Introduction to Used Car Payment Calculators
Used car payment calculators are invaluable tools for prospective buyers. They provide an estimate of monthly payments, helping consumers to understand the total cost of ownership and compare different financing options. These calculators streamline the car-buying process by allowing users to quickly assess their affordability and make informed decisions.
These calculators leverage pre-determined formulas to project monthly payments based on various input parameters, offering a crucial step in the pre-purchase planning phase. Understanding the calculations behind these estimates empowers consumers to confidently negotiate with dealerships and avoid overspending.
Common Features of Used Car Payment Calculators
Used car payment calculators typically incorporate several key features to facilitate accurate estimations. These features encompass various aspects of the financing process, allowing users to explore different scenarios and tailor their calculations. The core features facilitate a comprehensive overview of the car’s financial implications.
- Loan Amount: This field allows the user to specify the total amount borrowed for the car purchase. This value directly influences the monthly payment.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate significantly impacts the total cost of the loan. Calculators often allow users to input various interest rates to compare different financing options.
- Loan Term: The loan term, usually expressed in months, dictates the duration of the repayment period. Longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid.
- Down Payment: The down payment amount directly reduces the loan amount and consequently lowers the monthly payment.
- Trade-in Value (if applicable): This field allows users to account for any trade-in value of a vehicle, reducing the loan amount and lowering the monthly payments.
- Additional Fees: Calculators may allow for the input of additional fees like title, license, or registration fees. This provides a more comprehensive estimate of the total cost.
Input Fields Required by Calculators
The input fields required by these calculators are crucial for generating accurate estimations. A well-designed calculator requires appropriate input fields for the various components of the loan.
- Vehicle Price: The purchase price of the used car is a fundamental input, forming the basis for the loan amount.
- Loan Amount: The amount borrowed for the vehicle is directly influenced by the purchase price and any down payment.
- Interest Rate: The annual interest rate is a significant factor in determining the total cost of borrowing.
- Loan Term: The loan term in months dictates the repayment period, influencing monthly payments and total interest.
- Down Payment: This input represents the upfront payment made by the buyer, reducing the loan amount.
- Trade-in Value (optional): The value of a traded-in vehicle can reduce the loan amount.
Types of Used Car Payment Calculators
Various types of used car payment calculators cater to different needs and preferences. The choice of calculator type depends on the user’s access and comfort level with various technologies.
| Feature | Online Calculator | Mobile App |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Wide accessibility via web browsers, regardless of location or device. | Convenience for users with smartphones or tablets, offering on-the-go calculations. |
| Customization | Generally allows for a wide range of customization options, potentially including additional fees and complex scenarios. | Often offers limited customization options compared to online versions due to space constraints and platform limitations. |
Functionality and Usage
Used car payment calculators are powerful tools for prospective buyers. They streamline the complex process of determining affordable car financing options. By inputting key details, these calculators provide accurate estimates of monthly payments, total loan costs, and other essential financial information.
These calculators employ sophisticated algorithms to perform a variety of calculations based on user-supplied data. This empowers buyers to make informed decisions about financing terms and potential affordability. They are an indispensable resource for anyone navigating the used car market.
Calculation Methodology
Used car payment calculators employ a series of calculations to arrive at the final payment estimates. These calculations generally involve the following steps:
- Determining the loan amount: The calculator first subtracts the down payment from the purchase price to establish the loan amount. For example, if a car costs $20,000 and a down payment of $5,000 is made, the loan amount will be $15,000.
- Calculating the monthly payment: The core calculation revolves around the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. The formulas used for these calculations usually follow standard financial models, typically utilizing the present value of an ordinary annuity formula to compute the monthly payment.
Monthly Payment = [P x R x (1+R)^N]/[(1+R)^N-1]
where P is the principal loan amount, R is the monthly interest rate, and N is the total number of payments.
- Estimating total interest paid: The calculator determines the total interest paid over the life of the loan by multiplying the monthly payment by the total number of payments and then subtracting the loan amount. For instance, a 60-month loan at $500 per month would result in a total payment of $30,000. The total interest paid would be $15,000.
Inputting Data
Calculators offer various ways to input data, ensuring user convenience and accuracy.
- Manual Entry: This method allows users to directly type in values for the purchase price, down payment, loan term, interest rate, and other relevant information. This method is straightforward but requires careful attention to avoid errors.
- Import/Upload: Some calculators allow users to upload data from a spreadsheet or document, particularly useful when dealing with large datasets or multiple transactions. This feature significantly simplifies the input process, especially for individuals needing to compare multiple options.
Practical Example
Consider a used car with a purchase price of $18,000. A down payment of $3,000 is planned, with a loan term of 60 months and an interest rate of 6%.
- Loan Amount: The loan amount is $18,000 – $3,000 = $15,000
- Monthly Interest Rate: The annual interest rate of 6% is converted to a monthly rate by dividing by 12. Thus, the monthly interest rate is 6%/12 = 0.5% or 0.005
- Monthly Payment Calculation: Applying the formula above, the monthly payment is calculated based on $15,000, 0.005, and 60 months.
- Estimated Result: The calculator will estimate a monthly payment of approximately $300, including the estimated total interest paid over the 60-month loan term.
Step-by-Step Procedure
A typical procedure for using a used car payment calculator involves these steps:
- Gather Information: Collect details such as the purchase price, down payment amount, desired loan term, and interest rate.
- Input Data: Enter the gathered information into the calculator’s fields.
- Calculate: Press the “Calculate” button to initiate the calculations.
- Review Results: Carefully examine the displayed results, including the estimated monthly payment, total interest paid, and other relevant details.
Factors Influencing Payment
Understanding the factors that influence used car loan payments is crucial for prospective buyers. A thorough analysis of these elements empowers informed decision-making, ensuring a purchase that aligns with financial capabilities and goals. This section delves into the key determinants of a used car payment, providing a comprehensive overview of their impact.
Interest Rates
Interest rates directly affect the total cost of a loan. Higher rates lead to larger monthly payments and a higher overall cost of borrowing. Conversely, lower rates result in smaller monthly payments and a lower total cost. For example, a $20,000 loan with a 5% interest rate might have a monthly payment of $400, while the same loan with a 7% interest rate could have a payment of $450. The difference in monthly payments becomes substantial over the life of the loan, impacting the overall financial burden.
Loan Terms
Loan terms, specifically the loan duration, significantly influence monthly payments. A longer loan term, while potentially offering lower monthly payments, results in a higher total cost of borrowing over the life of the loan. This is because the interest accrues over a more extended period. Conversely, a shorter loan term leads to higher monthly payments but a lower total cost and quicker debt repayment. A loan for 60 months might have a monthly payment of $350, but the same loan for 72 months might have a payment of $300. This difference is important to consider when assessing the affordability and long-term financial implications of a loan.
Down Payments
A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, directly lowering the monthly payment and the total cost of the loan. For instance, a $20,000 vehicle with a $5,000 down payment will result in a loan of $15,000, which, with a 6% interest rate and a 60-month term, could have a lower monthly payment than the same vehicle with a $0 down payment. A higher down payment significantly reduces the financial burden associated with the loan.
Trade-in Values
The trade-in value of a vehicle significantly impacts the loan amount. A higher trade-in value reduces the loan amount needed to purchase the new vehicle. This, in turn, reduces the monthly payment and the overall cost of the loan. For example, if a buyer trades in a vehicle with a $3,000 value, the loan amount required for the new vehicle could be lower, potentially leading to a lower monthly payment. Accurate appraisal of the trade-in value is crucial for securing the most favorable financing terms.
Comparison of Calculators
.png)
Different used car payment calculators offer varying levels of detail and features. Understanding the differences between these tools is crucial for making informed decisions when financing a used vehicle. This section delves into the features of various calculators, comparing their functionalities and evaluating their accuracy.
Examples of Used Car Payment Calculators
Several online tools and software provide used car payment calculators. These calculators typically require inputting key details about the vehicle and financing terms to estimate monthly payments. Examples include those offered by major banks, credit unions, and independent financial websites. Some calculators might also offer additional features such as down payment assistance options or trade-in value estimates.
Comparison of Calculator Features
Different calculators offer varying levels of detail and features, catering to different user needs. A comprehensive comparison highlights the specific functionalities offered by various calculators.
| Calculator | Loan Term Options | Down Payment Options | Interest Rate Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 (Bank A) | 24, 36, 48, 60, 72 months | Flexible, ranging from 0% to 50% | Adjustable based on credit score and loan terms; a range of pre-determined rates available |
| Example 2 (Credit Union B) | 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 months | Fixed percentage or dollar amounts; no customization | Variable interest rates based on prevailing market rates; a fixed rate option is available |
| Example 3 (Financial Website C) | 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 months (plus custom options) | Flexible, allowing for various percentages or amounts | Variable interest rates; customizable with pre-determined options and user input |
Accuracy and Reliability of Calculators
The accuracy of used car payment calculators depends on the accuracy of the input data and the methodology employed by the calculator. Calculators that utilize established financial formulas and take into account potential fees or taxes tend to produce more reliable results. Inputting precise information such as the vehicle’s price, down payment, loan term, and interest rate is paramount for an accurate estimate. Comparing results from several reputable calculators can further enhance the reliability of the estimated payment. Consider calculators that offer detailed explanations of the calculation methodology to ensure the outcome is derived using a transparent approach. Users should also be aware that estimated figures are not guarantees, and actual payments may vary.
Advanced Features and Considerations
Used car payment calculators go beyond basic calculations to provide valuable insights for informed purchasing decisions. Advanced features often offer a deeper understanding of the loan’s structure, allowing users to make more calculated choices. This section delves into these advanced functionalities, highlighting their significance and practical applications.
Loan Amortization Schedules
Advanced calculators often include loan amortization schedules. These schedules break down the loan repayment plan over time, displaying the principal and interest components of each payment. Understanding the amortization schedule is crucial for visualizing the loan’s progression and managing financial expectations.
- Understanding Amortization: Amortization schedules display a detailed repayment timeline. This allows users to track the principal reduction and interest paid over the loan’s duration. For instance, in the early years of a loan, a larger portion of each payment goes towards interest, and as the loan progresses, more of the payment is applied to the principal. This allows users to see how much they’ll pay in interest over the life of the loan.
- Practical Application: Users can use amortization schedules to compare different loan terms or interest rates. By analyzing how the loan’s structure affects their monthly payments and total interest paid, users can identify the most cost-effective option.
Understanding Loan Terms and Interest Rates
Accurate calculations depend on precise input of loan terms and interest rates. The interest rate directly affects the total cost of the loan, while the loan term impacts monthly payments.
- Impact of Interest Rates: Higher interest rates result in greater interest payments over the loan’s life. For example, a 5% interest rate on a $10,000 loan over 60 months will result in a total interest payment of approximately $1,000 more than a 4% interest rate.
- Importance of Loan Term: Shorter loan terms typically result in higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid. Conversely, longer terms lead to lower monthly payments but higher total interest. A 36-month loan for a $10,000 car will have higher monthly payments than a 60-month loan but will cost less in total interest paid.
Fees and Charges
Used car loans often come with additional fees and charges beyond the interest rate. Understanding these fees is crucial for a complete financial picture.
- Examples of Fees: Common fees include origination fees, documentation fees, and prepayment penalties. These fees can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan.
- Impact on Calculations: Incorporating these fees into the calculation is essential to determine the true cost of the loan. A calculator that accounts for these fees provides a more realistic estimate of the total cost.
Adjusting for Different Loan Types
Calculators should account for various loan types to provide accurate results.
- Secured vs. Unsecured Loans: Secured loans, backed by collateral (like the car itself), often have lower interest rates. Unsecured loans, lacking collateral, typically have higher interest rates. Calculators should allow users to select the appropriate loan type for accurate results.
- Impact of Loan Type: The loan type affects both the interest rate and the eligibility criteria. A secured loan, due to the collateral, can offer more favorable terms, whereas an unsecured loan might be harder to obtain, and could involve higher interest rates.
User Interface and Experience
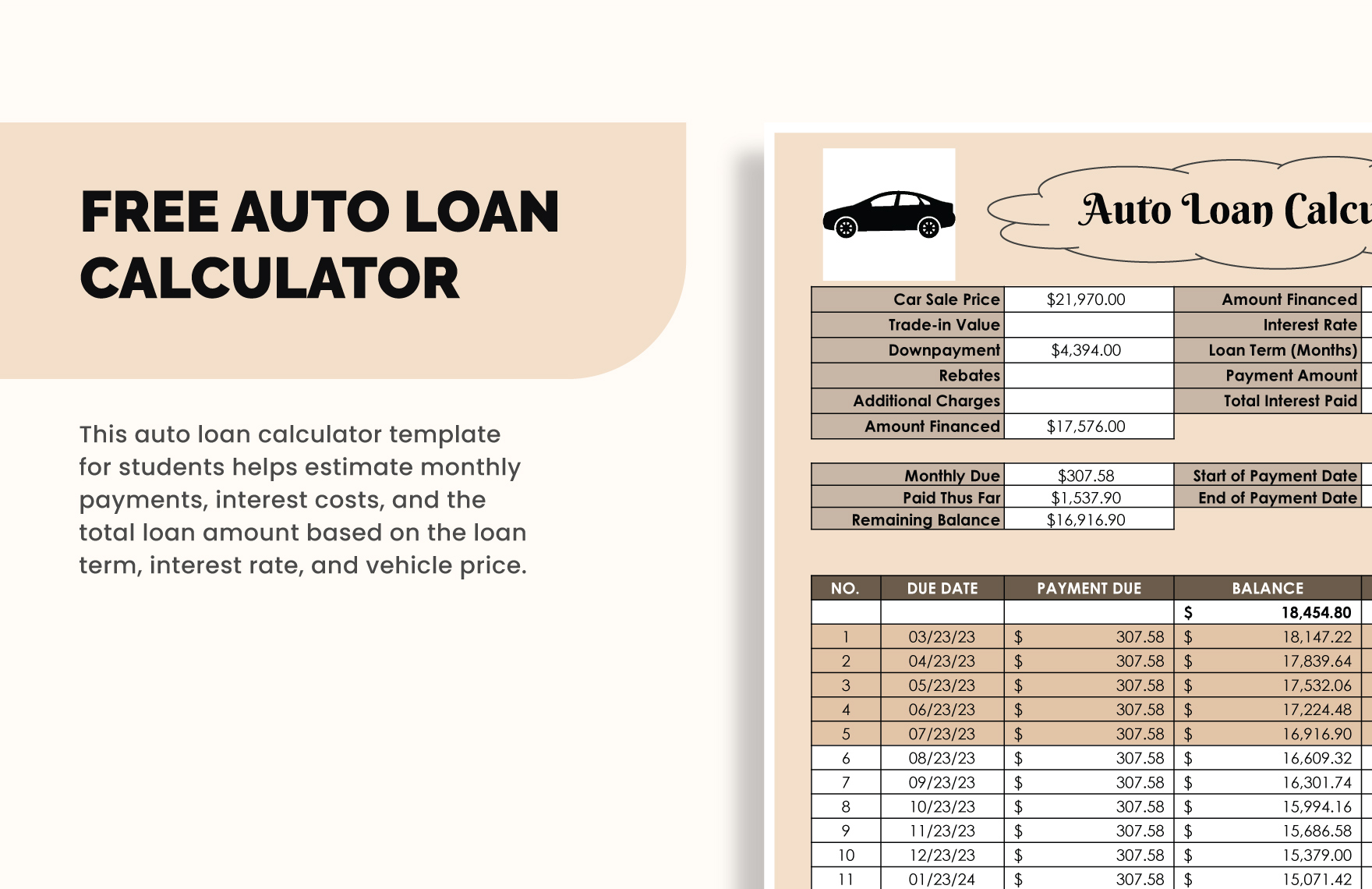
A user-friendly interface is paramount for used car payment calculators. A well-designed interface not only enhances the user experience but also ensures accurate results and facilitates easy comparison of various financing options. Intuitive navigation and clear presentation of information are key to empowering users to make informed decisions about their car purchases.
A user-friendly interface streamlines the process of obtaining used car loan estimates. Users should be able to quickly and easily input necessary information, view calculated results, and compare different financing options. This facilitates a smooth and positive user experience, increasing the likelihood of users finding the calculator useful and reliable.
Elements of a User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly interface for a used car payment calculator prioritizes clear input fields, intuitive navigation, and visually appealing presentation of results. Essential elements include:
- Clear and Concise Input Fields: Input fields should be clearly labeled with prompts or instructions, using language that is readily understandable. For example, instead of “Amount,” use “Loan Amount.” Error handling should be integrated to prevent incorrect or missing data, providing helpful feedback to the user.
- Intuitive Navigation: Users should easily navigate through the calculator’s different sections. Logical organization and clear labeling of sections (e.g., “Vehicle Details,” “Loan Details,” “Results”) are crucial.
- Visually Appealing Results Presentation: Calculated results should be presented in a visually appealing format. Use clear tables, charts, or graphs to display the results, making them easily understandable. Color-coding can also highlight important information or differences between options.
- Data Validation: Implement robust data validation to ensure accurate calculations. This includes checking for valid numerical inputs and ensuring that values are within realistic ranges. For example, loan terms should not exceed a certain limit. Clear error messages help users understand and correct mistakes immediately.
Sample User Interface Layout
The following table illustrates a sample layout for a used car payment calculator:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Details | Input fields for vehicle year, make, model, mileage, and purchase price. |
| Loan Details | Fields for loan amount, interest rate, loan term (in months), and down payment. |
| Results | A table displaying calculated monthly payment, total interest paid, and total loan amount. |
| Comparison | Option to compare different loan options with a side-by-side view of results. |
This table structure demonstrates a clear separation of input data and calculated results, providing an intuitive layout.
Importance of Clear and Concise Information Presentation
Clear and concise information presentation is critical for a user-friendly calculator. Users should be able to quickly grasp the key details without needing to search for information. This improves the user experience, ensuring they are empowered to make informed decisions. Ambiguous or confusing information can lead to errors and frustration.
Examples of Good and Bad User Interface Designs
A good user interface design for a used car payment calculator should be intuitive and easy to use. For instance, a clear layout with prominent labels and a logical flow of information is ideal. In contrast, a poor design might have cluttered input fields, obscure instructions, and confusing results presentation. Examples of good practices include use of white space, clear typography, and a visually appealing color scheme.
Importance of Mobile Responsiveness
Mobile responsiveness is essential for a used car payment calculator. Today, a significant portion of users access online tools through mobile devices. A calculator that is not mobile-responsive will offer a poor user experience, leading to frustrated users. A responsive design ensures that the calculator adapts to different screen sizes, providing an optimal experience on all devices. This adaptability is crucial for accessibility and user engagement.
Illustrative Examples and Scenarios

Used car payment calculators are powerful tools for navigating the complexities of vehicle financing. Understanding how these calculators work in different scenarios empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their purchases. This section provides practical examples to illustrate the calculator’s functionality in various situations.
Illustrative examples of used car payment calculations, including trade-ins, high-interest rates, limited budgets, and large down payments, highlight the calculator’s ability to provide accurate and detailed financial projections. These scenarios allow users to anticipate the total cost of a vehicle and make prudent financial choices.
Calculating a Used Car Payment for a Specific Scenario
To illustrate the calculation process, consider a used car with a price of $15,000. The buyer has a $3,000 down payment and plans to finance the remaining balance with a 5-year loan at a 6% interest rate. Using a reliable used car payment calculator, the monthly payment would be approximately $270. This example showcases the calculator’s ability to estimate monthly payments based on various factors.
Calculating a Payment with a Trade-In
A trade-in significantly impacts the financing process. Suppose the buyer is trading in a vehicle with a current market value of $2,500. This trade-in reduces the loan amount, and the calculation would factor in the trade-in value. If the loan amount becomes $12,500, the monthly payment, assuming the same terms as the previous example, would be adjusted accordingly, potentially to around $225. The calculator accurately reflects the reduced loan amount, leading to a lower monthly payment.
Scenario with High Interest Rates and its Impact on Payments
Higher interest rates significantly increase the overall cost of the loan. Consider a used car with a price of $18,000, a $2,000 down payment, and a 7-year loan at an 8% interest rate. This scenario results in a higher monthly payment of approximately $300 compared to the previous examples. This highlights how interest rates directly influence the affordability of a vehicle. Understanding the impact of varying interest rates is crucial for budgeting and planning.
Scenario with a Limited Budget
A limited budget necessitates careful consideration of vehicle affordability. If a buyer has a maximum monthly payment of $250 and is considering a $10,000 vehicle, the calculator can determine the maximum loan amount and loan term that align with the budget. In this case, the calculator would identify financing options that match the budget. This scenario emphasizes the calculator’s role in finding affordable financing options.
Illustrative Scenario with a Large Down Payment
A substantial down payment dramatically reduces the loan amount and lowers the monthly payment. If a buyer puts down $8,000 on a $16,000 vehicle, the loan amount decreases to $8,000. This example, with a 4-year loan at 5% interest, shows a significantly lower monthly payment, approximately $180. The calculator clearly demonstrates how a larger down payment contributes to a more manageable monthly payment.