Understanding Used Car Warranties
Used car warranties offer varying levels of protection, from basic powertrain coverage to comprehensive manufacturer or extended warranties. Navigating these options can be complex, but understanding the different types, terms, and conditions is crucial for making informed decisions. Knowing what’s covered and excluded, as well as potential voids, helps you avoid costly surprises down the road.
Used car warranties are a significant factor in the overall cost and value proposition. They can safeguard you against unexpected repairs, potentially saving thousands of dollars over the lifespan of the vehicle. However, it’s essential to analyze the specific coverage to ensure it aligns with your needs and budget.
Types of Used Car Warranties
Used car warranties come in various forms, each with unique coverage and cost implications. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the best fit for your circumstances.
- Manufacturer Warranties: These warranties are often offered by the original manufacturer and may still be applicable to used vehicles, depending on the vehicle’s age and mileage. Coverage is typically limited and may cover specific components like the engine or transmission for a certain period or mileage. They may be transferable but are usually contingent on specific conditions and may require a pre-purchase inspection.
- Extended Warranties: These are purchased separately from the dealership or a third-party provider. They offer additional protection beyond the manufacturer’s warranty, covering a broader range of components and often extending for a longer period or mileage. These can be lucrative, especially for older vehicles, but careful review of coverage and exclusions is critical.
- Powertrain Warranties: These warranties typically focus on the vehicle’s core powertrain components, including the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. They are commonly found in extended warranties and may cover repairs or replacements for these parts, depending on the specific terms of the agreement.
Warranty Coverage Comparison
The table below Artikels the key differences between the types of used car warranties.
| Warranty Type | Coverage | Exclusions | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer Warranty (Used) | Limited coverage, typically on specific components (engine, transmission). | Wear and tear, accidents, modifications, neglect, and other non-manufacturer-related issues. | Usually no additional cost if it still applies. |
| Extended Warranty | Broader coverage than manufacturer’s, often covering multiple components beyond the powertrain. | Exclusions vary greatly, such as accidents, repairs from non-certified mechanics, and normal wear and tear. | Significant cost, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars. |
| Powertrain Warranty | Focuses specifically on engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. | Exclusions may include body parts, electrical systems, or other non-powertrain components. | Generally more affordable than comprehensive extended warranties. |
Warranty Terms and Conditions
Warranty contracts contain crucial terms and conditions. Careful reading and understanding of these clauses is paramount.
- Definitions: The warranty contract should clearly define terms like “wear and tear,” “normal use,” and “mechanical failure.” These definitions determine the scope of coverage.
- Exclusions: Understanding what’s excluded from coverage is critical. Typical exclusions include accidents, damage from misuse, or repairs performed by unauthorized mechanics.
- Limitations: Warranty contracts often have limitations on the amount of coverage, the number of repairs, or the length of time the warranty is valid.
- Procedures: Knowing the procedure for filing a claim, including the required documentation and approval processes, is essential.
Reasons for Warranty Voidance
Certain actions can invalidate a used car warranty.
- Improper Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance or using non-recommended parts can lead to warranty voidance.
- Unauthorized Repairs: Having repairs performed by non-certified mechanics may void the warranty.
- Accidents and Damage: Accidents or damage to the vehicle often result in the warranty being voided, depending on the terms and conditions.
- Modifications: Uncertified modifications to the vehicle’s components can also lead to warranty voidance.
Typical Warranty Coverage
The table below provides a general overview of what might be covered in different warranties. Specific coverage varies widely, so always consult the contract.
| Component | Potential Coverage |
|---|---|
| Engine | Repairs or replacements due to manufacturer defects. |
| Transmission | Repairs or replacements due to manufacturer defects. |
| Drivetrain | Repairs or replacements due to manufacturer defects. |
| Electrical System | Repairs or replacements due to manufacturer defects, depending on the warranty type. |
| Body Parts | Repairs or replacements due to manufacturer defects, but often excluded in powertrain warranties. |
Factors Affecting Warranty Value

A used car warranty, while offering peace of mind, isn’t a one-size-fits-all proposition. Its value hinges on numerous factors, making it crucial to understand these elements before committing to a purchase. Assessing the warranty’s worth involves a careful evaluation of the vehicle’s condition, the remaining coverage, and the potential repair costs.
Impact of Vehicle Make and Model
Different car makes and models have varying propensities for specific mechanical issues. Some brands are known for reliable engines, while others might have a higher risk of transmission problems. A warranty on a vehicle known for particular reliability issues might offer less value than one on a model with a proven track record of longevity. For instance, a warranty on a used Toyota Camry, typically known for its durability, might have a higher perceived value compared to a warranty on a used car from a brand prone to costly engine repairs.
Influence of Mileage and Age
Mileage and age are directly correlated to a vehicle’s wear and tear. A warranty on a high-mileage or older vehicle might be less valuable because it’s more likely that the car has already experienced some component deterioration. The older the vehicle, the more likely it is that the warranty will cover repairs for issues that have developed from normal wear and tear. A warranty on a low-mileage vehicle, particularly if it’s still within the manufacturer’s original warranty period, often represents a better value proposition. For example, a 50,000-mile used car with a remaining warranty might be more valuable than a 100,000-mile car with the same warranty coverage.
Assessment of Vehicle Condition
The condition of the vehicle is paramount in evaluating a warranty’s worth. A vehicle in excellent condition with minimal wear and tear, even if older or higher mileage, might have a more valuable warranty compared to a car with visible signs of neglect or prior damage. Inspect the vehicle thoroughly, noting any damage or repairs, before considering a warranty. A well-maintained car, even with high mileage, might offer a better return on investment from a warranty than a vehicle with noticeable issues.
Comparison of Warranty Cost and Potential Repair Costs
Calculating the cost of a warranty against the potential repair costs is critical. A warranty’s value is determined by whether its price is lower than the potential cost of repairing major component failures. Consider the potential costs of a major engine or transmission repair, and compare that figure to the cost of the warranty. If the potential repair cost significantly exceeds the warranty price, the warranty becomes a more attractive financial option. For instance, a $500 warranty on a car that could require a $2,000 transmission repair offers a worthwhile value proposition.
Remaining Warranty Duration and Coverage
The duration of the remaining warranty period is a crucial factor. A warranty with a longer remaining duration generally has a higher value. The longer the coverage, the more protection you have against potential future repairs. Also, a comprehensive warranty covering a wide range of components and systems will be more valuable than a limited warranty. Analyze the scope of coverage carefully, noting which parts and systems are included.
Breakdown of Part and Labor Costs
A used car warranty typically covers both parts and labor associated with repairs. Understanding the proportion of each covered is vital. Some warranties might cover only parts, while others might include labor costs. If a component needs replacement, the warranty should cover both the cost of the part and the cost of the labor to install it. For example, a warranty covering a major component replacement might include the cost of the part and the labor needed to install it.
Cost Comparison Table
| Potential Repair | Estimated Cost | Warranty Cost | Warranty Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine Replacement | $3,000 | $1,000 | High |
| Transmission Repair | $2,500 | $750 | High |
| Electrical System Repair | $1,500 | $500 | Moderate |
| Minor Component Repair | $500 | $200 | Low |
This table illustrates a potential cost comparison between potential repairs and a warranty. Note that these are estimates and actual costs can vary.
Analyzing Warranty Coverage

Used car warranties, while offering potential protection, come with specific terms and conditions. Understanding these details is crucial to avoid unpleasant surprises down the road. Knowing what’s covered and excluded can help you make an informed decision about the value of a particular warranty.
Comprehensive knowledge of warranty coverage allows you to assess the true value of the protection offered. This includes understanding common exclusions, determining coverage criteria for repairs, and comparing various warranty providers to find the best fit for your needs. Identifying potential pitfalls and hidden costs is essential for making an informed purchasing decision.
Common Exclusions in Used Car Warranties
Used car warranties often have exclusions that limit coverage. These exclusions can be categorized based on factors like wear and tear, normal maintenance, accidents, or specific components. Knowing these limitations is key to making an informed decision.
- Wear and Tear: Items that naturally degrade over time due to normal use, such as tires, brakes, and upholstery, are typically excluded. Warranties typically only cover pre-existing defects, not routine maintenance or deterioration from typical use.
- Modifications and Repairs: Any modifications or repairs performed by an unauthorized mechanic or service provider can void a warranty, as can damage resulting from improper use or accidents.
- Damage from Accidents: Accidents are frequently excluded from coverage. This exclusion applies to damage resulting from collisions, rollovers, or other accident-related events. Some warranties might cover pre-existing defects, but not damage caused by an accident.
- Normal Maintenance: Routine maintenance items like oil changes, tire rotations, and filter replacements are typically excluded. These are considered part of regular vehicle upkeep and are not covered under warranty.
- Cosmetic Damage: Damage to the vehicle’s exterior, such as scratches or dents, is generally not covered by a used car warranty, unless it is related to a pre-existing defect.
Determining Coverage for Repairs
Determining if a repair is covered under a warranty often involves reviewing the warranty document. Look for specific details about the covered components, time limits, and any exclusions.
- Warranty Document Review: The warranty document is your primary reference. Carefully examine the terms and conditions to understand what is covered and excluded. Look for explicit definitions of “defect,” “repair,” and “damage.”
- Repair Description: Provide a detailed description of the repair needed. This description should include the symptoms, the affected parts, and any relevant history of the issue. This will assist in determining if the problem falls under the warranty’s coverage.
- Mechanic’s Assessment: Consult with a trusted mechanic to assess the nature of the problem. A mechanic’s assessment can help determine if the repair is due to a pre-existing defect covered by the warranty, or if it’s a result of wear and tear or damage.
Covered and Excluded Repair Examples
Examples of covered and excluded repairs can illustrate the complexities of warranty coverage.
- Covered Repair Example: A pre-existing defect in the engine’s cooling system that leads to a leak. This is a defect in a component and is covered under the warranty.
- Excluded Repair Example: A cracked windshield due to a rock chip. This is considered damage from an external event and is not covered under the warranty.
- Excluded Repair Example: Replacement of worn-out brake pads. This is considered normal wear and tear and is not covered.
Comparing Warranty Providers
Different warranty providers offer varying levels of coverage and terms. Consider factors like the scope of coverage, the repair process, and the provider’s reputation when choosing a warranty.
| Warranty Provider | Coverage Details | Repair Process | Reputation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Often comprehensive, covering specific components. | Directly managed by the manufacturer or its network. | Generally reliable but may have long wait times. |
| Third-Party | Variable coverage; some offer broader coverage. | Often involves a third-party claims process. | Reputation varies significantly; research is crucial. |
Potential Pitfalls and Hidden Costs
Hidden costs and potential pitfalls can be associated with used car warranties. Be aware of these factors to make a sound decision.
- High Premiums: Warranties can be expensive, particularly for older vehicles or those with a high-risk history.
- Limited Coverage: Some warranties might have significant exclusions, potentially leaving you responsible for many repairs.
- Hidden Fees: Look out for deductibles, administration fees, or other hidden costs that can significantly impact the total cost.
Assessing Value Proposition
A used car warranty can be a valuable tool in protecting your investment and potentially saving you significant money. However, its true value depends on various factors, including the vehicle’s age, mileage, and the specific terms of the warranty. Carefully evaluating the warranty’s value proposition is crucial to making an informed decision.
Situations Where a Warranty is Beneficial
Understanding when a warranty makes sense is key to maximizing its value. A warranty can be particularly beneficial in situations where the vehicle is likely to require substantial repairs in the near future, or where the cost of repairs without warranty coverage would be substantial.
- Vehicles with high-maintenance components (like transmissions or engines) or with a known history of frequent repairs benefit from warranty coverage. This is especially true for older models or vehicles that have already undergone significant wear and tear. This helps to mitigate potential repair expenses.
- A used car warranty provides peace of mind, especially for buyers unfamiliar with the car’s mechanical history. It minimizes the risk of unexpected repair bills.
- A warranty can protect buyers from potentially costly repairs on critical components, such as the engine, transmission, or electrical systems. This is particularly relevant when the vehicle is still under a manufacturer’s or extended warranty period, but the coverage has been transferred to the new owner.
- Warranties can be beneficial for vehicles with high-mileage or those approaching the age limit where major repairs are more likely. This is due to the increased likelihood of component failures with higher mileage and age.
Circumstances Where a Warranty Might Not Be Worth the Cost
Not every used car warranty is a worthwhile investment. Consider these factors before committing to a warranty.
- A well-maintained vehicle with a clean repair history and low mileage might not require a warranty. This is because the probability of costly repairs is lower.
- If the vehicle’s value is relatively low, a warranty might not be cost-effective compared to the potential savings. For example, a basic used vehicle with a low-price tag might have a warranty with minimal coverage, making the premium cost more than the expected repair savings.
- A warranty with limited coverage or a short duration may not offer sufficient protection against potential repair costs. The terms of the warranty should be scrutinized to ensure the scope of coverage meets the needs of the buyer.
Relationship Between Car Price and Warranty Value
The price of the used car plays a significant role in determining the value of the warranty. A more expensive vehicle usually warrants a higher potential repair cost, justifying a more comprehensive warranty.
- Higher-priced vehicles often come with more complex systems and higher-value components, potentially resulting in greater repair costs. A comprehensive warranty is more crucial for these vehicles.
- The warranty price should be proportionate to the price of the car and the anticipated repair expenses. A high-priced warranty for a low-priced vehicle may not be a sound investment.
Warranty Savings Scenarios
Warranties can save substantial money on repairs, as seen in the following example.
| Scenario | Potential Repair Cost | Warranty Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Engine replacement (high-mileage car) | $5,000 | Warranty covers 100% of the cost. |
| Transmission rebuild | $2,500 | Warranty covers 80% of the cost. |
| Electrical system repair | $1,200 | Warranty covers 50% of the cost. |
Unexpected Expenses Without a Warranty
Without a warranty, unforeseen repair expenses can quickly deplete savings and create financial stress.
- A sudden breakdown or unforeseen mechanical issue can lead to substantial and unexpected repair costs, potentially leading to significant financial burdens.
- The lack of a warranty can lead to substantial repair expenses that were not anticipated or budgeted for, which can be a serious financial risk for the vehicle owner.
Practical Considerations
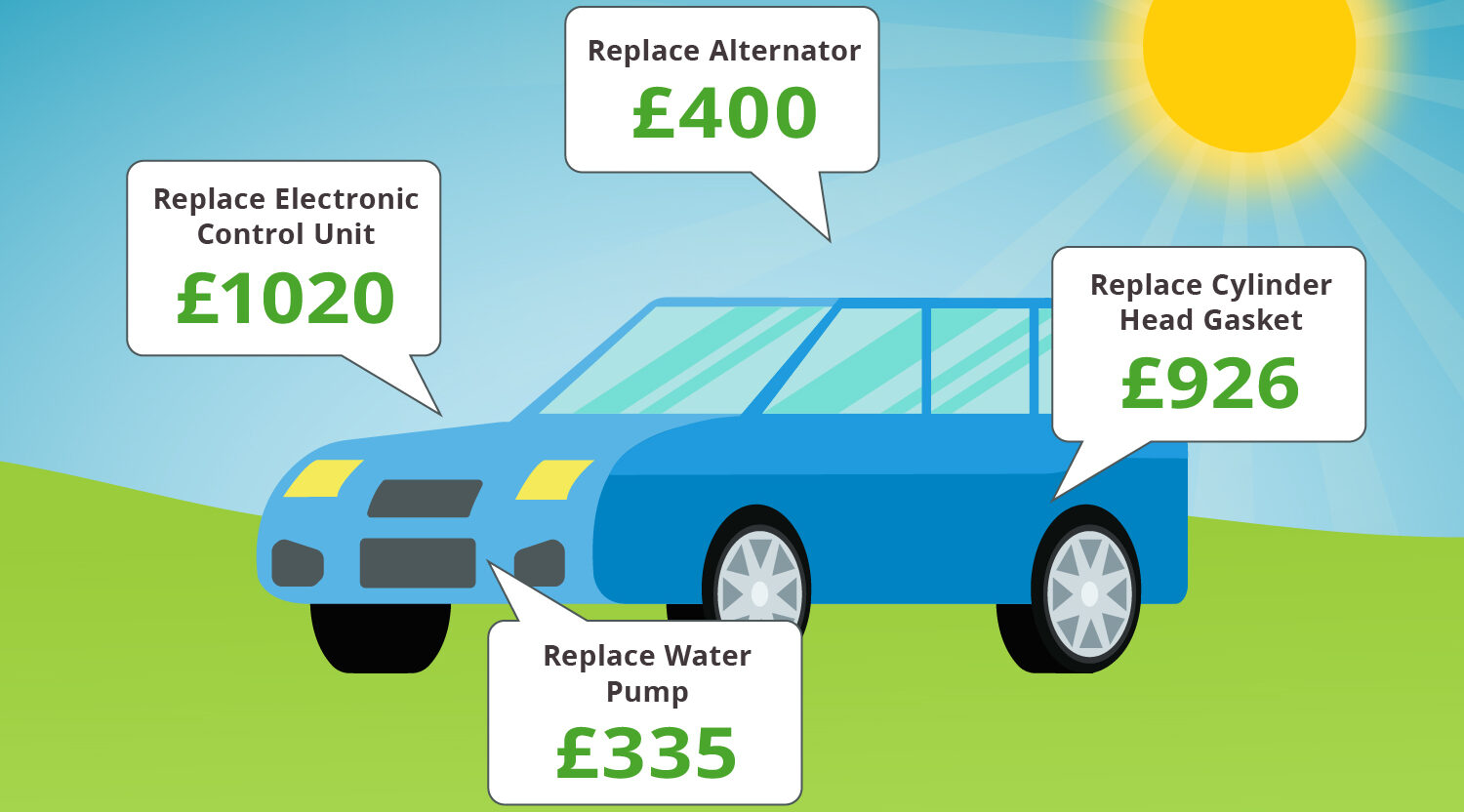
Purchasing a used car warranty can seem daunting, but the process is straightforward once you understand the steps involved. Knowing how to navigate the claim process, find reputable providers, and compare quotes empowers you to make an informed decision. This section details the practical aspects of securing and utilizing a used car warranty.
Purchasing a Used Car Warranty
Securing a used car warranty typically involves contacting a provider directly, either online or by phone. Many providers offer various coverage options, from basic repairs to comprehensive protection. You’ll need to furnish details about the vehicle, including its make, model, year, mileage, and any pre-existing conditions. Be prepared to provide documentation, such as the vehicle’s title and service history. This initial step ensures the warranty accurately reflects the vehicle’s condition and aligns with your needs.
Making a Warranty Claim
The claim process typically begins with notifying the warranty provider of the issue. A detailed description of the problem, including symptoms, dates, and relevant information, is crucial. Documentation, such as repair estimates and photos, significantly aids the claims process. Providers may require you to take the vehicle to an authorized repair facility, or they may offer a network of approved mechanics. Maintaining clear communication with the provider throughout the claim process is essential.
Finding Reliable Used Car Warranty Providers
Finding reputable used car warranty providers requires thorough research. Check online reviews and ratings from previous customers. Look for providers with a strong track record of honoring claims and offering excellent customer service. Providers with a clear and concise policy document, transparent claim procedures, and a customer support team readily available to answer questions are preferable. Reputable providers typically offer clear details regarding their coverage, exclusions, and claim process.
Comparing Warranty Quotes
Comparing quotes from different providers is essential to securing the best value. Carefully analyze the coverage details, including the types of repairs covered, the maximum payout amount, and any exclusions. Consider the provider’s reputation and customer reviews alongside the financial terms. By comparing quotes side-by-side, you can identify the warranty that best meets your specific needs and budget.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Warranty Claims
A successful warranty claim typically involves a clear, well-documented issue and a provider who promptly processes the claim. For example, a customer experiencing a faulty engine reported the issue immediately, provided repair estimates, and maintained clear communication. This resulted in a smooth and timely claim settlement. An unsuccessful claim, however, often stems from a lack of proper documentation, delayed reporting, or issues falling outside the warranty coverage. For example, a customer reported a problem weeks after the warranty expiration date, making the claim ineligible.
Warranty Provider Claim Procedures (Example)
| Provider | Claim Procedure |
|---|---|
| Warranty Direct | Submit a claim form online, provide repair estimates, and schedule an inspection with an approved mechanic. |
| Reliable Auto Protection | Contact customer support, provide details of the issue, and receive a claim number. Provide documentation for repair estimates and inspection. |
| Secure Car Care | Submit an online claim, attaching photos and repair estimates. The provider will contact a network mechanic for inspection. |
Illustrative Examples
Used car warranties can significantly impact the financial aspects of a purchase. Understanding the potential benefits and risks associated with different scenarios is crucial for making informed decisions. This section provides illustrative examples to demonstrate the value proposition of a warranty, highlighting the potential pitfalls of purchasing a used car without one.
Used Car with Warranty: A Case Study
A 2017 Honda Civic, with 50,000 miles, is listed for sale. The seller offers a 12-month/12,000-mile powertrain warranty. This warranty covers the engine, transmission, and associated components. If, within the warranty period, the vehicle experiences a significant mechanical issue, such as a failing transmission, the buyer can have the repair performed at no cost (minus any applicable deductibles). This protects the buyer from the substantial expense of a major repair, potentially saving thousands of dollars. The warranty provides peace of mind, allowing the buyer to focus on the vehicle’s overall condition rather than anticipating costly repairs.
Used Car without Warranty: A Case Study
A 2015 Toyota Camry, with 80,000 miles, is listed for sale without a warranty. While the vehicle may appear in excellent condition, the lack of warranty exposes the buyer to potential financial risks. If a major component, such as the water pump, fails unexpectedly, the buyer would be responsible for the entire repair cost. The cost of a water pump replacement, along with labor, could easily exceed several hundred dollars, impacting the overall affordability and value of the car. This scenario underscores the importance of considering the potential costs associated with unforeseen mechanical issues when purchasing a used car without a warranty.
Impact of Major Repair without Warranty
Imagine a used car without a warranty experiences a catastrophic engine failure. The cost of a new engine replacement, labor, and potential additional damages (like transmission or other component damage) could easily reach several thousand dollars. This unexpected expense can significantly impact the buyer’s budget and may even render the vehicle undrivable. A warranty would have shielded the buyer from this financial burden.
Warranty Protection against Substantial Expenses
A warranty can act as a safety net, mitigating the risk of significant repair costs. Consider a used car with a comprehensive warranty covering various components. If a critical part like the AC compressor malfunctions, the repair expense is covered by the warranty. This avoids the buyer having to absorb the total cost of the repair, potentially saving a substantial amount of money.
Comparison of Two Similar Used Cars
Consider two identical 2018 Subaru Impreza models, both with 70,000 miles. Car A comes with a 6-month/6,000-mile powertrain warranty, while Car B has no warranty. Assuming a major repair is required within the warranty period for Car A, the buyer is protected from the cost. Car B’s buyer, however, would bear the full expense. This highlights the financial difference between purchasing a vehicle with and without a warranty. This clear contrast emphasizes the financial security provided by a warranty.
Visual Representation of Warranty Aspects
Imagine a graphic displaying the various components covered by a used car warranty. This graphic could illustrate the engine, transmission, and other critical parts. The warranty period is shown in a clear, concise manner. A second graphic could illustrate a breakdown of potential repair costs for a similar car with and without a warranty. These visual aids help buyers quickly assess the value proposition of a used car warranty.