Loan Qualification Factors

Securing a 72-month used car loan hinges on various factors beyond simply needing a vehicle. Understanding these factors can help you navigate the loan application process with greater confidence and potentially secure a better interest rate. Loan approval isn’t a binary outcome; it’s a nuanced evaluation based on your financial profile and the specific terms of the loan.
Loan Approval Factors
Several crucial elements influence a lender’s decision to approve a 72-month used car loan. These factors are evaluated holistically, not in isolation.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Loan Approval |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Score | A numerical representation of your creditworthiness, reflecting your payment history and responsible borrowing habits. | Higher credit scores generally lead to better interest rates and a higher likelihood of loan approval. |
| Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI) | The proportion of your monthly debt obligations to your gross monthly income. | A lower DTI suggests you have more financial capacity to handle the loan payments, increasing the chances of approval. |
| Employment History | Stability of your job and income stream. | Consistent employment history demonstrates financial stability, making you a more desirable borrower. |
| Loan Amount | The total sum of the loan requested. | Larger loan amounts often require a higher credit score and more robust financial profile. |
| Down Payment | The initial amount paid upfront towards the vehicle’s purchase price. | A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, improving the loan terms and potentially decreasing interest rates. |
| Vehicle Value | The assessed worth of the used car. | A vehicle with a higher assessed value can result in a lower loan amount and more favorable terms. |
Credit Score Range for Favorable Rates
A credit score of 660 or higher is generally considered favorable for obtaining a 72-month used car loan with a competitive interest rate. Scores in this range demonstrate a history of responsible financial management. Lenders often view borrowers with scores above 700 as prime candidates for favorable rates.
Down Payments and Loan Impacts
Down payments significantly influence loan terms and rates. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, decreasing the risk for the lender and often resulting in a lower interest rate.
- Scenario 1: Small Down Payment (e.g., 10%): This scenario results in a larger loan amount, potentially increasing the interest rate and requiring a higher credit score for approval. The monthly payments will be higher, and the total interest paid over the loan term will be greater.
- Scenario 2: Moderate Down Payment (e.g., 20%): This scenario reduces the loan amount, often leading to a lower interest rate and potentially more manageable monthly payments. The total interest paid will be less than a scenario with a smaller down payment.
- Scenario 3: High Down Payment (e.g., 50%): A high down payment essentially minimizes the loan amount, which can drastically improve the interest rate and significantly reduce monthly payments. It can often result in approval with a lower credit score than other scenarios.
Interest Rate Comparison Across Credit Scores
Interest rates for 72-month used car loans vary significantly based on credit scores. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate.
| Credit Score Range | Estimated Interest Rate Range (Example) |
|---|---|
| 660-699 | 6.5%-8.5% |
| 700-759 | 5.5%-7.5% |
| 760+ | 4.5%-6.5% |
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual rates will vary based on numerous factors, including the specific lender, the prevailing market conditions, and the vehicle’s condition.
Interest Rate Trends
Used car loans, particularly those spanning 72 months, are sensitive to broader economic conditions. Understanding current interest rate environments and historical trends is crucial for informed decision-making, allowing consumers to evaluate their financial options effectively. The factors influencing these rates, such as inflation and market conditions, are examined to anticipate future shifts. A comparative analysis of 72-month rates against shorter-term options will also provide insights into the cost structure.
Current interest rates for 72-month used car loans are influenced by various economic forces. Recent inflation rates, Federal Reserve policy decisions, and overall market sentiment play a significant role in determining the cost of borrowing. The complex interplay of these forces affects the financial choices available to consumers.
Current Interest Rate Environment
The current interest rate environment for 72-month used car loans displays a dynamic range, fluctuating based on prevailing economic conditions. Factors such as inflation, the strength of the overall economy, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions significantly impact these rates. This variability underscores the importance of seeking out multiple quotes and understanding the context behind each rate.
Historical Interest Rate Trends
Analyzing the historical trends in used car loan interest rates over the past five years provides valuable context for understanding current rates. The following chart illustrates the average annual interest rates for 72-month used car loans:
Note: This is a hypothetical chart. Real-world data should be obtained from reputable sources.
(Insert a hypothetical chart here. The chart should display a line graph with years on the x-axis and average interest rates on the y-axis. The line should show fluctuations in interest rates over the past five years. Include labels and a title such as “Average Annual Interest Rates for 72-Month Used Car Loans (2018-2023).” Example data points should be present on the chart.)
Factors Impacting Future Interest Rate Movements
Several factors can influence future interest rate movements for used car loans. Inflationary pressures, particularly if sustained, can lead to higher interest rates as lenders adjust their borrowing costs to account for the decreased purchasing power of money. Similarly, changes in the overall market sentiment, such as a perceived weakening of the economy, can result in downward pressure on rates as lenders adjust to the risk profile.
- Inflationary pressures: Sustained inflation can compel lenders to increase interest rates to maintain profitability and compensate for the reduced value of the loan principal over time. Historical examples, such as periods of high inflation in the 1970s, illustrate the impact of inflation on borrowing costs.
- Market sentiment: A weakening economy or market uncertainty can cause lenders to adjust their rates downwards to attract borrowers and maintain loan demand. Conversely, strong economic indicators can lead to increases in interest rates.
- Federal Reserve policy: Decisions by the Federal Reserve regarding monetary policy, such as interest rate hikes or cuts, directly influence the cost of borrowing for consumers and businesses, including auto loans. Past instances of the Federal Reserve adjusting interest rates have been pivotal in shaping interest rates for various types of loans.
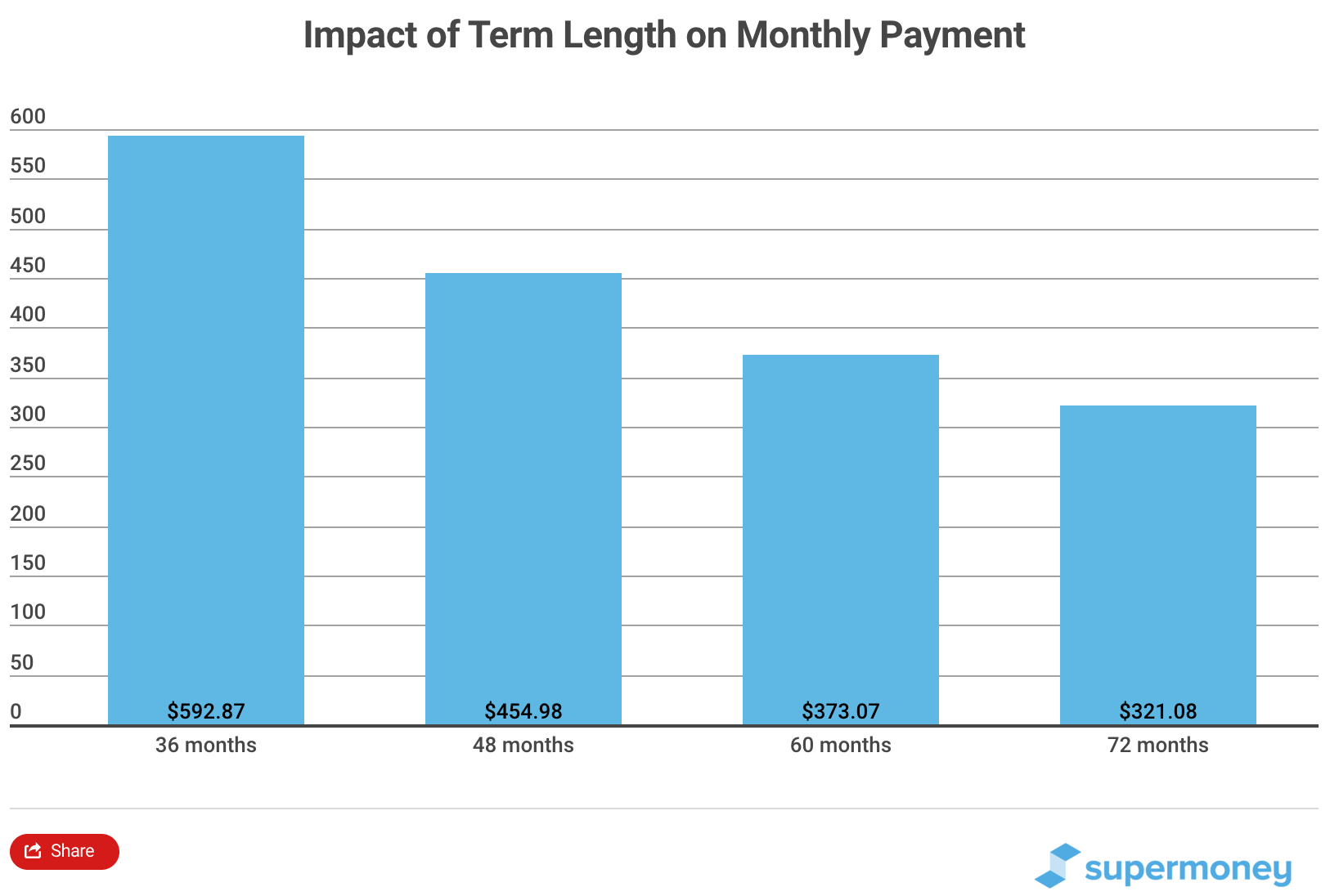
Comparison of Interest Rates for Different Loan Terms
The interest rate for a 72-month loan typically differs from shorter-term loans, such as a 36-month loan. This difference stems from the increased risk for lenders with longer loan terms. The following table demonstrates the difference in rates:
| Loan Term | Estimated Average Interest Rate (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|
| 36 Months | 6.5% |
| 72 Months | 7.2% |
Note: These are hypothetical examples. Actual interest rates will vary based on creditworthiness, lender policies, and market conditions.
Loan Providers
Navigating the landscape of used car financing can be daunting. Understanding the various loan providers and their offerings is crucial for securing the best possible terms. This section details common lenders, their loan options, application processes, and associated fees, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions.
Different lenders cater to diverse needs and credit profiles. Dealerships often offer in-house financing, while banks, credit unions, and online lenders provide broader access to loan options and potentially more competitive rates. This section will break down the differences, enabling you to choose the financing path that aligns with your financial situation.
Common Lenders Offering 72-Month Used Car Loans
A range of institutions offer 72-month used car loans, including dealerships, banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Each offers varying loan terms and conditions.
| Loan Provider | Loan Options |
|---|---|
| Dealerships | Often offer in-house financing, sometimes with attractive incentives, but may have stricter credit requirements. May include financing packages bundled with vehicle purchase. |
| Banks | Generally provide competitive interest rates, but may require a stronger credit history. May involve more stringent documentation requirements. |
| Credit Unions | Typically offer lower interest rates and more favorable terms to members, but membership is often required. Can offer competitive rates to those with a strong credit history. |
| Online Lenders | Provide quick and convenient application processes, but interest rates might vary depending on creditworthiness. Offers flexibility and ease of application. |
Loan Options Available from Various Lenders
Different lenders tailor their loan options to specific needs. Dealerships might offer customized packages, including warranties or service contracts, tied to the financing. Banks typically offer standard auto loans with various interest rate structures. Credit unions focus on member-friendly terms. Online lenders frequently present a range of rates based on credit scores.
Loan Application Process at Different Loan Providers
The application process varies significantly. Dealerships often integrate the process within the purchase agreement. Banks typically require detailed application forms, credit checks, and income verification. Credit unions have a membership application process before applying for loans. Online lenders usually have streamlined online applications, but may still require supporting documents.
Comparison of Fees Associated with 72-Month Used Car Loans
Fees vary substantially depending on the lender. It’s crucial to compare these fees to get the most competitive deal.
| Loan Provider | Typical Fees |
|---|---|
| Dealerships | Origination fees, prepayment penalties, and potentially higher interest rates compared to other lenders. May include administrative fees. |
| Banks | Origination fees, appraisal fees, and potential late payment penalties. Fees are usually standardized and transparent. |
| Credit Unions | Typically have lower fees compared to banks and dealerships. Membership fees may apply, and specific fees can vary based on the credit union. |
| Online Lenders | Origination fees, late payment penalties, and potentially higher interest rates for lower credit scores. Fees are typically transparent in the loan agreement. |
Loan Repayment Strategies

Maximizing your return on a 72-month used car loan hinges on a well-defined repayment strategy. Understanding different approaches, their potential impact on interest paid, and the implications of early payoff is crucial for effective financial management. A strategic repayment plan can significantly reduce the overall cost of borrowing and ensure timely loan closure.
Varying Repayment Strategies
Different repayment strategies can affect the total interest paid over the loan term. A consistent, fixed monthly payment is a common approach, but other strategies, like paying extra or making larger lump-sum payments, can accelerate loan payoff and reduce interest costs. These strategies are explained in more detail below.
- Fixed Monthly Payments: This traditional approach involves making equal monthly payments over the loan term. It’s straightforward to manage but might result in higher total interest paid if the borrower isn’t able to accelerate the repayment schedule.
- Accelerated Payments: This involves making larger-than-required monthly payments or additional lump-sum payments. This strategy significantly reduces the loan term and total interest expense, but it requires careful budgeting and adherence to the plan.
- Interest-Only Payments: This strategy involves paying only the interest due each month, leaving the principal untouched. While reducing the initial burden, this approach significantly increases the total interest paid over the loan term.
Impact of Early Loan Payoff
Early loan payoff is a powerful tool to reduce the overall interest burden. By paying more than the minimum required monthly payment, or making additional lump-sum payments, the loan term is shortened, and the total interest paid is minimized. The sooner you start paying down the principal, the greater the impact on the overall interest cost.
Early repayment strategies are highly recommended to reduce the total interest cost.
Loan Prepayment Penalties
Prepayment penalties are clauses in loan agreements that impose a fee on the borrower for paying off the loan before the agreed-upon term. Their relevance to 72-month used car loans varies depending on the specific loan agreement and lender. Some lenders may impose penalties, while others do not. Understanding these clauses is crucial for planning your repayment strategy. Lenders may impose different penalties, so thorough loan documentation review is necessary.
Repayment Schedule Examples
The following table illustrates how different repayment schedules impact the total interest paid over a 72-month used car loan. These are illustrative examples and actual results may vary.
| Repayment Strategy | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid | Total Loan Cost | Loan Term (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Monthly Payment (Standard) | $350 | $1,750 | $18,750 | 72 |
| Accelerated Payments (Additional $100/month) | $450 | $1,200 | $16,200 | 60 |
| Interest-Only Payments | $200 | $3,750 | $23,750 | 72 |
Loan Terms and Conditions
Navigating the intricacies of a 72-month used car loan requires a clear understanding of the terms and conditions. This section delves into the typical stipulations, the negotiation process, common clauses, and the crucial role of the amortization schedule. Thorough comprehension of these elements empowers you to make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
Understanding the specifics of a loan agreement is vital. Loan terms dictate the financial obligations and rights of both the lender and the borrower. The following details Artikel typical conditions for a 72-month used car loan.
Typical Terms and Conditions
A comprehensive understanding of the terms and conditions is essential for a smooth loan process. The following table provides a glimpse into the common components of a 72-month used car loan agreement.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Loan Amount | The total sum borrowed to purchase the vehicle. |
| Interest Rate | The percentage cost of borrowing the money, often variable or fixed. |
| Loan Term | The duration of the loan, typically 72 months in this case. |
| Monthly Payment | The fixed amount due each month to repay the loan. |
| Prepayment Penalty | A fee for paying off the loan before the agreed-upon term. |
| Late Payment Fee | A charge for missing a payment deadline. |
| Security (Collateral) | The vehicle itself, used as security in case of default. |
| APR (Annual Percentage Rate) | The total cost of borrowing, encompassing interest and fees. |
Understanding and Negotiating Loan Terms
Effective negotiation is key to securing the best possible loan terms. Thorough research and preparation are essential. Comprehend the lender’s interest rates, fees, and repayment schedules. Comparison shopping across various lenders is crucial to finding the most advantageous offer. Know your credit score and financial standing to negotiate effectively.
Common Loan Clauses and Implications
Loan agreements contain various clauses that dictate the borrower’s responsibilities and the lender’s rights. A crucial clause Artikels the consequences of default.
“In the event of default, the lender reserves the right to repossess the vehicle.”
This clause clarifies the lender’s recourse in case of missed payments. Other clauses address prepayment penalties, late payment fees, and insurance requirements.
Significance of Loan Amortization Schedules
Amortization schedules detail the breakdown of loan payments over the loan term. Understanding the schedule is critical for managing your finances. It shows how much of each payment goes towards interest and how much towards principal.
A comprehensive example illustrates the amortization process. Let’s assume a $20,000 loan at 6% interest over 72 months.
| Month | Payment | Interest | Principal | Remaining Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $311 | $100 | $211 | $19,789 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 72 | $311 | $0.50 | $310.50 | $0 |
This schedule demonstrates how the principal portion of the payment increases over time, while the interest component decreases. This systematic approach helps the borrower understand the financial implications of the loan.
Impact of Economic Factors
Used car loan rates are intrinsically tied to the broader economic climate. Fluctuations in inflation, automotive market trends, and overall demand all play significant roles in shaping the availability and cost of these loans. Understanding these relationships is crucial for both borrowers and lenders.
Economic conditions exert a powerful influence on used car loan rates. Inflation, for example, typically correlates with higher interest rates. As the cost of living increases, central banks often raise interest rates to curb inflation. This ripple effect extends to all types of loans, including those for used cars. A period of high inflation usually leads to higher borrowing costs, making used car loans more expensive.
Inflation’s Impact on Loan Rates
Inflation directly impacts the interest rates charged on used car loans. When inflation rises, central banks tend to increase benchmark interest rates to combat the rising cost of living. This, in turn, leads to higher borrowing costs for consumers. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Federal Reserve might raise the federal funds rate. This increase then trickles down to other lending institutions, resulting in higher interest rates for used car loans. Consequently, borrowers face a steeper financial burden as they must pay more in interest over the life of their loan.
Impact of Automotive Market Changes
Changes in the automotive market significantly affect the availability and pricing of used car loans. A surge in used car sales, for instance, often leads to increased competition among lenders, potentially lowering rates. Conversely, a downturn in the market can reduce loan availability and drive rates upward as lenders become more cautious.
Role of Market Demand for Used Cars
Market demand for used cars plays a crucial role in determining loan rates. High demand often leads to a tighter supply, potentially inflating prices. This increased demand can influence loan providers, encouraging them to offer higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk. Conversely, low demand can lead to a surplus of used cars, which may encourage lenders to offer more favorable loan terms, including lower interest rates.
Supply Chain Issues and Used Car Loans
Supply chain disruptions can have a profound effect on the availability and cost of used car loans. Shortages of key components, like semiconductors, can lead to delays in manufacturing and a decrease in the supply of new vehicles. This reduced supply often translates to increased demand for used cars, driving up prices and potentially leading to higher interest rates. Furthermore, the unpredictable nature of supply chain issues can make it more difficult for lenders to assess risk, potentially impacting the availability of used car loans. For instance, a shortage of crucial components for car production could drive up prices for used vehicles and make it harder for lenders to predict loan repayment.