Used Car Valuation Methods

Used car values are complex, influenced by a multitude of factors. Accurate valuation requires considering not just the car’s age and mileage, but also its condition, market trends, and even local supply and demand. Understanding the different methods employed by valuation services like Edmunds.com provides valuable insight into how these intricate factors converge to determine a fair price.
Different Used Car Valuation Methods
Numerous methodologies exist for assessing used car values. These range from simple, mileage-based approaches to sophisticated models that incorporate a variety of data points. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, impacting the accuracy and reliability of the final valuation.
Mileage-Based Valuation
Mileage-based valuation is a straightforward approach, often used as a preliminary step. It relies on the assumption that higher mileage typically corresponds to lower value, reflecting increased wear and tear on the vehicle. This method is relatively simple to implement, requiring only access to the car’s odometer reading. However, it neglects crucial factors such as the car’s overall condition, maintenance history, and the specific model’s depreciation patterns. A car with high mileage but meticulous maintenance and a strong market demand could potentially command a higher price than a car with lower mileage but lacking in proper maintenance.
Condition-Based Valuation
Condition-based valuation considers the physical state of the vehicle. This method accounts for factors like damage, wear and tear, and overall aesthetics. Inspecting the car’s exterior, interior, and mechanical components is crucial. However, subjectivity plays a significant role in condition assessment, potentially leading to discrepancies in valuation. Different appraisers might interpret the same condition differently, affecting the accuracy of the valuation. A car with a minor dent, for example, might be assessed differently by different appraisers, impacting the final valuation.
Market Data-Based Valuation
Market data-based valuation analyzes current market trends to establish the price range for a particular used car model. This method draws on comprehensive data from recent sales of similar vehicles, encompassing factors like year, make, model, trim level, and options. The accuracy of market data-based valuation is heavily influenced by the volume and comprehensiveness of the data utilized. Recent trends in the market, like increased demand for specific models or shortages of particular components, can significantly impact the pricing. For instance, a limited-edition model, even with high mileage, might command a premium price due to high demand and low supply.
Comparison of Valuation Methodologies
| Valuation Method | Strengths | Weaknesses | Edmunds’ Use (Likely) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mileage-Based | Simple to understand, readily available data | Doesn’t account for condition, maintenance, or market factors | Likely used as a baseline for initial estimates |
| Condition-Based | Considers wear and tear, potential issues, and overall condition | Subjectivity in assessment, time-consuming | Potentially used for advanced estimates, possibly combined with other methods |
| Market Data-Based | Reflects current market trends, accounts for demand and supply | Can be volatile, influenced by sudden market fluctuations | Likely heavily relied upon for final valuations |
Role of Market Trends and Supply/Demand Dynamics
Market trends and supply/demand dynamics play a crucial role in used car pricing. A surge in demand for a particular model, often due to limited availability or positive reviews, can lead to a price increase. Conversely, a decline in demand or an oversupply can result in lower prices. This dynamic interaction between supply and demand directly impacts the valuation of used cars, making it a complex interplay of factors. For example, the recent chip shortage affected new car production, leading to increased demand and consequently higher prices for used cars of certain models.
Factors Influencing Used Car Value
Used car values are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making it challenging to pinpoint an exact price for a specific vehicle. Understanding these determinants is crucial for both buyers and sellers to navigate the used car market effectively. A comprehensive analysis considers everything from the vehicle’s history and condition to market trends and location.
Numerous elements contribute to the overall value of a used car. Mileage, condition, features, make, model, year, and geographic location all play significant roles. Accurate assessment of these factors helps determine a fair price for both the buyer and seller, promoting transparency and reducing potential disputes.
Vehicle Mileage
Mileage is a critical factor in determining used car value. Higher mileage typically translates to a lower value due to increased wear and tear on components. This is directly correlated with the potential for greater maintenance needs and increased repair costs. For example, a car with 100,000 miles on the odometer will likely be worth less than a similar car with 50,000 miles. This is a general trend; specific mileage thresholds can vary based on the make, model, and condition of the vehicle.
Vehicle Condition
The overall condition of a used car significantly impacts its value. Significant damage, such as accidents, extensive rust, or neglect, will drastically reduce the price. Conversely, a well-maintained vehicle with minimal wear and tear will command a higher price. Exterior and interior condition are key factors. Minor imperfections might not be significant, but major issues like frame damage or significant interior deterioration significantly decrease the car’s value.
Vehicle Make, Model, and Year
The make, model, and year of a vehicle greatly influence its value. Vehicles from reputable brands and desirable models generally command higher prices. The age of the vehicle also plays a part, as newer models often hold their value better than older ones. Market demand and brand reputation heavily influence the pricing of used vehicles. For example, a used Toyota Camry from 2015 will likely have a higher value than a similar-year model from a less reputable brand.
Geographic Location
Geographic location also plays a crucial role in used car pricing. Supply and demand in a specific region can impact prices. High demand in a particular area may lead to higher prices, while areas with lower demand may see lower prices for comparable vehicles. Additionally, local taxes and fees can also affect the final selling price. For instance, a used car in a major metropolitan area with a high cost of living might fetch a higher price compared to a similar model in a rural area.
Relative Importance of Factors
| Factor | Importance (High/Medium/Low) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Mileage | High | Higher mileage typically results in lower value, due to increased wear and tear and potential maintenance costs. |
| Condition | Medium | Significant damage or neglect significantly reduces value, impacting both mechanical and aesthetic aspects. |
| Make/Model | High | Brand reputation and model desirability directly affect the perceived value of the vehicle. |
| Year | Medium | Newer models generally retain value better, but the specific impact depends on the vehicle’s features and market demand. |
| Geographic Location | Medium | Supply and demand dynamics in a specific region can affect prices for comparable vehicles. |
Edmunds.com’s Valuation Process
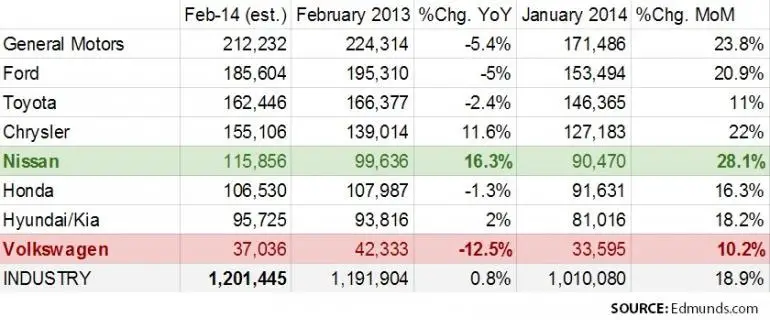
Edmunds.com provides a comprehensive used car valuation service, aiming to assist consumers in understanding the market value of vehicles. Their process goes beyond simply aggregating data; it involves sophisticated methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability. This detailed analysis delves into the specifics of Edmunds.com’s valuation approach, exploring the data sources, algorithms, and presentation methods.
Edmunds.com’s used car valuation process is designed to offer a precise and reliable estimate, considering a multitude of factors. This approach allows consumers to make informed decisions when buying or selling used cars. The process is iterative and continually refined to adapt to market fluctuations and evolving consumer preferences.
Data Sources Utilized
Edmunds.com leverages a vast array of data sources to inform its valuations. These sources contribute to the comprehensive and accurate used car value estimations. The data sources are crucial in providing a detailed picture of the market conditions.
- Market Transaction Data: Edmunds collects a substantial amount of data on actual used car sales transactions, including the price, year, make, model, mileage, condition, and location of the vehicles. This direct market data provides a strong foundation for their valuation models.
- Dealer Inventory Data: Information on the inventory of various dealerships across the country provides insights into the current supply and demand dynamics in different markets. This data contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the prevailing market trends.
- Consumer Reports and Reviews: Edmunds incorporates data from consumer reports and reviews, considering factors like reliability, safety ratings, and overall customer satisfaction. This qualitative data complements the quantitative market data.
- Manufacturer Information: Data from vehicle manufacturers, including specifications, features, and performance details, enhances the accuracy of the valuation process. This ensures a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s characteristics.
Algorithms and Models Employed
Edmunds.com likely employs a combination of statistical models and machine learning algorithms to process and analyze the vast amount of data collected. These models are crucial in producing accurate estimations of used car values.
- Regression Models: Edmunds likely uses regression models to identify the relationship between various factors and used car prices. These models allow them to predict the impact of different attributes on the final valuation.
- Machine Learning Models: Sophisticated machine learning algorithms, such as decision trees or support vector machines, could be employed to identify complex patterns and relationships in the data that might not be apparent using simpler models. These algorithms can adapt to changing market conditions.
- Dynamic Adjustment Models: The valuation process likely incorporates dynamic adjustments to account for market fluctuations. This ensures that the valuation remains relevant and responsive to real-time changes in supply and demand.
Valuation Process Differences
Edmunds.com’s valuation process differs from other sources in several key aspects. One major difference lies in the integration of various data points and the application of sophisticated models.
- Comprehensive Data Integration: Unlike some simpler sources, Edmunds integrates a broader range of data sources, including market transactions, dealer inventory, consumer reviews, and manufacturer information. This comprehensive approach provides a more nuanced and accurate valuation.
- Advanced Modeling Techniques: Edmunds may employ more advanced statistical and machine learning models to process and analyze the collected data. This allows them to identify complex relationships and trends that other sources might miss.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Edmunds.com’s valuations are likely updated frequently to reflect real-time market conditions, while some sources might offer static valuations or updates less frequently. This ensures that their valuations are more responsive to changing market trends.
Presentation of Valuation Information
Edmunds.com’s presentation of valuation information is user-friendly and detailed. This is crucial for helping consumers understand the value of a used car.
- Detailed Reports: The reports often include specific details like the vehicle’s year, make, model, mileage, condition, and location, in addition to the estimated value. This level of detail provides a clear understanding of the factors influencing the valuation.
- Visualizations: Edmunds.com might use graphs or charts to illustrate the trends in used car values over time. This visual representation helps users understand the market dynamics and the potential value fluctuations.
- Comparative Analysis: Edmunds.com might offer comparative analysis of different vehicles with similar specifications. This helps consumers make informed comparisons and assess the value of a specific vehicle in the context of the market.
Used Car Value Variations

Used car values aren’t static; they fluctuate significantly based on various factors. Understanding these variations is crucial for both buyers and sellers to make informed decisions. Different regions and local market conditions play a pivotal role in shaping used car prices. This section delves into the complexities of these price discrepancies.
Used car prices display substantial regional differences. These variations are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including supply and demand dynamics, economic conditions, and local market trends. A deeper understanding of these factors is essential for anyone navigating the used car market.
Regional and Market Price Comparisons
Used car prices vary significantly across different regions and markets. Factors like local economic conditions, population density, and consumer preferences contribute to these disparities. For instance, a high concentration of buyers in a particular region, combined with a limited supply of vehicles, can drive up prices. Conversely, a surplus of vehicles in a market with less demand will typically lead to lower prices.
Examples of Price Variations
Consider a hypothetical scenario where City A experiences high demand and low supply of used vehicles, resulting in an average price of $15,000. In contrast, City B may have lower demand and a higher supply, leading to an average price of $12,000 for comparable vehicles. These differences are not isolated cases but are indicative of broader trends in various regions.
Impact of Local Market Conditions
Local market conditions significantly influence used car prices. Economic downturns, employment rates, and population growth can all impact demand and supply. For example, a region experiencing an economic boom might see higher demand for used cars, while a region facing an economic downturn might witness a decrease in demand. Additionally, the availability of public transportation, proximity to job markets, and even seasonal trends can all contribute to local market conditions and thus, impact used car values.
Table Demonstrating Price Differences
| Location | Average Used Car Price | Factors Contributing to Difference |
|---|---|---|
| City A | $15,000 | High demand, low supply, strong job market, limited inventory of desirable models. |
| City B | $12,000 | Lower demand, higher supply, slower economic growth, abundant inventory of less desirable models. |
| Rural County C | $13,500 | Moderate demand, moderate supply, limited availability of specific models, lower transportation costs. |
Visual Representation of Data
Visualizing used car value data is crucial for understanding trends and making informed decisions. Effective graphs and charts transform complex numerical information into easily digestible insights, allowing consumers and dealers alike to quickly grasp pricing patterns and identify valuable opportunities. This section explores various visualization techniques, illustrating how to represent used car pricing data effectively.
Data visualization methods play a pivotal role in understanding used car values. By transforming raw data into graphical representations, we gain actionable insights into trends, relationships, and anomalies in the market. This allows for more accurate estimations of a car’s worth, enabling both buyers and sellers to make better decisions.
Mileage and Used Car Value Relationship
Understanding the correlation between mileage and used car value is essential for accurate valuations. A graph depicting this relationship allows for quick identification of depreciation patterns.

Description: The graph displays a scatter plot illustrating the relationship between car mileage (x-axis) and used car value (y-axis). The data points reveal a clear negative correlation, indicating that as mileage increases, the used car value generally decreases. This downward trend is noticeable across various car models, making the graph a valuable tool for understanding depreciation patterns. A trendline can be added to further emphasize the negative correlation.
Year-to-Year Value Comparison
Comparative analysis across different years for a specific car model is critical. This visualization allows for understanding the historical depreciation rate of a particular vehicle.
| Year | Average Value (USD) |
|---|---|
| 2018 | $25,000 |
| 2019 | $24,500 |
| 2020 | $23,000 |
| 2021 | $26,000 |
| 2022 | $27,500 |
Description: The table presents the average value of a 2018-2022 model year of a specific car model. This visualization highlights the fluctuation in value over time, indicating years of higher and lower average prices. Additional columns can be added to include factors like trim level or specific features for a more granular analysis.
Impact of Features on Value
Visualizing the influence of specific features on used car value allows for a focused analysis of how individual attributes affect pricing.

Description: The bar chart displays the impact of various features (e.g., sunroof, navigation system, leather seats) on the average used car value. Each bar represents a feature, and the height corresponds to its contribution to the overall value. This graphical representation clearly illustrates the added value associated with specific features, enabling buyers and sellers to understand the financial impact of those attributes.