Introduction to Used Car Calculators
Used car calculators are invaluable tools for both buyers and sellers in today’s automotive market. They streamline the process of determining a fair price for a used vehicle, saving time and effort while potentially mitigating the risk of overpaying or underselling. These tools leverage various factors to estimate a vehicle’s value, allowing users to make informed decisions based on accurate valuations.
These calculators provide a structured approach to evaluating used cars, considering key attributes that influence market price. They are designed to be user-friendly and accessible, enabling quick and efficient assessment of a vehicle’s worth, irrespective of location or market fluctuations.
Common Features of Used Car Calculators
Used car calculators typically incorporate a range of features to accurately assess a vehicle’s value. These features ensure a comprehensive and precise evaluation, considering various influencing factors.
- Year, Make, and Model: The calculator uses these fundamental attributes to establish a baseline value based on established market trends and historical data.
- Mileage: Mileage is a crucial factor, as higher mileage generally corresponds to a lower market value. The calculator accounts for this depreciation to provide a more accurate valuation.
- Condition: The condition of the vehicle, including visible damage, mechanical issues, and overall cleanliness, significantly impacts its price. Calculators may allow users to input details about the car’s condition to adjust the estimated value.
- Options and Features: Specific features and options, such as leather seats, sunroof, or navigation, can increase a vehicle’s value. Calculators can often account for these added features to give a more precise valuation.
- Market Data: The calculator often incorporates real-time market data or historical trends to provide a more accurate reflection of current pricing in a specific area. This ensures that the valuation is not based on outdated or isolated data points.
Types of Used Car Calculators
Used car calculators exist in various formats to suit different needs and preferences.
- Online Calculators: These calculators are accessible through web browsers and provide an immediate and convenient way to assess a vehicle’s value. Examples include specialized websites dedicated to used car valuations, or integrated tools within broader automotive marketplaces.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps offer a similar functionality to online calculators but are easily accessible on smartphones and tablets. They are often integrated with other features, such as car listings or dealer contact information.
- Dealer-Specific Tools: Some dealerships may offer their own calculators for customers to assess the value of a vehicle before potentially engaging in a transaction. This allows customers to have a better understanding of the price range before interacting with a salesperson.
Importance of Accurate Used Car Valuation
Accurate used car valuation is crucial for both buyers and sellers. It prevents overpaying or underselling, leading to more satisfactory and equitable transactions.
- Buyer Protection: Accurate valuations allow buyers to determine if a vehicle is priced competitively, preventing them from overpaying for a used car.
- Seller Satisfaction: Knowing the accurate market value allows sellers to price their vehicles appropriately, maximizing their potential return and potentially avoiding time-consuming negotiations.
Role of Used Car Calculators in the Buying and Selling Process
Used car calculators play a significant role in streamlining both the buying and selling processes. They assist in making informed decisions and navigating the complexities of the used car market.
- Pre-Transaction Assessment: Calculators allow potential buyers to assess the market value of a vehicle before contacting a seller or dealer, which allows for a more focused and effective negotiation process.
- Pricing Strategy: Sellers can leverage calculator results to determine a realistic selling price, increasing the likelihood of a quick and favorable sale.
Functionality and Features of Used Car Calculators
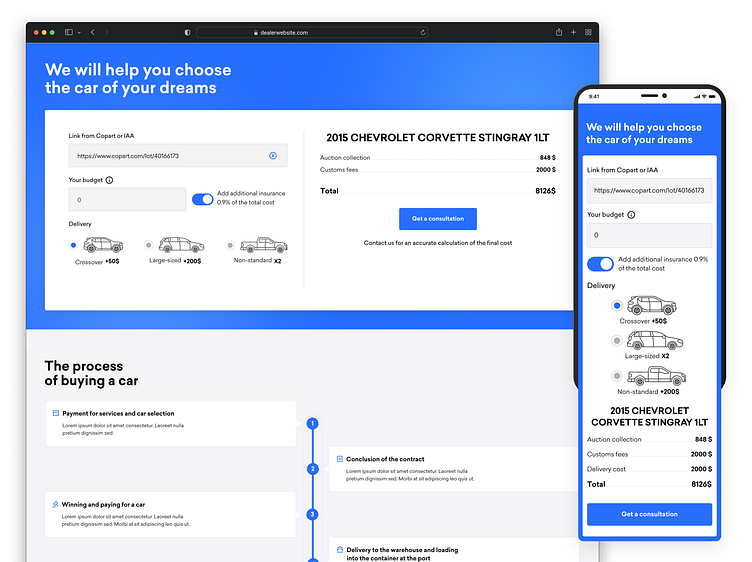
Used car calculators are powerful tools for potential buyers, offering a comprehensive overview of the financial implications of purchasing a used vehicle. These calculators streamline the often-complex process of evaluating the total cost of ownership, allowing for informed decisions based on realistic estimations.
Used car calculators provide a structured approach to evaluating the financial aspects of a used vehicle purchase, enabling potential buyers to assess the true cost of ownership, including the initial purchase price, financing options, and ongoing expenses. They offer a valuable service by simplifying the complex calculations involved in these purchases, allowing buyers to focus on making informed decisions.
Core Calculations Performed
Used car calculators typically perform several core calculations to help estimate the total cost of a used car purchase. These calculations are crucial for potential buyers to understand the financial implications before committing to a purchase. Depreciation, loan payments, and total cost of ownership are key aspects.
- Depreciation: Calculators estimate the loss in value of a vehicle over time. This calculation factors in various factors, including the vehicle’s age, mileage, and condition, to project its future worth. A typical calculation would use historical data and market trends to project the value decrease. For example, a 2018 model car with high mileage will depreciate more rapidly than a newer model with low mileage, and in good condition.
- Loan Payments: The calculator determines the monthly or other periodic payments associated with financing a used car purchase. This involves the principal amount, interest rate, and loan term. A 5-year loan at a 6% interest rate will result in significantly higher monthly payments than a 3-year loan with the same interest rate.
- Total Cost of Ownership: This calculation combines the purchase price, financing costs, insurance premiums, maintenance expenses, and fuel costs to project the overall cost of owning the car over a specific period. An accurate calculation can help a buyer compare the overall cost of different vehicles.
Input Fields Required
Used car calculators require specific input data to function accurately. These fields allow the calculator to produce relevant estimations for the user. Understanding the required information is crucial for generating reliable estimates.
- Vehicle Information: The calculator needs details like the vehicle’s make, model, year, mileage, and condition. This information helps in assessing the market value and potential depreciation.
- Financing Details: Inputting the desired loan amount, interest rate, and loan term is necessary for calculating the monthly payments and total interest paid. The user needs to understand that the longer the loan term, the lower the monthly payment, but the higher the total interest paid.
- Other Expenses: The calculator might request input on expected maintenance costs, insurance premiums, and fuel costs. These factors contribute to the overall cost of ownership.
Metrics for Assessing Value
Different metrics are used to evaluate the value of a used car. These factors collectively contribute to the overall assessment of a vehicle’s worth.
- Mileage: Higher mileage typically indicates greater wear and tear, impacting the car’s value and future maintenance costs. A car with 100,000 miles will likely have higher maintenance costs than a car with 50,000 miles.
- Model Year: Newer model years generally command higher prices due to technological advancements and improved features. A 2023 model of a car will usually have more modern features than a 2018 model.
- Condition: The physical condition of the vehicle plays a significant role in determining its value. A well-maintained vehicle will retain its value better than one with significant damage or neglect.
Financing Options
Used car calculators often incorporate various financing options. These options provide potential buyers with different ways to fund their purchase.
- Loan Terms: Calculators allow users to explore different loan terms (e.g., 36 months, 60 months). Understanding the different loan terms is crucial in planning the budget.
- Interest Rates: The calculator incorporates varying interest rates to display how different interest rates affect monthly payments and total costs. A higher interest rate will result in a larger amount of total interest paid.
- Down Payments: Calculators can estimate payments with different down payments, enabling buyers to explore various financial scenarios.
Estimating Total Cost of Ownership
Used car calculators can provide a comprehensive estimate of the total cost of ownership. This is essential for potential buyers to make informed decisions.
By inputting the vehicle details, financing terms, and anticipated expenses, the calculator aggregates these elements to provide a comprehensive cost estimate. This empowers buyers to assess the true financial burden of owning a used vehicle over a specified period.
Comparison of Different Used Car Calculators

Online used car calculators have become increasingly popular tools for estimating the value of a vehicle. However, the accuracy and comprehensiveness of these calculators can vary significantly. Understanding the differences between various calculators is crucial for making informed decisions when buying or selling a used car.
Accuracy of Valuation
Different calculators employ various methodologies to determine used car values. Some calculators rely on publicly available data, like recent sales records, while others utilize complex algorithms that incorporate factors like mileage, condition, and market trends. The accuracy of a calculator is heavily dependent on the data it uses and the sophistication of its valuation model. A calculator that draws from a large, constantly updated database of recent sales will generally provide more accurate estimates than one relying on older or less comprehensive data.
User Interface and Ease of Use
The user interface significantly impacts the usability of a used car calculator. A well-designed interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate. Clear prompts, user-friendly input fields, and visual representations of the results enhance the user experience. Conversely, a cluttered or confusing interface can frustrate users and potentially lead to errors in inputting information. Factors such as the calculator’s mobile-friendliness also play a crucial role, ensuring accessibility across different devices.
Range of Features Offered
The range of features offered by different calculators can vary substantially. Some calculators provide basic valuations, focusing primarily on price estimates. More advanced calculators may offer additional functionalities, such as calculating loan payments, comparing different models, or providing detailed breakdowns of the valuation factors considered. Calculators with comprehensive features often provide a more complete picture of the vehicle’s value and its financial implications.
Comparison Table
| Calculator | Accuracy | User Interface | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator A | High (based on large, recent sales data and sophisticated algorithm) | Intuitive and user-friendly; mobile-friendly | Basic valuation, loan payment calculation, model comparison |
| Calculator B | Moderate (relies on a smaller database, less complex algorithm) | Simple, but may be less intuitive | Basic valuation, basic loan payment calculation |
| Calculator C | Low (outdated data, limited features) | Cluttered and less user-friendly; not mobile-friendly | Basic valuation only |
Note: The accuracy ratings are relative and may vary based on the specific vehicle being evaluated.
Example of Different Valuation Models
Consider a 2015 Honda Civic with 50,000 miles. Calculator A, utilizing a comprehensive database and a sophisticated algorithm, might estimate its value at $12,500, factoring in condition and recent sales data. Calculator B, using a smaller database and simpler algorithm, might estimate it at $12,000. Calculator C, with outdated data, might estimate it at $11,000. The variance demonstrates the importance of understanding the underlying methodologies of different calculators.
User Experience and Interface Design
A user-friendly interface is crucial for a used car calculator’s success. A well-designed interface ensures ease of use, reduces frustration, and ultimately drives user engagement and satisfaction. This section details essential components, input methods, layout options, and UI elements that contribute to a positive user experience.
Effective design principles are paramount for user engagement. A calculator’s interface should be intuitive, visually appealing, and seamlessly integrate with the overall user journey. Users should easily grasp the calculator’s functionality and navigate through its various features without any undue effort.
Essential Components of a User-Friendly Interface
A robust used car calculator interface should incorporate several key components. These components include clear and concise input fields for essential details, such as the car’s make, model, year, mileage, and condition. An intuitive search function to find specific models or trim levels, along with an option to upload photos or specify features, enhances user experience. Moreover, a detailed summary table providing a comparative analysis of different models, alongside a breakdown of the calculation, should be presented. Finally, a clear and easily accessible “Calculate” button initiates the calculation process, providing a direct path to the results.
Intuitive Input Methods for Diverse Users
Different user groups require tailored input methods. For experienced car buyers, a streamlined interface with advanced search filters and data input options might be preferred. However, novice users would benefit from a guided input process with drop-down menus and helpful tooltips. To ensure inclusivity, the calculator should be compatible with various devices and offer a responsive design. The user should be able to effortlessly navigate between different sections and find the specific information they need quickly.
Layout Options for Input and Output
The layout of input and output significantly impacts the user experience. A well-organized table can showcase different car models side-by-side, highlighting relevant details. Consider a two-column layout, one for the input fields and the other for the results. Alternatively, a single-column layout can provide a concise display, particularly for users focused on a specific model. The layout should be adaptable, allowing users to switch between these layouts based on their preferences.
| Layout Option | Input Fields | Output Display |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Column | Detailed fields for each car model, allowing side-by-side comparison. | Clear table showing comparative analyses. |
| Single-Column | Concise input fields, focused on a specific car model. | Summary of results and detailed calculation steps. |
User Interface Elements and User Experience
Several UI elements contribute significantly to the user experience. Clear labels, concise instructions, and informative tooltips enhance understanding and ease of use. A visual representation of the calculation process can provide insights into the logic behind the results, fostering trust in the calculator. Visual cues, such as highlighting valid input fields or displaying loading indicators, enhance the user interface. Consistent design elements, such as color schemes and fonts, promote a seamless user experience.
Impact of Visual Design on User Trust and Engagement
Visual design significantly impacts user trust and engagement. A visually appealing and professional interface creates a positive first impression. High-quality images and graphics of the vehicles enhance credibility and engagement. A user-friendly color scheme, appropriate font choices, and clear typography all contribute to a polished and professional look. Using a responsive design ensures optimal display across various devices, fostering a positive and seamless user experience.
Data Sources and Accuracy
Used car calculators rely on various data sources to provide accurate valuations. Understanding these sources and their inherent limitations is crucial for interpreting the results. The accuracy of the calculated value directly impacts the user’s decision-making process, so reliable data is paramount.
Data Sources
Used car calculators leverage a combination of data sources to estimate market value. These sources include publicly available market data, manufacturer information, and proprietary databases. Market data encompasses listings from online marketplaces, dealer inventories, and industry reports. Manufacturer information often includes data on vehicle specifications, features, and historical sales patterns. Proprietary databases, sometimes developed by the calculator provider, incorporate additional data points like vehicle mileage, accident history, and specific condition reports. The diverse nature of these sources contributes to a comprehensive valuation approach.
Accuracy Considerations
The accuracy of a used car calculator’s output is directly influenced by the quality and comprehensiveness of the underlying data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to significant valuation discrepancies. For example, a calculator relying heavily on outdated market data might produce an inflated or deflated valuation. Furthermore, the absence of critical data points, such as vehicle mileage or accident history, can compromise the reliability of the assessment. The accuracy of used car valuation is also impacted by factors like geographic location, local market conditions, and individual vehicle condition.
Factors Influencing Accuracy
Several factors can impact the accuracy of used car valuations. Market fluctuations, particularly in high-demand or low-supply segments, can cause rapid changes in pricing. Seasonal variations in vehicle demand can also affect valuation models. Specific vehicle modifications, such as performance upgrades or custom paint jobs, may increase or decrease the value. The overall condition of the vehicle, including damage, maintenance history, and interior wear, significantly affects the final price. Calculators often incorporate these factors but their accuracy is dependent on the quality and thoroughness of the input data.
Verifying Data Accuracy
To enhance the reliability of the valuation, users can employ several methods to verify the data presented by a used car calculator.
| Verification Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Comparison with Market Listings | Comparing the calculator’s valuation with actual listings on online marketplaces (e.g., Craigslist, eBay) for similar vehicles in the same area. |
| Checking Manufacturer Information | Reviewing manufacturer-provided information regarding the vehicle’s specifications and features. |
| Consulting with Dealers | Contacting local dealerships to discuss the current market value of comparable vehicles. |
| Evaluating Vehicle Condition | Thoroughly inspecting the vehicle and considering any factors that could impact its value (e.g., mileage, damage, modifications). |
| Utilizing Multiple Calculators | Comparing the valuations from different calculators to identify potential inconsistencies or significant variations. |
Real-World Use Cases
Used car calculators are invaluable tools for both buyers and sellers, empowering informed decisions in a market often fraught with complexities. They provide a structured approach to evaluating the value of a vehicle, allowing users to factor in various crucial elements and potentially avoid costly mistakes. From pre-purchase assessments to strategic pricing strategies, these calculators can significantly impact the overall transaction experience.
Accurate valuation is critical in the used car market, and these calculators offer a way to understand market trends and adjust expectations accordingly. By incorporating factors like mileage, condition, and model year, these tools facilitate a more objective understanding of the vehicle’s true worth, leading to smoother negotiations and a more satisfying outcome for both parties.
Pre-Purchase Evaluation
Used car calculators are indispensable for evaluating a vehicle’s market value before committing to a purchase. By inputting relevant details like make, model, year, mileage, and condition, buyers can quickly assess the fair market price. This empowers them to negotiate more effectively, avoid overpaying, and identify potential red flags.
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gather Vehicle Information | Collect the make, model, year, mileage, condition, and any additional relevant details of the vehicle. |
| 2 | Input Data into Calculator | Enter the gathered information into the used car calculator. Ensure accuracy for the best results. |
| 3 | Analyze Results | Review the calculated market value and compare it to the asking price. Look for any discrepancies or unusual factors. |
| 4 | Negotiate | Use the calculated value as a basis for negotiation with the seller. Consider additional factors like financing options or warranties. |
Determining Selling Price
Determining a fair selling price is a crucial step in a successful used car sale. Used car calculators provide a starting point for understanding market value, helping sellers avoid undervaluing their vehicle. Inputting details like the car’s features, condition, and market trends allows sellers to establish a realistic asking price. This approach minimizes the time spent on negotiations and increases the likelihood of a swift and profitable sale.
Identifying Potential Red Flags
Used car calculators can assist in identifying potential red flags during a pre-purchase evaluation. By comparing the calculated value to the asking price, discrepancies may suggest hidden issues with the vehicle. This allows buyers to investigate further and potentially avoid acquiring a vehicle with undisclosed problems. For example, a significantly lower calculated value compared to the asking price might indicate mechanical issues or undisclosed damage.
Case Studies
One case study illustrates how a used car calculator helped a buyer avoid overpaying. A buyer, using a calculator, discovered the asking price for a specific used SUV was significantly higher than its fair market value. This knowledge empowered the buyer to negotiate a more reasonable price, saving them a substantial amount of money.
Another example highlights how a used car calculator helped a seller establish a competitive asking price. A seller, using a calculator, found that their used sedan’s market value was slightly below the average. This allowed them to adjust their pricing strategy and receive a quick sale at a price that was more competitive in the market.
Future Trends and Innovations

Used car calculators are evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in data science and technology. This evolution promises greater accuracy, user-friendliness, and more comprehensive features for consumers and businesses alike. The future will see a shift towards more sophisticated valuation models and personalized experiences, integrating real-time data and advanced analytics.
The increasing availability of vast datasets, coupled with the rise of AI and machine learning, is poised to revolutionize the way used car values are assessed. This transformation will enable more precise estimations, reducing the guesswork involved in valuing vehicles and improving the overall user experience. Furthermore, the integration of real-time market data will provide more up-to-date and dynamic valuations, ensuring that users have access to the most current information available.
Future Trends in Used Car Calculator Technology
The used car market is dynamic, and calculators must adapt to keep pace. Predictive analytics, incorporating historical sales data, current market conditions, and even external factors like economic indicators, will become increasingly important. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms promises to refine valuation models, leading to more accurate estimations and personalized recommendations.
Innovative Features for Future Used Car Calculators
Several innovative features could enhance the functionality of used car calculators. These include real-time market data integration, personalized recommendations based on individual preferences, and advanced filtering options for niche markets. Integration with vehicle maintenance records and repair history could also provide a more holistic view of a car’s condition and potential future costs. Another noteworthy feature would be a comparative analysis of multiple vehicles based on a user’s specific needs and budget.
AI and Machine Learning in Used Car Valuation
AI and machine learning (ML) can significantly improve used car valuation by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and making predictions that are more accurate than traditional methods. For example, ML algorithms can be trained on datasets encompassing vehicle specifications, mileage, accident history, and market trends to establish a robust valuation model. This advanced analysis can then provide insights into the value depreciation rate for different vehicle types and models, allowing for more accurate estimations. Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots could provide instant support and answers to user queries, significantly improving the user experience.
Comparison of Automated Valuation Models
| Technology | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Models | Traditional statistical models that predict car values based on historical data. | Relatively simple to implement, readily available tools. | May not capture complex relationships, susceptible to overfitting. |
| Machine Learning (Neural Networks) | Sophisticated algorithms that learn from large datasets, identifying complex patterns. | Can capture intricate relationships, high accuracy potential. | Requires substantial data, potentially complex implementation. |
| Hybrid Models | Combine elements of regression and machine learning. | Balance simplicity and accuracy, good for intermediate data. | May not reach the peak accuracy of dedicated ML models. |
The table above illustrates the strengths and weaknesses of different automated valuation models. Choosing the appropriate model depends on the availability and quality of data, and the desired level of accuracy.