Overview of Used Car Rates

Used car prices continue to be a dynamic market, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for both buyers and sellers navigating the current landscape. Recent data indicates fluctuating rates, driven by supply chain issues, economic conditions, and consumer demand. Regional disparities further complicate the picture, adding another layer of complexity to the overall market.
The fluctuating nature of used car pricing necessitates a nuanced understanding of the influencing factors. Supply chain disruptions, particularly in the semiconductor industry, have impacted new car production, which, in turn, has influenced the availability and pricing of used vehicles. Economic conditions, such as inflation and interest rates, also play a significant role. Consumer demand, which can vary based on economic outlook and available financing options, further shapes the market’s response.
Current Trends in Used Car Pricing
Used car prices have shown a notable trend of volatility in recent times. Factors like increased demand from consumers coupled with constrained supply of new vehicles have driven up used car values. This phenomenon, often referred to as the used car market boom, has affected various vehicle types differently. Furthermore, the pricing variations are evident across different regions.
Factors Influencing Used Car Rate Fluctuations
Several factors contribute to the fluctuations in used car rates. Supply chain disruptions, including delays in the production of new vehicles, have limited the supply of used cars. This scarcity has a direct impact on pricing, driving values upward. Economic conditions such as inflation and interest rates can also influence consumer spending habits, thereby affecting demand and consequently, used car prices. Consumer demand itself is a significant driver, fluctuating based on factors such as consumer confidence and the availability of financing options.
Regional Variations in Used Car Prices
The cost of used cars varies significantly across different regions. Geographic location plays a pivotal role, influencing factors like local demand, supply, and transportation costs. For instance, regions with higher population density and greater demand for vehicles tend to have higher used car prices. Furthermore, local regulations and taxes may also influence the overall pricing landscape.
Average Used Car Prices by Vehicle Type
| Vehicle Type | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Sedans | $15,000 – $25,000 |
| SUVs | $20,000 – $35,000 |
| Trucks | $25,000 – $40,000 |
These figures are estimates and may vary significantly based on the specific make, model, year, and condition of the vehicle. The table above provides a general overview of the average price ranges for different vehicle types.
Factors Affecting Used Car Prices

Used car prices are a dynamic reflection of various market forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers seeking to buy or sell used vehicles. The fluctuating nature of these prices is influenced by a complex interplay of supply, demand, economic conditions, and manufacturing processes.
The used car market is a microcosm of broader economic trends. Changes in consumer spending habits, interest rates, and manufacturing output all contribute to the shifting landscape of used car values. This analysis explores the key elements that influence used car prices today.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Fluctuations in supply and demand are fundamental drivers of used car prices. When demand outpaces supply, prices tend to rise, and vice-versa. This principle, a cornerstone of economics, applies directly to the used car market. Factors like seasonal variations, economic downturns, or shifts in consumer preferences can significantly impact the balance between supply and demand, leading to price volatility. For example, a sudden surge in demand during a period of low supply can quickly push prices upward, making vehicles more expensive for consumers.
Impact of Manufacturing Shortages
Manufacturing shortages, particularly of crucial components, have a direct and substantial effect on used car prices. When manufacturers face difficulties in producing new vehicles due to component scarcity, the supply of used cars is often reduced. This reduction in supply, coupled with consistent demand, results in a price increase for used vehicles. For instance, the semiconductor chip shortage of recent years significantly impacted new car production, leading to a corresponding rise in used car prices as the supply chain disruption rippled through the market.
Inflation’s Influence on Used Car Costs
Inflationary pressures affect the cost of virtually all goods and services, including used cars. As the general price level increases, the cost of materials and labor needed for car maintenance and repair also rises. This, in turn, increases the overall cost of used cars, as sellers factor in these escalating expenses when setting their prices. For example, rising fuel costs directly impact the cost of transporting goods, which indirectly affects the cost of used cars, which rely on these transportation costs.
Interest Rates and Car Loans
Interest rates play a critical role in determining the affordability of car loans. Higher interest rates increase the monthly payments associated with car loans, making vehicles less accessible to potential buyers. This reduced purchasing power can lead to a decrease in demand, and consequently, a decrease in used car prices. Conversely, lower interest rates make car loans more affordable, boosting demand and potentially increasing used car prices. For instance, a rise in interest rates can cause a decline in car sales, which in turn might lead to a decline in used car prices.
Correlation Between Factors and Used Car Prices
| Factor | Impact on Used Car Prices |
|---|---|
| Supply and Demand | Direct correlation; high demand, low supply = higher prices |
| Manufacturing Shortages | Indirect correlation; reduced supply = higher prices |
| Inflation | Direct correlation; rising prices = higher prices |
| Interest Rates | Indirect correlation; high rates = potentially lower prices |
Comparison of Different Used Car Markets
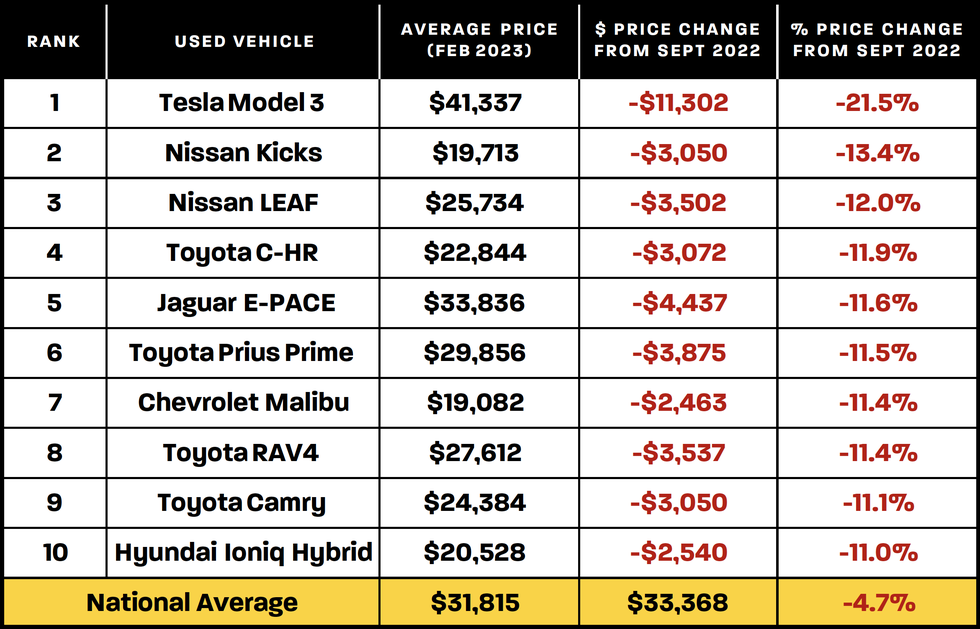
Used car prices fluctuate significantly across various geographical locations. Factors like local economic conditions, demand, supply, and even specific market trends within metropolitan areas contribute to these variations. Understanding these differences is crucial for both buyers and sellers, enabling informed decisions regarding purchasing and pricing used vehicles.
Metropolitan Area Comparisons
Used car rates exhibit substantial disparities between major metropolitan areas. Economic vitality, population density, and the presence of specialized car dealerships influence pricing. For example, areas with high job growth and strong local economies often see higher used car prices due to increased demand. Conversely, areas experiencing economic downturns may see used car prices decline as individuals reduce discretionary spending.
Urban vs. Rural Price Differences
Urban areas, typically characterized by higher population density and greater demand, generally experience higher used car prices compared to rural areas. The availability of a wider range of models and the presence of multiple dealerships within a concentrated urban environment drive up competition and, in turn, prices. Conversely, rural areas often see lower prices due to reduced demand and fewer options.
Impact of Local Economic Conditions
Local economic conditions play a pivotal role in shaping used car prices. During periods of economic growth, individuals have more disposable income, increasing demand for used cars. This increased demand often leads to higher prices. Conversely, during economic downturns, individuals may reduce discretionary spending, potentially leading to lower used car prices. For instance, a significant drop in employment in a particular area will likely lead to a reduction in demand and therefore lower used car prices.
State-Level Price Variations
Used car prices vary across states due to a combination of factors, including state-specific economic conditions, population density, and the prevalence of specific car dealerships. States with robust economies and high population density typically have higher used car prices. States with lower population density and fewer dealerships may see lower prices due to decreased demand and fewer options. For example, the high cost of living in California, combined with a high concentration of car dealerships, results in consistently higher used car prices than states with a lower cost of living.
Average Used Car Prices by Region (Illustrative Data)
| Region | Average Used Car Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| California | $25,000 |
| Texas | $22,000 |
| Florida | $23,500 |
| New York | $26,000 |
| Iowa | $18,500 |
Note: This table provides illustrative data only and is not exhaustive. Actual prices may vary based on specific models, years, and conditions of the used cars.
Impact of Specific Car Models
The used car market is highly influenced by the specific models available. Demand and pricing for certain vehicles are driven by factors like popularity, reliability, and perceived value. This section explores the price fluctuations of popular used models, examines the unique dynamics of luxury cars, and analyzes trends in the sports car segment.
Price Fluctuations of Popular Used Car Models
Various factors contribute to the fluctuating prices of used cars. Supply and demand dynamics, along with consumer preferences and market trends, are key determinants. A popular model with high demand will generally command a higher price compared to a less sought-after model, even if both are the same age and mileage. For instance, the Honda Civic, consistently a top seller, tends to hold its value better than less popular models in the same segment.
Factors Influencing Used Luxury Car Values
The value of used luxury cars is often influenced by factors beyond simple age and mileage. Features like specific trim levels, unique options, and the car’s overall condition play a significant role. The presence of rare or desirable features, such as specialized sound systems, high-performance engines, or unique paint jobs, can considerably increase the value of a used luxury vehicle. Furthermore, the brand’s reputation and the car’s history also contribute to the final price.
Pricing Trends of Used Sports Cars
The used sports car market exhibits distinct pricing trends compared to other vehicle categories. Factors such as the car’s performance specifications, manufacturer reputation, and rarity all impact its value. For example, a used sports car with a highly sought-after engine or a limited-edition model will command a premium price. Maintenance history and the car’s overall condition also contribute to the final valuation.
Average Used Car Prices of Popular Models
| Model | Average Price (USD) | Year | Mileage (Average) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry | $15,000 | 2018 | 50,000 |
| Honda Civic | $12,500 | 2019 | 45,000 |
| Ford F-150 | $25,000 | 2017 | 60,000 |
| BMW 3 Series | $28,000 | 2015 | 40,000 |
| Porsche 911 | $80,000 | 2012 | 30,000 |
Note: Average prices are estimates and can vary significantly based on specific features, condition, and market location.
Methods for Finding Accurate Used Car Rates
Navigating the used car market requires a strategic approach to pricing. Knowing how to find accurate used car rates empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid overpaying. This involves understanding the various resources available, evaluating their reliability, and interpreting the data presented.
Accurate used car pricing data is crucial for both buyers and sellers. Buyers can leverage this data to secure a fair price, while sellers can determine a competitive asking price. This empowers both sides with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in a complex market.
Resources for Finding Current Used Car Prices
Numerous resources provide insights into current used car prices. These range from online marketplaces to dealership websites and independent valuation services. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each resource is key to making informed decisions.
- Online Marketplaces: Major online marketplaces, such as Craigslist, Autotrader, and Kelley Blue Book (KBB), provide extensive listings of used cars. These sites often feature detailed information, including specifications, images, and previous owner history. However, the accuracy of listings can vary, requiring buyers to exercise caution in evaluating the reliability of the data.
- Dealership Websites: Dealerships often list their inventory on their websites, providing information on vehicles, prices, and any available financing options. While this information can be helpful, remember that dealerships may adjust prices to reflect their profit margins.
- Independent Valuation Services: Services like Kelley Blue Book (KBB) and Edmunds provide valuations based on various factors. These services typically provide more detailed assessments compared to basic online marketplaces. These resources offer a useful starting point, but their accuracy relies on the accuracy of the data input.
Accuracy of Online Pricing Tools
Online pricing tools are valuable resources but need careful consideration. The accuracy of online pricing tools depends on several factors, including the completeness and accuracy of the data input and the methodologies used to calculate values.
- Data Input: The accuracy of the valuations depends on the quality and completeness of the data inputted into the valuation models. Inaccurate data leads to unreliable results. Errors in vehicle year, mileage, or condition can significantly impact the final valuation.
- Methodology: Different tools use various methodologies to calculate values. Some consider factors like market trends, location, and specific car model specifications. Understanding the methodology behind a tool helps assess its reliability.
- Real-World Examples: Comparing the online valuation with the actual sales prices of similar vehicles in the local market provides insight into the tool’s accuracy. This comparison helps understand how well the online valuation reflects the current market trends.
Interpreting Online Listings and Determining Fair Market Value
Interpreting online listings requires careful consideration of various factors to determine a fair market value.
- Condition: The vehicle’s condition, including its exterior and interior, directly affects its value. Significant damage or wear and tear can significantly decrease the market value. A thorough inspection of the pictures and description is essential.
- Mileage: High mileage often indicates higher wear and tear, potentially impacting the vehicle’s value. Mileage is a crucial factor in determining the fair market value.
- Market Trends: Current market trends, including supply and demand, influence the fair market value. Understanding local market trends allows for a better estimation of a vehicle’s value.
Verifying Used Car Prices from Various Dealerships
Visiting multiple dealerships allows for a comprehensive understanding of the pricing landscape.
- Negotiation Strategies: Understanding negotiation strategies can be helpful in securing a fair price. Researching typical negotiation strategies for used cars can be helpful.
- Comparing Prices: Comparing prices across dealerships provides a better understanding of the market value. A range of prices provides insight into the value of the vehicle.
- Hidden Costs: Awareness of hidden costs, such as taxes, fees, or other charges, is crucial for making informed decisions. Understanding these additional costs can help prevent overpaying.
Comparison of Online Resources
A comparative analysis of online resources for used car pricing helps in choosing the most suitable tool.
| Resource | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Autotrader | Extensive listings, detailed information, good for comparisons | Accuracy of listings varies, some listings might be inaccurate |
| Kelley Blue Book (KBB) | Established reputation, detailed valuations, considered a reliable source | Valuations may not perfectly reflect local market trends |
| Edmunds | Comprehensive data, in-depth analysis, good for comparative research | Accuracy might vary depending on the data input |
Trends and Predictions
Used car prices are dynamic, responding to a complex interplay of economic forces, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer demand. Forecasting precise price movements is challenging, but understanding the underlying trends provides valuable insight for informed decision-making in the used car market. Analyzing past price fluctuations and considering potential future developments allows us to form a more nuanced understanding of the market.
Future Trends in Used Car Pricing
The used car market is experiencing a period of evolving dynamics. Factors like inflation, interest rates, and supply chain disruptions continue to influence prices. Additionally, changing consumer preferences and technological advancements play crucial roles in shaping the market. Anticipating these trends is essential for navigating the market effectively.
Impact of Economic Factors
Economic conditions significantly impact used car values. Rising inflation, for instance, often leads to higher used car prices as the cost of living increases. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions typically see a moderation in used car prices due to reduced consumer demand. Interest rates also play a crucial role, affecting borrowing costs and consumer spending, which directly impacts the market. For example, during periods of high-interest rates, financing options for used cars become less attractive, potentially leading to price reductions.
Potential Influence of New Car Models
The release of new car models often influences used car prices. The introduction of highly sought-after models can drive up the prices of older, comparable models. Conversely, the introduction of fuel-efficient or technologically advanced vehicles can reduce demand for older models, potentially leading to price declines. The demand for specific features and technologies in new models impacts the value proposition of comparable used vehicles. For example, the release of electric vehicles has impacted the prices of older, gas-powered models.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are reshaping the automotive industry. Innovations like electric vehicles, autonomous driving features, and connected car technologies are altering consumer preferences and influencing the value of different models. As technology matures and becomes more mainstream, it will likely affect the pricing of used vehicles. For example, as more consumers adopt electric vehicles, the demand for older gas-powered models may decrease, impacting their resale value.
Predicted Used Car Price Changes Over the Next Year
| Vehicle Type | Predicted Price Change (Estimate) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Compact Cars | -2% to +1% | Moderate demand, slight influence from new model releases. |
| Mid-size SUVs | +1% to +3% | Continued demand, potential for new model releases with premium features. |
| Luxury Sedans | +2% to +4% | Limited supply, strong demand from affluent buyers. |
| Electric Vehicles | -1% to +1% | Evolving market, fluctuating supply and demand. |
Note: These are estimates only and actual price changes may vary.
Visual Representation of Data
Visual representations are crucial for understanding complex data sets like used car prices. They transform raw figures into easily digestible insights, allowing for quick identification of trends, comparisons, and patterns. This section details visual representations of used car data, focusing on average prices, price trends, regional distribution, and their respective insights.
Average Used Car Prices by Vehicle Type
Understanding the price disparity between different vehicle types is essential for consumers and market analysis. A bar graph is a powerful tool for visualizing these differences.

Description: A bar graph illustrating the average used car prices across various vehicle types (e.g., sedans, SUVs, trucks, hatchbacks). Bars represent the average price for each vehicle type, enabling a direct comparison of their values. The y-axis displays the price range, and the x-axis lists the vehicle types. Colors are used to differentiate between vehicle types, enhancing visual clarity.
Trend of Used Car Prices Over the Past Year
Tracking price fluctuations over time is vital for assessing market dynamics and making informed decisions. A line graph effectively demonstrates this trend.

Description: A line graph depicting the monthly or quarterly changes in average used car prices over the past year. The x-axis shows the time period (e.g., months or quarters), and the y-axis represents the price range. The line illustrates the overall price trend, highlighting periods of increase or decrease, aiding in identifying fluctuations and potential future patterns. The graph incorporates error bars to indicate the degree of uncertainty in the price data.
Distribution of Used Car Prices Across Different Regions
Regional variations in used car prices can stem from factors such as local economic conditions, demand, and supply. A pie chart visualizes the proportion of used car prices in different regions.

Description: A pie chart showing the percentage of used car prices within different geographic regions (e.g., North, South, East, West). Each sector of the pie represents a region, and its size corresponds to the proportion of used car prices originating from that region. This visualization facilitates a quick understanding of the regional distribution of used car prices.
Data Table for Visual Representations
The following table summarizes the data used in the visualizations. Note that specific data values are placeholders and would be populated with actual figures.
| Visual Representation | Data Points | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bar Graph | Average used car prices (Sedans, SUVs, Trucks, Hatchbacks) | Compares average used car prices across different vehicle types. |
| Line Graph | Monthly/Quarterly average used car prices (Past 1 Year) | Displays the trend of used car prices over the past year, highlighting fluctuations. |
| Pie Chart | Percentage of used car prices in different regions (North, South, East, West) | Illustrates the distribution of used car prices across different geographic regions. |