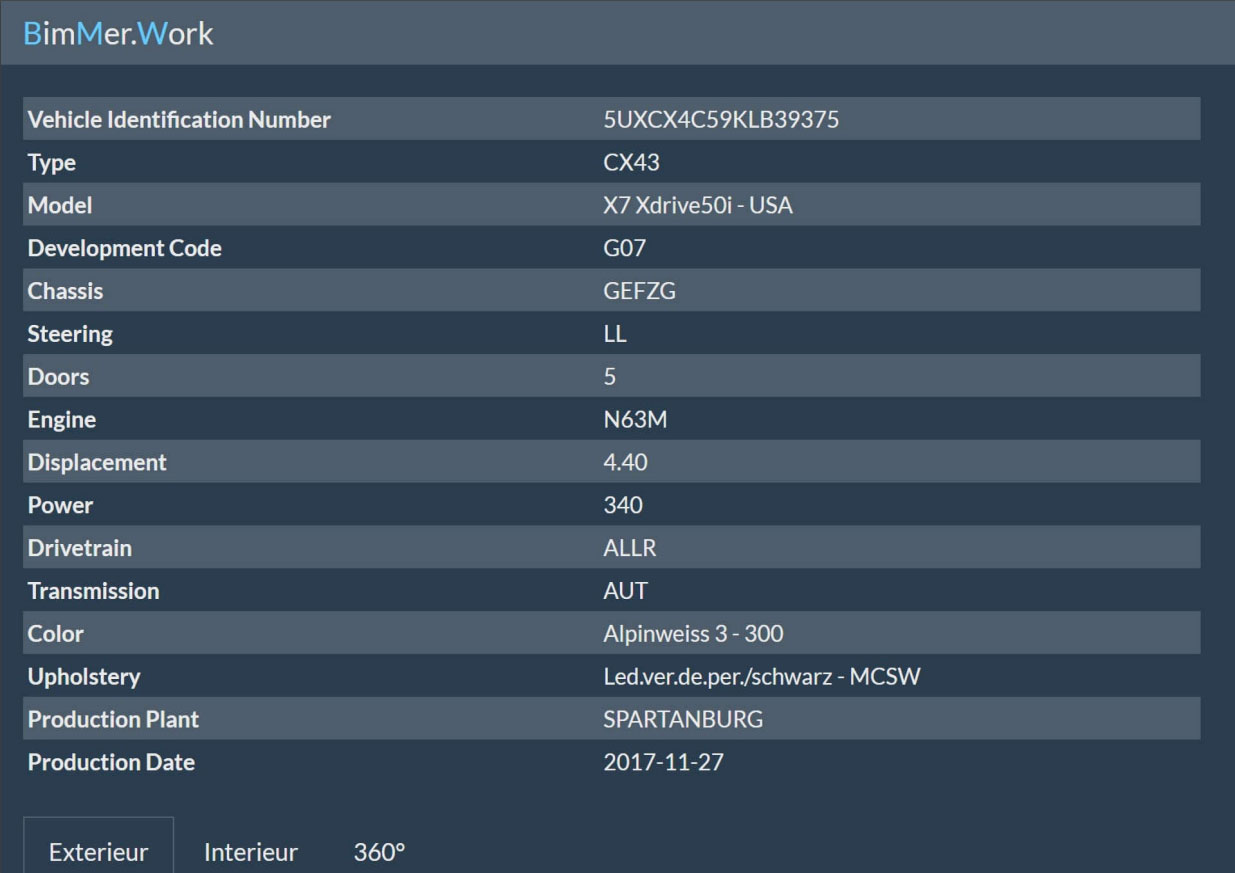
BMW VIN decoding is a crucial tool for various stakeholders involved in the automotive industry. It unlocks a wealth of information about a vehicle, enabling informed decisions in areas like sales, insurance, and repairs. This detailed understanding empowers businesses and individuals to manage risk, verify authenticity, and optimize processes related to BMW vehicles.
Understanding the specifics of a vehicle’s history and characteristics is essential for making accurate and timely decisions. Accurate identification of a vehicle’s origin, equipment, and service history are invaluable assets in various scenarios, from negotiating fair purchase prices to ensuring proper insurance coverage and efficient repairs.
Practical Uses in Car Sales
The ability to quickly and accurately decode a BMW VIN significantly impacts the car sales process. This process is critical for verifying a vehicle’s authenticity and history. Correctly identifying a vehicle’s features and previous maintenance history is crucial for establishing a fair sales price.
- Verification of Authenticity: Dealers can use VIN decoding to verify that a vehicle is legitimate and not stolen or involved in fraudulent activity. This safeguards against potential financial losses and reputational damage. For example, a used BMW advertised online with a suspicious VIN can be immediately investigated using decoding software to ensure it is not a stolen or cloned vehicle.
- Determining Vehicle History: A thorough VIN decoding reveals the vehicle’s maintenance history, previous owners, and any potential accidents or repairs. This crucial information is vital for negotiating a fair price and understanding the vehicle’s overall condition. For example, a car with frequent repairs or damage might be priced lower than a vehicle with a consistent service history.
- Identifying Options and Equipment: Decoding a VIN reveals specific options and equipment fitted to the vehicle, allowing dealers to accurately advertise and price the car accordingly. This transparency is beneficial for both buyers and sellers, promoting a more efficient transaction process. For example, a buyer might pay more for a vehicle with specific upgraded audio or navigation systems, as revealed by the VIN decoding.
Applications in Insurance
Insurance companies rely heavily on VIN decoding to assess risk and accurately evaluate insurance premiums. This process ensures appropriate coverage and helps prevent fraud.
- Evaluating Risk: Insurance companies use VIN decoding to determine the vehicle’s make, model, year, and specific features. This information helps them assess the risk associated with insuring the vehicle and establish appropriate coverage levels. For instance, a high-performance BMW model may carry a higher insurance premium due to its higher risk of damage.
- Claims Processing: During insurance claims, VIN decoding plays a critical role in confirming the vehicle’s identity and history. This helps prevent fraudulent claims and ensures that insurance coverage is applied appropriately. For example, if a vehicle is reported stolen, the VIN decoding confirms the vehicle’s existence and identity, facilitating a faster claim resolution process.
- Fraud Detection: Insurance companies utilize VIN decoding to detect fraudulent claims. The ability to verify the vehicle’s history and identify inconsistencies in the reported information is a vital aspect of fraud prevention. A vehicle reported as damaged in an accident but showing no such history in the VIN decoding might raise suspicion and trigger further investigation.
Utilization in Repair Processes
Accurate VIN decoding is essential for effective and efficient repairs. It allows mechanics to identify the correct parts and procedures for a specific BMW model.
- Identifying Correct Parts: Using the VIN, mechanics can access detailed specifications for a particular BMW model. This information is crucial for ordering the correct parts, ensuring compatibility and avoiding costly mistakes. For example, a VIN decoder would help differentiate between a 2015 BMW 3 series and a 2020 model, ensuring the correct parts are used for repairs.
- Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: The VIN often unlocks specific diagnostic information for the vehicle, guiding mechanics through the troubleshooting process. This information can significantly reduce repair time and improve accuracy. Knowing the vehicle’s history can help pinpoint potential issues or necessary repairs, saving time and money.
- Warranty Claims: Mechanics use VIN decoding to confirm the vehicle’s warranty status and identify the appropriate coverage for repairs. This process simplifies warranty claims and helps ensure customers receive the necessary support. For example, a VIN decoder can help determine whether a specific repair falls under the vehicle’s manufacturer warranty.
Tips for Accurate VIN Decoding
Accurate VIN decoding is crucial for verifying vehicle authenticity, identifying specific features, and ensuring proper documentation. Following these tips guarantees reliable information and prevents costly errors or misrepresentations. Incorrect decoding can lead to issues with insurance claims, legal disputes, and even fraudulent transactions.
Ensuring Accurate VIN Entry
Proper VIN entry is paramount for accurate decoding. Mistakes, even minor typos, can lead to inaccurate results. Use a clear and legible copy of the VIN, preferably from the vehicle’s title or registration documents. Double-check for any potential errors or discrepancies before entering the VIN into the decoder. Avoid using blurry or low-resolution images, as they can introduce errors. Compare the entered VIN to the source document to confirm its accuracy.
Verifying Decoded Information
Validating decoded information through cross-referencing with other sources significantly enhances accuracy. Check the decoded data against official vehicle databases, like those maintained by the manufacturer or government agencies. Compare the decoded details to the vehicle’s documentation, including the title and registration. Discrepancies may indicate potential issues, including fraudulent activity or inaccurate decoding.
Identifying Potential Fraudulent VINs
Recognizing fraudulent VINs is essential to prevent financial loss. Be wary of VINs that appear unusual or inconsistent. Look for VINs that don’t follow the established formatting patterns or have suspicious characters. Consult with experts or organizations specializing in VIN verification to assess potential risks. Check for VINs reported as stolen or involved in fraudulent activities.
Best Practices for Accurate VIN Decoding
- Use a clear, legible copy of the VIN from official documents.
- Double-check the VIN for any errors or typos before entering it into the decoder.
- Compare the decoded information with official vehicle databases and documentation.
- Be cautious of unusual or inconsistent VINs, and consult experts if needed.
- Cross-reference decoded information with official records to verify accuracy.
- Avoid using low-quality images or blurry copies of the VIN.
Illustrative Examples of BMW VINs
Understanding the structure and components of a BMW Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is crucial for accurate decoding. This section provides illustrative examples of various BMW VINs, along with their decoded information, to demonstrate the different formats and the meaning of each character within the VIN. By examining these examples, you can gain a deeper understanding of the information encoded within a BMW VIN.
BMW VIN Example Formats
BMW VINs adhere to a standardized format, but variations exist based on the model year and specific vehicle configuration. The following examples showcase different formats commonly encountered.
Note: The decoded information below represents typical examples. Actual decoded data may vary slightly based on the specific vehicle and data source.
| VIN Example | Decoded Information | BMW Model (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| WBAXXXXXXX1234567 |
|
BMW 3 Series Sedan |
| 1Y5XXXXXXX1234567 |
|
BMW X5 SUV |
| 7JAXXXXXXX1234567 |
|
BMW M5 Sedan |
Meaning of Different Characters in a BMW VIN
Each character within a BMW VIN holds specific meaning. A comprehensive understanding of these characters allows for precise decoding and extraction of critical information.
- The first three characters (e.g., WBA, 1Y5, 7JA) identify the manufacturer (BMW) and provide clues about the model, trim, and body style.
- The middle sequence of characters (e.g., XXXXXXXX) details specific features, engine type, and optional equipment.
- The final characters (e.g., 1234567) represent the vehicle’s unique identification number within the production run.
These examples illustrate the varying formats and the diverse information encoded within a BMW VIN. The specific characteristics and meaning of the characters will vary depending on the specific model, year, and optional equipment.