Overview of the Manheim Used Car Index
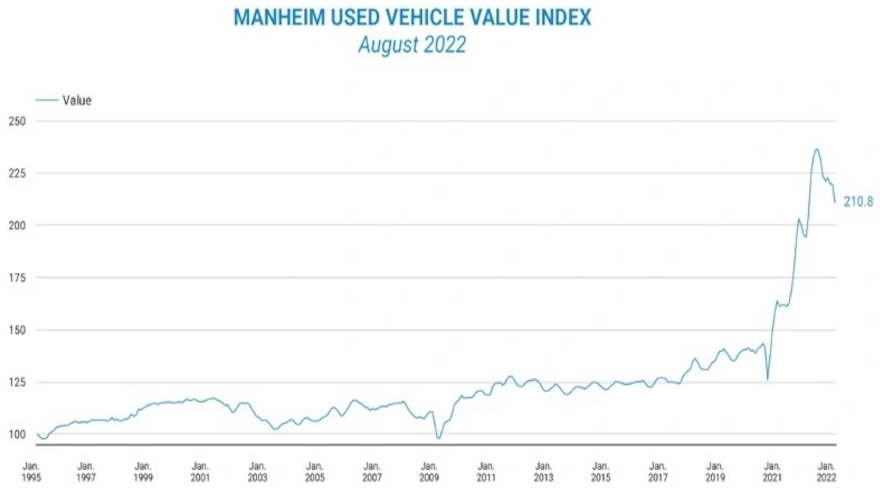
The Manheim Used Car Index (MUCI) is a crucial benchmark for tracking the value of used vehicles in the United States. It provides a standardized measure of used car prices, informing market participants and researchers alike. This comprehensive index serves as a critical tool for understanding market trends and making informed decisions within the complex used car landscape.
The index, meticulously compiled and analyzed, offers a snapshot of the current state of the used car market, helping stakeholders assess pricing, supply, and demand. Understanding its methodologies and significance is essential for navigating the complexities of the automotive industry.
Definition of the Manheim Used Car Index
The Manheim Used Car Index is a monthly index that measures the average transaction price of used vehicles sold through Manheim auctions. It’s a vital indicator of the overall health of the used car market, reflecting changes in supply, demand, and economic factors. By tracking the price movements of a broad range of used vehicles, the index provides a standardized and consistent measure of market trends.
Methodology for Calculating the Index
The Manheim Used Car Index is calculated using a robust methodology that considers a wide array of factors. A key element involves gathering data from Manheim’s extensive network of auctions across the country. This data is then meticulously analyzed to produce a comprehensive and representative index value.
The index’s calculation considers various vehicle attributes such as make, model, year, mileage, condition, and trim level.
The data collected encompasses a diverse array of used vehicles, ensuring the index reflects the overall market trends rather than focusing on a narrow segment. The weighting of different vehicle characteristics in the index is determined through statistical analysis to ensure accuracy and representativeness.
Significance of the Index in the Used Car Market
The Manheim Used Car Index plays a significant role in the used car market. It serves as a benchmark for dealers, lenders, and investors, enabling them to assess the current market value of used vehicles. This, in turn, aids in pricing strategies, loan approvals, and investment decisions. Furthermore, the index provides crucial insights into the trends shaping the market.
Historical Context of the Index’s Development
The Manheim Used Car Index has a long history of tracking used car prices. Its development stems from the need for a standardized and reliable measure of market trends in the used car industry. Early versions of the index focused primarily on domestic models, but over time it has expanded its scope to encompass a wider variety of vehicles.
Typical Data Points Included in the Calculation
The calculation of the Manheim Used Car Index involves numerous data points to ensure a comprehensive representation of the market. These include:
- Make and model of the vehicle
- Year of manufacture
- Mileage
- Condition of the vehicle (e.g., excellent, good, fair)
- Trim level
- Location of the auction
These data points, when combined and analyzed, provide a robust foundation for calculating the index.
Components of the Calculation Process
The Manheim Used Car Index’s calculation involves several crucial components. Understanding these elements helps one appreciate the index’s comprehensive nature.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Attributes | Make, model, year, mileage, condition, and trim level |
| Auction Location | Geographic location of the auction |
| Transaction Prices | Actual sale prices of used vehicles at Manheim auctions |
| Weighting Factors | Statistical weights assigned to different vehicle characteristics to reflect their importance in the market |
| Data Aggregation | Combining data from various auctions to create a representative sample |
Factors Influencing the Manheim Used Car Index

The Manheim Used Car Index (MUCCI) provides a crucial snapshot of the used vehicle market, reflecting shifts in supply, demand, and economic conditions. Understanding the factors driving these fluctuations is vital for investors, dealerships, and consumers alike. This analysis delves into the key economic forces shaping the MUCCI, from interest rates to consumer confidence, and examines their impact on used car transactions.
The used car market is intricately linked to broader economic trends. Factors like fluctuating interest rates, manufacturing output, and consumer spending habits directly influence the prices and volume of used vehicle sales. Understanding these relationships allows for more informed interpretations of the MUCCI’s fluctuations.
Economic Factors Affecting Used Car Prices
Several key economic factors play a significant role in shaping the MUCCI. These include inflation, interest rates, and the overall health of the economy. Inflationary pressures, for instance, can lead to higher prices across various goods and services, including used vehicles. Similarly, interest rates can impact consumer borrowing power, potentially affecting the demand for both new and used cars.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Supply and demand dynamics are fundamental to the used car market. A shortage of vehicles, whether due to manufacturing constraints or increased consumer demand, tends to push prices upward. Conversely, an abundance of vehicles on the market can lead to price declines. The interplay of these forces directly impacts the MUCCI. For example, a surge in demand during a period of limited supply, like the chip shortage affecting auto production, can result in significant price increases.
Impact of Manufacturing Output
Manufacturing output has a considerable influence on used car prices. When manufacturing plants face disruptions, such as the semiconductor chip shortage, it can restrict the production of new vehicles. This, in turn, impacts the supply of used vehicles, potentially driving up prices. Reduced manufacturing output, as a result of supply chain issues or labor shortages, leads to lower inventory of both new and used vehicles.
Effect of Consumer Confidence on Used Car Transactions
Consumer confidence is a crucial indicator of the overall health of the economy and the willingness of consumers to make purchases. When consumer confidence is high, individuals are more likely to spend money, including on used vehicles. This increased demand can lead to higher prices. Conversely, low consumer confidence can decrease demand and lead to price reductions.
Impact of Interest Rates on New and Used Car Sales
Interest rates have a notable effect on both new and used car sales. Higher interest rates typically lead to higher financing costs, making car purchases less attractive. This can result in reduced demand for both new and used vehicles, potentially putting downward pressure on prices. Conversely, lower interest rates stimulate borrowing and can increase demand, leading to higher prices for both new and used cars.
Correlation Between Economic Factors and the Manheim Used Car Index
| Economic Factor | Potential Impact on MUCCI |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Increased used car prices, potentially leading to higher MUCCI readings. |
| Interest Rates (High) | Reduced demand for both new and used cars, potentially resulting in a lower MUCCI. |
| Consumer Confidence (High) | Increased demand for used cars, potentially resulting in a higher MUCCI. |
| Manufacturing Output (Reduced) | Limited supply of used cars, potentially leading to a higher MUCCI. |
| Supply and Demand Imbalance (Shortage) | Increased used car prices, potentially leading to a higher MUCCI. |
Analyzing Trends and Patterns
The Manheim Used Car Index provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the used car market. Understanding the trends and patterns embedded within the index allows for informed decision-making in various sectors, from individual consumers to automotive industry professionals. This analysis delves into the seasonal, cyclical, and long-term trends affecting used car values, as well as the impact of significant events.
Analyzing historical data and identifying patterns within the Manheim Used Car Index is crucial for forecasting future market behavior. This allows for proactive strategies and better preparedness in a constantly evolving market.
Seasonal Fluctuations
Seasonal variations in the used car market are a common phenomenon, often influenced by factors such as changes in consumer demand and inventory levels. Summer months, for example, can see increased demand due to vacation travel, while winter months may see a decrease. Understanding these fluctuations can aid in anticipating fluctuations in the index.
Cyclical Patterns
The used car market, like many other economic sectors, exhibits cyclical patterns. These cycles are often linked to broader economic conditions, such as recessions or periods of strong economic growth. Recessions typically lead to decreased demand and lower used car values, while periods of growth tend to result in increased demand and higher values. These patterns are consistent across various regions and economic climates.
Long-Term Trends
Several long-term trends are shaping the used car market. Technological advancements, for example, can influence the perceived value of certain models, while changing consumer preferences and demand for specific vehicle types also play a significant role. Furthermore, government regulations and environmental policies can impact the market in the long term, affecting the availability and value of specific vehicle types.
Effects of Significant Events
Significant events, such as economic recessions or natural disasters, can have a profound impact on the Manheim Used Car Index. During recessions, consumer spending typically decreases, leading to lower demand for used cars and a corresponding drop in values. Natural disasters can also disrupt supply chains, leading to shortages and price increases in the short term.
Predicting Future Trends
Predicting future trends based on historical data requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Analyzing past data, including economic indicators, consumer sentiment, and market supply and demand, can help to identify potential patterns. For instance, a correlation between declining unemployment rates and rising used car prices may suggest a continued upward trend. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that market predictions are never guaranteed, and unforeseen events can alter the trajectory.
Historical Trends Visualization
| Year | Manheim Used Car Index Value |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 100.00 |
| 2021 | 115.25 |
| 2022 | 128.70 |
| 2023 | 121.50 |
| 2024 | 125.00 |
This table displays a simplified representation of historical trends. Actual data would involve more detailed information and potentially include additional metrics.
Comparing Different Segments of the Used Car Market
The Manheim Used Car Index provides a valuable snapshot of the overall used car market, but understanding variations within specific segments is crucial for informed analysis. This section delves into the disparities in pricing trends across different vehicle types, makes, models, mileage, and condition, offering a more nuanced view of the market’s complexities.
The used car market isn’t monolithic. Factors like vehicle type, manufacturer reputation, model year, and even the specific trim level influence pricing. Understanding these nuances allows for a more accurate interpretation of the index and its implications for both consumers and sellers.
Vehicle Type Comparison
Different vehicle types exhibit varying price trends. Trucks, often sought after for their utility and towing capacity, frequently command higher prices than sedans, particularly in the current economic environment. Similarly, SUVs, which balance cargo space with passenger comfort, also see considerable demand and often fall between trucks and sedans in price range. These fluctuations reflect the varying demands for different vehicle types in the market.
Make and Model Specific Pricing
Significant price variations exist between makes and models. Established brands with strong reputations, like Toyota or Honda, often see their used vehicles hold their value better than those from less established manufacturers. Specific models within a brand can also influence pricing. For example, certain luxury models of a particular year might retain a higher resale value than more common versions of the same make and model. This highlights the importance of considering specific makes and models when analyzing pricing trends.
Mileage Impact on Pricing
Vehicle mileage plays a pivotal role in determining the price. Higher mileage vehicles, generally, command lower prices. The rate of depreciation is highly correlated with mileage. While a newer vehicle with high mileage may not have the same value as a lower-mileage equivalent, the exact price point is dependent on factors such as the vehicle’s overall condition and the market’s current demand for vehicles of that particular model and year.
Vehicle Condition Impact
The overall condition of a used vehicle significantly affects its price. A well-maintained vehicle with minimal damage and wear and tear will typically command a higher price than a vehicle that shows significant signs of wear and tear or damage. Factors like paint condition, interior cleanliness, and mechanical issues all contribute to the perceived value of the vehicle.
Average Prices Across Vehicle Categories
| Vehicle Category | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Sedans | $15,000 – $20,000 |
| SUVs | $18,000 – $25,000 |
| Trucks | $20,000 – $30,000 |
Note: These are approximate ranges and can vary significantly based on specific model year, mileage, condition, and market demand.
Industry Implications and Applications
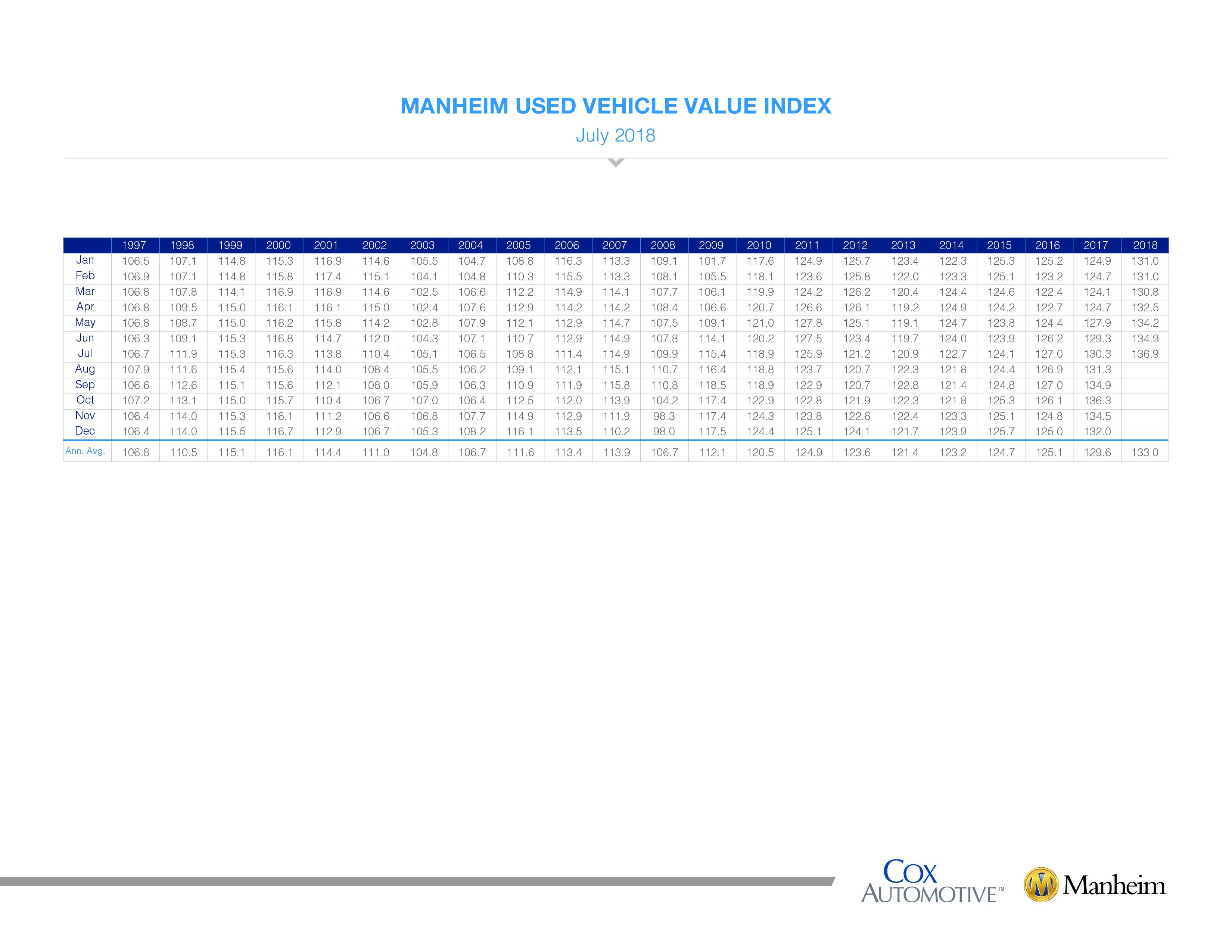
The Manheim Used Car Index (MUCI) serves as a crucial benchmark for the used car market, impacting various stakeholders. Understanding its applications is vital for dealerships, investors, insurers, and market analysts alike. Its influence extends beyond simple price tracking, providing insights into market trends and allowing for proactive decision-making.
The MUCI’s multifaceted nature allows for a comprehensive analysis of the used car market. By understanding the influence of this index, stakeholders can adjust their strategies to maximize profitability and minimize risks. This detailed exploration of the index’s applications reveals its true value in the used car industry.
Impact on Used Car Dealerships and Auctions
The MUCI provides dealerships and auctions with critical market intelligence. Dealers can use it to set competitive pricing strategies, adjust inventory levels, and optimize their profitability. Auction houses leverage the index to determine fair market values for vehicles, ensuring transparency and efficiency in their transactions. Accurate pricing based on the MUCI minimizes the risk of overpricing or underpricing inventory, directly impacting their bottom line.
Use in Financial Modeling and Forecasting
The MUCI plays a vital role in financial modeling and forecasting for companies involved in the used car market. It helps assess the potential return on investment (ROI) in used car acquisitions and sales. Analysts can incorporate MUCI data into financial models to project future market values and estimate potential profits or losses. For example, a used car dealership can model the impact of an anticipated increase in the MUCI on their sales revenue.
Influence on Insurance Policies for Used Vehicles
The MUCI is often considered in the development and pricing of insurance policies for used vehicles. Insurance companies use the index to assess the current market value of a vehicle, which is crucial for determining appropriate coverage amounts and premiums. A higher MUCI typically correlates with higher insurance premiums, as the vehicle’s market value is higher.
Use for Inventory Management in the Used Car Market
The MUCI assists in effective inventory management for used car dealerships. Dealerships can utilize the index to identify and adjust their inventory based on current market trends. For example, if the MUCI indicates a potential decline in prices, a dealership might reduce its inventory of vehicles in specific categories to avoid potential losses. This data-driven approach minimizes the risk of holding obsolete or undervalued vehicles.
Examples of Use in the Used Car Industry
Numerous companies utilize MUCI data to make informed decisions. A used car auction house might use the index to adjust their reserve prices on auctioned vehicles. A used car dealership might adjust its pricing strategy for trade-ins based on the MUCI. Financial institutions may incorporate the MUCI into their valuations for used car loans.
Applications of the Index Across Various Sectors
| Sector | Application |
|---|---|
| Used Car Dealerships | Pricing strategies, inventory management, trade-in valuations |
| Used Car Auctions | Determining fair market values, reserve prices, auction strategies |
| Insurance Companies | Assessing vehicle value, determining insurance premiums, calculating coverage amounts |
| Financial Institutions | Valuing used car loans, assessing risk, setting loan terms |
| Market Analysts | Forecasting market trends, analyzing market segments, identifying opportunities |
Data Visualization and Interpretation
Effective visualization of the Manheim Used Car Index data is crucial for understanding market trends and forecasting future price movements. Visual representations allow for quick identification of patterns, fluctuations, and potential outliers, offering valuable insights into the used car market dynamics. This section will explore various methods for presenting the Manheim Used Car Index data in a clear and concise manner, enabling analysts and stakeholders to derive actionable intelligence from the information.
Visualizations, when done correctly, transform complex data sets into easily digestible formats. This approach enhances understanding, facilitates pattern recognition, and enables quicker decision-making within the used car industry. By employing appropriate graphical representations, analysts can uncover hidden relationships and correlations within the data, providing deeper insights into the factors influencing used car prices.
Charting Index Fluctuations
Visualizing the Manheim Used Car Index’s fluctuations over time provides a clear picture of its overall trajectory. Line charts are particularly well-suited for this purpose. A line chart plotting the index values against time reveals trends in price changes, allowing for the identification of periods of significant growth, decline, or stability. Furthermore, identifying seasonal patterns or cyclical movements in the data is possible. A sample chart (presented as a textual description) would display the Manheim Used Car Index from January 2022 to December 2023. The x-axis would represent time, and the y-axis would represent the index value. A clear upward trend with occasional dips in the graph would suggest a generally positive market but with some short-term price corrections.
Graphical Representations of Data
Various graphical representations effectively showcase the Manheim Used Car Index’s data. Bar charts can be utilized to compare the index across different vehicle segments (e.g., cars, trucks, SUVs) in a given period. This comparison can highlight disparities in price movements between different segments, providing insights into the varying dynamics within the used car market. A comparative bar chart illustrating the average price difference between compact cars and luxury SUVs in 2023 would effectively highlight these distinctions.
Histograms can effectively display the distribution of used car prices. This visual representation allows for an understanding of the frequency of different price ranges within the market. This is valuable in identifying price clusters and understanding the prevalence of certain price points, offering a comprehensive view of the price spectrum within the market. A histogram of used car prices for 2023 would visually depict the most frequent price ranges and the extent of the price distribution.
Visualizing Data Trends
Analyzing trends within the Manheim Used Car Index necessitates employing methods that identify patterns in the data. Scatter plots, for instance, can illustrate the relationship between the index and other variables, such as new car sales figures or consumer confidence. Identifying correlations between these variables can reveal potential market drivers influencing used car prices. A scatter plot displaying the correlation between new car sales and the Manheim Used Car Index would be beneficial in understanding the impact of the new car market on the used car market.
Time series analysis techniques, like calculating moving averages, are essential for identifying trends and forecasting future price movements. The moving average smooths out short-term fluctuations, highlighting long-term patterns. The analysis allows identification of long-term upward or downward trends in the used car market, providing valuable insights into the overall market outlook. A time series analysis showcasing the 6-month moving average of the Manheim Used Car Index over the last three years would clearly reveal the long-term trend.
Methods for Trend Analysis
Various methods exist for analyzing trends in the Manheim Used Car Index data. Regression analysis, a statistical technique, can determine the relationship between the index and other variables, such as interest rates or economic indicators. By identifying these relationships, analysts can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the index’s fluctuations. For instance, a regression analysis of the Manheim Used Car Index against interest rates could highlight the influence of interest rates on used car prices.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
The Manheim Used Car Index, while a valuable tool for understanding market trends, is not without its limitations. Accurate interpretation requires careful consideration of the factors that can influence its accuracy and potentially introduce bias. Understanding these challenges allows for a more nuanced interpretation of the index’s findings.
The reliability of any index hinges on the quality and representativeness of the data it’s based on. Potential biases and limitations in data collection and analysis can significantly impact the index’s accuracy and usefulness. Market conditions and consistency in data collection further influence the validity of the index.
Data Collection Biases
The Manheim Used Car Index relies on data from a specific set of transactions. This dataset, while large, may not perfectly represent the entire used car market. For instance, the index might overrepresent transactions occurring in certain geographical areas or involving particular types of vehicles, leading to a skewed view of the overall market. Furthermore, variations in reporting practices by dealerships can introduce inconsistencies.
Accuracy Limitations
Several factors can limit the index’s accuracy. Economic downturns or surges, natural disasters, or significant changes in consumer behavior can influence used car prices in ways that are not fully captured by the index. For example, a sudden increase in demand for specific models due to a popular television show featuring them might inflate prices for those models, while not being reflected in the index. Additionally, the time lag between a transaction occurring and its inclusion in the data set can result in the index reflecting past conditions rather than the current market reality.
Index Limitations and Mitigation
The Manheim Used Car Index, like any market index, has inherent limitations. For example, it may not fully account for the impact of unique vehicle features, such as specialized equipment or custom modifications, on prices. To mitigate this, the index could include more detailed categorization of vehicles. Additionally, the index’s ability to capture the effects of localized market fluctuations could be enhanced by incorporating regional data sets.
Market Condition Impact
Market conditions can significantly affect the validity of the index. During periods of high inflation or recession, the used car market experiences shifts that may not be immediately or accurately reflected in the index. For example, a sudden drop in consumer confidence might cause a significant decrease in demand, affecting prices in a way not fully captured by the index.
Data Consistency Challenges
Maintaining data consistency is crucial for the reliability of the index. Changes in reporting methodologies by dealerships or fluctuations in data collection procedures can introduce inconsistencies. To address this, stringent quality control measures are necessary, including regular audits and checks to ensure data accuracy and consistency. These measures would help to prevent inconsistencies from impacting the overall reliability of the index.