Factors Affecting Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Used car loans, like new car loans, are influenced by a complex interplay of economic and financial factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions and secure the most favorable interest rates. Interest rates are not static; they fluctuate based on a multitude of conditions, impacting the affordability and accessibility of used car financing.
The interest rate a borrower receives for a used car loan is not arbitrary; it’s a calculated reflection of the risk the lender assumes. Lenders carefully weigh various elements, including the borrower’s creditworthiness, market conditions, and their internal risk assessment procedures. This careful evaluation ensures the lender’s financial well-being and minimizes the potential for losses.
Economic Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Economic conditions play a significant role in shaping used car loan interest rates. Interest rates often mirror broader market trends. Periods of economic expansion, with low unemployment and high consumer confidence, typically see lower interest rates across the board, including used car loans. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions are often accompanied by higher interest rates due to increased perceived risk. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, interest rates on various types of loans, including used car loans, rose substantially.
Credit Scores and Credit History
A borrower’s credit score and credit history are paramount in determining the interest rate they qualify for. Lenders use credit scores to assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. A higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate, as it signifies a lower risk for the lender. Conversely, a lower credit score indicates a higher risk, resulting in a higher interest rate. This is because borrowers with strong credit histories demonstrate a responsible approach to managing debt, making them more attractive to lenders. For example, a borrower with a credit score of 750 might qualify for a lower interest rate than a borrower with a credit score of 650.
Lender’s Risk Assessment Process
Lenders employ a comprehensive risk assessment process to evaluate the creditworthiness of a borrower. This process goes beyond simply reviewing credit scores. It involves scrutinizing factors such as the borrower’s income, employment history, debt-to-income ratio, and other financial obligations. The lender assesses the borrower’s ability to meet the loan repayment obligations, considering various potential economic and personal circumstances. This holistic approach helps lenders determine the appropriate interest rate, striking a balance between offering a competitive rate and managing their risk.
Impact of Prevailing Market Interest Rates
Used car loan interest rates are intrinsically linked to prevailing market interest rates. When overall interest rates in the economy rise, used car loan interest rates tend to follow suit. Conversely, when overall interest rates fall, used car loan interest rates are likely to decrease. This correlation reflects the interconnected nature of financial markets. For example, if the Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate, it’s highly probable that interest rates for various loans, including used car loans, will increase.
Comparison of Interest Rates Across Financial Institutions
Interest rates for used car loans can vary significantly between different financial institutions. Factors like the lender’s lending policies, fees, and overhead costs can all contribute to variations in interest rates. Banks, credit unions, and online lenders each have unique approaches to assessing risk and pricing their loans. Shopping around and comparing offers from multiple lenders is crucial to finding the most competitive interest rate. For instance, a credit union might offer a lower interest rate than a bank for a similar loan product.
Factors Impacting Used Car Loan Interest Rates
| Factor | Description | Relative Importance (High/Medium/Low) |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Score | A measure of creditworthiness, reflecting a borrower’s ability to repay loans. | High |
| Credit History | A record of past borrowing and repayment behavior. | High |
| Loan Amount | The total amount borrowed for the car. | Medium |
| Loan Term | The duration of the loan. | Medium |
| Market Interest Rates | The prevailing rates in the broader financial market. | High |
| Lender’s Risk Assessment | The lender’s evaluation of the borrower’s creditworthiness and risk. | High |
| Vehicle Condition | The overall condition of the used car. | Medium |
| Vehicle Year and Make | The age and model of the vehicle. | Medium |
Types of Used Car Loans and Their Interest Rates
Used car loans come in various forms, each with its own set of terms and conditions. Understanding these differences is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions that align with their financial situations and borrowing needs. Different loan types often have varying interest rates, impacting the overall cost of the loan. This section delves into the specifics of secured and unsecured used car loans, highlighting their key distinctions and potential implications for borrowers.
Secured Used Car Loans
Secured used car loans are backed by the vehicle itself. This means the lender has the right to repossess the car if the borrower defaults on the loan. This security feature often translates into lower interest rates for the borrower. The car acts as collateral, reducing the lender’s risk and allowing for more favorable terms. This type of loan offers a sense of security to the lender, enabling them to provide potentially more favorable terms. This is particularly useful when credit scores are not ideal, as the car’s value directly impacts the loan’s terms.
Unsecured Used Car Loans
Unsecured used car loans, in contrast, are not backed by any collateral. These loans rely solely on the borrower’s creditworthiness. Because of the higher risk for the lender, interest rates for unsecured loans tend to be higher compared to secured loans. Borrowers with excellent credit scores may find unsecured loans attractive, potentially offering slightly better terms compared to secured loans. This type of loan requires a robust credit history to qualify. A borrower’s credit history is meticulously reviewed to assess their ability to repay the loan.
Comparison of Interest Rates
The interest rate on a used car loan is influenced by several factors, including the borrower’s creditworthiness, the loan term, and the prevailing market conditions. Interest rates for secured loans generally fall within a lower range than unsecured loans, which is a direct consequence of the collateral. For example, a borrower with a strong credit score might secure a secured loan with a 5% interest rate, while an unsecured loan with a similar credit score might have a 7% interest rate. These examples illustrate the typical difference in interest rates.
Loan Types and Interest Rates Table
| Loan Type | Description | Typical Interest Rate Range (Example) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secured Loan | Loan secured by the vehicle as collateral. | 4%-7% | Lower interest rates, easier qualification for some borrowers with less-than-perfect credit. | Risk of repossession if loan is not repaid. |
| Unsecured Loan | Loan not secured by any collateral; relies solely on borrower’s creditworthiness. | 7%-12% | No risk of losing the vehicle if the loan is not repaid. | Higher interest rates, more stringent qualification criteria. |
Interest Rate Negotiation Strategies

Negotiating a used car loan interest rate can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan. By employing effective strategies, you can potentially secure a lower interest rate and save money over the life of the loan. Understanding the factors influencing interest rates and possessing a clear understanding of your financial situation is crucial in achieving a favorable outcome.
Comparing Offers from Multiple Lenders
Comparing offers from multiple lenders is paramount in the used car loan negotiation process. Different lenders have varying interest rates and terms, making comparison essential for finding the most advantageous offer. Thorough research and comparison shopping can lead to substantial savings. This involves contacting multiple lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders, to obtain personalized interest rate quotes. This proactive approach allows for a comprehensive evaluation of available options.
Leveraging Your Credit Score
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining your interest rate. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate. Improving your credit score through responsible financial practices, such as maintaining a low debt-to-income ratio and consistently paying bills on time, can directly influence your interest rate negotiation power. Taking steps to understand and address any credit report inaccuracies can also positively impact your negotiation position.
Negotiating Loan Terms
Negotiating loan terms beyond the interest rate can influence the overall cost of the loan. This involves discussing factors like the loan duration, monthly payments, and prepayment penalties. Understanding the potential impact of these factors on your financial situation is crucial. A shorter loan term, for example, may lead to higher monthly payments but lower overall interest paid. Alternatively, a longer loan term might offer lower monthly payments but increase the total interest accumulated. These decisions should be made thoughtfully, weighing the short-term and long-term financial implications.
Successful Interest Rate Negotiation Tactics
Successful interest rate negotiation tactics often involve a combination of preparation, assertiveness, and a clear understanding of your financial position. One tactic involves presenting a compelling case for a lower rate, backed by comparable offers from other lenders. This showcases your research and strengthens your position in the negotiation. Another effective approach is to express your willingness to secure the loan quickly, demonstrating your financial responsibility and urgency. A calculated approach that emphasizes the importance of the loan to you is essential.
Step-by-Step Negotiation Strategies
- Research and Comparison: Thoroughly research interest rates offered by various lenders. Compare terms, fees, and APRs to identify the best possible offer. Gather information about current market rates and potential discounts.
- Prepare Your Financial Documents: Gather all relevant financial documents, including your credit report, pay stubs, and bank statements. This demonstrates your financial responsibility and allows the lender to assess your creditworthiness accurately.
- Identify Your Negotiation Strengths: Assess your credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and overall financial situation. Highlight any positive aspects that might improve your negotiation position, such as a stable job history or a low debt-to-income ratio.
- Present Your Case: Articulate your desired interest rate, supported by comparable offers from other lenders. Demonstrate your understanding of the market rates and your financial commitment to the loan.
- Be Prepared to Walk Away: If the lender isn’t willing to meet your desired terms, be prepared to walk away from the deal. This demonstrates your resolve and strengthens your position in the negotiation process.
Impact of Loan Terms on Interest Rates
Understanding the intricacies of used car loan interest rates requires a deep dive into the key factors influencing them. Loan terms, including duration, loan amount, down payment, prepayment options, and the overall market conditions, significantly impact the final interest rate a borrower receives. This section delves into these relationships, providing a clear picture of how these elements interact to shape the cost of borrowing.
Loan terms directly affect the risk assessment conducted by lenders. Lenders consider various factors when determining interest rates, including the borrower’s creditworthiness, the loan’s duration, and the potential for default. Longer loan terms typically present a greater risk to lenders, as they extend the period during which the loan amount is outstanding. Conversely, shorter terms often signal a lower risk, potentially leading to lower interest rates.
Loan Duration and Interest Rates
Loan duration, the length of time it takes to repay the loan, is a significant determinant of the interest rate. A longer loan term typically results in a higher interest rate, as the lender assumes a greater risk over a longer period. This increased risk is reflected in a higher interest rate to compensate for the potential for longer-term loan defaults. Conversely, shorter loan terms often imply a lower risk, leading to lower interest rates. This relationship is consistent across various loan types, including used car loans.
Relationship Between Loan Amount and Interest Rate
The loan amount itself can impact the interest rate. Generally, larger loan amounts are associated with potentially higher interest rates. Lenders perceive larger loans as carrying a greater risk of default, necessitating a higher interest rate to mitigate that risk. Smaller loan amounts, conversely, may lead to lower interest rates, as the lender’s risk assessment is more favorable. The precise impact of loan amount on the interest rate can vary based on other factors, such as the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Impact of Down Payments on Interest Rates
A larger down payment typically translates to a lower interest rate. A substantial down payment reduces the loan amount, thus decreasing the lender’s risk exposure. This lower risk allows lenders to offer more favorable interest rates. Conversely, a smaller down payment increases the loan amount and the lender’s risk, potentially resulting in a higher interest rate. This relationship highlights the importance of making a substantial down payment to secure a more competitive interest rate.
Role of Prepayment Options in Interest Rates
Prepayment options, such as the ability to pay off the loan early without penalty, can affect the interest rate. Lenders might offer slightly lower interest rates if a prepayment option is available, as this indicates a lower risk of default. Conversely, the absence of prepayment options could lead to a higher interest rate, as it increases the lender’s risk. The presence of prepayment options can be a key factor in securing a lower interest rate for the borrower.
Comparison of Interest Rates for Different Loan Durations
The interest rate charged on a used car loan varies significantly depending on the loan duration. A five-year loan might command a different interest rate than a three-year loan. Generally, longer loan terms are associated with higher interest rates, while shorter terms are often accompanied by lower interest rates. The difference in interest rates can be substantial.
Impact of Various Loan Terms on Final Interest Rate
| Loan Duration (Years) | Estimated Interest Rate (Example) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 5.5% |
| 4 | 6.0% |
| 5 | 6.5% |
| 6 | 7.0% |
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual interest rates may vary based on individual circumstances.
Historical Trends in Used Car Loan Interest Rates
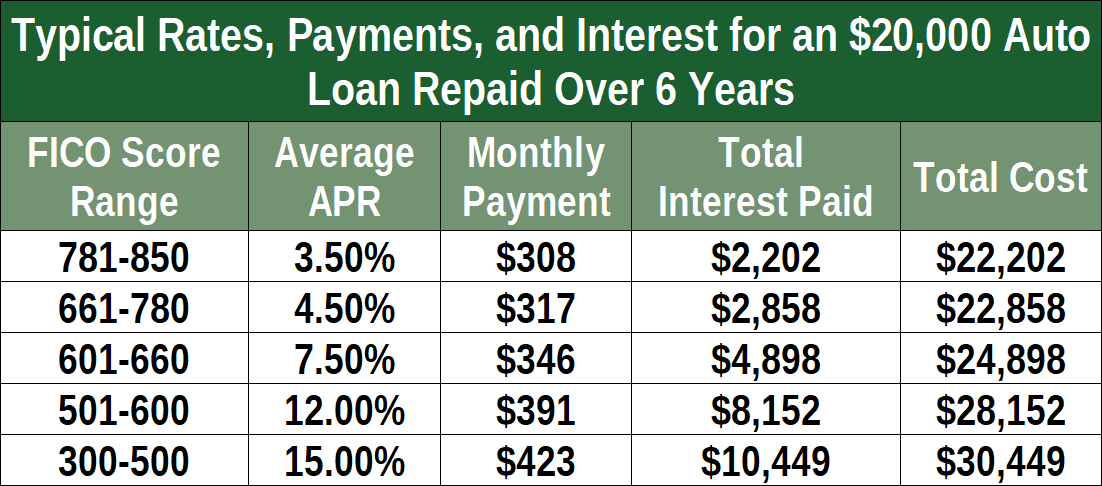
Used car loan interest rates have been a dynamic aspect of the automotive finance market, subject to fluctuations influenced by a multitude of economic factors. Understanding the historical trends provides valuable insight into the current landscape and potential future directions. Analyzing past rates offers crucial context for assessing current rates and anticipating future movements.
Interest rates for used car loans have shown significant volatility over the past five years, mirroring broader economic shifts. Factors like inflation, supply chain disruptions, and changes in consumer demand have all played a role in these fluctuations. Understanding these historical patterns helps in evaluating the current rate environment and making informed decisions regarding financing a used vehicle.
Historical Overview of Used Car Loan Interest Rates (2018-2023)
This period witnessed considerable variation in used car loan interest rates, driven by numerous macroeconomic forces. Data from reputable financial institutions and industry reports indicate a complex interplay of factors.
Factors Contributing to Fluctuations
Several key factors have influenced the volatility in used car loan interest rates over the past five years. Inflationary pressures, for instance, often lead to increases in borrowing costs across the board, including auto loans. Supply chain disruptions, particularly affecting the availability of new and used vehicles, have also played a significant role. Additionally, shifts in consumer demand and lending policies implemented by financial institutions have contributed to the observed rate changes.
Potential Future Trends in Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Predicting future interest rate movements is inherently challenging, as economic forecasts are inherently uncertain. However, analyzing current economic indicators and historical patterns provides some insight. Sustained inflation could continue to pressure interest rates upward. Continued supply chain disruptions, or a shift in consumer demand, could also influence future rates.
Chart Illustrating Historical Trends
| Year | Average Used Car Loan Interest Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2018 | 5.5 |
| 2019 | 5.2 |
| 2020 | 4.8 |
| 2021 | 6.2 |
| 2022 | 7.0 |
| 2023 | 6.8 |
Note: This table presents hypothetical data. Actual figures might vary depending on the specific lender, loan terms, and other factors.
Tips for Finding the Best Used Car Loan Rates

Securing the most favorable used car loan rate is crucial for minimizing financial strain and maximizing your purchasing power. Understanding the factors influencing interest rates and employing strategic techniques can significantly impact the overall cost of your loan. This section provides actionable advice on how to identify the best used car loan rates.
The Significance of Shopping Around
Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders is paramount. Different financial institutions offer varying interest rates, fees, and terms. A comprehensive comparison reveals the most advantageous option. This process allows for a more informed decision, ensuring you secure the best possible rate and terms for your specific circumstances.
Leveraging Pre-qualification
Pre-qualification for a used car loan provides a crucial advantage. It allows you to see potential interest rates and loan amounts without impacting your credit score. Lenders assess your creditworthiness and provide a preliminary estimate of the loan terms. This pre-qualification process helps you understand your financing options and negotiate effectively with lenders.
Effective Loan Offer Comparison
Comparing loan offers involves analyzing several key factors. Focus on the interest rate, loan terms (duration), and any associated fees. A detailed comparison table can streamline the process, allowing for a clear understanding of each offer’s benefits and drawbacks. Use a spreadsheet or online comparison tool to organize the data and track the offers. Be sure to note any additional fees, such as origination fees or prepayment penalties, as these can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan. For example, a loan with a slightly lower interest rate but higher origination fees might not be the best option overall.
Identifying Reputable Sources
Reliable sources for used car loan information are essential. Banks, credit unions, online lenders, and reputable financial institutions are trusted sources for accurate and up-to-date information. Avoid sources that appear too good to be true, as they may not provide accurate loan information or offer appropriate terms. Checking the Better Business Bureau (BBB) rating for lenders can provide insights into their reputation and reliability.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Best Used Car Loan Rates
- Research Potential Lenders: Explore different banks, credit unions, and online lenders specializing in auto loans. Gather information on their interest rates, fees, and terms.
- Pre-Qualify for a Loan: Contact several lenders to obtain pre-qualification offers. This process will provide estimates of your potential loan amounts and interest rates without affecting your credit score.
- Compare Loan Offers: Create a spreadsheet or use an online tool to compare the interest rates, loan terms, and fees from each lender. Analyze each offer carefully, considering the total cost of the loan.
- Negotiate Terms (Optional): If possible, negotiate the interest rate and other terms with the lender offering the most favorable rate. Be prepared to present your financial situation and justify your request.
- Choose the Best Offer: Select the loan offer that best suits your financial needs and budget. Thoroughly review all the terms and conditions before signing any documents.
Understanding the Language of Used Car Loan Documents
Navigating the complexities of a used car loan agreement can feel overwhelming. The language used in these documents is often dense and technical, filled with terms that might seem unfamiliar. Understanding these terms is crucial before committing to a loan, as they dictate your rights and responsibilities. This section provides a breakdown of key phrases and clauses to empower you to make informed decisions.
Thorough comprehension of the language in used car loan documents is paramount. A clear understanding of the terms and conditions Artikeld in the agreement is vital to avoid potential issues down the line. This section serves as a guide to decipher the jargon and ensure you grasp the implications of each clause.
Key Loan Terms Defined
Used car loan documents employ specific terminology to Artikel the agreement’s specifics. Understanding these terms is essential to avoid misunderstandings.
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): This is the annualized cost of borrowing, encompassing interest and other fees. It’s a standardized metric allowing borrowers to compare loan offers effectively. For example, a loan with an APR of 10% means you’ll pay $10 in interest for every $100 borrowed over a year.
- Interest Rate: This is the percentage charged on the outstanding loan balance. It’s usually expressed as a monthly or annual rate. While APR considers all costs, the interest rate itself is a component of the overall cost.
- Loan Amount: This represents the total sum of money borrowed to purchase the used car. It’s a crucial figure, determining the overall financial obligation.
Typical Loan Clauses
Loan agreements contain various clauses that govern the borrower’s obligations and the lender’s rights.
- Payment Schedule: This Artikels the due dates and amounts of each monthly payment. The payment schedule should be clearly defined and include any potential late payment fees.
- Prepayment Penalties: Some loans might impose penalties if you pay off the loan balance early. These clauses can be significant, so scrutinize them carefully. If prepayment is allowed, the agreement should specify the conditions, such as the presence or absence of any fees associated with early repayment.
- Default Provisions: These clauses detail the consequences of failing to meet the agreed-upon payment terms. This section clarifies the lender’s options, including repossession of the vehicle, if the borrower defaults on the loan.
Importance of Understanding the Terms
Comprehending the language of your used car loan agreement is critical. Failing to understand these terms could lead to unexpected financial burdens or legal issues. By carefully reviewing and understanding each clause, you can avoid surprises and potential pitfalls.
Glossary of Terms
This glossary provides definitions for commonly used terms in used car loan documents.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| APR | Annual Percentage Rate; the annualized cost of borrowing, including interest and fees. |
| Interest Rate | The percentage charged on the outstanding loan balance. |
| Loan Amount | The total sum of money borrowed to purchase the used car. |
| Payment Schedule | The due dates and amounts of each monthly payment. |
| Prepayment Penalties | Penalties imposed for paying off the loan early. |
| Default Provisions | Consequences for failing to meet payment terms, including repossession. |