Overview of the Used Car Market
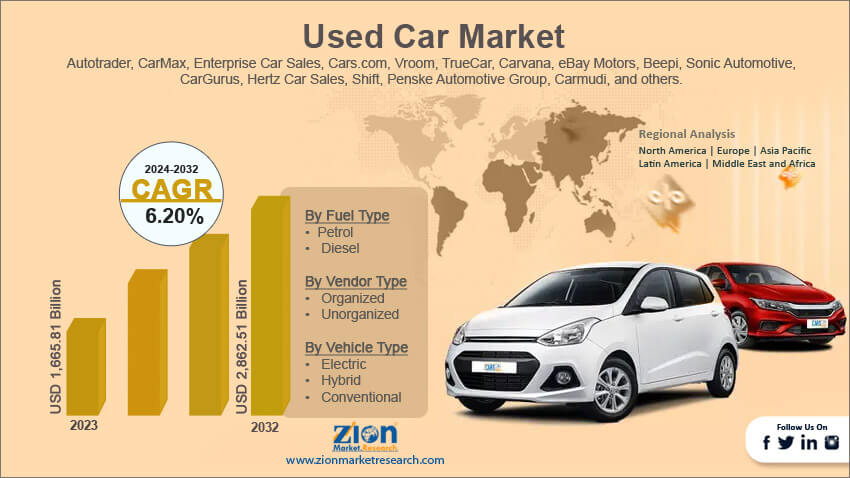
The used car market is a dynamic and complex segment of the automotive industry, significantly influenced by global economic trends, supply chain disruptions, and consumer behavior. Understanding the current state of this market is crucial for both consumers and businesses involved in the buying and selling of used vehicles. The interplay of factors like inflation, interest rates, and even geopolitical events can dramatically shift prices and demand.
The current used car market is characterized by fluctuating prices, a delicate balance between supply and demand, and varying conditions across different regions. Several key factors play a pivotal role in determining the cost of used cars. These factors include the initial manufacturing cost, the vehicle’s condition and mileage, the overall market demand, and the prevailing economic climate. Understanding these factors is vital for consumers to make informed decisions and for businesses to anticipate market shifts.
Key Factors Influencing Used Car Prices
Several factors contribute to the price fluctuations in the used car market. These include manufacturer production rates, the overall health of the economy, and even consumer confidence. The interplay of these forces often results in unpredictable price swings, making it challenging for both buyers and sellers to navigate the market effectively.
- Manufacturer Production Rates: Changes in production capacity from automakers can impact the supply of new vehicles, leading to secondary effects on the used car market. Reduced production often leads to a scarcity of vehicles, pushing up used car prices. Conversely, an increase in production can result in a surplus of used vehicles, leading to price reductions.
- Economic Conditions: The health of the overall economy directly influences the demand for used cars. During periods of economic prosperity, consumers are more likely to purchase vehicles, driving up prices. Recessions or economic downturns can reduce demand, causing prices to fall. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis saw a significant drop in used car prices as consumer spending decreased.
- Consumer Confidence: Consumer confidence plays a critical role in the demand for used vehicles. When consumers feel confident about the future, they are more inclined to purchase cars, driving up prices. Conversely, periods of economic uncertainty or anxiety can decrease demand, leading to price reductions.
Overall Trends in the Used Car Market
Understanding the overall trends in the used car market is crucial for both consumers and businesses to adapt effectively. These trends are often shaped by the interplay of various economic and societal factors. Supply chain issues and fluctuating fuel prices also play a significant role in influencing the market.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between supply and demand remains a key driver in the used car market. Shortages of new vehicles due to supply chain disruptions have historically led to increased prices for used cars. Conversely, an increase in the availability of used vehicles can lead to price decreases. This dynamic is constantly evolving, influenced by various factors including production issues and global events.
- Impact of Macroeconomic Factors: Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and interest rates, have a significant impact on the used car market. Inflationary pressures can erode purchasing power, reducing consumer demand and potentially leading to lower used car prices. Conversely, high-interest rates can impact consumer borrowing capacity, decreasing demand for used cars.
Used Car Prices in Different Regions
Regional variations in used car prices are influenced by a combination of local economic conditions, consumer preferences, and the availability of specific vehicle models.
| Region | Average Used Car Price (USD) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| North America (US) | $25,000 | Strong demand, high manufacturing costs, supply chain issues |
| Western Europe | €20,000 | Varying regulations, diverse vehicle preferences, strong demand for certain models |
| Asia (Japan) | ¥2,500,000 | Strong used car culture, government regulations, and limited new vehicle supply |
| South America (Brazil) | R$ 50,000 | Local economic conditions, fluctuating currency exchange rates, and demand for specific models |
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The used car market’s volatile nature is largely shaped by intricate supply and demand dynamics. Factors ranging from economic conditions to manufacturer production rates influence the availability and desirability of used vehicles. Understanding these forces is crucial for accurately assessing market trends and anticipating future price fluctuations.
Key Factors Driving Supply
The supply of used cars is influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors. Historically high new car sales often translate to a larger pool of used vehicles entering the market. Government incentives for purchasing new cars can indirectly impact the used car market, as they may reduce the perceived need to acquire a used vehicle. Additionally, the overall health of the economy plays a significant role. During periods of economic downturn, consumers may be more likely to hold onto their vehicles longer, thereby decreasing the supply of used cars. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) could eventually influence the supply of used internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Factors Affecting Demand
Consumer preferences and economic conditions are key determinants of used car demand. Interest rates and consumer confidence levels directly impact borrowing costs and purchasing power. High-interest rates often deter consumers from taking out loans for larger purchases, such as cars. The rising popularity of specific car models, often fueled by positive reviews and features, can drive up demand for those models, influencing the prices of used cars.
Comparison of Supply and Demand for Different Car Models
Demand for certain used car models is significantly higher than others. Luxury models, particularly those from prestigious brands, frequently experience higher demand due to their perceived status and features. Likewise, certain models known for reliability and performance, like those of specific manufacturers, often see a strong demand. Supply of these desirable models is often lower than that of less sought-after vehicles. Conversely, the supply of less desirable models, possibly due to lower initial sales, can be greater. This difference in supply and demand significantly impacts the prices of used cars across various models.
Effect of Inventory Levels on Prices
The relationship between inventory levels and used car prices is a direct one. Low inventory levels often result in higher prices, as consumers compete for the limited available options. Conversely, a substantial inventory of used cars can exert downward pressure on prices. This phenomenon is often observed during periods of economic uncertainty or shifts in consumer preferences.
Role of Used Car Dealerships in Influencing Supply and Demand
Used car dealerships play a crucial role in mediating supply and demand in the market. Their inventory management strategies, marketing efforts, and pricing policies can significantly impact the availability and affordability of used vehicles. Dealerships often acquire vehicles through various channels, such as auctions and private sales, influencing the overall supply. Their sales strategies and pricing decisions influence the demand. For example, aggressive marketing campaigns or attractive financing options can increase demand for specific models.
Relationship Between Supply, Demand, and Prices
| Supply | Demand | Prices |
|---|---|---|
| High | Low | Low |
| Low | High | High |
| High | High | Moderate |
| Low | Low | Moderate |
This table illustrates the general relationship between supply, demand, and used car prices. The interaction between these three factors is complex and dynamic, often leading to fluctuations in the market.
Pricing and Valuation
Used car pricing is a complex interplay of factors, significantly influenced by supply and demand dynamics, market trends, and the intrinsic characteristics of each vehicle. Accurate valuation methods are crucial for both buyers and sellers, ensuring fair transactions and preventing overpricing or undervaluation. This section delves into the methodologies used to determine used car value, analyzing the impact of various attributes on pricing, and illustrating how market fluctuations affect the final price.
Determining the worth of a used car is a multifaceted process that considers a range of variables. It’s not simply a matter of deducting depreciation from the original price; a multitude of factors come into play, including market conditions, the vehicle’s condition, mileage, and model year. Different valuation methodologies aim to capture these nuances and provide a comprehensive assessment.
Valuation Methodologies
Various approaches exist for determining the fair market value of a used car. These methods incorporate different criteria and weighting factors, leading to varying results. A common method involves using online resources and databases that compile historical sales data and current market prices. These resources, frequently updated, provide a comparative basis for assessing the worth of a specific car. Another approach is utilizing professional appraisal services, which often involve a physical inspection of the vehicle. This allows for a more detailed evaluation of the car’s condition and potential hidden issues, potentially resulting in a more precise valuation.
Impact of Mileage, Condition, and Model Year
Mileage, vehicle condition, and model year are critical determinants of a used car’s value. Higher mileage often translates to lower prices, reflecting increased wear and tear on the vehicle. The condition of the car, including the presence of damage or repairs, significantly impacts the final price. A well-maintained vehicle in excellent condition will typically command a higher price compared to a car with visible signs of neglect or significant repairs. Similarly, newer model years often command higher prices, reflecting the car’s advanced technology and potentially reduced wear and tear.
Role of Market Trends
Market trends play a pivotal role in used car pricing. Economic downturns or recessions can impact demand and supply, affecting the price of used cars. For example, during a recession, fewer people may be willing to purchase a used car, potentially leading to a decline in prices. Conversely, periods of economic growth can increase demand, leading to price increases. Fluctuations in the price of new cars can also influence used car prices.
Examples of Market Fluctuations
The 2020-2022 period showcased a significant example of how market fluctuations can drastically affect used car prices. The COVID-19 pandemic caused disruptions in the supply chain, leading to a shortage of new vehicles. This scarcity, coupled with high demand, propelled used car prices to record highs. Conversely, when supply chain issues began to ease, and the market returned to equilibrium, used car prices eventually adjusted downward.
Average Price Ranges for Different Car Types
| Car Type | Average Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Compact Cars | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Mid-size Sedans | $15,000 – $25,000 |
| SUVs | $18,000 – $35,000 |
| Luxury Cars | $25,000 – $75,000+ |
Note: These are estimated averages and can vary significantly based on specific models, years, mileage, and condition.
Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
Consumer behavior in the used car market is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for both sellers and buyers, enabling informed decisions and strategic market positioning. Consumers’ preferences, influenced by economic conditions and technological advancements, shape the demand and pricing dynamics within the used car market.
Common Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences in the used car market are driven by a variety of factors. These preferences often align with specific needs and priorities, including price, fuel efficiency, safety features, and vehicle condition. A strong emphasis on reliability and low maintenance costs is a significant driver for many consumers. Furthermore, the aesthetic appeal of the vehicle, such as its design and exterior features, can also play a crucial role in the buying decision.
Impact of Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence significantly impacts used car purchases. During periods of economic uncertainty or recession, consumers may postpone major purchases, including used vehicles. Conversely, when consumer confidence is high, there is often increased demand for used cars, driving up prices. For instance, economic recoveries following recessions often witness a surge in used car sales as consumers feel more secure about their financial situations.
Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Several factors influence consumer decisions in buying used cars. Beyond price and condition, factors such as the vehicle’s mileage, safety ratings, and available features play a significant role. Consumers increasingly prioritize fuel efficiency, considering the rising cost of fuel. The availability of financing options and the overall reliability of the car brand also contribute to the decision-making process. For example, a higher safety rating for a used car model could influence a consumer to prioritize it over other options with similar price points.
Role of Online Platforms
Online platforms have revolutionized the used car market, significantly influencing consumer behavior. Online marketplaces provide extensive information about vehicles, allowing consumers to compare models, features, and prices across different sellers. The ease of researching and finding used cars online has led to more informed purchasing decisions. Online reviews and ratings from previous buyers also play a crucial role in shaping consumer choices.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the used car market include the increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), even in the used market, and the rise of subscription services for vehicles. The demand for used EVs is growing, although availability and pricing may pose challenges. Subscription services offer a flexible and convenient way to access vehicles, particularly for those seeking short-term transportation needs.
Consumer Preferences Across Demographics
Consumer preferences in the used car market vary across different demographics. A table showcasing these preferences is provided below:
| Demographic | Key Preferences | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Millennials | Fuel efficiency, technology features, affordability | Hybrid or electric vehicles, used cars with advanced infotainment systems, and budget-friendly options. |
| Gen Z | Sustainability, technology, connectivity | Electric vehicles, vehicles with advanced driver-assistance systems, and strong connectivity features. |
| Baby Boomers | Reliability, comfort, proven brands | Used cars from established brands known for their durability and comfort features. |
| High-income earners | Luxury features, performance, low mileage | Used luxury vehicles, high-performance models, and vehicles with low mileage. |
| Families | Space, safety, reliability | SUVs, minivans, or used cars with multiple safety features. |
Impact of External Factors
The used car market is not an isolated entity; its performance is heavily influenced by a complex interplay of external factors. These factors can significantly impact supply, demand, pricing, and overall market trends. Understanding these influences is crucial for accurately assessing the market’s current state and predicting future developments.
Influence of New Car Sales
New car sales directly affect the used car market. A robust new car market often leads to a greater supply of used vehicles entering the market, potentially driving down prices. Conversely, a downturn in new car sales can result in a decreased supply of used cars, which could increase prices. This dynamic interplay between new and used car markets is essential to understanding the overall market health. For instance, during periods of economic uncertainty, consumers might delay purchasing new cars, leading to a smaller supply of used vehicles entering the market and subsequently impacting pricing.
Impact of Government Policies
Government policies, such as tax incentives for new car purchases or regulations on emissions standards, can substantially impact the used car market. Policies affecting new car sales can significantly alter the supply of used vehicles available. Regulations on emissions standards, for example, can influence the value and desirability of older vehicles. Government subsidies for electric vehicles, for instance, could impact the used car market by affecting the demand for older, less environmentally friendly models.
Effects of Economic Conditions on Used Car Prices
Economic conditions play a pivotal role in shaping used car prices. During periods of economic prosperity, consumers tend to have more disposable income, leading to higher demand for used cars. Conversely, economic downturns often result in reduced consumer spending and lower demand, impacting used car prices. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, saw a significant drop in used car prices as consumer confidence and purchasing power declined.
Influence of Fuel Prices on Used Car Demand
Fuel prices directly affect the demand for used cars. Higher fuel prices often lead to a greater demand for fuel-efficient vehicles, influencing the prices of used vehicles known for their fuel economy. Conversely, when fuel prices are low, the demand for fuel-efficient vehicles may decrease. This dynamic illustrates the significant correlation between fuel costs and the used car market.
Impact of Insurance Rates on the Used Car Market
Insurance rates affect the used car market in several ways. Higher insurance rates for specific vehicle models or years can impact the demand for those models, as they translate into higher ownership costs. This can lead to a decrease in the value of affected used vehicles. Insurance premiums can also influence the overall pricing of used cars, as consumers factor in the associated cost when considering a purchase. A recent example could be the rising premiums for certain models, leading to a decrease in their demand in the used car market.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Used Car Prices
| Economic Indicator | Potential Impact on Used Car Prices |
|---|---|
| GDP Growth | Positive correlation: Higher GDP growth often leads to higher demand and prices. |
| Unemployment Rate | Negative correlation: Higher unemployment rates typically result in lower demand and prices. |
| Inflation Rate | Positive correlation: Higher inflation often leads to higher used car prices as a result of general price increases. |
| Interest Rates | Positive correlation: Higher interest rates can impact affordability and lead to reduced demand. |
| Consumer Confidence | Positive correlation: High consumer confidence usually results in higher demand and prices. |
This table illustrates a potential correlation between economic indicators and used car prices. It is important to note that these correlations are not always direct or absolute, and other factors can influence the market.
Future Projections
The used car market is poised for significant evolution in the next five years, driven by a complex interplay of technological advancements, economic factors, and evolving consumer preferences. Predicting precise outcomes is challenging, but analyzing current trends and potential catalysts offers valuable insights into likely trajectories.
Understanding the factors shaping the future is crucial for all stakeholders, from individual consumers to dealerships and manufacturers. Forecasting market trends and anticipating potential challenges and opportunities will be essential for navigating the evolving landscape.
Potential Factors Influencing Future Market Trends
Several factors are expected to significantly impact the used car market in the coming years. These include shifts in consumer demand, evolving technological capabilities, and macroeconomic conditions.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences are constantly evolving, impacting the demand for specific vehicle types. Hybrid and electric vehicles are gaining popularity, influencing the resale value of gasoline-powered cars. The rise of subscription services and shared mobility is altering the way people interact with vehicles, which in turn impacts the used car market. The need for practicality and affordability will continue to shape the preferences of many consumers, likely leading to increased demand for certain used models.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology in vehicles is transforming the used car market. Connectivity features, autonomous driving capabilities, and advanced safety systems are increasingly incorporated into new models, potentially influencing the desirability and pricing of used vehicles. The increasing availability of data about vehicle performance and maintenance history could also impact pricing and valuation.
- Economic Conditions: Economic fluctuations can significantly impact consumer spending habits and the used car market. Economic downturns may lead to reduced demand, while periods of economic growth may stimulate the market. Inflation, interest rates, and employment rates will all play a significant role in shaping future trends.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Market Participants
Navigating the evolving used car market presents unique challenges and opportunities for various stakeholders.
- Dealerships and Auction Houses: Dealerships and auction houses must adapt to changing consumer preferences and incorporate digital technologies to remain competitive. Expanding their online presence, offering transparent pricing, and providing comprehensive vehicle information will be crucial. Successfully integrating data analytics into their operations will enable better inventory management and market prediction.
- Consumers: Consumers will need to adapt to the changing technological landscape by researching vehicles effectively and considering the long-term implications of their purchases. Reliable online resources and tools that provide detailed information about used vehicles will become increasingly important. A comprehensive understanding of vehicle history and maintenance records will help consumers make informed decisions.
Illustrative Examples of Possible Future Scenarios
Predicting precise outcomes is challenging, but exploring potential scenarios provides valuable insights.
- Scenario 1: Continued growth in electric vehicle adoption leads to a decline in demand for traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Used gasoline-powered cars may experience a significant price correction. Conversely, the used electric vehicle market will experience growth, and prices could increase.
- Scenario 2: A global economic downturn results in reduced consumer spending, leading to a decline in used car sales. Pricing could experience a significant decrease across various vehicle categories.
Factors Driving the Evolution of Used Car Market Technology
The used car market is undergoing a rapid technological transformation, driven by several key factors.
- Data Analytics: The increasing availability of data about vehicle performance, maintenance history, and market trends allows for more accurate pricing and valuation. This data-driven approach can help improve decision-making for both buyers and sellers.
- Digitalization: The rise of online platforms and digital tools is transforming how consumers search for, evaluate, and purchase used cars. This shift towards digitalization has increased transparency and efficiency.
Projected Price Changes for Different Vehicle Categories
The following table illustrates potential price changes for different vehicle categories over the next five years.
| Vehicle Category | Projected Price Change (2024-2029) |
|---|---|
| Luxury Sedans | +5% to +10% |
| Compact SUVs | +3% to +8% |
| Mid-size Trucks | +2% to +7% |
| Electric Vehicles | +10% to +15% (depending on model) |
Note: These are illustrative projections and may vary based on specific market conditions.
Market Segments

The used car market is a complex ecosystem, encompassing a wide range of buyers and sellers with diverse needs and motivations. Understanding these distinct market segments is crucial for navigating the intricacies of this dynamic market and capitalizing on potential opportunities. Segmenting the market allows for targeted strategies in advertising, pricing, and inventory management, ultimately increasing profitability and customer satisfaction.
The used car market is not monolithic; rather, it’s composed of various segments, each with its own set of characteristics, preferences, and influencing factors. This segmentation allows for a more nuanced approach to understanding the market’s dynamics, enabling businesses to tailor their offerings to meet the specific needs of different buyer groups.
Characteristics of Different Buyer Groups
Different buyer groups within the used car market possess varying needs and preferences, which are shaped by factors like budget, vehicle type, usage requirements, and personal preferences. Understanding these characteristics is critical for tailoring marketing strategies and inventory management to each segment’s unique requirements.
- Budget-Conscious Buyers: These buyers prioritize affordability and are often looking for vehicles within a specific price range. They may compromise on features and vehicle condition to stay within their budget constraints. This segment often includes first-time car buyers, those with limited disposable income, or those needing a reliable, basic transportation option.
- Family Buyers: These buyers prioritize safety, space, and reliability for their families. They often seek vehicles with multiple seating options, ample cargo space, and advanced safety features. Factors like child-safety ratings and fuel efficiency are often high on their list of considerations.
- Commuters: This segment is primarily concerned with fuel efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance costs, given their daily commute. They typically seek vehicles that offer a comfortable and economical ride, with an emphasis on minimizing downtime and costs associated with vehicle ownership. A frequent factor is the vehicle’s proximity to public transportation and parking.
- Luxury Car Enthusiasts: These buyers prioritize prestige, performance, and exclusivity. They often seek vehicles with high-end features, advanced technology, and a unique aesthetic. Factors like brand recognition, horsepower, and interior design play a significant role in their purchasing decisions.
- Investors/Flippers: This segment purchases used cars with the intention of reselling them at a profit. They carefully analyze market trends, vehicle condition, and potential resale value to maximize their return. They often focus on vehicles that are in high demand or have potential for customization.
Factors Influencing Market Segments
Several factors influence the preferences and decisions of different used car buyer segments. These include economic conditions, market trends, vehicle features, and individual needs and preferences.
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns or recessions often lead to a shift in consumer preferences toward more affordable used vehicles. High inflation may also influence purchasing power, driving buyers to more cost-effective options. Interest rates also play a significant role in affordability, particularly for financing.
- Market Trends: Emerging technologies, safety features, and vehicle types influence the demand for particular models. Buyers often adapt to these trends, leading to fluctuations in the demand for certain used vehicles.
- Vehicle Features: Features like safety ratings, fuel efficiency, horsepower, and interior comfort affect the attractiveness of a used vehicle to different segments. Buyers’ priorities for features often align with their needs and lifestyles.
- Individual Needs and Preferences: Personal circumstances, such as family size, commute distance, and personal style, significantly influence the choice of a used vehicle. This can range from needing a vehicle for cargo space to the importance of specific interior design.
Unique Challenges and Opportunities
Each segment presents unique challenges and opportunities for businesses operating in the used car market. Understanding these aspects is critical for effective market positioning and strategy development.
- Addressing the Needs of Budget-Conscious Buyers: Offering competitive pricing, providing clear and transparent information on vehicle condition, and highlighting essential features can effectively attract budget-conscious buyers.
- Meeting the Demands of Family Buyers: Providing a selection of family-friendly vehicles, including those with safety ratings and ample space, can appeal to this segment. Detailed safety information is crucial.
Example of Different Types of Used Car Buyers
- Sarah, a young professional: She’s looking for a reliable, fuel-efficient car for her daily commute, prioritizing a low price point. She may also consider a car with modern technology, such as smartphone integration.
- The Johnson Family: They need a spacious SUV with multiple safety features for their growing family. They prioritize a reliable vehicle capable of accommodating their needs and safety concerns.
Comparison Table of Used Car Segments
| Segment | Characteristics | Needs & Preferences | Influencing Factors | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budget-Conscious | Affordable, basic features | Low price, reliability | Economic conditions, limited budget | Attracting buyers, maintaining profitability | Targeted advertising, competitive pricing |
| Family | Spacious, safe, reliable | Safety, space, comfort | Family size, safety ratings | Maintaining quality control, providing options | Highlighting family-friendly features |
| Commuters | Fuel-efficient, reliable | Economy, low maintenance | Daily commute, fuel prices | Managing inventory, attracting budget-conscious commuters | Focus on fuel efficiency and low maintenance |
| Luxury Enthusiasts | Prestige, performance, unique | Exclusivity, high-end features | Brand recognition, performance | Competitive pricing, maintaining high standards | Highlighting unique features, maintaining prestige |
| Investors/Flippers | Reselling for profit | High resale value, condition | Market trends, vehicle demand | Accurate valuation, maintaining quality | Identifying profitable vehicles, efficient transactions |