Job Description & Responsibilities

A used car manager plays a crucial role in a dealership, overseeing the entire process of acquiring, preparing, and selling used vehicles. This role requires a blend of sales acumen, operational efficiency, and a deep understanding of the used car market. Their responsibilities extend beyond simply selling cars; they’re key to maximizing profitability and maintaining a positive customer experience.
Typical Responsibilities
Used car managers are responsible for a wide range of tasks, ensuring smooth operations and maximizing profitability. These duties often include managing inventory, negotiating deals, handling paperwork, and maintaining accurate records.
- Inventory Management: This encompasses acquiring vehicles, ensuring they meet quality standards, and pricing them competitively. Managers must carefully evaluate incoming vehicles, addressing any necessary repairs or reconditioning to maximize their value and minimize potential issues.
- Sales Negotiation: A key responsibility involves skillfully negotiating deals with customers to achieve the best possible price and terms. This includes identifying customer needs, presenting vehicles, and closing sales effectively. Successful negotiation often involves a deep understanding of the market value and competitor pricing.
- Paperwork and Compliance: Managers handle all the necessary paperwork, ensuring compliance with regulations and legal requirements. This includes preparing sales contracts, completing title transfers, and maintaining accurate records of all transactions.
- Customer Relations: A used car manager fosters positive relationships with customers throughout the sales process. This involves actively listening to customer needs, providing clear explanations, and resolving any issues that may arise.
Tasks and Duties
The day-to-day activities of a used car manager are diverse and often involve multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Vehicle Evaluation: Inspecting used vehicles to assess their condition, value, and marketability. This involves identifying potential problems, determining repair needs, and accurately valuing the vehicles.
- Pricing Strategy: Developing and implementing a pricing strategy that considers market trends, competitor pricing, and the condition of the vehicle. A thorough market analysis is crucial to ensure pricing is both competitive and profitable.
- Reconditioning Coordination: Managing the reconditioning process, ensuring vehicles are presented in the best possible condition. This might involve coordinating with mechanics, body shops, or detailing services.
- Sales Process Management: Guiding the sales process, from initial customer contact to closing the sale, while ensuring all steps are completed efficiently and professionally.
Responsibility Levels
The responsibilities of a used car manager vary based on experience level.
| Responsibility Level | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Assisting with inventory management, basic sales tasks, and customer service. Focus on learning the processes and procedures of the dealership. |
| Mid-Level | Managing a specific inventory segment, negotiating deals, and coordinating with internal teams. Demonstrates increasing independence and leadership. |
| Senior-Level | Overseeing all aspects of used car operations, developing pricing strategies, and managing a team of sales associates. Takes on a strategic leadership role within the dealership. |
Used Car Manager vs. Sales Manager
While both roles are vital in a dealership, they have distinct responsibilities. A used car manager focuses primarily on the acquisition, preparation, and pricing of used vehicles. A sales manager, on the other hand, is responsible for leading and motivating a sales team and managing the overall sales process for all vehicles, both new and used.
Skills and Knowledge
A successful used car manager requires a combination of hard and soft skills.
- Negotiation Skills: Strong negotiation skills are essential to secure favorable deals and maximize profits. This includes understanding the dynamics of negotiation, building rapport with customers, and finding common ground.
- Sales Proficiency: Proven sales experience, coupled with a deep understanding of customer needs, is critical for closing deals and building customer relationships. Effective communication and presentation skills are essential.
- Market Knowledge: A thorough understanding of the used car market, including trends, pricing, and competitor analysis, is necessary to make informed decisions. Knowledge of local and national market conditions is important.
- Operational Proficiency: Proficiency in inventory management, vehicle reconditioning, and paperwork processes is essential for smooth operations. This includes knowing dealership procedures and regulations.
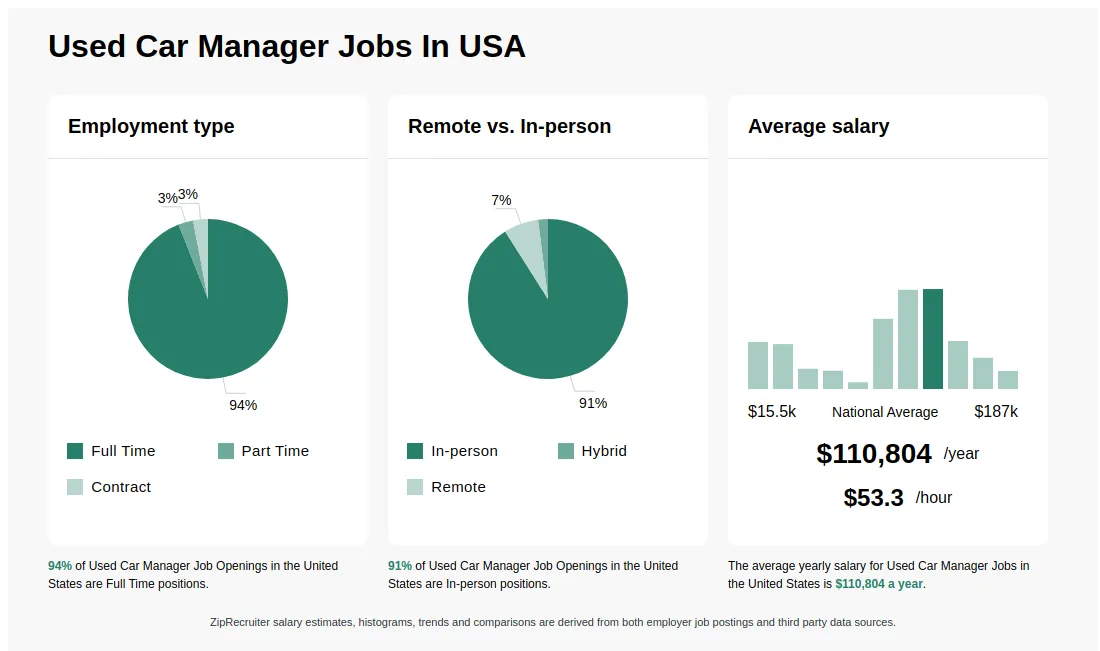
Salary & Benefits
Used car managers play a crucial role in dealership operations, requiring a blend of sales expertise, negotiation skills, and a deep understanding of vehicle valuations. Compensation for this position reflects the importance of their function, varying based on experience, location, and dealership size. This section details typical salary ranges, common benefits, and factors affecting compensation.
Typical Salary Ranges
Compensation for used car managers is a complex equation, factoring in various experience levels and geographical locations. Salaries generally increase with years of experience in the automotive industry and with demonstrated success in achieving sales targets and managing inventory. Geographic location also significantly influences compensation due to varying cost of living and market demand for used car managers.
Salary Expectations by Region
Regional differences in the cost of living and the demand for used car managers significantly impact salary expectations. A comprehensive analysis of salary expectations across different regions is crucial for prospective and current used car managers to benchmark their compensation against industry standards.
| Region | Entry-Level (0-2 Years) | Mid-Level (3-5 Years) | Senior-Level (6+ Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast US | $50,000 – $65,000 | $65,000 – $85,000 | $85,000 – $105,000 |
| Midwest US | $45,000 – $60,000 | $60,000 – $80,000 | $80,000 – $100,000 |
| South US | $40,000 – $55,000 | $55,000 – $75,000 | $75,000 – $95,000 |
| West US | $55,000 – $75,000 | $75,000 – $95,000 | $95,000 – $120,000 |
Common Benefits Packages
Used car managers, like other employees in the automotive industry, often receive comprehensive benefit packages. These benefits packages typically include health insurance (medical, dental, and vision), paid time off (vacation, sick leave, and holidays), and retirement plans (401(k) or similar). Some dealerships may also offer additional perks such as company vehicles or employee discounts.
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive health insurance plans are standard, often including options for various levels of coverage.
- Paid Time Off: Vacation and sick leave are common, with the amount of time off varying based on experience and company policies.
- Retirement Plans: Many dealerships offer retirement plans, such as 401(k) plans, to help employees save for their future.
- Other Perks: Some dealerships offer additional benefits, like company vehicles or discounts on services and products.
Compensation Across Dealership Sizes
Dealership size is a key factor in compensation. Larger dealerships, with greater sales volume and more complex operations, typically offer higher salaries compared to smaller dealerships. This reflects the increased responsibility and workload associated with managing a larger inventory and a higher volume of transactions.
Factors Influencing Salary Variations
Several factors contribute to the variance in used car manager salaries. Experience, location, dealership size, performance metrics, and market conditions all play a significant role in determining the final compensation package. For instance, a highly experienced manager in a high-demand location at a large dealership may command a higher salary than a less experienced manager in a less competitive market.
Job Market Trends
The used car market is a dynamic sector, constantly evolving with shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and economic fluctuations. Understanding these trends is crucial for used car managers to adapt their strategies and skillsets to remain competitive and successful. This section explores current trends, emerging technologies, and the impact on the used car manager role.
Current Trends in the Used Car Market
The used car market is experiencing significant shifts driven by factors like supply chain disruptions, fluctuating fuel prices, and changing consumer preferences. These factors influence the manager’s role in several ways, including inventory management, pricing strategies, and customer service approaches. For example, shortages of certain models have driven up prices, impacting profit margins and creating challenges in satisfying customer demand.
Emerging Technologies in Used Car Management
Technological advancements are transforming the used car management process. Digital tools, such as advanced vehicle inspection software and online marketplaces, are streamlining operations. The use of AI and machine learning is automating tasks like pricing analysis and risk assessment. These technologies allow for more efficient inventory management and improved customer experience.
Automation’s Impact on Used Car Manager Responsibilities
Automation is reshaping the used car manager role, shifting focus from repetitive tasks to strategic decision-making. Tasks like data entry, basic vehicle assessments, and some aspects of pricing are being automated. Used car managers are now required to focus on strategic initiatives such as market analysis, customer relationship management, and negotiating favorable deals. For instance, automated valuation tools can quickly analyze comparable sales, freeing up managers to concentrate on complex negotiations.
International Variations in the Used Car Market
The used car market presents different characteristics across countries. Factors like local regulations, cultural preferences, and economic conditions affect the way used cars are purchased and sold. For example, stricter emissions standards in some regions impact the types of vehicles available and their prices. This necessitates a tailored approach to management strategies in different countries.
High-Demand Skills for Used Car Managers
The demand for specific skills in used car managers is increasing. Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities are vital for navigating complex market conditions. Furthermore, digital literacy and proficiency in data analysis tools are essential for leveraging technology effectively. Excellent communication and negotiation skills are paramount for building customer relationships and securing profitable deals. Moreover, a comprehensive understanding of vehicle mechanics, maintenance, and repair processes is important for informed decision-making. The ability to adapt to new technologies and market trends is crucial for success.
Career Paths & Advancement
Used car managers often find themselves at a crossroads, navigating the complexities of the automotive industry while simultaneously charting their own career trajectories. The skills and experience gained in used car management are surprisingly transferable, opening doors to a variety of other roles and opportunities within the automotive sector and beyond. This section details potential career paths and the necessary steps for advancement, including examples of successful transitions.
Used car management positions provide a robust foundation for professional growth. A deep understanding of inventory management, negotiation, customer service, and sales strategies are crucial components of this role, which are highly sought after in various other automotive and business management positions. These transferable skills make used car managers attractive candidates for a range of career advancements.
Potential Career Paths
Used car managers possess a unique blend of skills that can translate into various roles within the automotive industry and beyond. The ability to manage inventory, negotiate deals, and provide excellent customer service are transferable skills that are highly valued in many business contexts.
- Automotive Sales Management: Used car managers can transition to overseeing entire sales teams, developing strategies, and managing performance. This often involves more strategic planning, team leadership, and potentially higher levels of responsibility for profit and loss.
- General Sales Management: The experience gained in managing used car sales can be applied to other sales sectors. This involves similar skills in sales process optimization, team management, and sales targets.
- Inventory Management: Used car managers are adept at managing inventory levels and forecasting demand. This skillset is directly transferable to inventory management positions in other industries, such as retail or logistics.
- Business Development: Used car managers develop strong negotiation and relationship-building skills. These skills are valuable in business development roles, where identifying and pursuing new business opportunities is key.
- Finance and Accounting: A deep understanding of pricing, cost analysis, and profitability, which are crucial for used car management, can translate to finance and accounting roles, particularly in the automotive or retail sector.
Necessary Steps for Career Advancement
Several key steps can facilitate career progression from used car manager to more senior roles. Continuous professional development and a proactive approach to skill enhancement are essential.
- Continuing Education: Pursuing certifications related to automotive sales, business management, or negotiation can significantly enhance a candidate’s marketability and open doors to more senior positions.
- Networking: Building relationships with industry professionals through conferences, workshops, or online forums can provide valuable insights and potentially lead to new opportunities.
- Demonstrating Leadership: Taking initiative, mentoring junior staff, and actively participating in team projects can showcase leadership potential and increase visibility within the organization.
- Seeking Mentorship: A mentor in a senior management position can offer valuable guidance and support in navigating the complexities of career advancement.
Examples of Successful Transitions
Several used car managers have successfully transitioned into higher-level positions. For instance, a manager with 5+ years of experience and a strong track record in used car sales can often advance to a sales manager position. This showcases how valuable the experience and skills acquired in used car management are.
- Sales Manager Transition: An experienced used car manager, with a proven history of exceeding sales targets and managing high-performing teams, can transition seamlessly to a sales manager position.
- Inventory Management Specialist: A manager with a strong understanding of forecasting, cost analysis, and inventory control can transition to an inventory management specialist role, especially in a large dealership or automotive retail environment.
Skills & Qualifications
A successful used car manager requires a unique blend of technical and interpersonal skills. They need to be proficient in vehicle evaluations, negotiation, and sales strategies, while also fostering strong customer relationships and maintaining a positive work environment. The ability to manage inventory effectively, adhere to company policies, and adapt to market changes is crucial for success in this role.
Effective used car managers excel at understanding and applying the principles of sales and customer service. Their ability to build rapport with customers and present vehicles accurately and persuasively is essential for driving sales and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Essential Hard Skills
Understanding the nuances of used car valuation is paramount for a used car manager. This includes knowledge of market trends, repair costs, and historical sales data. Strong analytical skills are needed to evaluate vehicles, compare them to market prices, and determine optimal pricing strategies. Proficiency in inventory management software and CRM systems is essential for efficient record-keeping and customer relationship management. This includes data entry, report generation, and understanding the processes to ensure smooth operations.
Key Soft Skills
Strong communication skills are vital for effective negotiation, customer interaction, and internal team collaboration. Active listening, empathy, and the ability to articulate complex information clearly and concisely are essential qualities for building strong customer relationships. Problem-solving skills are critical for resolving customer concerns, managing inventory issues, and adapting to changing market conditions. Time management and organizational skills are essential for meeting sales targets, managing schedules, and ensuring efficient workflow.
Skill Categorization
| Importance Level | Hard Skills | Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| High | Vehicle Evaluation, Pricing Strategy, Inventory Management, CRM Software, Sales Techniques | Communication, Negotiation, Customer Service, Time Management, Problem-Solving |
| Medium | Market Research, Repair Cost Analysis, Legal Compliance, Finance Principles | Adaptability, Teamwork, Stress Management, Conflict Resolution |
| Low | Specific Automotive Certifications (e.g., ASE), Industry Knowledge, Compliance with Regulations | Empathy, Active Listening, Persuasion, Enthusiasm |
Relevant Certifications & Educational Backgrounds
A strong educational foundation in business administration, sales, or a related field can provide a solid base for success. Certifications such as Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) certifications can demonstrate technical expertise in vehicle evaluation and maintenance. Completing courses in sales techniques and negotiation strategies can further enhance the ability to interact with customers effectively and reach sales goals. Specific industry certifications, like those offered by the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA), are highly valued in the used car management field.
Comparing Skills Across Roles
The specific skills needed for different used car management roles may vary. For example, a used car manager focused on high-end vehicles might require specialized knowledge of luxury car models, their maintenance costs, and pricing strategies. Conversely, a manager focusing on more budget-friendly vehicles might need proficiency in understanding used car market trends and negotiating with customers on more basic models. In both cases, strong communication, negotiation, and customer service skills remain crucial for success.
Education & Training
/car_salesman-108359672-58b643c73df78cdcd8a01bf0.jpg)
A successful used car manager possesses a blend of practical experience and theoretical knowledge. Beyond on-the-job training, formal education and continuous learning are crucial for staying ahead in this dynamic field. This involves understanding market trends, customer expectations, and the ever-evolving regulations in the automotive industry.
A solid educational foundation, combined with relevant training programs and certifications, equips used car managers with the necessary skills to excel in their roles. This includes a deep understanding of vehicle valuations, sales strategies, and customer service techniques.
Typical Educational Backgrounds
Used car managers often benefit from a background in business administration, sales, or a related field. A bachelor’s degree, while not always mandatory, can provide a strong foundation in management principles, marketing, and finance. However, experience in the automotive industry, such as working as a sales associate or technician, is often considered equally valuable, and sometimes more valuable, than a degree. This practical experience provides hands-on knowledge of vehicles, market dynamics, and customer interactions.
Relevant Training Programs
Numerous training programs offer specialized knowledge for aspiring and current used car managers. These programs typically cover topics like vehicle appraisal, negotiation techniques, sales management, and customer service. Some automotive dealerships may provide in-house training programs tailored to their specific needs and operations. Industry associations and professional organizations also offer courses and certifications that enhance expertise in used car management.
Potential Educational Requirements & Certifications
The educational requirements and certifications needed for used car managers vary depending on the specific role and responsibilities. The following table provides examples of potential requirements for different positions:
| Role | Potential Educational Requirements | Certifications |
|---|---|---|
| Used Car Sales Manager | Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration, or equivalent experience. | Automotive Industry certifications (e.g., Certified Automotive Manager). |
| Used Car Appraiser | Appraisal certifications from recognized organizations. | Automotive appraisal certifications (e.g., Certified Vehicle Appraiser). |
| Used Car Sales Associate | High school diploma or equivalent, supplemented by in-house training. | No mandatory certifications, but industry-specific certifications can be beneficial. |
Online Courses in Used Car Management
Numerous online platforms offer courses related to used car management. These courses provide flexibility and convenience, enabling individuals to acquire new skills and knowledge at their own pace. They cover topics such as vehicle inspection, sales techniques, customer relationship management, and financial management. Examples include courses from online learning platforms and automotive industry-specific training providers. A significant benefit of online courses is the accessibility to a wider range of instructors and diverse perspectives.
Importance of Continuous Learning
The automotive industry is constantly evolving. New technologies, market trends, and regulatory changes necessitate continuous learning for used car managers. Staying updated with the latest advancements in vehicle technology, sales strategies, and industry regulations is vital for maintaining a competitive edge and delivering excellent customer service. Keeping up-to-date with industry trends and new regulations ensures that managers remain proficient and effective in their roles.
Tools & Technologies
Used car managers rely heavily on a range of tools and technologies to efficiently manage inventory, track sales, and maximize profitability. Modern practices require a deep understanding of these tools to navigate the dynamic used car market. This includes a blend of software, digital platforms, and data analysis techniques.
Common Tools Used by Used Car Managers
Used car managers utilize a diverse set of tools to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and optimize profitability. These tools include specialized software for inventory management, sales tracking, customer relationship management (CRM), and financial reporting. Furthermore, data analysis plays a critical role in understanding market trends, pricing strategies, and overall performance.
Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software is crucial for tracking the details of each vehicle in the lot. This software allows managers to input data on vehicles, including make, model, year, mileage, condition, and any damage. This allows for quick and accurate searching for vehicles based on criteria, and automated updates for pricing, inventory status, and sales. Examples of such software include Dealertrack, AutoTrader, and Carfax.
Sales Tracking Software
Effective sales tracking software provides real-time insights into sales performance. It captures data on each sale, including the customer, price, and terms. This data allows managers to analyze sales trends, identify top-performing vehicles, and adjust pricing strategies. Many of these tools integrate with inventory management systems for a complete view of operations.
Digital Platforms in the Used Car Market
Digital platforms have revolutionized the used car market, impacting both buying and selling processes. Websites like Autotrader and Kelley Blue Book provide extensive information about vehicles, including pricing, reviews, and specifications. Online marketplaces facilitate direct interaction between buyers and sellers, increasing transparency and efficiency. This increased digital presence requires managers to understand and utilize these platforms effectively.
Data Analysis in Used Car Management
Data analysis plays a vital role in understanding market trends and customer behavior. Used car managers utilize data to analyze pricing trends, identify popular models, and forecast future demand. Sophisticated data analysis tools can provide insights into customer preferences, allowing for better targeted marketing and improved sales strategies. The integration of data analytics with CRM systems allows for a comprehensive understanding of customer interaction and purchase history.
Essential Software and Tools for Used Car Managers
| Category | Software/Tool | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Dealertrack, AutoTrader, Carfax | Tracks vehicle details, updates pricing, manages inventory status, and facilitates sales. |
| Sales Tracking | CRM Software, Sales Management Systems | Records sales data, analyzes sales trends, and supports effective pricing strategies. |
| Market Research | Kelley Blue Book, Edmunds | Provides insights into vehicle values, market trends, and customer preferences. |
| Data Analysis | Business Intelligence Software, Spreadsheet Programs | Enables analysis of sales data, inventory data, and market trends to improve decision-making. |
| Digital Platforms | Online Marketplaces (Autotrader, etc.) | Facilitates direct interaction between buyers and sellers, increasing transparency and efficiency. |
Dealership & Business Structure
Used car dealerships, like other businesses, operate within specific organizational structures that significantly impact how used car managers perform their duties. Understanding these structures is crucial for aspiring used car managers to anticipate the demands and expectations of various dealership models. The typical structure, roles, and responsibilities of a used car manager are interconnected and vary depending on the size and business model of the dealership.
The organizational structure of a used car dealership often reflects a hierarchical design, with varying levels of authority and responsibility. This structure allows for efficient workflow and specialization of tasks, ensuring the smooth functioning of the dealership. The used car manager’s role within this framework is pivotal, as they bridge the gap between sales, operations, and customer satisfaction.
Typical Organizational Structure of a Used Car Dealership
A typical used car dealership organizational structure often features departments like sales, finance, service, and parts. Each department has specific responsibilities and reports to a higher-level manager. The used car manager is often part of the sales or operations division, directly overseeing the used car inventory.
Role of a Used Car Manager
The used car manager plays a crucial role in managing the used car inventory, ensuring its profitability and efficient turnover. Their responsibilities typically include vehicle valuation, pricing, marketing, and customer service related to the used car sales process. They are also responsible for inventory control, ensuring the accuracy of vehicle information, and maintaining the showroom’s condition.
Impact of Different Business Models
Different business models, such as franchised dealerships, independent dealerships, or online-only platforms, affect the used car manager’s role. Franchised dealerships often have established procedures and standardized practices that the used car manager must adhere to. Independent dealerships offer more flexibility, requiring the used car manager to be more adaptable and proactive in developing strategies. Online-only dealerships demand a strong digital presence and efficient online inventory management.
Responsibilities in Various Dealership Sizes
The responsibilities of a used car manager can differ based on the size of the dealership. In smaller dealerships, the used car manager may handle a broader range of tasks, including customer service, marketing, and vehicle preparation. Larger dealerships often have specialized roles, where the used car manager focuses more on inventory management, pricing strategies, and negotiating with wholesalers.
Key Functions of a Dealership
“A well-organized dealership functions like a well-oiled machine, where every department works in harmony to achieve common goals.”
- Sales: Generating leads, closing deals, and building customer relationships. This often includes negotiation and sales closing techniques, along with knowledge of the sales process, market conditions, and competitor pricing.
- Finance: Processing paperwork, ensuring financial transactions comply with regulations, and managing loan applications.
- Service: Maintaining vehicles, handling customer service requests, and performing repairs. The used car manager might have oversight of the service department’s interaction with used car customers.
- Parts: Providing parts to the service department and ensuring proper inventory control.
- Operations: Managing the day-to-day operations of the dealership, including inventory control, vehicle maintenance, and adherence to policies and procedures.