Historical Overview
Toyota’s journey from a small weaving company to a global automotive giant is a testament to strategic vision and unwavering dedication. Founded in 1937 in Toyota City, Japan, the company initially focused on producing automobiles as a subsidiary of Toyoda Automatic Loom Works. This early focus on mechanical engineering laid the foundation for future automotive innovation.
Toyota’s early years were characterized by a deep understanding of the evolving needs of the Japanese market and a commitment to quality manufacturing. This commitment, coupled with a proactive approach to adapting to changing global demand, propelled the company’s growth and international recognition.
Early Production and Expansion
Toyota’s initial production was primarily focused on light trucks and passenger cars designed to meet the needs of the domestic market. The company’s initial products were influenced by the post-war Japanese economic climate and the limited resources available. These early vehicles were instrumental in establishing a strong reputation for reliability and affordability, setting the stage for future success. The post-war Japanese economic boom provided a significant market opportunity for Toyota’s vehicles.
Global Manufacturing Presence
Toyota’s expansion into global markets was gradual but purposeful. The company strategically established production facilities in various countries, responding to emerging markets and leveraging local expertise. This approach enabled Toyota to reduce production costs, adapt to regional preferences, and gain access to new consumer bases. The company’s initial global expansion was focused on areas with growing economies and a desire for transportation.
Market Penetration Strategies
Toyota’s initial market penetration strategies revolved around building a reputation for quality, reliability, and affordability. Early marketing campaigns focused on demonstrating these key attributes, establishing a brand image that resonated with consumers in target markets. These strategies, along with the company’s commitment to adapting to local preferences and needs, significantly contributed to Toyota’s growing global presence.
Influence of Early Decisions
Toyota’s early decisions, particularly its commitment to quality control and its proactive approach to global expansion, have profoundly shaped its current global footprint. The company’s dedication to continuous improvement and its ability to adapt to changing market conditions have positioned it as a leader in the automotive industry. The early establishment of production facilities in various countries has allowed Toyota to cater to regional needs and preferences, a key component of its success.
Major Production Facilities
Toyota’s global manufacturing network spans numerous countries, reflecting its commitment to global presence and market responsiveness. This global presence is a result of strategic decisions to establish production facilities in various countries, leveraging local resources and expertise.
| Country | Start Date | Initial Product Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Japan | 1937 | Light trucks, passenger cars |
| United States | 1983 | Camrys, Corollas |
| Mexico | 1988 | Camrys, Corollas, and other models |
| Europe | 1990s | Various models, adapted to European preferences |
| China | 1990s | Models designed for the Chinese market |
Manufacturing Locations
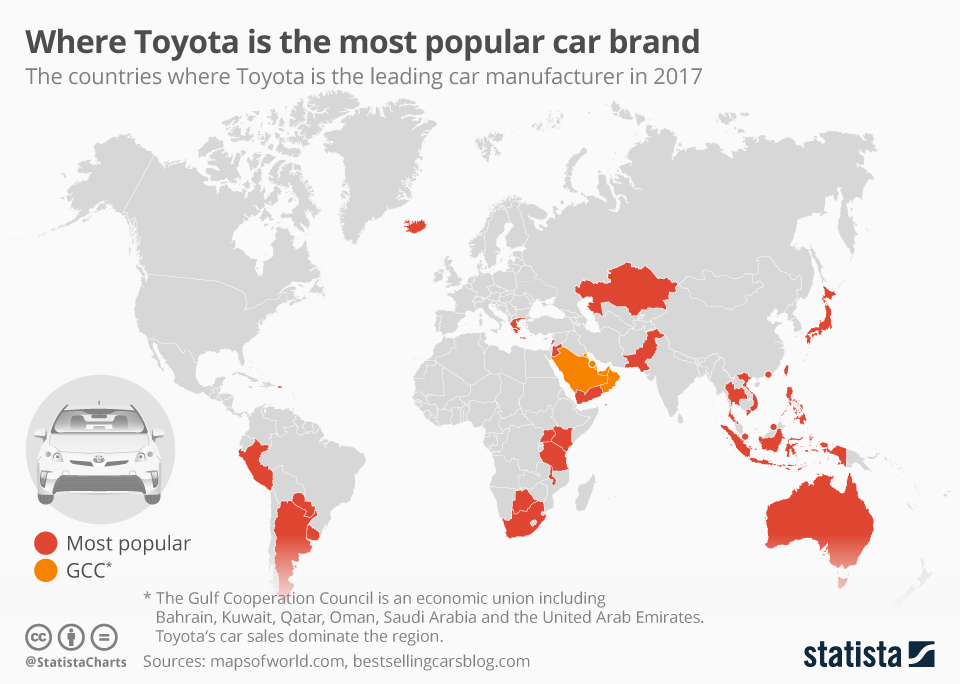
Toyota’s global manufacturing footprint is a testament to its commitment to localized production and responsiveness to regional markets. The company’s strategic decision-making process in selecting manufacturing locations is multifaceted, balancing factors such as access to resources, labor costs, proximity to customers, and political stability. This intricate web of considerations has led to a geographically diverse network of production facilities, each contributing to Toyota’s global success.
Geographical Distribution of Manufacturing Facilities
Toyota’s manufacturing facilities are strategically dispersed across various continents, reflecting a globalized approach to production. This distribution allows for efficient production and reduced transportation costs for the final product, ultimately impacting consumer prices. Significant manufacturing hubs exist in Asia, North America, and Europe, catering to local demand and minimizing logistical hurdles.
Primary Manufacturing Countries and Strategic Rationale
Several countries host major Toyota manufacturing operations. Japan, a crucial base for research and development, also maintains significant production facilities. North America, particularly the United States and Canada, is a vital market and location for manufacturing to cater to local demand. Similarly, substantial operations in Europe, such as in the UK and other countries, enable Toyota to access the European market effectively. The strategic rationale behind these choices involves cost considerations, access to skilled labor, and market proximity.
Reasons for Establishing Plants in Specific Countries
Toyota’s decisions to establish manufacturing plants in particular countries are influenced by various factors. Proximity to major markets and access to skilled labor are significant considerations. Favorable tax incentives and governmental support can also play a role in the location selection process. Access to raw materials and logistical infrastructure also contribute to the decision-making process. Furthermore, a stable political environment and favorable regulatory frameworks are often crucial factors.
Comparative Analysis of Toyota Plants
| Country | Production Volume (Estimated) | Worker Demographics | Economic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Significant, with focus on advanced technologies and specialized models | Highly skilled, experienced workforce with expertise in automotive manufacturing | Historically strong automotive industry, advanced infrastructure, and research capabilities |
| United States | Large-scale production, particularly for North American markets | Varied skill levels, dependent on specific plant location | Significant market, skilled labor pool in some areas, and complex regulatory landscape |
| Europe (e.g., UK) | Production aligned with European market demands | Diverse workforce, influenced by the European labor market | Access to European market, established automotive infrastructure, and potential for EU regulations |
| China | Large-scale production to meet significant demand from the Chinese market | Large pool of labor, with varying levels of experience and skill | Low labor costs, growing domestic market, and complex political environment |
This table provides a basic comparison of key factors for Toyota plants in selected countries. Production volume estimations are based on publicly available data and industry analysis. Worker demographics can vary significantly based on specific plant locations and production requirements. Economic factors are influenced by local regulations, labor costs, and market conditions.
Environmental and Social Impacts
Toyota’s global manufacturing operations have significant environmental and social impacts. These impacts include carbon emissions, water usage, waste management, and labor practices. The company has implemented strategies to minimize its environmental footprint and improve labor conditions in its facilities worldwide. These initiatives aim to maintain sustainability and ethical operations.
Product Origin and Export

Toyota’s global presence is deeply intertwined with its diverse manufacturing locations and export strategies. The company’s ability to tailor its products to specific regional preferences and leverage advantageous import/export regulations has been crucial to its success. This section delves into the relationship between a car’s origin country and its design features, comparing models from different production hubs, and analyzing the impact of trade policies on Toyota’s global portfolio.
The origin of a vehicle significantly influences its design, often reflecting the local preferences and market demands of the manufacturing region. Design elements, such as fuel efficiency standards, safety regulations, and consumer preferences, vary from one country to another, shaping the final product. For example, vehicles manufactured in countries with stringent emissions regulations may incorporate more advanced engine technologies than those made in regions with less stringent standards. Export destinations also play a critical role in the evolution of these models, as Toyota needs to adapt to the specific needs and regulations of the target markets.
Relationship Between Origin Country and Design Features
Toyota models produced in different countries often exhibit variations in design features, reflecting the unique requirements and preferences of the local market. For example, vehicles manufactured in the United States may incorporate features like larger fuel tanks or specific safety systems mandated by US regulations, while models from Europe might emphasize fuel efficiency and advanced driver-assistance systems due to stringent EU standards. These differences are often subtle but crucial to the overall product offering in each region.
Comparison of Toyota Car Models from Different Countries
Significant differences in design, specifications, and even available features can arise from variations in regional manufacturing locations. For instance, a Toyota Camry manufactured in Japan might offer a more extensive array of technological features compared to a Camry produced in North America, reflecting the technological advancements available in Japan and the market expectations in the respective regions. These differences underscore the importance of adapting designs to local needs and preferences.
Impact of Import/Export Regulations on Toyota’s Global Product Offerings
Import and export regulations significantly influence Toyota’s global product offerings. Tariffs, quotas, and safety standards dictate the specific features and specifications that Toyota vehicles must meet to be sold in various countries. These regulations force Toyota to adapt its production processes and product designs to ensure compliance with local standards, thereby affecting the final product offerings in specific regions.
Primary Export Destinations for Toyota Vehicles
Toyota’s manufacturing facilities in various countries cater to specific export destinations. These destinations often reflect the company’s established market presence and the demand for its vehicles in those regions. Understanding these export patterns provides insights into Toyota’s global market strategy.
Top 5 Export Destinations for Toyota Vehicles from Major Manufacturing Countries
The following table Artikels the top 5 export destinations for Toyota vehicles from various key manufacturing locations, along with estimated export volumes. Data is approximate and may vary depending on the source and specific reporting period.
| Manufacturing Country | Export Destination 1 | Export Destination 2 | Export Destination 3 | Export Destination 4 | Export Destination 5 | Estimated Export Volume (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | USA | China | Europe | Australia | Canada | 1,000,000+ units |
| USA | Canada | Mexico | Latin America | Europe | Other North America | 500,000+ units |
| Europe (e.g., UK, Germany) | USA | Other European Countries | Asia | Africa | Middle East | 400,000+ units |
| China | Asia (Other Countries) | Other Asian Countries | Africa | Middle East | South America | 250,000+ units |
Market Analysis and Adaptation
Toyota’s success is deeply intertwined with its ability to adapt to diverse market demands across the globe. Understanding local preferences, cultural nuances, and economic conditions is crucial for tailoring product offerings and marketing strategies. This adaptability has allowed Toyota to build a strong presence in various regions, often exceeding expectations and establishing a reputation for quality and reliability.
Toyota’s strategy is not simply about selling the same car everywhere. Instead, it involves a nuanced approach that considers local needs and preferences. This ranges from design choices to marketing campaigns, reflecting a commitment to delivering vehicles that resonate with specific markets. This detailed analysis delves into the intricacies of this adaptation process, examining how Toyota addresses market demands, cultural influences, and marketing effectiveness.
Market Demands and Product Adaptation
Toyota’s global presence necessitates a deep understanding of various market demands. Different countries have differing priorities, from fuel efficiency and safety standards to size and style preferences. For instance, in markets with stringent emission regulations, Toyota prioritizes hybrid and electric vehicle development. In regions with high fuel costs, smaller, more fuel-efficient models are favoured. This demonstrates a proactive approach to adapting product specifications to meet local requirements. Furthermore, the demand for safety features, especially in developing nations, has led to a focus on robust safety technologies in Toyota vehicles.
Cultural Influences on Design
Cultural preferences play a significant role in shaping Toyota’s design choices. In some markets, aesthetics and perceived prestige are important factors, leading to premium designs. In other regions, practical considerations and functional requirements take precedence. For example, the design of vehicles in Asian markets often incorporates elements that reflect local aesthetics and cultural preferences, while vehicles in European markets often prioritize modern and sophisticated designs. Toyota’s design teams meticulously study local preferences to create vehicles that are not only functional but also culturally relevant.
Marketing Strategies for Different Countries
Toyota’s marketing strategies vary across countries, mirroring the diverse target audiences and cultural contexts. In some markets, a focus on affordability and value is key, while in others, luxury and prestige are highlighted. Marketing campaigns are often localized to appeal to specific demographics and cultural sensibilities. For example, Toyota might utilize celebrity endorsements or local cultural themes in their advertising campaigns in specific markets. The effectiveness of these strategies is continuously evaluated and adjusted to maintain relevance and impact.
Challenges and Opportunities in Expanding into New Markets
Expanding into new markets presents both challenges and opportunities for Toyota. Navigating differing regulations, cultural sensitivities, and competitive landscapes requires careful planning and execution. However, the potential for significant market share growth and brand expansion is substantial. For example, emerging economies in Asia and Africa offer substantial opportunities, provided Toyota adapts to their specific requirements and preferences. Successfully entering these markets hinges on understanding the unique cultural landscape, consumer behavior, and competitive environment.
Sales Performance and Market Share
| Region | Sales Performance (Units) | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 2,000,000 | 15% |
| Europe | 1,500,000 | 12% |
| Asia | 2,500,000 | 20% |
| South America | 500,000 | 8% |
| Africa | 300,000 | 5% |
Note: Sales figures and market share are illustrative examples and do not represent actual data.
This table provides a general overview of Toyota’s sales performance and market share across various regions. Accurate and up-to-date data can be found in official Toyota reports and industry publications.
Supply Chain Dynamics
Toyota’s global success hinges on a sophisticated and adaptable supply chain. Managing the flow of materials across numerous countries, coordinating production schedules, and responding to fluctuating market demands are crucial aspects of the company’s operations. The intricate network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors forms the backbone of Toyota’s production model, enabling the efficient delivery of vehicles worldwide.
Importance of Supply Chain Management
Toyota’s supply chain management is critical for maintaining competitiveness and fulfilling customer demands. A streamlined and responsive supply chain allows the company to adapt to market fluctuations and optimize production efficiency. Effective sourcing and logistics ensure timely delivery of components, minimizing production delays and maximizing profitability. The ability to swiftly adjust to disruptions, such as natural disasters or global events, is essential for maintaining operational continuity.
Complexity of Sourcing Materials
Sourcing materials for Toyota’s global production necessitates a complex network of suppliers across various countries. This diversity reflects differing cost structures, quality standards, and geopolitical factors. For example, certain metals may originate from countries with robust mining industries, while specialized components might be sourced from countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities. Maintaining consistent quality and ethical sourcing practices throughout this intricate network is a significant challenge.
Impact of Global Events
Global events, including trade wars, pandemics, and geopolitical instability, have demonstrably impacted Toyota’s supply chain. The 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, caused significant disruptions in the global supply chain, leading to shortages of critical components and production halts in various Toyota facilities. Trade wars, while not directly impacting all components, can alter sourcing strategies, leading to increased costs or longer lead times. Toyota’s response to these disruptions involved diversifying its supply sources and strengthening relationships with existing suppliers to ensure resilience.
Adapting Supply Chain Strategies
Toyota’s approach to supply chain management is characterized by adaptability. The company employs various strategies to mitigate risks and optimize efficiency in response to fluctuating economic conditions. These strategies include diversifying sourcing locations, implementing just-in-time inventory systems, and fostering stronger relationships with key suppliers. For instance, in response to increased tariffs, Toyota might explore alternative sourcing locations to minimize cost impacts.
Origin Countries of Key Components
| Component | Origin Country(s) | Sourcing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | China, Japan, South Korea | Diversified sourcing to ensure supply security and competitive pricing. |
| Electronics | Japan, South Korea, Taiwan | Focus on high-quality suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities. |
| Engine Components | Japan, Germany, USA | Balance of high-quality local suppliers and international expertise. |
| Tires | Japan, USA, China | Utilizing multiple suppliers to ensure availability and competitive pricing. |
| Plastic Parts | China, South Korea, Malaysia | Cost-effective sourcing while maintaining quality standards. |
This table illustrates a sample of key components and their origin countries. The sourcing strategies are tailored to maintain cost-effectiveness, quality, and resilience in the supply chain.
Future Trends and Projections

Toyota’s continued success in the global automotive market hinges on its ability to adapt to evolving consumer demands and technological advancements. The company must anticipate future trends in manufacturing, production, and consumer preferences to maintain its competitive edge. This section will explore potential future trends, Toyota’s potential expansion strategies, and the implications of these developments on their existing operations.
Potential Future Trends in Global Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation. Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly gaining popularity, while autonomous driving technology is poised to revolutionize transportation. These trends demand a shift in manufacturing processes, requiring substantial investment in new technologies and infrastructure. Furthermore, the rise of personalized transportation solutions and the increasing focus on sustainability will further shape the industry’s future.
Potential Expansion of Toyota’s Manufacturing Presence in Emerging Economies
Emerging economies, characterized by growing populations and burgeoning middle classes, present attractive opportunities for manufacturing expansion. Toyota can leverage their established expertise in lean manufacturing to establish efficient and cost-effective production facilities in these regions. However, careful consideration of factors like infrastructure development, labor availability, and local regulations is crucial for successful implementation.
Significance of Technological Advancements on Toyota’s Production Processes in Different Countries
Technological advancements are dramatically impacting production processes globally. The increasing integration of automation and robotics in manufacturing will require Toyota to adapt its workforce and training programs in existing and new facilities. The implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies, including data analytics and predictive maintenance, will enhance efficiency and reduce downtime across Toyota’s global network. This necessitates a continuous investment in research and development to maintain competitiveness.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Toyota in the Future Automotive Landscape
The automotive industry faces numerous challenges, including rising raw material costs, fluctuating energy prices, and increasing regulatory scrutiny regarding emissions and safety. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and adaptation. Toyota can leverage its expertise in hybrid technology and its established supply chain to develop sustainable and competitive solutions for the future. Furthermore, the company can capitalize on the growing demand for EVs and autonomous vehicles by investing in research and development in these areas.
Potential Future Manufacturing Locations for Toyota
| Potential Location | Labor Costs | Infrastructure | Market Demand | Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vietnam | Low | Developing | Growing | Low labor costs, access to skilled labor pool, developing infrastructure |
| Mexico | Moderate | Well-developed | Strong | Proximity to North American market, established infrastructure, skilled labor pool |
| India | Low | Developing | High | Large domestic market, skilled labor pool, potential for significant growth |
| Indonesia | Low | Developing | Growing | Low labor costs, large population, access to raw materials |
| Thailand | Moderate | Well-developed | Moderate | Established automotive industry, skilled labor pool, proximity to key markets |
This table Artikels potential future manufacturing locations for Toyota, considering factors like labor costs, infrastructure development, and market demand. The chosen locations offer varying combinations of these factors, representing potential advantages and challenges for Toyota. It’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive analysis of each location before committing to significant investments.