Introduction to Used Car Price Index

A used car price index is a statistical measure that tracks the average price of used vehicles over time. It provides a valuable snapshot of the market’s health and direction, reflecting shifts in supply, demand, and economic conditions. By monitoring these fluctuations, consumers, investors, and industry professionals can make informed decisions regarding purchasing, selling, and investment strategies.
Understanding used car price trends is crucial for various stakeholders. For consumers, it helps anticipate potential costs and make informed decisions when buying a used car. For businesses, it informs inventory management, pricing strategies, and future projections. Investors in the automotive sector can utilize the index to assess market potential and make strategic investments.
Key Factors Influencing Used Car Values
Several factors significantly impact the value of used cars. Supply and demand dynamics are paramount, with high demand often leading to price increases. Vehicle condition, mileage, and model year all contribute to the perceived value. Additionally, market conditions, including economic downturns or recessions, can significantly impact used car prices. The availability of financing options and the prevailing interest rates can also affect the affordability and demand for used vehicles.
Historical Trends of Used Car Prices
Analyzing historical used car price trends reveals crucial insights into market behavior. Fluctuations in prices often mirror broader economic trends, with periods of economic growth typically correlating with increased demand and higher prices. Conversely, economic downturns often result in a decrease in demand and consequently, used car prices.
Used Car Price Index: Historical Data
| Year | Average Price (USD) | Market Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | $25,000 | Supply chain disruptions, increased demand due to pandemic lockdowns |
| 2021 | $30,000 | Continued supply chain issues, record-high demand, chip shortage |
| 2022 | $28,500 | Inflationary pressures, easing of some supply chain constraints |
| 2023 | $26,000 | Interest rate increases, decreased demand, improved supply |
Note: Data is illustrative and represents general trends. Specific figures may vary depending on the region and the specific vehicle model.
Methodology of Used Car Price Index Calculation
The used car price index provides a crucial metric for tracking market trends and understanding the dynamics of used vehicle values. Accurate calculation of this index relies on a robust methodology that considers various factors affecting pricing. This methodology ensures consistency and comparability over time, allowing for meaningful analysis of market fluctuations.
The index’s construction involves a systematic approach to data collection, price averaging, and the incorporation of weighting factors to reflect the importance of different vehicle characteristics. Understanding these methodologies is essential for interpreting the index’s results and their implications for the used car market.
Data Collection Process for Used Car Price Information
A comprehensive and representative dataset is fundamental for an accurate used car price index. This requires meticulously gathering data points from diverse sources, ensuring that the sample is statistically significant and geographically diverse. The process involves collecting pricing information from various online marketplaces, dealerships, and private sellers. This data collection process must adhere to strict protocols to maintain data integrity and minimize bias. Standardized data entry procedures are vital for ensuring consistent data quality and comparability across different data points. For instance, a consistent format for listing features, mileage, and condition is essential.
Methods Used to Average Used Car Prices
Several methods can be employed to average used car prices, each with its own advantages and limitations. A common approach involves calculating the arithmetic mean, which sums all prices and divides by the total number of vehicles. Alternatively, weighted averages can be used, giving more significance to vehicles with higher sales volume. Other methods, such as geometric means, might be applied to mitigate the impact of extreme values. Selecting the appropriate averaging method is critical for producing a representative index.
Comparison of Different Methodologies for Calculating the Index
Different methodologies for calculating the used car price index yield varying results. The choice of methodology impacts the sensitivity of the index to price fluctuations and the representation of the overall market. For example, an arithmetic mean might be more sensitive to outliers than a weighted average. A thorough comparison of methodologies is crucial to selecting the method that best reflects the intended purpose of the index. The robustness and accuracy of the index depend heavily on the selected methodology.
Weighting Factors Used in the Calculation
Weighting factors are critical components in the calculation of the used car price index. These factors reflect the relative importance of various vehicle characteristics in determining price. Factors like make, model, year, mileage, condition, and optional features all contribute to a vehicle’s value and thus influence the weighting scheme. Weighting factors can be determined through statistical analysis of historical sales data or market surveys, providing a more nuanced representation of the used car market.
Table Comparing Different Data Sources Used for the Index
Different data sources offer varying degrees of representativeness and access to information. This table illustrates the potential advantages and disadvantages of various data sources.
| Data Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Online Marketplaces (e.g., eBay, Craigslist) | Wide availability of listings, potentially large sample size | Potential for inaccurate or incomplete information, inconsistent data formatting |
| Dealership Databases | Reliable, detailed information, potentially high accuracy | Limited geographic coverage, potential for bias |
| Government Agencies (e.g., DMV records) | Comprehensive records of registered vehicles, potential for broad coverage | Limited pricing information, potential for delay in data availability |
| Independent Market Research Firms | Expert analysis, comprehensive data sets | Potential for cost and time constraints |
Components Affecting Used Car Prices
Used car prices are dynamic and influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these components is crucial for accurately interpreting market trends and predicting future price movements. These factors, from supply and demand to economic conditions, shape the value of pre-owned vehicles, and their analysis is essential for investors, consumers, and market analysts alike.
Analyzing the components driving used car price fluctuations provides valuable insights into market behavior. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions about purchasing, selling, or investing in used vehicles. Understanding the interplay between these factors enables a more nuanced comprehension of the market, going beyond simple supply and demand relationships.
Key Components Influencing Used Car Prices
A multitude of factors contribute to the fluctuations in used car prices. These components interact in intricate ways, making the used car market a complex and dynamic environment.
- Supply and Demand: The fundamental economic principle of supply and demand plays a critical role in determining used car prices. When the supply of used cars exceeds demand, prices tend to decrease. Conversely, a high demand with limited supply often leads to increased prices. Examples include limited production runs of specific models, making them more valuable, or a sudden surge in demand due to a specific market need.
- Economic Conditions: Economic factors significantly impact the used car market. During periods of economic growth, consumer confidence and purchasing power increase, often leading to higher used car prices. Conversely, economic downturns can reduce consumer spending, causing prices to fall. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, used car prices decreased as consumers cut back on discretionary spending.
- Specific Car Models or Makes: Demand for certain car models or makes can influence their prices. Vehicles with established reputations for reliability, performance, or desirability often command higher prices in the used market. Factors such as brand loyalty, model desirability, and perceived quality contribute to these price differentials. For example, classic muscle cars often see substantial price increases due to nostalgia and collector interest.
- Maintenance and Condition: The condition of a used car is a crucial determinant of its price. Cars with low mileage, meticulous maintenance records, and minimal damage typically fetch higher prices than those with higher mileage, significant repairs, or accidents. This is a direct reflection of the vehicle’s overall value proposition and its expected future maintenance requirements.
- Interest Rates and Financing: Interest rates directly affect the cost of financing a vehicle. Higher interest rates often discourage car purchases, potentially decreasing used car prices. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate the market, resulting in increased demand and consequently higher prices.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Used Car Prices
The relationship between economic indicators and used car prices is complex and often indirect. Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation, provide insight into the broader economic climate. The following table demonstrates the potential correlation between these indicators and used car prices.
| Economic Indicator | Potential Impact on Used Car Prices | Example |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | Positive correlation; higher growth usually correlates with higher prices. | A period of robust economic expansion often leads to increased consumer spending and demand for used vehicles. |
| Unemployment Rate | Negative correlation; higher unemployment typically correlates with lower prices. | During periods of high unemployment, consumers are more likely to postpone major purchases like used cars. |
| Inflation Rate | Complex relationship; high inflation can lead to higher prices, but it can also affect consumer purchasing power. | Rising inflation erodes the real value of money, potentially impacting affordability and demand for used cars. |
| Interest Rates | Negative correlation; higher rates usually correlate with lower prices. | Higher interest rates make financing more expensive, potentially deterring consumers from buying used cars. |
Analyzing Used Car Price Index Trends
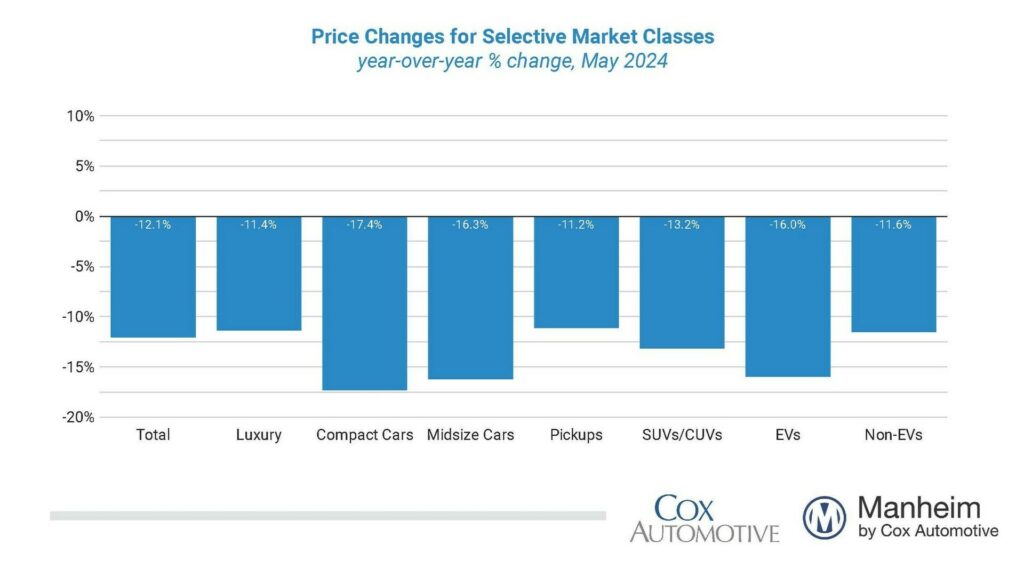
Understanding the trends in the used car price index is crucial for market participants, including consumers, dealers, and investors. This analysis provides insights into price fluctuations, potential drivers, and historical context, enabling informed decisions within the automotive sector. A clear understanding of these trends allows for better forecasting and preparedness for future market shifts.
Identifying Price Trends
The used car price index is a valuable tool for identifying upward or downward trends in used vehicle values. Analyzing historical data, comparing current values to previous periods, and observing seasonal patterns can reveal these trends. By plotting the index over time, a clear visual representation of the trend emerges, whether it’s a steady incline, a significant dip, or a fluctuating pattern.
Potential Causes of Price Fluctuations
Numerous factors can influence used car prices. Supply and demand dynamics play a significant role. Periods of low inventory, coupled with high demand, often lead to price increases. Conversely, a surplus of vehicles on the market, potentially due to increased production or decreased demand, can depress prices. Economic conditions, such as interest rates and inflation, also significantly impact consumer purchasing power, thus affecting demand and ultimately influencing used car prices. Furthermore, government regulations, such as emissions standards, and technological advancements, can impact the value of specific vehicle models over time.
Comparison with Historical Data
Comparing recent trends in the used car price index with historical data provides valuable context. This comparison reveals whether current fluctuations are part of a broader cyclical pattern or represent a unique market phenomenon. Examining past economic cycles and correlating them with price index movements helps in identifying potential future price trends. Historical data also helps to determine the relative magnitude of current fluctuations in the context of the overall market.
Price Index Breakdown by Vehicle Type
Different vehicle types often exhibit varying price trends. For instance, luxury vehicles may experience more significant price fluctuations compared to compact models. The price index can be segmented to reveal these variations. This breakdown enables a more granular understanding of the market dynamics specific to different vehicle categories. Analysis of each segment allows for targeted strategies in the market.
Yearly Variations in the Used Car Price Index
| Year | Used Car Price Index Value | Year-over-Year Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 120 | – |
| 2021 | 150 | 25% |
| 2022 | 165 | 10% |
| 2023 | 158 | -4% |
This table provides a concise overview of yearly variations in the used car price index. It illustrates the changes in the index from one year to the next, enabling a clear visualization of the trend over time. Year-over-year variations highlight the dynamics of the market and the factors contributing to these fluctuations.
Factors Affecting Used Car Supply
The availability of used cars on the market is a dynamic phenomenon, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing used car price index trends and predicting future market movements. Supply-side considerations are just as important as demand-side considerations in shaping the overall market equilibrium.
Manufacturer Production
Manufacturer production significantly impacts the initial supply of new vehicles, which, in turn, affects the used car market. A surge in new car production often leads to a greater influx of used vehicles entering the market. Conversely, a downturn in production can result in a reduced supply of used cars. This relationship is particularly evident in markets where new car sales are highly correlated with overall economic conditions. For example, during economic downturns, new car sales may decline, leading to a slower rate of used car entry into the market.
Regulatory Policies
Government regulations play a critical role in shaping used car supply. Emission standards, safety regulations, and import/export restrictions directly influence the number of vehicles available for sale. Stringent emission standards, for instance, can result in older vehicles being removed from circulation faster than previously, thus decreasing the supply of used cars. Conversely, relaxed regulations might lead to a greater supply of older vehicles. This illustrates how regulatory frameworks significantly impact the used car market.
Market Events
Various market events can disrupt the predictable flow of used car supply. Natural disasters, pandemics, or major economic shocks can all create temporary shortages or surpluses of used cars. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted global supply chains, leading to delays in the production and availability of new vehicles. This, in turn, affected the rate at which used cars entered the market. Other market events, such as significant changes in consumer preferences, can also influence the supply of used cars.
Relationship Between Used Car Supply and Prices
| Used Car Supply | Price Trend |
|---|---|
| High Supply | Generally Lower Prices |
| Low Supply | Generally Higher Prices |
| Stable Supply | Prices fluctuate based on other market factors |
The table above provides a basic overview of the relationship between used car supply and prices. It’s important to note that this is a simplified representation, and numerous other factors, including demand, condition of the vehicles, and market sentiment, also influence prices.
Applications and Uses of the Used Car Price Index
The used car price index serves as a crucial tool for understanding the dynamics of the used car market. It provides valuable insights into price trends, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions across various sectors. This index is instrumental in analyzing market fluctuations, assessing financial risks, and ultimately shaping consumer and business strategies.
Utilization by Stakeholders
The used car price index is a vital resource for numerous stakeholders. Dealers utilize it to price their inventory effectively, anticipating market changes and adjusting their strategies. Financial institutions rely on the index for risk assessment and loan evaluation. Insurance companies leverage it to adjust insurance premiums and accurately assess vehicle values. Finally, consumers can use it to understand market trends and make more informed purchasing decisions.
Financial Modeling Applications
The used car price index is an essential component in various financial models. It helps predict future market conditions, enabling businesses to forecast revenue and expenses related to used car sales. For example, a declining index might signal reduced demand, prompting businesses to adjust inventory levels or explore alternative strategies. Moreover, the index informs valuation models for used car dealerships, facilitating informed investment decisions. The index also aids in the development of financial models for used car loan products, ensuring appropriate risk assessment and interest rate adjustments.
Impact on Insurance Policies
The used car price index directly influences insurance policies. By reflecting the current market value of used cars, the index enables insurance companies to adjust insurance premiums based on the risk associated with each vehicle. For example, a significant increase in the index might suggest higher repair costs and thus higher insurance premiums for similar vehicles. Conversely, a decrease might result in lower premiums. This adjustment ensures the premiums remain aligned with the actual market value of the vehicles.
Used Car Valuation
The index is a critical tool for accurately valuing used cars. It provides a standardized and objective measure of market value, helping in determining fair market prices for used cars in transactions. By reflecting current market trends, the index allows for informed decision-making in the sale and purchase of used vehicles. Furthermore, it assists in establishing a benchmark for appraisal purposes, ensuring accurate valuation for insurance claims and other financial transactions.
Consumer Purchasing Decisions
The index provides valuable information to consumers when making used car purchasing decisions. It allows them to understand the current market value of a vehicle, comparing it to the asking price. Consumers can use the index to negotiate prices effectively, ensuring they’re getting a fair deal. For example, a consumer can use the index to identify vehicles that are undervalued in the current market, potentially securing a better purchase.
Table Illustrating Applications
| Stakeholder | Application |
|---|---|
| Dealers | Pricing inventory, forecasting market trends, adjusting sales strategies |
| Financial Institutions | Risk assessment, loan evaluation, asset valuation |
| Insurance Companies | Premium adjustments, risk assessment, claims evaluation |
| Consumers | Informed purchasing decisions, price negotiation, understanding market trends |
| Appraisers | Establishing a benchmark for valuation, ensuring accurate assessments |
Regional Variations in Used Car Prices
Used car prices, while influenced by national trends, exhibit significant regional variations. These disparities reflect a complex interplay of factors, including local supply and demand dynamics, economic conditions, and the availability of specific vehicle models. Understanding these regional nuances is crucial for both consumers and businesses operating in the used car market.
Regional variations in used car prices are a direct result of the interplay between local market conditions and broader national trends. Different regions experience varying levels of demand, supply, and economic activity, all of which contribute to price fluctuations. Understanding these local nuances allows for a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of the used car market.
Regional Differences in Used Car Price Indexes
Regional used car price indexes reveal substantial disparities across different geographic areas. These variations are not simply random fluctuations but are often rooted in the unique characteristics of each region.
Impact of Geographical Location on Price Fluctuations
Geographical location plays a significant role in shaping used car prices. Proximity to major manufacturing hubs, high-population density areas, or areas with specific demand characteristics often leads to price discrepancies. For example, areas with higher unemployment rates may see lower demand for used vehicles, resulting in lower prices. Conversely, areas with booming industries or high population growth might experience increased demand and subsequently higher used car prices.
Causes for Regional Disparities
Several factors contribute to regional disparities in used car prices. These include:
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Areas with a higher concentration of used car dealerships or auction facilities often have a greater supply, potentially leading to lower prices. Conversely, regions with limited availability may experience higher prices.
- Economic Conditions: Regional economic conditions, such as employment rates, income levels, and consumer spending habits, significantly influence demand and consequently, used car prices. Areas experiencing economic hardship may see decreased demand and lower prices.
- Vehicle Availability: The availability of specific makes and models of used cars varies geographically. Regions with higher concentrations of certain vehicle types or unique car models may command higher prices due to limited availability.
- Transportation Costs: Transportation costs associated with moving vehicles from one region to another can impact the prices. Higher transportation costs may result in higher prices in regions further away from manufacturing centers or major supply sources.
- Local Taxes and Regulations: Regional differences in taxes, fees, and regulations for used cars can influence the final sale price.
Examples of Regional Variations in Price Indexes
A study by [Name of reputable organization] found substantial differences in used car price indexes across various US states. For instance, states with a high concentration of car manufacturers often saw lower prices compared to states with lower production and greater demand.
Table of Regional Variations in Used Car Prices
| Region | Average Used Car Price Index (2023) | Factors Influencing Prices |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 115 | High demand, limited supply, higher transportation costs |
| Midwest | 108 | Moderate demand, average supply, relatively lower transportation costs |
| South | 110 | Moderate demand, increasing supply, varying transportation costs |
| West | 112 | Varying demand and supply based on specific states, relatively higher transportation costs in some areas |
Note: Index values are hypothetical examples and represent the relative price differences between regions. Actual data from reputable sources should be consulted for precise figures.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates are crucial macroeconomic factors that significantly influence used car prices. These forces interact in complex ways, impacting both the supply and demand sides of the market. Understanding these relationships is essential for interpreting trends in the used car price index.
Impact of Inflation on Used Car Prices
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. When inflation rises, the real value of savings decreases, making consumers less likely to save for a new or used car purchase. This can lead to increased demand for used cars as consumers seek to acquire vehicles at current prices before the cost increases further. Conversely, if inflation remains low, consumers may postpone purchases, as the real value of their savings is not eroding at a rapid pace. Higher inflation often leads to higher prices for used cars as sellers seek to maintain profit margins.
Effect of Interest Rates on Consumer Borrowing and Used Car Purchases
Interest rates directly affect the cost of borrowing money. Higher interest rates increase the monthly payments on loans, making car purchases less affordable for consumers. This can lead to a decrease in demand for used cars, particularly those financed through loans. Conversely, lower interest rates incentivize borrowing, increasing the number of consumers who can afford to purchase a used vehicle, thereby stimulating demand and potentially pushing up prices.
Influence of Economic Factors on the Used Car Price Index
The used car price index is a reflection of these economic forces. As inflation rises, the price of used cars tends to increase to compensate for the reduced purchasing power of the currency. Conversely, as interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing rises, potentially decreasing the demand for used cars and causing a downward pressure on the index. The interaction of these forces makes accurate predictions complex but important for informed financial decision-making.
Correlation Between Inflation, Interest Rates, and the Used Car Price Index
A strong correlation exists between inflation, interest rates, and the used car price index. Higher inflation often accompanies rising interest rates, as central banks typically raise interest rates to combat inflation. This dual pressure can lead to a significant impact on the used car price index, potentially causing a decrease in demand, and hence, a decline in prices. However, the relationship is not always straightforward and can vary based on market conditions.
Table Illustrating the Correlation Between Inflation/Interest Rates and Used Car Prices
| Inflation Rate (%) | Interest Rate (%) | Impact on Used Car Prices |
|---|---|---|
| High (e.g., 8%) | High (e.g., 6%) | Potential for decreased demand and price decrease. |
| Moderate (e.g., 3%) | Low (e.g., 2%) | Stable or slightly increasing prices, driven by other factors. |
| Low (e.g., 1%) | Low (e.g., 1%) | Stable or slightly decreasing prices, driven by other factors. |
| High (e.g., 10%) | High (e.g., 8%) | Potential for a significant decrease in demand and potentially higher prices to offset inflation. |
Note: This table provides a simplified illustration and does not account for other market factors that can influence used car prices.
Future Predictions and Projections
Forecasting used car prices requires careful consideration of various intertwined factors. Economic conditions, consumer demand, supply chain disruptions, and technological advancements all play a role in shaping future trends. Accurately predicting the used car price index over the next five years is challenging, but analyzing historical data and current market dynamics provides a framework for potential outcomes.
Understanding the interplay between these factors allows for the development of plausible scenarios, each with its own set of assumptions and potential outcomes. The resulting projections, while not guarantees, offer valuable insights into the possible future trajectory of the used car market and its price index.
Potential Market Disruptions
Several factors could significantly impact the used car market and, consequently, the price index. Supply chain bottlenecks, particularly in semiconductor production, could lead to shortages of new vehicles, driving up demand for used cars. Changes in interest rates and financing options can influence consumer purchasing power, impacting demand and, consequently, prices. Major geopolitical events, such as trade wars or international conflicts, could disrupt global supply chains and impact the availability and cost of used cars. Natural disasters or other unforeseen events could also introduce temporary disruptions to the market.
Possible Scenarios for the Used Car Market
Different scenarios are possible for the used car market and price index over the next five years. These scenarios account for various potential economic and market conditions.
- Scenario 1: Steady Growth – If economic growth remains moderate, consumer demand for used cars is stable, and supply chain disruptions are minimal, the used car price index might exhibit a gradual but steady upward trend. The rate of growth could vary depending on the interplay of factors like interest rates and new car availability.
- Scenario 2: Inflationary Pressures – If inflation rises significantly, impacting consumer purchasing power, the used car price index could experience a more substantial increase, potentially outpacing inflation. This scenario also factors in the increasing cost of parts and maintenance, driving up the prices of used vehicles.
- Scenario 3: Supply Chain Disruptions – Persistent or unexpected disruptions in the supply chain, potentially caused by global events or natural disasters, could lead to fluctuations in the price index. This scenario considers the impact on the availability of parts and the potential for shortages of certain used car models. The price index could see sharp spikes and drops depending on the severity and duration of these disruptions.
Future Price Projections
Predicting exact price points is inherently uncertain, but a range of potential outcomes based on the previously Artikeld scenarios is presented below.
| Scenario | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steady Growth | 2.5% increase | 2.8% increase | 3.0% increase | 3.2% increase | 3.5% increase |
| Inflationary Pressures | 4.0% increase | 4.5% increase | 5.0% increase | 5.5% increase | 6.0% increase |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | -1.0% decrease | +2.0% increase | -0.5% decrease | +3.0% increase | +4.0% increase |
Note: These projections are illustrative and do not represent definitive forecasts. Actual outcomes could vary significantly depending on unforeseen circumstances.