Understanding Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Used car loans, while offering a convenient way to acquire a pre-owned vehicle, come with varying interest rates. Understanding the factors influencing these rates is crucial for securing the most favorable terms. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of used car loan interest rates, from creditworthiness to loan terms and lender comparisons.
Interest rates for used car loans are not fixed but rather depend on a complex interplay of various factors. These factors are carefully evaluated by lenders to determine the risk associated with each loan application. By understanding these elements, borrowers can gain a clearer picture of the factors impacting their loan approval and the interest rate they’ll be offered.
Factors Influencing Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Several key factors significantly impact the interest rate a borrower receives for a used car loan. These factors are meticulously considered by lenders to assess the potential risk associated with each loan application.
- Creditworthiness: A borrower’s credit history, including credit score, payment history, and outstanding debts, plays a pivotal role in determining the interest rate. Lenders use this information to assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate, reflecting a lower risk for the lender. Conversely, a lower credit score suggests a higher risk, resulting in a higher interest rate.
- Loan Amount: The amount borrowed for the vehicle affects the interest rate. Larger loan amounts typically result in higher interest rates due to the increased financial risk for the lender. The amount of the loan relative to the vehicle’s appraised value is also considered.
- Loan Term: The duration of the loan, often expressed in months or years, influences the interest rate. Shorter loan terms generally lead to lower monthly payments but potentially higher interest rates. Longer loan terms result in lower monthly payments but may carry higher interest rates over the life of the loan.
- Vehicle Condition and Value: The condition and estimated value of the used car are critical factors. Lenders evaluate the vehicle’s condition to determine its resale value and potential for repossession in case of default. A vehicle in excellent condition with a higher market value typically qualifies for a lower interest rate.
- Market Interest Rates: Overall market interest rates play a significant role. When market interest rates rise, used car loan interest rates tend to follow suit. Conversely, falling market rates often lead to lower interest rates for used car loans.
Creditworthiness and Interest Rates
Creditworthiness is paramount in securing a favorable interest rate for a used car loan. Lenders meticulously evaluate a borrower’s credit history to assess their ability to repay the loan.
- Credit Score: A higher credit score demonstrates a responsible repayment history, reducing the risk for the lender and often leading to a lower interest rate. A credit score of 700 or higher is often considered a good score.
- Payment History: Consistent on-time payments on existing debts indicate a responsible financial management style. Missed or late payments increase the risk for the lender and often result in higher interest rates.
- Outstanding Debts: The total amount of outstanding debts relative to income is a critical factor. A higher ratio of debt to income increases the risk for the lender and can lead to higher interest rates.
Types of Used Car Loan Programs and Interest Rates
Various loan programs cater to diverse borrower needs and credit profiles. The interest rates associated with these programs vary depending on the terms and conditions.
- Subprime Loans: These loans are designed for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit scores. Interest rates for subprime loans are typically higher than for prime loans, reflecting the increased risk for the lender.
- Secured Loans: These loans are secured by the vehicle itself. In case of default, the lender can repossess the vehicle to recover the outstanding loan amount. Secured loans often have lower interest rates than unsecured loans, as the vehicle acts as collateral.
- Unsecured Loans: These loans do not require collateral. Interest rates for unsecured loans are generally higher than for secured loans due to the increased risk for the lender.
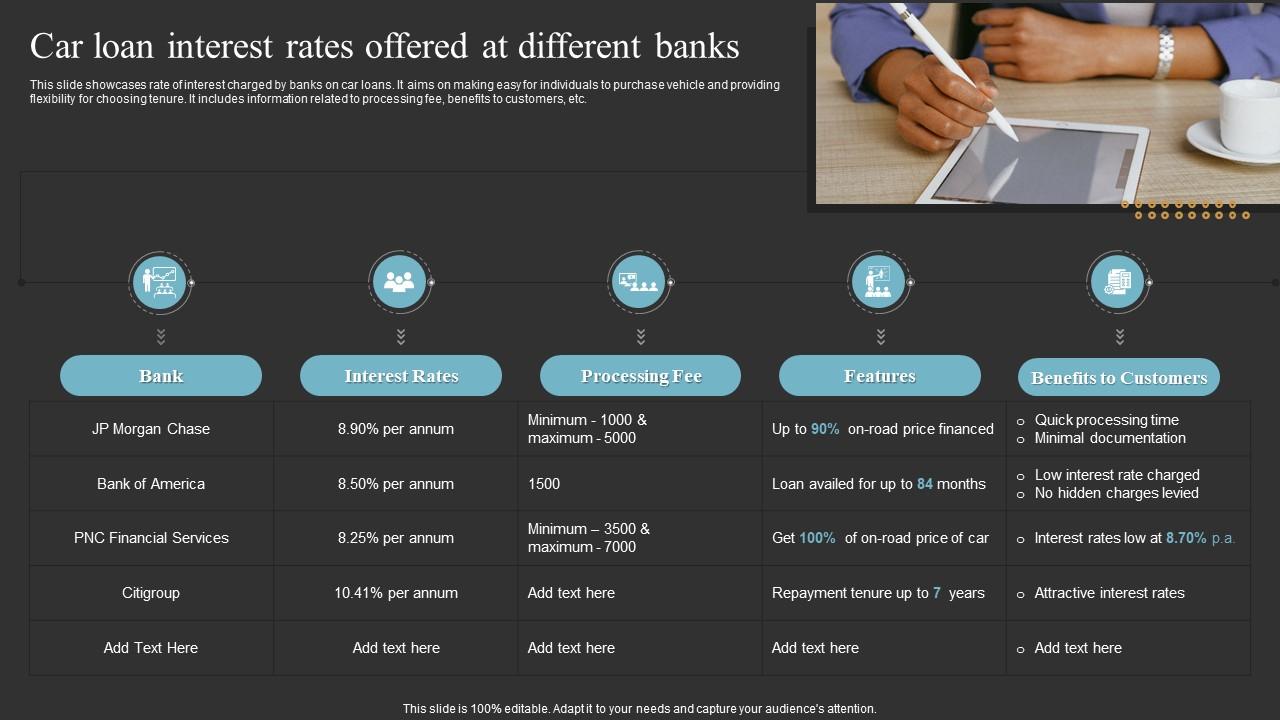
Comparison of Interest Rates Across Financial Institutions
Interest rates for used car loans vary significantly across different financial institutions. Borrowers should compare rates from multiple lenders to secure the most favorable terms.
| Lender Name | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Months) | Credit Score Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 6.5% | 60 | 680+ |
| Credit Union B | 7.0% | 72 | 660+ |
| Online Lender C | 7.5% | 60 | 650+ |
Note: These are example rates and may not reflect current market conditions. Actual rates will vary based on individual borrower profiles and lender policies.
Securing a Used Car Loan
Securing a used car loan involves several steps. Thorough preparation and understanding of the loan process can help borrowers secure the best possible terms.
- Gather Documents: Compile necessary documents such as identification, proof of income, and credit history.
- Pre-Approval: Obtain pre-approval from multiple lenders to compare interest rates and terms.
- Negotiation: Negotiate terms and conditions with the lender to secure the most favorable interest rate and loan terms.
Interest Rate Trends and Forecasts
Used car loan interest rates are constantly evolving, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors and market dynamics. Understanding these trends is crucial for both borrowers and lenders to make informed decisions. Recent fluctuations highlight the importance of staying updated on these trends to navigate the lending landscape effectively.
Recent Trends in Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Interest rates for used car loans have exhibited volatility in recent years, responding to shifts in overall economic conditions. This variability has made it challenging to predict precise future rates. Factors like inflation, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, and the general state of the economy all play significant roles. Data on historical patterns can offer valuable insights into potential future movements, but past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results.
Historical Patterns of Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Analyzing historical data provides context for understanding current trends. Interest rates for used car loans have shown a cyclical pattern, rising and falling in response to economic cycles. Periods of economic growth often correlate with higher interest rates, while recessions typically lead to lower rates. However, the relationship is not always straightforward and other factors like supply and demand for used cars also play a role.
Expert Opinions on the Predicted Future Direction of Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Experts offer varying predictions for the future direction of used car loan interest rates. Some economists anticipate a continued period of elevated rates, influenced by persistent inflation pressures. Others believe that rates may moderate as the economy adjusts to current conditions. It’s important to remember that economic forecasts are not always accurate and various scenarios could influence the outcome. For instance, a significant shift in consumer spending could affect demand and consequently, interest rates.
Comparison of Interest Rate Trends for Used Car Loans with Other Types of Auto Loans
Used car loan interest rates often differ from those for new car loans. New car loans typically have lower rates due to the higher perceived value and reduced risk associated with a newer vehicle. However, the difference can vary based on creditworthiness and specific lender policies. The interest rate structures for used car loans and other types of auto loans can be affected by factors like vehicle condition, loan term, and borrower credit score.
Impact of Economic Factors on Used Car Loan Interest Rates
Economic factors significantly impact used car loan interest rates. Inflation, for example, can lead to higher rates as lenders adjust to rising costs. A recessionary period can result in lower rates, as lenders compete for borrowers in a slower economy. The interplay of these factors influences the overall borrowing environment. These factors, coupled with the fluctuating demand and supply of used cars, contribute to the volatility in interest rates.
Table: Historical Trend of Used Car Loan Interest Rates (2018-2023)
| Year | Average Interest Rate | Economic Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 5.5% | Economic Expansion |
| 2019 | 5.2% | Economic Expansion |
| 2020 | 4.8% | Economic Recession/COVID-19 Pandemic |
| 2021 | 6.2% | Economic Recovery/Inflation |
| 2022 | 7.1% | High Inflation/Rising Interest Rates |
| 2023 | 6.8% | Inflation Cooling/Interest Rate Stabilization |
Shopping for the Best Used Car Loan

Securing the most favorable used car loan hinges on meticulous comparison and negotiation. Understanding the prevailing interest rate environment and potential lender variations is crucial. This guide details the steps to navigate the loan application process effectively, maximizing your chances of securing a competitive interest rate and favorable terms.
Comparing Used Car Loan Offers
Thorough comparison is paramount to securing the most suitable used car loan. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, loan terms, and fees. A systematic approach to comparing these offers is essential.
To effectively compare used car loan offers, gather quotes from multiple lenders. This process involves contacting several banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Be prepared to provide necessary information, including your credit score, income, and the details of the vehicle you’re purchasing.
Key Aspects to Consider
Several key aspects influence the overall attractiveness of a used car loan. These factors encompass interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate is a crucial determinant of the overall cost of the loan. A lower interest rate translates to lower monthly payments and reduced total interest paid over the life of the loan. For instance, a 5% interest rate will result in significantly lower monthly payments compared to a 10% interest rate for the same loan amount and term.
- Loan Term: The loan term dictates the duration over which you repay the loan. A shorter term typically means higher monthly payments but lower total interest charges. Conversely, a longer term leads to lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs. For example, a 36-month loan will have higher monthly payments than a 60-month loan for the same amount.
- Fees: Scrutinize all associated fees, including origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment penalties. These fees can significantly impact the overall cost of the loan. Always request a comprehensive breakdown of all fees.
Questions to Ask Lenders
Thorough questioning of lenders ensures you fully grasp the loan terms and conditions.
- Interest Rate Details: Inquire about the specific interest rate applicable to your situation, any potential adjustments, and the factors influencing the rate.
- Loan Term Options: Ask about available loan terms and the associated monthly payment variations for different terms. For instance, a 60-month loan might have lower monthly payments than a 48-month loan but a higher overall interest cost.
- Fees and Charges: Request a detailed breakdown of all fees and charges, including origination fees, processing fees, and prepayment penalties.
- Additional Costs: Inquire about any other potential costs, such as appraisal fees or documentation fees, that might be associated with the loan.
Using Online Tools
Online tools offer a convenient means to compare used car loan interest rates from various lenders.
Numerous websites provide loan comparison tools. These tools typically allow you to input loan details and instantly receive personalized quotes from multiple lenders. These tools help you quickly identify the best loan options available. For example, Bankrate.com or NerdWallet.com provide such comparative analysis features.
Reading the Fine Print
Carefully reviewing the loan agreement’s fine print is crucial.
Understanding the complete loan agreement ensures awareness of all terms, conditions, and potential risks. Pay close attention to details such as prepayment penalties, late payment fees, and any other stipulations that might affect the loan’s cost or repayment schedule. These details often dictate the overall cost and conditions of the loan. For instance, hidden fees or clauses can significantly impact the final loan cost.
Comparing Loan Options
A table summarizing key features facilitates quick comparison.
| Lender | Interest Rate | Loan Term (months) | Fees | Other Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 5.5% | 60 | $150 origination fee | No prepayment penalty |
| Credit Union B | 6.0% | 48 | $100 origination fee | Prepayment penalty of 2% |
| Online Lender C | 5.8% | 72 | No origination fee | Late payment fee of $25 |
Impact of Different Credit Scores
Your credit score significantly impacts the interest rate you’ll pay on a used car loan. Lenders use credit scores as a key indicator of your creditworthiness, reflecting your ability to repay the loan. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate, as it suggests a lower risk of default. Conversely, a lower credit score increases the risk, leading to a higher interest rate.
Understanding how your credit score influences your interest rate is crucial for securing the most favorable terms for your used car loan. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions during the loan application process.
Credit Score Ranges and Associated Interest Rates
Different credit score ranges represent varying levels of creditworthiness. Lenders categorize borrowers into these ranges to assess the risk of loan default. The interest rate offered is directly correlated to the perceived risk associated with each score range. This means borrowers with higher scores, who are perceived as less risky, typically qualify for lower interest rates.
Impact of Credit Scores on Interest Rates
A substantial difference in interest rates can arise between borrowers with high and low credit scores. For instance, a borrower with a strong credit score in the excellent range might secure a used car loan with an interest rate as low as 4.5%, while a borrower with a fair credit score might face an interest rate as high as 12%. This difference reflects the risk assessment made by the lender.
| Credit Score Range | Typical Interest Rate | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent (750-850) | 4.5%-7.5% | Borrowers with excellent credit scores demonstrate a history of responsible debt management, reducing the risk of default for lenders. |
| Good (700-749) | 7.5%-9.5% | Borrowers in this range generally have a good track record of repaying their debts, but the risk is slightly higher compared to those with excellent scores. |
| Fair (650-699) | 9.5%-12% | This range indicates a moderate level of credit risk. Lenders often offer higher interest rates due to the increased probability of default. |
| Poor (600-649) | 12%+ | Borrowers in this category present a higher risk for lenders, resulting in significantly higher interest rates. |
| Very Poor (<600) | 15%+ | The highest risk category, these borrowers often face the highest interest rates. Securing a loan might be challenging in this case. |
Comparison of Interest Rates for Different Credit Scores
A borrower with a good credit score (725) might receive a used car loan interest rate of 8.5%, while a borrower with a poor credit score (625) might be offered a rate of 15%. This 6.5% difference highlights the importance of maintaining a good credit score to secure favorable loan terms. The difference in rates can translate into substantial savings or additional costs over the life of the loan. A borrower with a fair credit score (675) might receive a rate of 11%. This demonstrates a clear correlation between creditworthiness and the interest rate offered.
Factors Affecting Loan Approvals

Securing a used car loan hinges on more than just the vehicle’s condition and price. Lenders meticulously evaluate various factors to assess the applicant’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. Understanding these factors is crucial for a smooth and successful application process.
Essential Documents for Loan Applications
Loan applications require specific documentation to verify the applicant’s identity, financial stability, and repayment capacity. These documents are crucial for lenders to make informed decisions. A complete and accurate submission significantly increases the likelihood of approval.
- Proof of Identity: Valid government-issued photo identification, such as a driver’s license or passport, is essential to establish the applicant’s identity. This document is paramount in preventing fraudulent applications.
- Proof of Income: Recent pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements are required to demonstrate the applicant’s income and financial capacity to repay the loan. This is a critical component of assessing affordability and risk.
- Proof of Employment: Employment verification, such as a recent employment letter or a recent pay stub, verifies the applicant’s current employment status and tenure. A stable employment history is often favored by lenders.
- Credit Report: A credit report provides a comprehensive overview of the applicant’s credit history, including payment history, outstanding debts, and credit utilization. A positive credit report typically improves the chances of loan approval.
- Down Payment Documentation: If a down payment is made, documentation proving the source of funds for the down payment is needed. This might include bank statements or other verifiable financial records.
- Vehicle Information: A copy of the vehicle’s title and a comprehensive vehicle inspection report are necessary for valuation and verification purposes. This allows lenders to assess the car’s market worth and potential risks.
Significance of Income and Employment History
A borrower’s income and employment history are crucial factors in determining loan approval. Lenders analyze the consistency and stability of income to gauge the applicant’s ability to meet monthly loan repayments. A steady job with a demonstrable income history usually leads to a higher likelihood of loan approval and potentially better interest rates. Consistent income stream provides a strong foundation for lenders to assess the borrower’s reliability and financial capacity to manage the loan obligations.
Importance of Comprehensive Financial History
A detailed financial history, including credit reports, bank statements, and tax returns, provides a comprehensive view of the applicant’s financial standing. Lenders use this information to assess the applicant’s ability to manage debt and their overall financial responsibility. A history of timely payments and low debt-to-income ratios usually translates into a better chance of loan approval. Lenders use a comprehensive financial history to evaluate the applicant’s risk profile and determine their creditworthiness.
Role of Down Payment in Interest Rates
A larger down payment typically reduces the loan amount, which lowers the risk for the lender. This, in turn, can lead to a lower interest rate. The down payment acts as a buffer against potential losses if the borrower defaults on the loan. A larger down payment demonstrates the borrower’s commitment to the loan and reduces the financial burden on the lender.
Types of Collateral for Used Car Loans
In some cases, lenders may require collateral to secure the loan. The most common form of collateral for used car loans is the vehicle itself. If the borrower defaults, the lender can repossess the vehicle to recover the outstanding loan amount.
| Document Type | Purpose | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Proof of Identity | Verify applicant’s identity | Essential for preventing fraud and establishing legitimacy |
| Proof of Income | Demonstrate ability to repay | Crucial for assessing affordability and risk |
| Proof of Employment | Verify current employment | Indicates stability and consistency of income |
| Credit Report | Assess creditworthiness | Provides a comprehensive view of payment history and debt management |
| Vehicle Information | Verify vehicle details and value | Critical for assessing the vehicle’s market worth and potential risks |
Alternatives to Traditional Loans
Beyond traditional bank loans, various financing options are available for used car purchases. These alternatives can offer different terms and conditions, potentially impacting interest rates, eligibility requirements, and overall affordability. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for consumers seeking the most suitable financing option for their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternative Financing Options
Several options exist beyond traditional bank loans, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These include dealership financing, private party financing, and online lenders. Understanding the nuances of each approach can help buyers make informed decisions.
- Dealership Financing: Dealerships often offer in-house financing options. These loans are frequently tied to specific dealerships, potentially providing convenience for some buyers. The interest rates may be competitive or not, and eligibility criteria can vary widely. Dealerships may also offer incentives, like extended warranties or other add-ons, as part of the financing package. For example, a buyer might find a lower interest rate with a dealership loan if they are a loyal customer or meet specific requirements set by the dealership.
- Private Party Financing: Private party financing involves a direct loan from an individual or a group of individuals. This can offer potentially lower interest rates compared to traditional loans, particularly if the buyer has a strong relationship with the lender. However, the eligibility criteria are often stricter, and the buyer must be cautious to ensure that the transaction is legitimate. This method often involves personal agreement and direct negotiations, potentially leading to less transparent terms. For example, an established business owner might offer a lower interest rate on a used car loan to a client as a form of business incentive.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders provide a digital platform for securing used car loans. These lenders often have streamlined application processes and can offer competitive interest rates. The process is often faster than traditional financing, but eligibility may be dependent on credit scores and other factors. For example, an online lender might have a wider range of loan options for borrowers with different credit profiles than a traditional bank.
Comparison of Loan Types
Different financing options offer varying degrees of flexibility and terms. A comparison table outlining key characteristics can help in making informed decisions.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Eligibility Criteria | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Bank Loan | Generally higher | Credit history, income verification | Established process, access to wider range of products | Potential for higher interest rates, more stringent eligibility |
| Dealership Financing | Variable | Dealership-specific requirements | Convenience, potential incentives | Interest rates may not be competitive, limited options |
| Private Party Financing | Potentially lower | Strong relationship with lender, thorough background check | Potentially lower interest rates | Higher risk, less transparency, less regulatory oversight |
| Online Lender | Variable | Credit score, income verification | Fast application process, potentially competitive rates | Less personal interaction, potentially hidden fees |