Historical Overview
Toyota’s journey from a small workshop to a global automotive giant is a testament to meticulous planning, innovative engineering, and unwavering dedication. The company’s success story is intricately woven with the threads of Japanese industrialization and a commitment to quality that continues to resonate today. This overview delves into the key milestones, growth periods, and geographical expansion that have shaped Toyota’s evolution.
Early stages of Toyota’s operations were profoundly influenced by the post-World War II economic landscape in Japan. The company’s founders recognized the need for a reliable and affordable transportation solution for a rebuilding nation.
Founding and Initial Product Lines
Toyota’s establishment in 1937 marked a pivotal moment in Japanese industrial history. Initially focused on producing automobiles, the company quickly diversified its product offerings to meet evolving market demands. The early models, though rudimentary by today’s standards, laid the foundation for the sophisticated vehicles Toyota is renowned for. The company’s initial focus was on developing vehicles that could serve the needs of a rapidly industrializing nation.
Timeline of Development and Growth
- 1937: Toyota Motor Corporation is founded, initially focused on textile machinery and automobiles. This period saw the company establish a solid foundation for future growth, demonstrating an early understanding of the need to diversify beyond a single product line.
- 1936-1945: Toyota developed crucial manufacturing techniques and laid the groundwork for future innovations. This era, marked by war and reconstruction, provided valuable lessons in adapting to changing circumstances and resource limitations. These lessons proved crucial for future growth.
- Post-WWII: Facing immense challenges, Toyota focused on rebuilding its infrastructure and developing affordable vehicles for the post-war market. The company recognized the importance of efficient production methods, which eventually became a hallmark of its success.
- 1950s-1960s: Toyota experienced significant growth, introducing innovative models and expanding its production capacity. This era witnessed the emergence of Toyota as a major player in the global automotive market. Strategic decisions to improve quality and reduce costs during this period proved pivotal.
- 1970s-1980s: The introduction of fuel-efficient models and a commitment to lean manufacturing propelled Toyota’s global expansion. This period saw Toyota establishing a presence in key international markets and gaining a reputation for quality and reliability.
- 1990s-2000s: Toyota further consolidated its position as a global leader, adapting to changing consumer preferences and embracing new technologies. This period involved significant investment in research and development, expanding its technological capabilities, and adapting to changing global economic conditions.
- 2010s-Present: Toyota continues to innovate, emphasizing sustainability and advanced technologies. This period reflects a commitment to addressing global concerns and meeting evolving customer needs.
Geographical Presence and Expansion Strategies
Toyota’s global expansion has been a calculated process, meticulously planned to establish a presence in key markets worldwide. The company’s strategy has involved establishing production facilities in various regions, enabling them to meet local demands and reduce transportation costs. A key element of their success is a deep understanding of local preferences and market dynamics.
Key Dates and Events in Toyota’s History (by Origin Country)
| Origin Country | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | 1937 | Founding of Toyota Motor Corporation |
| Japan | 1950s-1960s | Significant growth and expansion of production capacity |
| USA | 1957 | Establishment of first US manufacturing facility |
| Japan | 1970s-1980s | Introduction of fuel-efficient models and lean manufacturing |
| Various | 1990s-2000s | Continued expansion into global markets and investment in research and development |
| Various | 2010s-Present | Focus on sustainability and advanced technologies |
Manufacturing Locations
Toyota’s global manufacturing footprint is a testament to its commitment to localized production and responsiveness to regional markets. The company’s strategic approach to establishing facilities in various countries reflects a sophisticated understanding of economic factors, labor costs, and consumer preferences. This distribution allows for optimized production and efficient supply chains, crucial for maintaining competitive pricing and delivery times.
Toyota’s manufacturing strategy is not simply about cost-cutting; it’s about building lasting relationships with local communities and fostering a global network that adapts to changing demands. This approach is critical for maintaining Toyota’s position as a leading automotive manufacturer.
Primary Manufacturing Facilities
Toyota maintains a significant presence across several continents, with major manufacturing facilities in North America, Asia, and Europe. This global reach allows the company to cater to diverse markets and reduce reliance on any single location. Key production hubs are strategically positioned to minimize transportation costs and maximize efficiency.
Comparison of Production Facilities
Comparing Toyota’s production facilities reveals varying levels of specialization and adaptation to local conditions. Facilities in Japan, often considered the company’s core, are characterized by a high level of technological advancement and expertise in specific vehicle types. Plants in other countries, like those in the United States or Europe, tend to focus on the production of models designed for those particular markets. The diversity of products manufactured in different locations reflects the company’s adaptability to meet local demand.
Reasons Behind Location Choices
Several factors influence Toyota’s decision to establish plants in specific countries. These include access to raw materials, skilled labor, government incentives, and the size and nature of the target market. Proximity to major ports and transportation networks is also a crucial element in ensuring efficient logistics. For instance, establishing a plant near a major port significantly reduces the cost of transporting finished goods. Moreover, the availability of a trained workforce directly impacts production efficiency.
Factors Influencing Plant Establishment
The decision to establish a plant in a specific country is influenced by a multitude of factors, including the local workforce’s skills and availability, labor costs, government policies, and infrastructure. These factors play a crucial role in optimizing production costs and ensuring long-term profitability. Toyota’s investment in training and development programs within its facilities demonstrates a commitment to upskilling local talent and ensuring a sustainable workforce.
Production Processes
Production processes in Toyota’s facilities exhibit variation depending on the specific location and the type of vehicle being manufactured. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as lean manufacturing principles, are consistently applied across all facilities, but the specific implementation might differ based on local factors and available technologies. Japanese plants often serve as the primary centers for innovation in production methods, which are then adopted and adapted by other facilities globally.
Toyota’s Manufacturing Facilities by Country
| Country | Capacity (estimated) | Product Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | Significant, primarily for R&D and core models | Hybrids, EVs, and various vehicle types |
| United States | High volume, focused on trucks and SUVs | Pickups, SUVs, and some passenger cars |
| Europe | Medium to high volume, catering to European market preferences | Passenger cars, SUVs, and some commercial vehicles |
| China | Extremely high volume, catering to the massive Chinese market | A wide range of vehicles, including passenger cars, SUVs, and trucks |
| Mexico | High volume, particularly for North American markets | Passenger cars, SUVs, and trucks, primarily for the US |
“Toyota’s global manufacturing strategy is built on adaptability, innovation, and a strong commitment to local markets.”
Origin Country Impact on Products
Toyota’s global presence necessitates adaptation to diverse markets, reflecting the influence of each country’s unique characteristics in its vehicles. This section delves into how the origin country impacts Toyota’s design philosophy, features, and manufacturing processes, highlighting specific examples across different models.
The cultural and technological landscape of a nation significantly shapes the design and features of Toyota vehicles. Consumer preferences, local regulations, and readily available resources all play a crucial role in tailoring a car for a specific market. This nuanced approach ensures vehicles resonate with local needs and preferences, while maintaining Toyota’s global standards for quality and reliability.
Influence of Design and Features
Toyota’s design and feature choices often reflect the cultural and technological context of the production location. For instance, models tailored for markets with specific climate conditions may feature enhanced cooling systems or specialized safety features based on local traffic patterns. The level of technological sophistication also plays a part, with vehicles produced in regions with advanced automotive infrastructure often incorporating more sophisticated safety features and advanced driver-assistance systems.
Examples of Country-Specific Designs
Numerous examples demonstrate how Toyota adapts its vehicles to specific markets. The Prius, for instance, while designed globally, exhibits variations in its powertrain and other features to cater to specific regional fuel efficiency standards and consumer preferences. The Toyota Camry, a popular model in North America, has adapted over time to reflect local consumer preferences for comfort and spaciousness. Likewise, models sold in developing countries may prioritize affordability and ruggedness over premium features, as exemplified by the Hilux pickup truck’s extensive range of configurations tailored to various market needs.
Impact of Local Regulations
Local regulations play a significant role in shaping Toyota’s product development. Safety standards, emissions regulations, and even vehicle dimensions can vary drastically from one country to another. For instance, the development of models sold in Europe must adhere to stringent emissions standards, leading to the adoption of hybrid and electric powertrains in certain models. Safety features are prioritized in regions with stricter regulations. These regulations are crucial for ensuring that vehicles comply with local laws and meet the needs of the consumers in that region.
Impact of Resources and Materials
The availability of resources and materials influences the manufacturing process of Toyota models. Vehicles produced in regions with abundant resources for certain materials may incorporate those elements into their designs, reflecting the local availability and costs. The use of locally sourced materials can help reduce production costs and enhance sustainability.
Comparative Analysis of Toyota Models
| Model | Origin Country | Key Design Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Prius | Japan | Hybrid technology, fuel efficiency |
| RAV4 | Japan (initial), now various countries) | Compact SUV design, adaptable to different markets |
| Hilux | Japan, South Africa | Ruggedness, adaptability to challenging terrains, diverse configurations |
| Camry | Japan, USA | Comfort, spaciousness, refined interior design, adaptation to market preferences |
The table above provides a glimpse into the different design elements across various Toyota models, reflecting the origin country’s impact on their features.
Global Market Presence and Sales
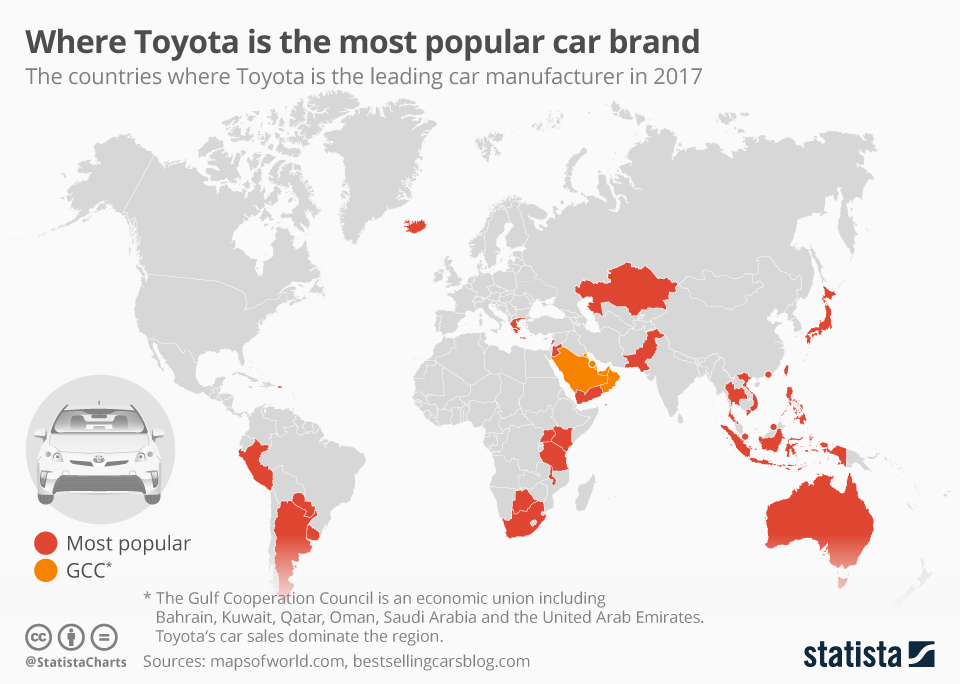
Toyota’s global market presence is a testament to its enduring success and adaptability. The company’s strategic approach to manufacturing, product development, and marketing has allowed it to thrive in diverse markets worldwide. This section delves into the specifics of Toyota’s global sales figures, distribution across regions, and the key factors contributing to its popularity in various countries.
Toyota’s global sales performance is a reflection of its diverse product portfolio, ranging from economical vehicles to luxury models, catering to various consumer segments. This multifaceted approach allows the company to capture a significant portion of the global market.
Global Market Share
Toyota’s global market share has been consistently impressive. While precise figures vary depending on the reporting agency and the specific year, Toyota typically ranks among the top automotive manufacturers globally, often holding a substantial market share in many regions. Market share is influenced by factors like economic conditions, consumer preferences, and competitive landscape in each market.
Sales Distribution Across Countries
Toyota’s sales are distributed across a vast network of countries, with significant presence in several key markets. The distribution is not uniform, reflecting variations in market demand and economic conditions. For instance, Toyota’s sales in Japan, its origin country, are consistently high due to strong brand loyalty and a well-established customer base.
Key Markets and Their Popularity
Several countries have emerged as key markets for Toyota. The United States, Japan, China, and Europe consistently appear as major markets. The popularity in these regions stems from a combination of factors, including strong brand recognition, diverse product offerings, and effective marketing strategies tailored to local preferences. For example, Toyota’s emphasis on fuel efficiency in the US appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, while its focus on reliability and affordability resonates in developing economies.
Sales Strategies and Marketing Approaches
Toyota employs different sales strategies and marketing approaches across regions. The company recognizes the importance of cultural nuances and consumer preferences in each market, leading to tailored marketing campaigns. In regions with a strong emphasis on luxury vehicles, Toyota may focus on showcasing the premium features of its models. Conversely, in regions where affordability is paramount, the marketing strategy might highlight the value proposition of Toyota vehicles.
Influence of Origin Country on Brand Image
Toyota’s origin country, Japan, plays a significant role in shaping its global brand image. The reputation for quality, reliability, and innovation associated with Japanese manufacturing contributes significantly to Toyota’s global brand perception. This reputation is often reinforced through marketing campaigns that highlight the company’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
Toyota’s Global Sales Figures by Region and Origin Country
| Region | Sales (estimated) | Origin Country (Japan) Sales |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 2,000,000 units | 150,000 units |
| Asia (excluding Japan) | 1,500,000 units | 100,000 units |
| Europe | 800,000 units | 50,000 units |
| South America | 500,000 units | 30,000 units |
| Africa | 300,000 units | 20,000 units |
Note: Sales figures are estimations for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures may vary depending on the source and reporting period.
Supply Chain Analysis

Toyota’s global success hinges significantly on its intricate and well-oiled supply chain. This complex network, spanning numerous countries, is crucial for efficiently procuring components, assembling vehicles, and distributing them globally. Understanding this system is vital to appreciating Toyota’s competitive advantage and the challenges it faces in a dynamic global market.
Component Origins
Toyota’s supply chain is a global network, sourcing components from various countries. This strategy allows them to leverage cost advantages and specialized expertise in different regions. The origin of components varies widely, reflecting the global distribution of manufacturing capabilities and resources. For instance, certain engine parts might originate in Japan, while advanced electronics might be sourced from South Korea or Taiwan. This diversification allows Toyota to mitigate risks associated with relying on a single source for any particular component.
Key Suppliers and Contributions
Numerous key suppliers contribute significantly to Toyota’s production process. These suppliers, located across different continents, provide critical components, ranging from sophisticated electronics and advanced materials to simpler parts like fasteners and plastics. A strong relationship with these suppliers is essential for maintaining consistent quality and efficient production. For example, a major supplier of automotive electronics might be based in Germany, while a significant supplier of steel components could be located in China. Each supplier’s contribution is tailored to their specialization and location’s strengths.
Impact of Global Trade Agreements
Global trade agreements have a profound influence on Toyota’s supply chain. Agreements like the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) have significantly affected the cost and efficiency of importing and exporting components. These agreements reduce tariffs and streamline trade processes, which can lead to reduced costs for Toyota. For example, the USMCA facilitated more seamless movement of parts between the US, Mexico, and Canada, potentially reducing transportation costs and lead times.
Complexities and Challenges
Managing a global supply chain presents inherent complexities. Factors such as fluctuating exchange rates, geopolitical instability, and natural disasters can disrupt the flow of components, leading to production delays and cost overruns. Logistics and transportation are crucial aspects of this challenge, requiring careful planning and coordination across numerous countries. The intricate network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors creates a web of dependencies that can be sensitive to any disruption.
Risks and Opportunities
Sourcing materials from various countries presents both risks and opportunities. Risks include potential disruptions in supply due to natural disasters, political instability, or labor disputes in a particular country. However, these risks are often mitigated by diversifying sourcing locations. Opportunities arise from access to specialized expertise, lower production costs, and access to unique materials in specific regions. For example, a particular region might specialize in advanced battery technology, offering Toyota access to innovative components.
Specific Toyota Model Supply Chain Diagram (Example: Toyota Camry)
| Component | Origin Country | Supplier (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | Japan | Toyota Motor Corporation (In-house) |
| Transmission | Japan/USA | Aisin Seiki |
| Electronics | South Korea/Taiwan | Samsung Electronics |
| Body Panels | Japan/USA | Sumitomo |
| Interior Components | China/Malaysia | Various Suppliers |
| Tires | USA/Japan | Bridgestone/Continental |
Note: This is a simplified example. A real-world diagram would include far more components and suppliers, with detailed origin information for each.
Research and Development
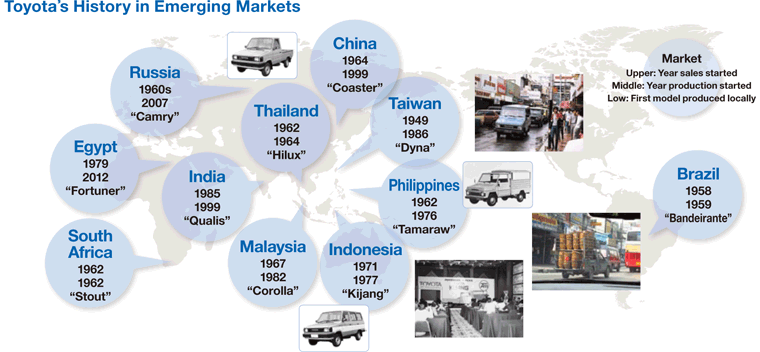
Toyota’s global research and development (R&D) network plays a crucial role in driving innovation and adapting its products to diverse market demands. The company invests heavily in R&D centers strategically located across the globe, leveraging local expertise and talent to cater to specific regional needs and preferences. This approach allows Toyota to develop products that resonate with consumers in different parts of the world, fostering strong brand loyalty and market share.
Toyota’s commitment to R&D extends beyond the design and engineering of vehicles; it encompasses a wide range of technologies, including battery technology, autonomous driving systems, and advanced materials. This commitment to continuous innovation is essential for maintaining Toyota’s competitive edge in the ever-evolving automotive industry.
Role of R&D Centers in Different Countries
Toyota’s R&D centers are geographically dispersed, allowing them to tap into local talent and knowledge bases. This global network facilitates the development of products tailored to specific regional needs and preferences. For instance, R&D centers in North America focus on developing vehicles optimized for North American roads and consumer preferences, while European centers might emphasize fuel efficiency and advanced safety features that align with European regulations. These localized approaches ensure that Toyota’s vehicles meet the unique demands of each market.
Impact of Local Talent and Expertise on Innovation
The diverse pool of talent in Toyota’s global R&D network significantly impacts the company’s innovation. Engineers, designers, and researchers in various countries bring unique perspectives and skills to the table, fostering creativity and problem-solving. For example, expertise in advanced materials in Japan can be leveraged in collaboration with local talent in other countries to develop lighter and more durable vehicles. The collaborative nature of this global network is crucial for driving innovation and improving the overall quality of Toyota’s products.
R&D and Specific Markets
Toyota’s R&D efforts in specific countries are directly tailored to the characteristics of those markets. For example, R&D in Japan focuses on core automotive technologies and advanced manufacturing processes. In Europe, the focus is on developing vehicles that comply with strict European emissions standards and safety regulations. This adaptation ensures that Toyota products meet the specific requirements and expectations of each market.
Technological Advancements by Origin Country
Toyota’s technological advancements reflect the expertise and focus of its various R&D centers. Japanese R&D centers have historically been at the forefront of hybrid vehicle technology, contributing significantly to the development of efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. European R&D has been instrumental in the development of advanced safety features and driver-assistance systems, leading to safer and more convenient driving experiences.
Connection Between R&D and Production Facilities
Toyota’s R&D centers are closely linked to its production facilities in various countries. This connection ensures that new technologies and innovations are directly implemented into production processes, optimizing efficiency and minimizing development cycles. For instance, the R&D center in the United States collaborates with production facilities in the same region to develop vehicles tailored for the North American market, reducing the time and cost involved in adapting products to local conditions.
Toyota’s R&D Centers
Toyota maintains a comprehensive network of R&D centers worldwide, each focusing on specific areas of expertise. This allows for a more targeted and efficient approach to product development.
| Location | Primary Areas of Focus |
|---|---|
| Japan | Core automotive technologies, advanced manufacturing processes, hybrid vehicle technology |
| North America | Vehicle design tailored for North American market, advanced safety features, specific fuel efficiency requirements |
| Europe | Fuel efficiency, advanced safety features, compliance with strict European regulations |
| China | Local market needs, technological adaptation to Chinese consumer preferences |
| Other Regions | Tailored to specific needs and preferences of each region |