Overview of Used Car Market Trends

The used car market has undergone significant shifts in recent years, moving away from the historically high prices seen during the pandemic. This change reflects a complex interplay of factors, including shifts in new car sales, supply chain disruptions, and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding these trends is crucial for both consumers and industry professionals navigating the current market.
The recent decline in used car prices is primarily attributable to a combination of factors, including easing supply chain constraints, increased new car production, and a shift in consumer demand. The post-pandemic surge in demand, driven by limited supply and pent-up consumer spending, has subsided, leading to a more balanced market. This equilibrium is reflected in a more stable price environment for used vehicles.
Recent Trends in the Used Car Market
The used car market has seen a noticeable shift from the record highs of 2021 and 2022. Prices are gradually coming down, driven by increased supply and reduced demand. This shift is not uniform across all makes and models, with some segments experiencing steeper declines than others.
Factors Contributing to These Trends
Several factors have contributed to the current used car market trends. Increased new car production has relieved some of the pressure on used car supply. Supply chain disruptions, which were significant contributors to high prices, have begun to subside. Furthermore, consumer demand, fueled by pent-up demand and low-interest rates, has moderated, reducing the pressure on prices.
Relationship Between New Car Sales and Used Car Prices
The relationship between new car sales and used car prices is inverse. When new car production increases, the supply of used cars typically increases, which can put downward pressure on used car prices. Conversely, reduced new car production can lead to decreased used car supply, driving up prices. This relationship is evident in historical data, demonstrating a cyclical pattern in used car pricing.
Historical Data on Used Car Prices
Historical data shows a significant spike in used car prices between 2020 and 2022, reaching unprecedented highs. This was driven by several factors, including the pandemic’s impact on production and supply chains, along with strong consumer demand. The subsequent decline represents a return to more normalized pricing, although fluctuations remain possible.
Impact of Supply and Demand on Used Car Prices
The fundamental economic principles of supply and demand significantly impact used car prices. During periods of high demand and low supply, prices increase. Conversely, periods of ample supply and moderate demand lead to price decreases. The current market is experiencing a shift from high demand and low supply to a more balanced state.
Comparison of Used Car Prices Across Makes and Models Over Time
| Make and Model | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry | $22,000 | $26,000 | $28,000 | $25,500 |
| Ford F-150 | $35,000 | $40,000 | $45,000 | $42,000 |
| Honda Civic | $18,000 | $21,000 | $23,000 | $20,500 |
Note: These are illustrative figures and do not represent precise data. Actual prices vary significantly based on specific trim levels, mileage, and condition.
Factors Influencing Price Drops
The recent decline in used car prices reflects a complex interplay of economic forces. Factors such as fluctuating inflation, interest rate adjustments, and shifts in consumer spending patterns all contribute to the observed downward trend. Understanding these influences is crucial for accurately assessing the current market dynamics and anticipating future price movements.
The used car market is highly sensitive to broader economic conditions. Changes in inflation, interest rates, and consumer confidence ripple through the economy, impacting demand and supply for used vehicles. This dynamic interplay often results in temporary price fluctuations, but the current decline appears to be a consequence of several intertwined factors.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates have a significant impact on the affordability of used cars. High inflation erodes purchasing power, making vehicles more expensive relative to other goods and services. Conversely, rising interest rates increase borrowing costs for consumers, potentially reducing demand for used cars financed through loans. This combination of factors can create a downward pressure on prices. For instance, the recent period of high inflation and rising interest rates has made used cars less attractive to consumers seeking alternative investment opportunities.
Consumer Spending Patterns
Changes in consumer spending patterns play a crucial role in shaping demand for used cars. When consumer confidence wanes or spending shifts towards other sectors, the demand for vehicles can decrease. This reduced demand, coupled with a stable or increasing supply of used cars, often leads to price reductions. For example, the shift towards prioritizing experiences over material possessions in some demographics has likely contributed to a decreased demand for used cars, pushing prices down.
Impact of Economic Indicators
Various economic indicators influence used car values. Unemployment rates, GDP growth, and consumer sentiment all affect consumer purchasing power and willingness to acquire vehicles. Strong economic indicators tend to correlate with increased demand and higher prices, while weaker indicators can depress demand and lead to price reductions. For example, a significant increase in unemployment often corresponds to a decrease in demand for discretionary purchases, such as used vehicles.
Possible Explanations for the Price Drop
Several factors could explain the observed price drop in the used car market. These include:
- Decreased consumer demand due to economic uncertainty.
- Increased supply of used vehicles due to reduced sales in the new car market.
- Adjustments to inflation and interest rates.
- Shift in consumer preferences towards alternative transportation options.
- Increased competition among used car dealers.
The interplay of these factors contributes to the current downward trend.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Used Car Prices
The following table illustrates the potential correlation between specific economic indicators and used car prices:
| Economic Indicator | Potential Impact on Used Car Prices |
|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | Increased inflation typically correlates with higher used car prices, while decreasing inflation may lead to lower prices. |
| Interest Rates | Higher interest rates can reduce demand for financed used cars, leading to price drops. |
| Consumer Confidence | Low consumer confidence often results in decreased demand and lower used car prices. |
| Unemployment Rate | High unemployment rates generally correlate with reduced demand for used cars, leading to price drops. |
| GDP Growth | Strong GDP growth usually indicates higher consumer spending, leading to increased demand and potentially higher used car prices. |
Regional Variations in Price Drops
Used car prices are not falling uniformly across all regions. Significant discrepancies exist between states and countries, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for accurate assessments of the overall market and for individual consumers looking to buy or sell used vehicles.
Regional differences in used car price drops stem from a multitude of interconnected factors. These include variations in local economic conditions, supply and demand dynamics, regulatory frameworks, and even the prevalence of specific vehicle types in different markets. The interplay of these elements often leads to contrasting trends in various geographical locations.
Factors Contributing to Regional Disparities
Local economic conditions significantly impact used car prices. Regions experiencing robust economic growth often see increased demand for vehicles, potentially leading to slower price declines or even price increases. Conversely, regions facing economic downturns might see a faster decline in used car values. Furthermore, specific industries in a region can influence demand. For instance, a region with a significant automotive manufacturing presence may experience unique fluctuations based on industry performance.
State-Specific Price Trends
Different states exhibit varying trends in used car prices. For instance, states with high population density and robust job markets might experience less pronounced price drops compared to states with slower economic growth or a high concentration of specific industries with varying economic conditions. The availability of financing options and consumer spending habits also play a significant role.
Comparative Analysis of Price Trends
A comparative analysis of price trends in different states or countries reveals considerable variation. States with higher average incomes might see less drastic price drops than those with lower average incomes. Furthermore, differences in vehicle registration and inspection procedures can affect the used car market. A thorough analysis must consider local market conditions, including factors such as the availability of financing options and the general spending habits of consumers.
Role of Local Market Conditions
Local market conditions play a pivotal role in determining price fluctuations. These conditions include factors such as local supply and demand imbalances, economic activity, and the availability of alternative transportation options. For instance, a region with a high concentration of rental car services might see less pressure on used car prices than a region with a lower reliance on alternative transportation. Furthermore, the prevalence of specific vehicle types in a region, whether due to historical trends or current demand, also plays a role.
Regional Price Comparison Table
| Region | Average Used Car Price (USD) | Price Drop Percentage (Year-to-Date) | Key Market Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | $30,000 | -5% | High demand, strong economy, limited supply of vehicles. |
| Texas | $28,000 | -8% | High population, strong job market, robust demand. |
| New York | $32,000 | -4% | High population, strong economy, high demand. |
| Ohio | $25,000 | -10% | Lower average income, slower economic growth. |
Note: This table provides illustrative data. Actual prices and trends may vary depending on specific models, years, and other factors.
Impact on Consumers and Dealers

Falling used car prices present a complex picture for both consumers and dealers. While lower prices are generally welcome for buyers, they can create challenges for those in the used car industry. The shifting market dynamics necessitate a careful examination of potential benefits, drawbacks, and long-term implications.
Consumer Benefits
Lower used car prices offer significant advantages for consumers. Increased purchasing power allows for more options within their budget, potentially leading to a greater selection of vehicles. This translates into more choices and better negotiation opportunities, allowing consumers to find vehicles that precisely meet their needs and preferences. Consumers might also be incentivized to explore less common makes or models, which could potentially lead to a more diverse selection of used cars.
Consumer Drawbacks
Despite the advantages, potential drawbacks exist. Reduced prices might not always translate into substantial savings, especially if consumers are not particularly discerning. Furthermore, the fluctuating nature of the market could lead to uncertainty in terms of future price trends, potentially causing hesitancy among buyers. Some may worry about the long-term value retention of vehicles purchased at significantly lower prices, particularly if they are older models.
Dealer Impacts
The used car market downturn presents challenges for dealerships. Lower prices might lead to reduced profit margins, potentially impacting their ability to maintain inventory levels and overall profitability. Inventory management becomes crucial as dealerships face pressure to adapt to the new market realities. Dealers may need to implement strategies to maintain customer loyalty and attract buyers, possibly through innovative sales techniques or enhanced customer service initiatives.
Potential for Increased Demand
The decrease in used car prices can stimulate demand. More buyers might enter the market, drawn by the attractive affordability. This increased activity could lead to higher sales volume, but dealerships need to carefully manage inventory and pricing strategies to capitalize on this potential. Increased demand might also lead to more competition among dealers, pushing them to enhance their service offerings.
Implications for Used Car Financing
Lower prices might affect the terms and conditions of used car financing. Lenders may adjust their interest rates or loan terms in response to the market fluctuations. This could impact the overall affordability of used cars for some consumers. Dealers need to adapt to potential changes in financing options to ensure continued sales.
Effect on Used Car Auctions
Used car auctions are significantly affected by price drops. Lower bids and reduced sales volume are common occurrences. Auction houses need to adjust their strategies to attract buyers and maintain profitability. This necessitates more flexible pricing policies and potentially new auction formats to accommodate the changed market landscape.
Summary Table: Pros and Cons
| Consumers | Dealers | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Increased purchasing power, more options, potentially better negotiation power. | Increased sales volume, potential for adapting to a changing market. |
| Cons | Uncertainty about future prices, potential for less significant savings, potential for lower value retention. | Reduced profit margins, challenges in inventory management, pressure to adapt sales strategies. |
Future Predictions and Potential Scenarios
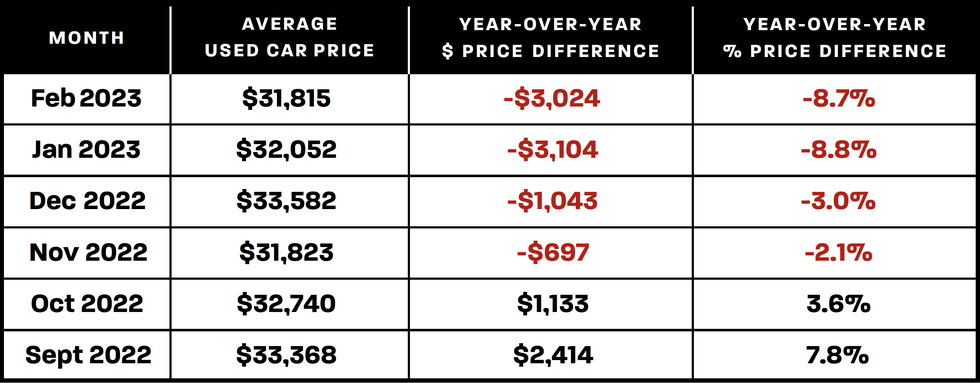
The used car market is experiencing a dynamic shift, and forecasting its future trajectory requires careful consideration of intertwined economic factors. While recent price drops are evident, the path forward remains uncertain, with various potential scenarios shaping the market’s evolution. Understanding these scenarios is crucial for both consumers and dealers as they navigate the evolving landscape.
The future of used car prices hinges on a multitude of economic indicators, including inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic growth. These factors influence consumer spending and demand, directly impacting the supply and demand equilibrium in the market. Moreover, the ongoing semiconductor chip shortage and its potential impact on new car production, as well as broader industry supply chain disruptions, will play a role in influencing the used car market.
Potential Scenarios for Future Used Car Prices
The used car market’s future trajectory will be influenced by a complex interplay of economic and industry-specific factors. Several potential scenarios Artikel possible price movements.
- Sustained Price Drops: Continued economic headwinds, combined with a surplus of used vehicles on the market, could lead to sustained price reductions. This scenario assumes a prolonged period of reduced consumer demand, coupled with a relatively stable supply of used cars. Examples of sustained economic downturns impacting auto markets exist in previous decades. For instance, the 2008 recession led to significant decreases in new and used car prices as consumer confidence waned.
- Price Stabilization: A scenario where prices stabilize after the current period of decline. This suggests that the market has reached a new equilibrium point, with demand and supply factors balancing out. Factors like increased consumer confidence and a leveling off of inflation could contribute to this outcome. This stabilization could occur if the current inventory of used vehicles begins to decrease, potentially due to increased demand or decreased supply.
- Further Price Declines: A further drop in used car prices could result from a combination of economic pressures and an ongoing supply of vehicles. This could occur if inflation remains high and consumer confidence continues to be negatively impacted. This scenario would necessitate a deeper economic downturn and a continued surplus of used vehicles.
Impact on Specific Vehicle Types
The impact of future price movements will likely vary across different vehicle types. Factors such as vehicle age, model year, and fuel efficiency can influence price sensitivity.
- Luxury Vehicles: Luxury vehicles might experience a more moderate price drop compared to mass-market models. This is because the demand for luxury vehicles is often less sensitive to price fluctuations, and supply might not be as affected by market downturns as mass-market vehicles. This is especially true if luxury vehicles are perceived as having more stable and less affected supply chains.
- Fuel-Efficient Vehicles: Fuel-efficient vehicles might see a slower rate of price decline. The increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability and the desire for fuel economy could result in sustained demand and, subsequently, higher prices compared to other models.
- Older Models: Older models might be more susceptible to significant price drops. The availability of newer vehicles and the reduced demand for older models could lead to a greater price disparity compared to newer vehicles.
Potential Future Scenarios Table
| Scenario | Description | Impact on Prices | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustained Price Drops | Prolonged economic downturn, high inventory | Significant and sustained decrease | Potential for significant savings, but uncertainty |
| Price Stabilization | Market equilibrium reached | Prices stabilize at a new level | Predictable pricing, but potentially lower savings |
| Further Price Declines | Deepening economic crisis, surplus inventory | Further decrease in prices | Significant savings but high uncertainty |
Visual Representation of Data
Visualizing data is crucial for understanding complex trends and patterns in the used car market. Graphs, charts, and infographics provide a clear and concise summary of historical price movements, regional variations, and the impact of economic factors. This allows for easier comprehension and identification of key insights that might otherwise be missed in raw data.
Historical Trend of Used Car Prices
A line graph displaying the historical trend of used car prices over time is essential. The x-axis would represent the time period (e.g., years), and the y-axis would show the average price of a specific vehicle type (e.g., a 2015 Honda Civic). This visualization would clearly show the upward and downward trends in prices, allowing for the identification of peaks and troughs in the market. A trend line superimposed on the data points would further highlight the overall direction of the price movement.
Comparison of Prices Across Vehicle Categories
A bar chart comparing prices across different vehicle categories is helpful. The x-axis would represent the vehicle category (e.g., compact cars, SUVs, trucks), and the y-axis would display the average price for each category. Color-coding the bars for each category would enhance readability and allow for quick visual comparisons. This chart would reveal which vehicle categories are experiencing the most significant price drops.
Regional Price Variations
A geographically-based heatmap is a suitable visualization for regional price variations. The map would color-code different regions based on the average used car prices in each area. Areas with significantly higher or lower prices than the national average would stand out, providing insights into regional differences in supply and demand. The map can further highlight differences in price drops across various regions, indicating that regional factors like local economic conditions and availability of used cars are important.
Impact of Economic Indicators
A bar graph showcasing the impact of economic indicators on used car prices is beneficial. The x-axis would list key economic indicators (e.g., unemployment rate, inflation rate, interest rates), and the y-axis would represent the percentage change in used car prices correlated with those indicators. The graph would show the relationship between economic indicators and used car prices, allowing for a visual correlation between economic conditions and market fluctuations. For instance, a decrease in consumer confidence might correspond with a decline in used car prices.
Summary of Key Findings
An infographic summarizing the key findings would consolidate all the information into a visually appealing and easily digestible format. It should highlight the major trends observed in used car prices, including historical price movements, regional variations, and the impact of economic indicators. The infographic should include key statistics, such as average price drops across various vehicle types and regions. This comprehensive infographic would serve as a readily accessible visual summary of the current used car market.