Researching Potential Vehicles
Finding the perfect used car involves meticulous research. Thorough investigation of available options, coupled with careful evaluation of key factors, significantly increases the likelihood of a successful purchase. Understanding the various avenues for research and the crucial criteria to consider is essential for informed decision-making.
Comprehensive research is crucial when buying a used car. It’s not just about finding a vehicle that meets your needs; it’s about finding the best vehicle that fits your budget and driving experience preferences. This involves navigating various resources and employing strategic filtering methods.
Different Resources for Research
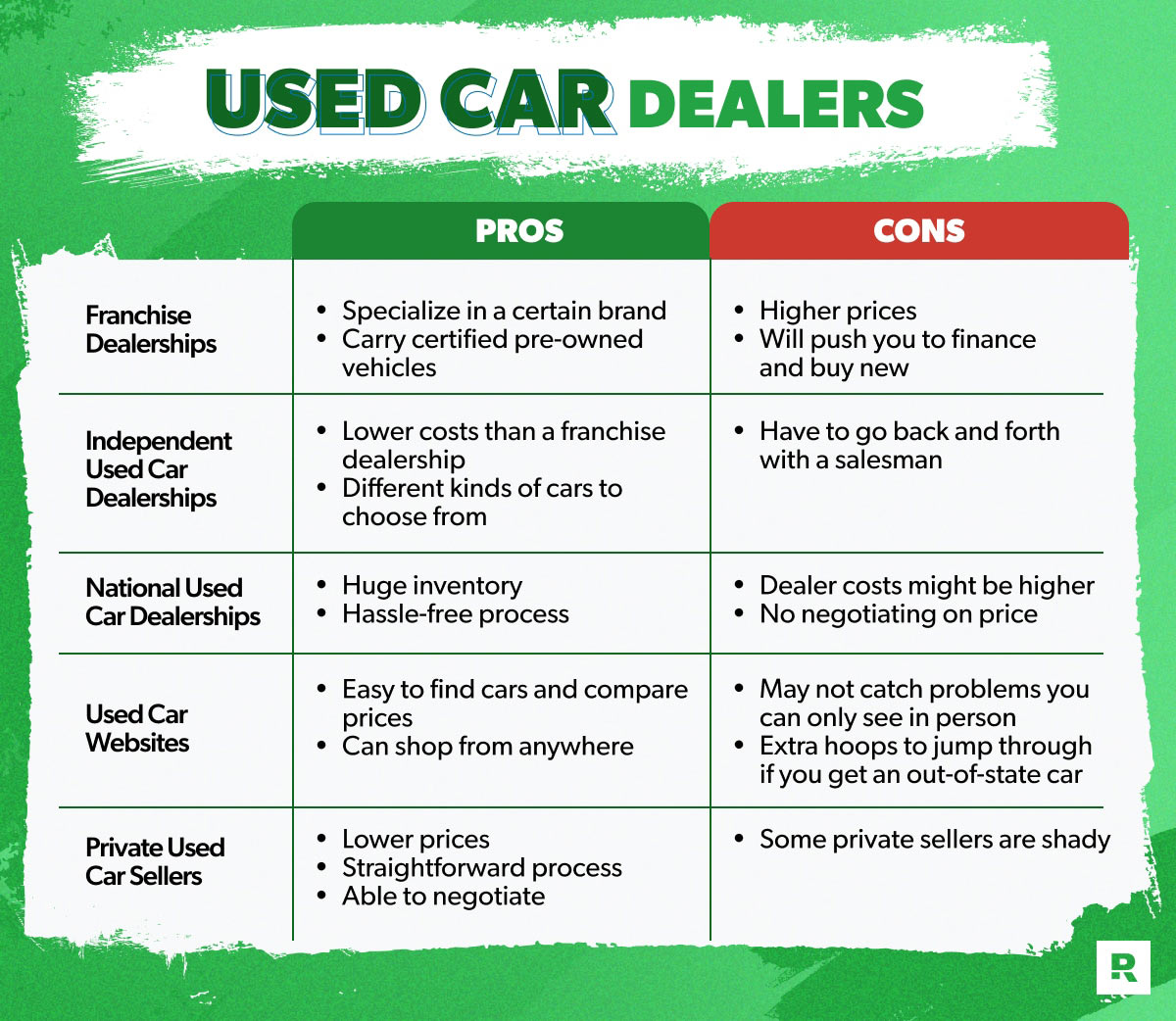
Various resources are available for researching used cars. Online listings, dealerships, and private sellers each offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these nuances will empower you to make the most informed choices.
- Online Listings: Platforms like Craigslist, Autotrader, and Kelley Blue Book provide vast databases of used vehicles. These online marketplaces typically feature detailed specifications, photos, and seller information, enabling efficient comparison shopping. They often allow for extensive filtering based on specific criteria.
- Dealerships: Dealerships often maintain a selection of used vehicles, often with additional services like financing options and warranties. Visiting dealerships allows for a firsthand inspection of the vehicle and interaction with knowledgeable staff. However, dealerships might have higher prices compared to other options.
- Private Sellers: Private sellers, often listed on platforms like Craigslist or Facebook Marketplace, frequently offer used vehicles at potentially lower prices. Direct negotiation is a common practice. However, conducting thorough due diligence and inspection is critical with private sellers, as there are often fewer guarantees or warranties.
Filtering Search Results
Efficiently narrowing down your search is key to finding the ideal used car. Filtering search results based on your specific requirements allows for a focused search.
- Criteria for Filtering: Utilizing search filters based on make, model, year, mileage, and price range significantly narrows down the search results, allowing for focused comparison shopping. Precise filtering allows you to identify vehicles that match your specific preferences and budget constraints.
Comparison of Online Marketplaces and Dealerships
This table highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using online marketplaces versus visiting dealerships directly.
| Feature | Online Marketplaces | Dealerships |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Potentially lower prices due to competition and private sellers. | Potentially higher prices due to overhead costs and markups. |
| Inspection | Limited or no in-person inspection before purchase. | Direct inspection of the vehicle is possible. |
| Negotiation | Negotiation is possible, but often more complex. | Negotiation is often more straightforward and streamlined. |
| Services | Limited or no financing or warranty options. | Often provides financing and warranty options. |
| Convenience | High convenience due to extensive online listings and filtering options. | Requires physical visits to dealerships. |
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Car
Selecting a used car involves evaluating various factors. Understanding the significance of these elements will help you make a well-informed decision.
- Fuel Efficiency: The fuel efficiency of a vehicle directly impacts long-term costs. Higher fuel efficiency translates to lower fuel expenses over time. Consider factors like MPG (miles per gallon) when making a choice.
- Safety Ratings: Safety ratings from reputable organizations provide crucial insights into a vehicle’s crashworthiness and overall safety features. Research and consider the safety ratings before making a purchase decision.
- Maintenance History: Knowing the vehicle’s maintenance history is critical. A well-maintained vehicle is less prone to unexpected repairs, potentially saving you money in the long run. Request records or documentation of previous maintenance. If available, a pre-purchase inspection from a trusted mechanic can identify potential issues.
Evaluating the Vehicle
Buying a used car involves more than just finding a good price. Thorough evaluation is crucial to ensuring you’re getting a vehicle that aligns with your needs and budget, and avoids potential future problems. A comprehensive inspection, including a history check and test drive, will help you make an informed decision.
A critical step in the used car buying process is a thorough evaluation of the vehicle’s condition and history. This process will uncover potential issues and help you negotiate a fair price. This is paramount to avoid costly repairs down the line.
Pre-Purchase Inspection
A pre-purchase inspection is essential for uncovering potential mechanical or structural problems before committing to a purchase. This inspection is akin to a diagnostic test, proactively identifying any hidden issues that could lead to costly repairs. It helps you negotiate a fair price based on the vehicle’s actual condition.
- Preparation: Gather necessary tools, including a flashlight, pen, and notepad. Take photos of any potential issues, and have a trusted mechanic or knowledgeable friend assist you if possible.
- Exterior Inspection: Check for dents, rust, scratches, or any signs of damage. Inspect the paint job for uniformity and signs of repair. Look for any loose panels or misaligned parts. Note any evidence of prior accidents.
- Interior Inspection: Assess the interior for wear and tear. Look for tears, stains, or excessive wear on the upholstery. Verify the functionality of all interior controls, including the radio, climate control, and power windows. Pay attention to the smell of the car, as a musty or unusual odor can indicate potential problems.
- Undercarriage Inspection: Inspect the undercarriage for rust, leaks, and damage. Look for signs of recent maintenance, such as fresh fluids or recent repairs.
Key Areas of Examination
A comprehensive examination involves a systematic review of critical vehicle components. This thoroughness ensures you make an informed decision.
- Engine: Listen for unusual noises, like knocking or rattling. Check the engine oil level and condition. Look for leaks and signs of overheating. Note the engine’s overall responsiveness. Observe the appearance of the belts and hoses.
- Transmission: Test the gears for smooth shifting and lack of hesitation. Check for any unusual noises during shifts. Verify the fluid level and condition.
- Body: Thoroughly examine the body for any signs of damage, such as dents, rust, or scratches. Check for alignment issues and any repairs that might have been performed. Note the overall condition of the body panels.
Vehicle History Checks
Verifying a vehicle’s history is a crucial part of the evaluation process. This can reveal past accidents, damage, or maintenance issues.
- VIN Checks: A Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) check provides a detailed history of the vehicle, including accidents, title issues, and maintenance records. Many online services provide these checks, allowing you to verify the vehicle’s history. This is a vital step to avoid potential legal and financial issues.
- Online Reports: Online services like Carfax and AutoCheck provide detailed reports on the vehicle’s history, including maintenance records, accidents, and title issues. These reports are valuable tools for evaluating the vehicle’s overall condition.
Test Driving
A test drive is an essential part of evaluating a used car. It allows you to experience the vehicle’s performance and handling firsthand.
- Initial Assessment: Assess the responsiveness of the accelerator and brake pedals. Notice any unusual noises or vibrations. Check for smooth operation of all controls, including the wipers, lights, and mirrors. Evaluate the overall driving experience.
- Highway Driving: Drive on the highway to assess the vehicle’s stability and handling at higher speeds. Note any unusual vibrations or noises. Pay attention to the vehicle’s acceleration and braking performance.
- City Driving: Drive in city traffic to assess the vehicle’s maneuverability and responsiveness in tight spaces. Evaluate the vehicle’s handling and responsiveness in various driving conditions. Test the turning radius.
Negotiating the Price
Successfully negotiating the price of a used car requires a blend of research, preparation, and assertive communication. Knowing the market value of similar vehicles, understanding the car’s condition, and possessing a strong understanding of the seller’s motivations are all key elements to a successful negotiation. This phase of the process allows you to confidently advocate for your interests while respecting the seller’s perspective.
Negotiation is a dynamic process, not a one-size-fits-all approach. Flexibility and adaptability are crucial. Be ready to walk away if the price doesn’t align with your assessment of the vehicle’s value. The ultimate goal is to reach a mutually agreeable price that reflects the car’s true worth.
Strategies for Negotiating a Fair Price
Effective negotiation strategies are essential for securing a favorable price. Understanding the seller’s perspective and tailoring your approach to that context can significantly impact the outcome. Researching comparable vehicles in your area is crucial for establishing a baseline price. A strong understanding of market value gives you leverage in the negotiation process.
Questions to Ask the Seller About the Vehicle’s History and Maintenance
Thorough questioning about the vehicle’s history and maintenance is critical for assessing its true condition. Understanding the vehicle’s past is paramount to making an informed decision. This section Artikels key inquiries to uncover potential issues or discrepancies.
- Vehicle History Report: Request a detailed vehicle history report to uncover any accidents, salvage titles, or outstanding liens. A clean history report is a significant indicator of the car’s overall condition and reliability.
- Maintenance Records: Inquire about the vehicle’s maintenance history. Regularly documented maintenance records provide insight into the car’s care and potential problem areas. Look for records of oil changes, tire rotations, and other routine maintenance.
- Modifications and Repairs: Ask about any modifications or repairs performed on the vehicle. This will help you understand any potential changes to the car’s original specifications and any unresolved issues.
- Odometer Accuracy: Verify the accuracy of the odometer reading. Discrepancies can suggest potential concerns or attempts to conceal mileage.
Identifying Potential Red Flags During Negotiations
Recognizing potential red flags during negotiations is crucial for protecting yourself from potentially problematic situations. Be wary of sellers who are unwilling to provide clear and detailed information or who exhibit evasive or contradictory responses.
- Evasive or Unclear Responses: Be cautious of sellers who are evasive or provide unclear answers to your questions. Vague or contradictory information may indicate a reluctance to disclose potentially problematic aspects of the vehicle.
- Unwillingness to Provide Documentation: Hesitation or refusal to provide maintenance records, repair invoices, or vehicle history reports should raise concerns. These documents offer valuable insight into the vehicle’s history.
- High-Pressure Tactics: Avoid sellers who employ high-pressure tactics to rush the negotiation process. Taking your time to assess the vehicle and its price is essential.
- Unusual Asking Price: Compare the asking price to similar vehicles in the area. An unusually high price, especially compared to comparable models, might signal hidden problems.
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Effective negotiation tactics require a balance of assertiveness and respect. Emphasize your research and understanding of the vehicle’s market value to support your position.
- Research-Based Counteroffers: Support your counteroffers with evidence from comparable sales. This demonstrates a genuine understanding of the vehicle’s market value.
- Active Listening and Questions: Actively listen to the seller’s concerns and respond with informed questions to understand their perspective. Demonstrate your genuine interest in the vehicle and the process.
- Walk Away Power: Be prepared to walk away if the price doesn’t meet your expectations. This demonstrates your confidence and commitment to finding a fair deal.
- Consider Additional Costs: Be prepared to negotiate the price while also considering the costs of additional services such as title transfer, taxes, and registration fees.
Completing the Purchase
Securing a used car involves more than just finding the right vehicle. Successfully completing the purchase requires careful attention to paperwork, financing options, and the overall process. This crucial step ensures a smooth transition from prospective buyer to proud owner.
Purchase Agreement and Paperwork
The purchase agreement is a legally binding contract outlining the terms of the sale. It details the vehicle’s condition, price, and payment method. Thoroughly reviewing this document is paramount before signing. Crucially, ensure all agreed-upon details are accurately reflected. It’s advisable to have a trusted individual review the agreement alongside you to ensure clarity and protect your interests.
Financing Options
Numerous financing options are available for used car purchases. These range from traditional bank loans to dealer financing. Understanding the terms and conditions of each option is vital. Consider factors such as interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees. Shopping around for different loan options can significantly impact the overall cost of the vehicle.
Essential Documents
A comprehensive list of documents is required during the purchase process. These documents verify your identity, financial capability, and the vehicle’s history. These essential documents are crucial for a smooth and successful transaction. Gathering these documents in advance streamlines the process.
- Valid driver’s license and proof of insurance.
- Proof of residency (utility bill, lease agreement).
- A copy of your loan approval letter (if applicable).
- A copy of your bank statements (if applicable).
- Vehicle title and any liens or encumbrances associated with the vehicle.
- Vehicle registration information.
- Verification of the vehicle’s odometer reading.
Payment Methods
Various payment methods are available to complete the purchase. Choosing the most suitable option depends on personal preferences and financial circumstances. Consider the fees and convenience associated with each method.
| Payment Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | Paying the full purchase price in cash. | Avoids interest charges and potential loan fees. | Requires significant funds upfront. |
| Check | Paying with a personal check. | Common payment method. | Can take time to clear. |
| Bank Transfer | Transferring funds electronically from your bank account. | Fast and efficient. | May have limitations on the amount or recipient. |
| Credit Card | Paying with a credit card. | Convenient for large purchases. | Higher interest rates compared to other options. |
| Loan | Taking out a loan from a bank or financial institution. | Allows you to finance the purchase. | Interest charges and loan terms need to be considered. |
Post-Purchase Considerations

Buying a used car is a significant investment. Beyond the initial purchase, ongoing maintenance and smart choices can significantly impact the car’s longevity and your overall satisfaction. Proactive steps after the sale are crucial for maximizing your investment and ensuring a positive ownership experience.
Thorough post-purchase care extends beyond simply filling the gas tank. It encompasses preventative maintenance, securing appropriate insurance, and building a reliable relationship with a trusted mechanic. These strategies safeguard your investment, protect you from unexpected expenses, and ensure your vehicle continues to perform optimally for years to come.
Vehicle Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential for preserving the vehicle’s condition and extending its lifespan. Neglecting regular upkeep can lead to costly repairs down the road. A proactive approach to maintenance can save you money and headaches in the long run.
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are vital for engine health. The frequency depends on the vehicle’s make, model, and driving conditions, but typically ranges from every 3,000 to 7,500 miles, or every three to six months. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations is critical for optimal performance and longevity. Ignoring oil changes can lead to significant engine damage.
- Tire Rotations and Inflation: Rotating tires ensures even wear and tear, extending their lifespan. Tire rotation should be performed every 5,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on the vehicle and driving habits. Proper tire inflation is crucial for safety and fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires can lead to increased fuel consumption and decreased tire life.
- Fluid Checks and Top-Ups: Regular checks of coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid are essential. These fluids are crucial for proper vehicle function. Low fluid levels can cause significant mechanical issues and should be addressed immediately.
- Filter Replacements: Air filters, cabin filters, and fuel filters need periodic replacement. These filters ensure optimal engine performance and prevent the buildup of debris. The frequency of replacement varies depending on the vehicle and driving conditions, typically every 12,000 to 20,000 miles.
- Brake Inspections: Regular brake inspections are crucial for safety. Brake pads and rotors should be inspected at least every 5,000 to 10,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. Addressing brake issues promptly is critical for preventing accidents.
Vehicle Insurance
Insurance is a critical aspect of vehicle ownership. It protects you financially in case of accidents, theft, or damage. Choosing the right insurance coverage is vital for peace of mind and financial security. Insurance provides a safety net in unforeseen circumstances.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Comprehensive coverage protects against damage caused by events other than collisions, such as vandalism, hail, or fire. This coverage is crucial for comprehensive protection.
- Collision Coverage: Collision coverage pays for damage to your vehicle in a collision, regardless of fault. This coverage is vital for protecting your investment.
- Liability Coverage: Liability coverage protects you if you are at fault in an accident. It covers the other party’s damages. This is a legal requirement in most jurisdictions.
Establishing a Relationship with a Trusted Mechanic
Finding a reliable mechanic is a valuable asset. A trusted mechanic can provide expert advice, perform maintenance, and address issues promptly. Building this relationship is crucial for long-term vehicle care.
Developing a rapport with a mechanic who understands your vehicle and its specific needs is crucial. This will help you avoid costly repairs and ensure that your vehicle remains in top condition. Finding a mechanic who is honest, knowledgeable, and experienced will save you time and money in the long run. This relationship ensures you receive accurate diagnoses and effective repairs.
Safety and Legal Aspects
Buying a used car involves more than just the price and condition. Understanding the legal framework, potential safety hazards, and seller accountability is crucial to a smooth and secure transaction. Failing to address these aspects can lead to costly repairs, legal battles, or even personal safety concerns.
Thorough due diligence and a cautious approach are paramount in protecting your interests throughout the entire process. This section details essential considerations regarding legal requirements, seller verification, warranties, and recourse options in case of issues.
Legal Requirements for Used Car Purchases
Knowing the legal requirements in your area is essential for a safe and compliant used car purchase. These regulations vary by jurisdiction but typically cover aspects such as vehicle history verification, mandatory disclosures, and sales documentation. Always consult your local Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or equivalent agency for specific requirements. The DMV provides resources and guidelines specific to your location.
Thorough Background Checks on Sellers
While not always legally mandated, conducting a thorough background check on the seller, if possible, can significantly reduce the risk of fraudulent activities or hidden issues. Checking the seller’s reputation online, through business registries, or by contacting the seller’s previous customers can provide valuable insights.
Examples of Warranties and Limitations
Used car warranties, if offered, are contracts that obligate the seller to repair or replace certain components under specific conditions. These warranties can vary widely in coverage, duration, and limitations. Some common examples include powertrain warranties, covering major engine and transmission components, or bumper-to-bumper warranties, covering a broader range of vehicle systems. Importantly, always review the specific terms and conditions carefully, including any exclusions or limitations. These exclusions may prevent coverage for certain problems.
Legal Recourse Options in Case of Problems
If issues arise after purchasing a used car, understanding your legal options is crucial. This section provides a table outlining common recourse options.
| Problem Category | Potential Legal Recourse | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Misrepresentation or Fraud | Small Claims Court, Consumer Protection Agency | If the seller knowingly misrepresented the car’s condition or engaged in fraudulent activities, legal action can be pursued. Specific laws in your area may dictate the processes involved. |
| Breach of Warranty | Contract Dispute Resolution, Mediation | If a warranty is violated, legal options involve addressing the contract terms and seeking mediation or pursuing formal legal action. This is often dependent on the warranty terms and conditions. |
| Hidden Defects | Negotiation, Small Claims Court | If significant hidden defects are discovered, negotiation with the seller is often the first step. Failing a resolution, small claims court might be necessary. The extent of recourse depends on the nature and severity of the defect. |
| Vehicle Safety Issues | State Motor Vehicle Agencies, Product Liability Lawsuits | If safety concerns arise, reporting to the state motor vehicle agency and potentially pursuing a product liability lawsuit are options. This is often contingent on the severity and nature of the safety hazard. |
Alternatives and Comparisons
Choosing the right vehicle involves considering various factors beyond just the purchase price. Understanding alternatives like leasing and the nuances of buying from private sellers or dealerships can significantly impact your overall cost and ownership experience. Furthermore, various financing options are available, each with its own terms and conditions. A thorough understanding of these alternatives can lead to a more informed and advantageous purchase.
Evaluating the best approach for your needs necessitates a careful comparison of buying a used car versus leasing a new one, considering the pros and cons of each. Likewise, the different avenues for acquiring a used vehicle – dealerships or private sellers – each present unique advantages and disadvantages that need to be carefully weighed. Understanding the various financing options available for used car purchases is equally crucial, as it allows for tailored solutions aligned with your financial situation.
Buying Used vs. Leasing New
A critical decision involves choosing between buying a used car and leasing a new one. Each option has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Buying a used car often provides a lower initial cost and potentially greater ownership flexibility, while leasing a new car typically offers lower monthly payments and access to newer technology. However, used car ownership may involve unforeseen repair costs, while a lease generally restricts mileage and potentially results in a hefty termination fee. Careful consideration of your budget, driving needs, and long-term financial goals is crucial for making the right choice.
Buying from a Private Seller vs. a Dealership
Purchasing from a private seller often presents a potentially lower price point, while a dealership typically offers warranties, financing options, and the convenience of a structured transaction. However, buying from a private seller requires thorough due diligence, including independent inspections and verifying the vehicle’s history. Dealerships may have higher prices but provide a streamlined process and support for potential issues. Consider your comfort level with independent vehicle assessments and your preference for a straightforward transaction when making this decision.
- Private Seller Advantages: Potentially lower price, greater negotiation flexibility.
- Private Seller Disadvantages: Requires thorough research and inspection, no warranty, potential for hidden issues.
- Dealership Advantages: Warranties, financing options, streamlined process, assistance with potential issues.
- Dealership Disadvantages: Higher prices, less negotiation flexibility.
Financing Options for Used Cars
Numerous financing options exist for used car purchases, each with distinct terms and conditions. These options include traditional bank loans, credit unions, and online lenders. Understanding the terms and conditions of each option is vital for securing the most favorable financing.
| Financing Option | Interest Rate | Loan Term | Documentation Required | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Loan | Variable | 2-7 years | Credit history, income verification | Established lending platform, potential for lower interest rates | Stricter eligibility criteria, longer approval process |
| Credit Union | Variable | 2-7 years | Credit history, income verification | Competitive rates, often better customer service | Limited availability, eligibility criteria can vary |
| Online Lender | Variable | 1-5 years | Credit history, income verification, proof of employment | Faster approval process, accessible to a broader range of borrowers | Potentially higher interest rates, less personal touch |
“Comparing financing options is crucial for securing the best possible terms and rates.”
Specific Vehicle Types

Navigating the used car market involves understanding the nuances of different vehicle types. Each category—sedans, SUVs, trucks, and others—presents unique considerations regarding fuel efficiency, maintenance needs, and overall performance. Careful evaluation of these factors is crucial to making an informed decision that aligns with your individual needs and budget.
Sedans
Sedans typically offer a balance of fuel efficiency, maneuverability, and affordability. Their compact size often translates to lower fuel consumption, making them an attractive option for city driving or individuals seeking economic transportation. However, sedans often have less cargo space compared to SUVs or trucks.
- Fuel Efficiency: Sedans generally excel in fuel efficiency, making them a cost-effective choice for daily commuting. For example, a well-maintained Honda Civic can achieve impressive mileage figures, potentially saving you money on gas over the long term.
- Maintenance Needs: Routine maintenance for sedans is often less expensive than for larger vehicles. Parts are generally readily available, and labor costs tend to be lower for standard servicing procedures.
- Evaluation Considerations: Pay close attention to the engine’s condition, transmission smoothness, and the overall interior and exterior wear and tear. Look for signs of significant damage or neglect, particularly in areas susceptible to wear like the suspension and brakes. Thoroughly inspect the car’s history report and service records for any potential red flags.
SUVs
SUVs offer a blend of passenger space, cargo capacity, and enhanced ground clearance. They are popular for their versatility, accommodating families and individuals needing ample space for cargo or passengers. However, SUVs often have higher fuel consumption compared to sedans.
- Fuel Efficiency: SUVs, depending on the model and engine, can have varying fuel efficiency. Hybrid or electric options can mitigate the fuel consumption concerns. For instance, a Toyota RAV4 Hybrid can achieve significantly better mileage than a comparable non-hybrid SUV.
- Maintenance Needs: Maintenance costs for SUVs can be higher due to their complex mechanical systems and often larger component sizes. This includes the potential for costly repairs, particularly for larger engines or sophisticated transmissions. Always consider the potential maintenance implications when evaluating the price.
- Evaluation Considerations: Thoroughly inspect the suspension and drivetrain, as these components are crucial for the SUV’s off-road capabilities or on-road stability. Look for signs of rust or corrosion, especially in areas like the undercarriage and wheel wells. Evaluate the vehicle’s cargo space to ensure it meets your needs.
Trucks
Trucks are versatile vehicles, offering significant towing and hauling capacity. Their robustness and capability make them attractive for businesses or individuals requiring heavy-duty transportation. However, trucks typically have lower fuel efficiency compared to sedans or SUVs.
- Fuel Efficiency: Trucks are known for their lower fuel efficiency compared to other vehicle types. The size and weight of the vehicle directly affect fuel consumption. A diesel engine can provide some improvement, but the overall impact on mileage will be lower.
- Maintenance Needs: Maintenance for trucks often involves more specialized parts and labor. Potential repairs for heavy-duty components like transmissions or axles can be quite expensive.
- Evaluation Considerations: Pay close attention to the truck’s towing and hauling capacity. Inspect the bed for rust, dents, or other damage. Examine the engine’s condition and any associated accessories, like the cooling system or electrical components.
Other Vehicle Types
This category encompasses vehicles like minivans, coupes, convertibles, and specialty vehicles. Each type presents unique considerations.
- Evaluation Considerations: Minivans are ideal for families, prioritizing passenger and cargo space. Coupes emphasize style and performance, while convertibles prioritize open-air driving. Specialty vehicles, such as motorcycles or RVs, have distinct requirements and should be evaluated based on their intended use.