Introduction to Used Car Finance Calculators
Used car finance calculators are essential tools for potential buyers to understand the financial implications of purchasing a pre-owned vehicle. These calculators streamline the process of determining the affordability and overall cost of a used car loan, allowing individuals to make informed decisions. By inputting key details, users can quickly estimate monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of the loan.
These calculators are valuable because they allow users to compare different financing options and visualize the long-term financial commitment. This empowers them to budget effectively and avoid overspending on a vehicle. They provide a clear picture of the true cost of the car, helping buyers to negotiate more effectively and potentially save money.
Purpose and Functionality
Used car finance calculators are designed to provide a detailed estimate of the cost of financing a used car. They determine the monthly payments, total interest, and overall loan cost based on user-provided information. This allows potential buyers to plan their budgets and compare different financing options. The calculators are user-friendly, allowing quick and easy access to financial projections.
Input Fields
The accuracy of a used car finance calculator depends heavily on the input data provided. Typical input fields include the purchase price of the used car, the down payment amount, the desired loan term (e.g., 36, 48, or 60 months), and the interest rate. These inputs are crucial for generating accurate and personalized results. Additional fields may include trade-in value, if applicable.
Calculations Involved
The calculators utilize formulas to determine the monthly payment and total loan cost. The most common formula used is the present value of an ordinary annuity formula. This formula accounts for the interest rate, loan term, and principal amount to calculate the periodic payment. The total interest paid is then determined by subtracting the principal from the total amount paid over the loan term. The calculations take into account the specific financing terms, including the interest rate.
Key Components of a Used Car Loan
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase Price | The total cost of the used car. | $15,000 |
| Down Payment | The upfront payment made by the buyer. | $3,000 |
| Loan Amount | The amount borrowed from the lender. | $12,000 |
| Loan Term | The duration of the loan in months. | 60 months |
| Interest Rate | The annual interest rate charged on the loan. | 6% |
| Monthly Payment | The amount paid each month to repay the loan. | $250 |
| Total Interest Paid | The total interest accumulated over the loan term. | $1,800 |
| Total Loan Cost | The sum of the purchase price and total interest paid. | $16,800 |
Types of Used Car Financing Options
Choosing the right financing option for your used car purchase is crucial for managing your budget and securing a favorable deal. Different financing avenues offer varying terms, interest rates, and conditions, impacting the overall cost and affordability of the vehicle. Understanding these options empowers you to make an informed decision aligned with your financial situation and needs.
Comparing Financing Options
Various avenues offer used car financing, each with unique characteristics. A thorough understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of each option is essential for a sound financial strategy.
Bank Loans
Bank loans often provide competitive interest rates, especially for borrowers with established credit histories. They typically offer longer repayment terms, which can ease monthly payments. However, the application process can be more rigorous, requiring comprehensive documentation and credit checks. Banks frequently impose stricter eligibility criteria compared to other financing options. A favorable credit score and a demonstrated ability to repay the loan are crucial for securing approval. Example: A borrower with a strong credit history might secure a lower interest rate and a longer repayment term from a bank compared to a dealership.
Dealership Financing
Dealerships frequently offer in-house financing options, often with streamlined application processes. This can expedite the purchase process. However, interest rates might be higher than those from banks or other lenders. The terms and conditions may also be less flexible. Dealership financing is generally a convenient option, especially for those who are comfortable with the dealership’s terms and conditions.
Personal Loans
Personal loans can be a viable alternative for used car financing, providing flexibility in terms and potentially lower interest rates compared to dealership financing. They often have more straightforward application procedures compared to bank loans, though eligibility criteria still apply. However, personal loans are often unsecured, potentially resulting in higher interest rates for those with less-than-ideal credit profiles. A personal loan might be a suitable option for those seeking more flexibility or those who have difficulty qualifying for a bank loan.
Factors Influencing Financing Choice
Several factors influence the selection of a particular financing method. These include the borrower’s credit score, the amount of the loan, the desired repayment term, and the interest rates offered by different lenders. A meticulous comparison of interest rates, fees, and terms across different lenders is crucial to secure the best possible financing deal.
Interest Rate and Term Comparison
| Financing Source | Average Interest Rate (estimated) | Typical Loan Term (months) |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Loan | 4-8% | 36-60 |
| Dealership Financing | 6-10% | 24-48 |
| Personal Loan | 6-12% | 12-60 |
Note: Interest rates and terms are estimates and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
Impact of Interest Rates and Loan Terms
Understanding the interplay between interest rates and loan terms is crucial for securing the best possible used car financing. Interest rates directly influence the cost of borrowing, while loan terms dictate the duration of the loan. These factors significantly impact both your monthly payments and the total cost of the vehicle.
The relationship between interest rates, loan terms, and your overall car loan cost is a complex one. Higher interest rates result in greater monthly payments and a higher total cost of the loan. Conversely, longer loan terms, while often leading to lower monthly payments, increase the overall cost over the life of the loan due to the accumulated interest. Choosing the right balance between these factors is essential for managing your finances effectively.
Interest Rate Impact on Monthly Payments and Total Loan Costs
Interest rates are the price you pay to borrow money. A higher interest rate translates to a higher monthly payment and a larger total cost of the loan. This is because a higher interest rate means more interest accrues over the life of the loan. For instance, a 5% interest rate will lead to lower monthly payments compared to a 7% interest rate for the same loan amount and term.
Loan Term Impact on Monthly Payments and Total Loan Costs
Loan terms, representing the duration of the loan, also significantly affect monthly payments and total costs. Shorter loan terms typically result in higher monthly payments but lower total loan costs. This is because less time is available for interest to accumulate. Conversely, longer loan terms lead to lower monthly payments but a higher total loan cost due to the compounding interest over a more extended period.
Example of Monthly Payments for Various Interest Rates and Loan Terms
The following table illustrates the impact of different interest rates and loan terms on monthly payments for a $20,000 used car loan.
| Interest Rate (%) | Loan Term (Years) | Monthly Payment | Total Loan Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3 | $673 | $2,019 |
| 5 | 5 | $417 | $2,501 |
| 7 | 3 | $693 | $2,179 |
| 7 | 5 | $447 | $2,735 |
| 9 | 3 | $725 | $2,325 |
| 9 | 5 | $483 | $2,937 |
Relationship Between Interest Rates, Loan Amounts, and Loan Durations
The relationship between these three factors is interconnected. A larger loan amount, coupled with a higher interest rate and longer loan duration, results in a significantly higher total loan cost. This highlights the importance of careful consideration when determining the loan amount, interest rate, and desired loan duration. For example, a larger loan amount at a higher interest rate for a longer duration leads to a substantially greater total interest paid. A significant factor to note is the compounding nature of interest, which accentuates the difference in total costs over longer loan periods.
Understanding the formula behind these calculations allows for informed financial decisions.
Features and Benefits of Advanced Calculators

Advanced used car finance calculators go beyond basic loan calculations, providing a more comprehensive view of the total cost of ownership. These tools empower consumers with detailed insights, enabling more informed decisions and potentially saving money. By incorporating additional factors, advanced calculators help users understand the true financial implications of a used car purchase.
Beyond simply calculating monthly payments, advanced calculators offer a wealth of additional features, significantly impacting the overall cost and decision-making process. These features allow users to personalize their calculations, taking into account various real-world scenarios and potential costs, ultimately leading to a more accurate assessment of the entire transaction.
Trade-In Value Considerations
Understanding the value of a trade-in vehicle is crucial in evaluating the true cost of a new purchase. Advanced calculators can incorporate the trade-in value, allowing users to see how it affects the loan amount and monthly payments. This feature helps users accurately compare the costs of different used car options. For example, if a user has a trade-in, an advanced calculator would subtract the trade-in value from the purchase price of the new vehicle. This reduces the loan amount and potentially lowers monthly payments, which can be significant, especially for those with limited budgets.
Insurance Costs and Taxes
Insurance costs and taxes are significant expenses often overlooked in basic calculations. Advanced calculators incorporate these costs into the overall cost analysis, providing a more realistic picture of the total expenditure. For example, a calculator might include an estimate for insurance premiums based on the vehicle’s make, model, and driver profile, adding to the total cost of ownership. Similarly, calculating the estimated sales tax amount adds further realism.
Detailed Cost Breakdown
Advanced calculators often provide a detailed breakdown of all costs, enabling a comprehensive understanding of each expense associated with the purchase. This breakdown allows users to scrutinize each component of the transaction, enabling them to evaluate the financial implications of different choices. This clarity is particularly helpful in identifying potential hidden costs and understanding how various factors influence the overall expenditure.
Example: Impact on Decision Making
Imagine two used cars with similar features and prices. An advanced calculator, incorporating trade-in value, insurance, and taxes, reveals that one car, despite its lower purchase price, results in a significantly higher overall cost due to a higher insurance premium. This detail might lead a buyer to choose the slightly more expensive car with a lower overall cost of ownership.
Basic vs. Advanced Calculators
| Feature | Basic Calculator | Advanced Calculator |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Amount Calculation | Yes | Yes |
| Monthly Payment Calculation | Yes | Yes |
| Trade-in Value | No | Yes |
| Insurance Costs | No | Yes |
| Sales Tax | No | Yes |
| Detailed Cost Breakdown | No | Yes |
Impact on Overall Cost
The incorporation of these additional features significantly impacts the overall cost of purchasing a used car. By considering trade-in values, insurance, and taxes, advanced calculators provide a more realistic and complete picture of the total expenditure. This comprehensive approach allows for better financial planning and informed decision-making, potentially saving users money in the long run. For instance, factoring in insurance and taxes can lead to a more accurate comparison of used cars, as the total cost of ownership may vary significantly. The example of a trade-in value being subtracted from the purchase price, effectively reducing the loan amount, further illustrates this point.
Understanding Loan Costs and Fees

Navigating the world of used car financing often reveals hidden costs beyond the advertised price. Understanding these loan costs and fees is crucial for making informed decisions and avoiding financial surprises. This section delves into the various expenses associated with used car loans, highlighting potential pitfalls and providing methods for accurate cost comparisons.
Loan agreements for used cars typically include more than just the interest rate. Various fees and charges can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan, making careful scrutiny essential. These costs can sometimes be substantial, and neglecting them can lead to an inflated total loan amount.
Loan Costs and Fees
Understanding the different types of loan costs and fees is vital for comparing financing options. These fees can include origination fees, documentation fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment penalties. Accurate assessment of these factors is key to making a financially sound decision.
- Origination Fees: These upfront charges are often a percentage of the loan amount, and they’re levied by the lender to cover administrative expenses associated with processing the loan. For example, a $5,000 loan with a 2% origination fee would result in a $100 fee.
- Documentation Fees: These fees cover the costs of processing and verifying the necessary documents for the loan application, including title transfer and vehicle inspection. These costs vary widely and are typically a flat fee.
- Prepayment Penalties: Some lenders charge penalties if the loan is paid off early. These penalties can be a percentage of the remaining loan balance or a fixed amount. Understanding these potential penalties is essential to plan for future financial needs.
- Late Payment Penalties: Late payments incur penalties, often a percentage of the missed payment or a fixed amount. These charges can add up quickly if payments are consistently delayed.
Hidden Costs
Hidden costs can significantly affect the total loan amount. These are not always explicitly stated in the initial loan offer.
- Application Fees: Some lenders may charge an application fee for processing the loan application, which can be a percentage of the loan amount or a fixed amount.
- Acquisition Costs: Costs associated with acquiring the vehicle, such as taxes, title transfer fees, and registration fees, can be significant. These costs are often overlooked in a quick price comparison.
- Service Contracts: Service contracts or extended warranties can be offered as part of the financing package. While they may seem beneficial, they can significantly increase the overall loan cost. Evaluating the necessity and cost-effectiveness of such contracts is critical.
Calculating Total Loan Cost
Calculating the total loan cost is essential for comparing different financing offers.
Total Loan Cost = Principal + Interest + Fees + Other Charges
To determine the total loan cost, add the principal amount, total interest paid over the loan term, all applicable fees, and any other associated charges.
Comparing Financing Offers
Comparing financing offers requires a holistic approach, considering the total loan cost, not just the interest rate.
- Detailed Breakdown: Request a detailed breakdown of all fees and charges from each lender to accurately compare offers.
- Total Loan Cost Analysis: Calculate the total cost of each loan offer using the formula above. This allows for a direct comparison based on the true cost of borrowing.
- Long-Term Implications: Consider the long-term implications of each loan offer. A lower initial interest rate might not always translate to a lower total cost if hidden fees are significant.
Using Calculators for Informed Decisions
Used car finance calculators are invaluable tools for making informed purchasing decisions. They empower buyers to compare various financing options, understand the true cost of a loan, and ultimately negotiate a more favorable deal. By meticulously analyzing loan terms, interest rates, and associated fees, buyers can avoid costly pitfalls and make financially sound choices.
Comparing Financing Options
A key benefit of using a used car finance calculator is the ability to compare different financing options side-by-side. This comparison allows buyers to see the impact of varying interest rates, loan terms, and down payments on their monthly payments and total loan costs. This critical analysis helps buyers choose the financing option that best aligns with their budget and financial goals. The calculator facilitates this comparison by displaying a clear and concise summary of each option, making it easier to identify the most suitable choice.
Using the Calculator Effectively: A Step-by-Step Guide
This guide Artikels a systematic approach to using a used car finance calculator effectively:
- Input Accurate Information: Ensure that all input data, including the vehicle price, desired loan amount, down payment, interest rate, and loan term, is precise. Inaccurate data will lead to inaccurate results.
- Explore Different Loan Terms: Experiment with various loan terms to understand how different lengths of repayment affect monthly payments and total interest costs. A longer term often results in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest paid.
- Compare Interest Rates: Input different interest rates to visualize the significant impact on the total cost of the loan. A lower interest rate translates to lower monthly payments and overall interest paid.
- Adjust Down Payment Amounts: Vary the down payment amount to see how it affects monthly payments and the loan amount. A larger down payment typically reduces the loan amount and thus, the interest payable.
- Analyze Loan Costs and Fees: Carefully review all associated fees and charges. These hidden costs can significantly impact the overall financial burden of the loan. Consider loan origination fees, prepayment penalties, or other associated charges.
- Identify the Best Fit: After thorough analysis, identify the financing option that best aligns with your financial situation and goals. Prioritize a low interest rate, manageable monthly payments, and minimal loan costs.
Negotiating a Better Deal
Armed with the insights from the calculator, buyers can confidently negotiate a better deal with the seller. Understanding the true cost of financing empowers buyers to present a more informed counteroffer. For instance, if the calculated monthly payment exceeds the buyer’s budget, they can use this data to negotiate a lower price for the vehicle.
“By understanding the true cost of financing, buyers can effectively counter with more informed offers, potentially saving significant amounts of money.”
A used car finance calculator is a crucial tool for effectively comparing various financing options and negotiating a more favorable deal. By understanding the impact of different loan terms, interest rates, and down payments, buyers can confidently make informed purchasing decisions and secure the best possible financing terms.
Comparison Shopping and Negotiation Strategies
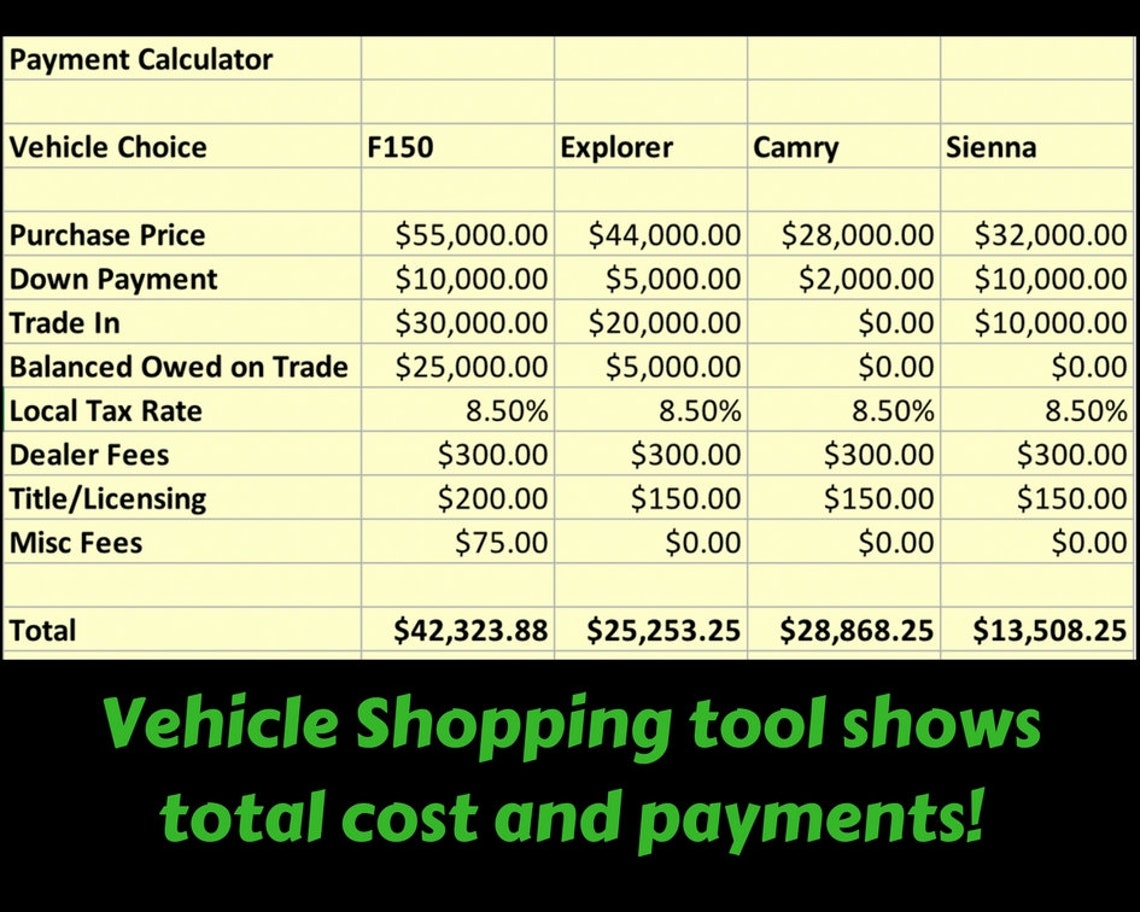
Maximizing your chances of securing the best used car loan involves a proactive approach to comparison shopping and negotiation. Understanding how lenders arrive at interest rates and loan terms allows you to strategically navigate the process and potentially save significant money. This section delves into the importance of comparing quotes and effective negotiation tactics to secure the most favorable financing options.
Comparing quotes from multiple lenders is crucial to obtaining the most competitive interest rates and loan terms. This approach allows you to identify potential discrepancies in pricing and ensures you aren’t settling for less favorable terms. By leveraging comparison tools, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of available options and make informed decisions.
Importance of Comparing Lender Quotes
Thorough comparison shopping is essential for securing the best possible loan terms. Different lenders have varying interest rates, fees, and loan structures. Failing to compare quotes could result in paying significantly more in interest over the life of the loan. Comparing quotes from multiple lenders allows you to identify the best possible deal.
Strategies for Negotiating Better Interest Rates and Terms
Negotiation is a crucial aspect of securing favorable used car financing. Effective negotiation strategies can yield substantial savings. While some lenders are more flexible than others, proactive negotiation can often lead to improved interest rates and terms. Be prepared to articulate your needs and be willing to walk away if terms aren’t satisfactory.
Negotiation Tactics Summary
| Negotiation Tactic | Description | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Approval | Securing pre-approval from a lender before contacting dealerships. | Provides leverage during negotiations, demonstrating a strong financial position. |
| Presenting Alternatives | Highlighting other financing options available to the lender. | Demonstrates awareness of alternative offerings and may encourage the lender to offer more favorable terms. |
| Demonstrating Financial Responsibility | Showing a strong credit history and a stable income. | Increases credibility and persuasiveness during negotiations, potentially leading to lower interest rates. |
| Proposing a Higher Down Payment | Offering a larger down payment than initially planned. | May result in a lower interest rate or better loan terms. |
| Understanding Loan Fees | Thoroughly investigating all loan fees and charges. | Facilitates informed decision-making and enables negotiations regarding unreasonable or excessive fees. |
| Walking Away | Refusing unfavorable terms and exploring other options. | Preserves your negotiating power and encourages the lender to reconsider their offer. |
Factors Influencing Negotiation Outcomes
Several factors influence the success of negotiation strategies. These include the borrower’s credit score, the prevailing interest rates, the amount of the loan, and the lender’s willingness to negotiate. Furthermore, the complexity of the negotiation and the skill of the borrower are also key considerations. A strong credit score often results in more favorable terms, while higher interest rates may necessitate more aggressive negotiation strategies. Understanding these factors empowers you to approach negotiations with a clear strategy.
Illustrative Scenarios and Case Studies
Used car finance calculators are powerful tools for making informed decisions. By exploring various scenarios and case studies, you can better understand how different financing options affect the total cost of ownership and identify potential financial pitfalls. This section provides real-world examples to illustrate the calculator’s practical applications.
Real-World Case Study: Sarah’s Used Car Purchase
Sarah wants to buy a used sedan for $15,000. She has a good credit score and decides to explore financing options with different interest rates and loan terms. Using a finance calculator, she discovers that a 48-month loan at 6% interest will result in a monthly payment of $350, while a 60-month loan at the same interest rate would lower the monthly payment to $280. However, the longer loan term results in a significantly higher total interest paid, nearly $1,000 more over the life of the loan. This demonstrates how loan terms directly impact both monthly payments and the overall cost of the vehicle.
Identifying Potential Financial Pitfalls
Calculators can highlight potential financial pitfalls associated with specific financing choices. For instance, a calculator can reveal that high interest rates dramatically increase the total cost of the loan, making it crucial to shop around for the best rates. A high-interest loan can lead to paying significantly more in interest over the life of the loan, potentially making a seemingly affordable monthly payment far more expensive in the long run.
Different Financing Scenarios and Cost Impact
Different financing scenarios significantly impact the total cost of a used car. A lower interest rate results in a lower total interest paid, reducing the overall cost of the vehicle. Similarly, a shorter loan term lowers total interest payments but increases monthly payments.
- Scenario 1: Lower Interest Rate, Longer Term: This scenario results in lower monthly payments but a higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. For example, a 5-year loan at 3% interest might have a lower monthly payment than a 3-year loan at 5% interest, but the total interest paid will be higher on the 5-year loan.
- Scenario 2: Higher Interest Rate, Shorter Term: This results in higher monthly payments but a lower total interest paid over the life of the loan. For example, a 3-year loan at 8% interest might have a higher monthly payment than a 5-year loan at 6% interest, but the total interest paid will be lower on the 3-year loan.
- Scenario 3: Adding Loan Fees: Loan fees, such as origination fees, can significantly increase the total cost of the loan. Calculators can help estimate the impact of these fees on the overall cost and help determine if the financing option is truly worth the extra cost.
Analyzing Financing Options for Different Situations
A finance calculator empowers you to compare various financing options, tailoring your choice to specific circumstances. For example, if you prioritize lower monthly payments, you can explore longer loan terms. Conversely, if you prioritize lower total interest costs, you can opt for a shorter loan term.
| Scenario | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Months) | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A | 5% | 60 | $280 | $1,050 |
| Scenario B | 7% | 48 | $350 | $700 |
The table above demonstrates how different financing options affect monthly payments and total interest costs. Analyzing these scenarios with a calculator allows you to select the most suitable financing option for your financial situation.
Tips for Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Using a used car finance calculator can significantly aid in making informed purchasing decisions. However, several pitfalls can lead to costly errors if not carefully considered. Understanding these common mistakes and implementing preventive measures will empower you to navigate the process effectively.
Effective use of a finance calculator requires a meticulous approach to data entry and an understanding of the calculator’s limitations. Recognizing potential errors and validating results is crucial for achieving the best possible outcome.
Common Input Errors and Their Impact
Incorrect data input is a frequent source of inaccurate calculations. Mistakes in entering the vehicle price, down payment, loan term, or interest rate can significantly alter the final loan amount, monthly payments, and total interest paid. For instance, a $500 error in the vehicle price could translate to a substantial difference in the loan amount, affecting the overall cost of the vehicle.
- Precise Vehicle Pricing: Ensure the price reflects the actual agreed-upon price, including any associated fees or taxes. A $500 difference in vehicle price, when used in the calculator, will affect the total loan amount. A smaller error might not seem significant but can impact the total cost over the loan term.
- Accurate Interest Rate Input: Using the advertised annual percentage rate (APR) is essential. Different lenders might offer varying rates, so comparing offers is vital. An incorrect interest rate can lead to substantial differences in monthly payments and total interest costs.
- Accurate Down Payment Information: Enter the exact down payment amount to get an accurate loan amount and monthly payment calculation. A slight discrepancy can affect the loan term, impacting the total cost of the vehicle.
- Correct Loan Term Selection: The loan term directly impacts monthly payments and total interest. A shorter loan term may have higher monthly payments but lower total interest, while a longer term has lower monthly payments but higher total interest. Selecting the correct loan term is crucial.
Assessing Calculator Validity
Verifying the calculator’s accuracy is paramount. A trustworthy calculator should align with recognized financial formulas and display transparent calculations.
- Compare Results: Use multiple calculators from different sources to compare results. Significant discrepancies between calculators might signal potential issues.
- Review Formula Transparency: Look for calculators that clearly display the underlying formulas used in the calculations. This transparency allows for a better understanding of how the results are derived.
- Check for Hidden Fees: Be wary of calculators that do not explicitly disclose hidden fees, such as origination fees or prepayment penalties. Scrutinize the fine print to avoid surprises.
- Consider Lender Offers: Compare the calculator’s results with offers from lenders directly. This provides a crucial benchmark for assessing the calculator’s accuracy and helps you avoid inflated costs.
Ensuring Accurate Input Data
Precise data entry is essential for reliable results.
- Double-Check Figures: Double-check all entered figures, especially sensitive data like vehicle price, down payment, and interest rate.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Seek independent verification of pricing and interest rates from various sources to ensure accuracy.
- Review Lender Agreements: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the loan agreement before finalizing the purchase. Any hidden fees or penalties should be understood.
- Use Official Documents: Rely on official documents like purchase agreements, loan agreements, and financial statements to validate the accuracy of the data entered into the calculator.