Introduction to Used Car Finance Calculators
Used car finance calculators are invaluable tools for anyone considering purchasing a used vehicle. They streamline the complex process of determining affordable financing options, allowing potential buyers to explore various loan scenarios and make informed decisions. These calculators leverage mathematical formulas to estimate monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan costs, significantly aiding in budgeting and comparison shopping.
These calculators are particularly useful for those unfamiliar with the intricacies of financing or who want to compare different loan options quickly. They empower consumers to understand the financial implications of various loan terms and interest rates before committing to a purchase.
Key Features of Used Car Finance Calculators
Used car finance calculators typically provide a comprehensive overview of financing options. They facilitate comparisons of different loan terms and interest rates, empowering buyers to select the most favorable financing arrangement. This feature is crucial in navigating the complexities of the used car market, where numerous financing options and rates are often available.
- Loan Amount: The initial amount borrowed for the car purchase. This value is directly correlated to the price of the vehicle, and any down payment made will reduce this figure.
- Interest Rate: The percentage rate charged on the loan. Different lenders and loan terms will typically have different interest rates. The interest rate significantly impacts the total cost of the loan.
- Loan Term: The duration of the loan repayment period, typically expressed in months. A longer loan term results in lower monthly payments but increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Down Payment: The upfront payment made by the buyer. A higher down payment reduces the loan amount and can lead to more favorable loan terms and lower monthly payments.
- Monthly Payment: The estimated amount payable each month. This is a crucial figure for budgeting and assessing the affordability of the loan.
- Total Interest Paid: The overall interest cost accumulated over the entire loan term. This is a significant factor in determining the true cost of the loan.
Importance of Using Calculators for Informed Decision-Making
Using a used car finance calculator is crucial for informed decision-making. It allows consumers to thoroughly analyze different financing scenarios and understand the complete cost of a loan, including interest charges. This process helps prevent overspending and ensures the chosen financing plan aligns with individual financial capabilities.
A well-designed calculator can provide detailed breakdowns of monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan costs. This transparency allows for better budgeting and avoids potentially costly mistakes.
Example Input Fields
| Input Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Loan Amount | The total amount borrowed for the vehicle. For example, $15,000. |
| Interest Rate | The annual percentage rate (APR) charged on the loan. For example, 6%. |
| Loan Term | The duration of the loan in months. For example, 60 months. |
| Down Payment | The upfront payment made by the buyer. For example, $2,000. |
Different Types of Used Car Financing Options
Securing financing for a used car involves exploring various options, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these choices is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. A well-researched approach to financing can significantly impact the overall cost and terms of your used car purchase.
Loan Financing
Loan financing is a common approach for used car purchases. It involves borrowing a specific amount of money from a lender (bank, credit union, or online lender) to buy the car. Repayment occurs in installments over a predetermined period, typically ranging from a few months to several years, with interest added to the principal amount. This allows you to own the car outright after the loan is paid off.
Lease Financing
Leasing a used car is an alternative to purchasing it outright. It’s a contractual agreement where you pay a monthly fee for the use of the car for a specified period (typically shorter than loan terms). At the end of the lease, you return the car to the lessor. This option can be attractive for those who prefer lower upfront costs and want to avoid the full financial commitment of ownership. It’s important to understand the potential for penalties if the vehicle’s condition deviates significantly from the agreed-upon terms.
Dealer Financing
Dealerships often offer financing options through in-house lenders or partner financial institutions. This can be convenient as the process is handled within the dealership. However, the terms and interest rates might not always be the most competitive compared to other options. It’s wise to compare dealer financing offers with other available options to ensure you’re getting the best possible deal.
Comparing Financing Options
| Option Type | Benefits | Drawbacks | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loan Financing | Own the car outright after payment; potentially lower monthly payments for longer terms; greater flexibility in repayment terms. | Interest accrues over the loan period; requires good credit history for favorable interest rates; fixed monthly payments can be challenging during unexpected financial changes. | Good credit score; stable income; ability to demonstrate repayment capacity. |
| Lease Financing | Lower upfront costs; potentially lower monthly payments compared to loan financing for the same vehicle; flexibility in exchanging the vehicle if needed. | Do not own the vehicle at the end of the lease; mileage restrictions; penalties for exceeding mileage limits or causing damage; potential for higher total cost if you decide to purchase the vehicle at the end of the lease. | Good credit score; ability to demonstrate financial stability; willingness to adhere to the lease terms. |
| Dealer Financing | Convenience of having the process handled within the dealership; potentially faster processing time. | Interest rates might not be as competitive as other options; limited comparison options for optimal rates; might be tied to specific dealerships or brands. | Good credit score; stable income; willingness to accept the specific terms offered by the dealership. |
Example Financing Options
A used sedan priced at $15,000 might have financing options like:
- Loan (Option 1): 60-month loan with an interest rate of 7%. Monthly payment would be approximately $280, with a total cost of $20,000.
- Lease (Option 2): 36-month lease with a monthly payment of $350, including maintenance. The lease does not include the purchase of the vehicle.
- Dealer Financing (Option 3): 48-month loan with an interest rate of 8%, offered by the dealership. The monthly payment would be roughly $350, with a total cost of $18,500.
These examples illustrate the variability in terms and conditions. Comparing various financing options is essential to make a well-informed decision that aligns with your financial situation.
Factors Affecting Used Car Loan Costs
Understanding the factors influencing used car loan costs is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Different variables play a significant role in determining the interest rate and monthly payment, ultimately impacting the overall cost of financing. Careful consideration of these factors can help borrowers secure the most favorable loan terms possible.
Credit Score Impact
A strong credit score significantly influences interest rates. Lenders assess creditworthiness to gauge the borrower’s likelihood of repaying the loan. Higher credit scores typically translate to lower interest rates, reducing the overall cost of financing. Conversely, borrowers with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates, increasing the monthly payment and total loan cost. For example, a borrower with a credit score of 750 might secure a lower interest rate (e.g., 4.5%) compared to a borrower with a score of 650 (e.g., 7%).
Loan Amount and Term Influence
The loan amount and term directly impact the monthly payment and overall cost of the loan. A larger loan amount typically results in a higher monthly payment and potentially a higher interest rate. A longer loan term reduces the monthly payment but increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan. For instance, a $15,000 loan for a 5-year term might have a lower monthly payment than a $15,000 loan for a 7-year term, but the total interest paid would be higher for the longer term.
Down Payment Impact on Loan Terms
A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, thereby lowering the monthly payment and potentially securing a lower interest rate. This directly impacts the loan terms, as a smaller loan amount typically leads to better terms. For example, a $5,000 down payment on a $20,000 car reduces the loan amount to $15,000, potentially leading to a lower interest rate and a lower monthly payment.
Interest Rate Impact on Monthly Payments
Interest rates directly affect the monthly payment for a fixed loan amount and term. Higher interest rates result in higher monthly payments, while lower interest rates lead to lower monthly payments. The following table illustrates the impact of different interest rates on monthly payments for a $10,000 loan with a 5-year term.
| Interest Rate (%) | Monthly Payment |
|---|---|
| 3.0 | $190.12 |
| 4.0 | $200.06 |
| 5.0 | $210.15 |
| 6.0 | $220.39 |
| 7.0 | $230.81 |
These figures are estimates and may vary depending on the lender and other factors.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions

Navigating the complexities of used car financing requires a thorough understanding of the key loan terms. Knowing how these terms are calculated and their impact on the overall cost is crucial for making informed decisions. This section will delve into the meaning of crucial loan terms, demonstrate their calculation, and illustrate their effect on your monthly payments and total loan cost.
Loan terms are the specific conditions Artikeld in a financing agreement. These terms dictate the cost and duration of the loan. Understanding these elements is essential to ensure you’re getting the best possible deal. A clear understanding of these terms helps you avoid potential pitfalls and negotiate favorable financing options.
Key Loan Terms Explained
Loan agreements contain several key terms, each playing a role in determining the total cost and repayment schedule. Understanding these elements empowers you to make well-informed choices.
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): The APR represents the annual cost of borrowing, encompassing both the interest rate and other fees. It’s a standardized measure used to compare different loan offers. APR considers all financing charges, providing a comprehensive picture of the loan’s true cost. A higher APR results in a greater overall loan cost.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate is the percentage of the loan amount charged as interest over a specific period. It’s a key component of the APR. Interest rates are often expressed as a percentage per annum (e.g., 5%). A lower interest rate typically translates to lower monthly payments and a lower total cost of the loan.
- Loan Term: The loan term is the duration for which the loan is taken out, typically expressed in months or years. A longer loan term usually results in lower monthly payments but a higher total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Monthly Payment: The monthly payment is the fixed amount due each month to repay the loan, including principal and interest. It’s a critical factor in determining your affordability. A longer loan term or a higher interest rate leads to a higher monthly payment.
Calculating Loan Costs
The calculation of loan costs involves several factors. A key aspect is understanding how the APR, interest rate, loan term, and monthly payment interact. The interest rate is a percentage of the principal amount charged over time. This interest accumulates and is added to the principal amount over the life of the loan.
The formula for calculating monthly payment (M) is often given as: M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1] where:
P = Principal loan amount
i = Monthly interest rate (annual interest rate divided by 12)
n = Total number of payments (loan term in months)
Loan Term Examples
Let’s consider examples of different loan terms with varying interest rates to illustrate how these factors affect the overall loan cost.
| Loan Term (months) | Interest Rate (%) | Monthly Payment (example $10,000 loan) | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | 5.0 | $310.72 | $525.24 |
| 48 | 5.0 | $235.45 | $1024.68 |
| 60 | 5.0 | $195.11 | $1573.80 |
| 36 | 7.5 | $336.24 | $811.00 |
These examples demonstrate how a longer loan term results in lower monthly payments but increases the total interest paid. Conversely, a higher interest rate leads to higher monthly payments and a greater overall cost.
Benefits of Using a Used Car Finance Calculator
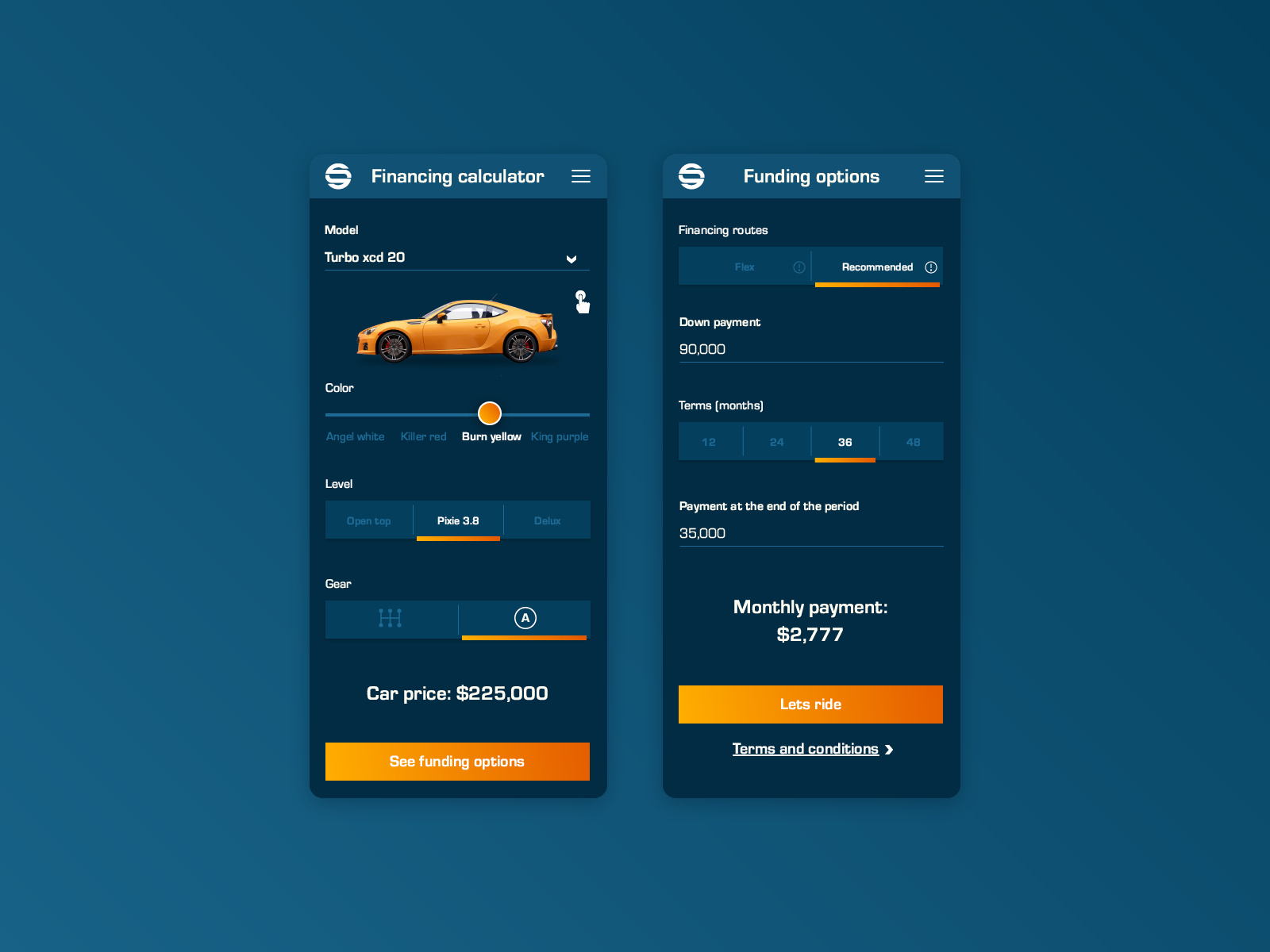
Utilizing a used car finance calculator offers significant advantages over manual calculations, streamlining the process and providing a clearer picture of the true cost of ownership. These tools are indispensable for making informed decisions when navigating the complexities of financing a used vehicle.
Accurate estimations of the true cost of ownership are crucial for responsible budgeting. A finance calculator can accurately reflect the total cost, encompassing not only the principal loan amount but also interest, fees, and potential insurance costs. This detailed breakdown is often difficult to achieve through manual calculations, which can lead to oversights and financial strain.
Streamlined Cost Estimation
A used car finance calculator automatically calculates the total amount financed, interest accrued, and other fees. This automated process eliminates the need for complex calculations and reduces the risk of errors. For example, a borrower considering a $15,000 used car loan with a 5% interest rate and a 60-month term can quickly ascertain the total cost using a calculator. Manual calculations, while possible, would be time-consuming and prone to errors, especially with varying loan terms and interest rates.
Time-Saving Advantages
The time-saving benefits of a used car finance calculator are substantial. Instead of spending hours meticulously calculating loan amounts, interest, and fees, a user can obtain precise results in seconds. This efficiency is especially valuable for individuals with limited time or those needing quick decisions on financing options. A quick calculation can save hours, enabling potential buyers to focus on other important aspects of the car-buying process.
Comparative Analysis of Financing Options
Used car finance calculators facilitate the comparison of different financing options. Users can input various loan terms and interest rates to instantly see how different deals impact their overall costs. This comparative analysis allows for informed choices and helps identify the most cost-effective financing option available. For instance, a borrower can quickly compare loans from different lenders, considering factors like interest rates, loan terms, and fees. This ability to compare options ensures a sound decision-making process.
Accurate Cost Breakdown
The calculator’s ability to break down the loan’s total cost into individual components—principal, interest, taxes, and fees—is essential for transparency. This detailed breakdown allows consumers to understand the true cost of ownership, which can help them avoid surprises and budget effectively. This transparency is invaluable for consumers who may not be familiar with the intricacies of used car financing.
Comparison of Different Used Car Finance Calculators
Navigating the diverse landscape of online used car finance calculators can be daunting. Each calculator presents a unique set of features and functionalities, impacting the accuracy and ease of use. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions when securing financing for your next used vehicle. This section will delve into the comparative analysis of various calculators, examining their strengths and weaknesses.
Varying Features and Functionalities
Different used car finance calculators offer a range of features. Some calculators provide basic calculations, focusing primarily on loan amounts and monthly payments. More advanced calculators may incorporate additional functionalities, such as comparing interest rates from different lenders, estimating the total cost of ownership, and calculating potential loan approvals based on credit scores. These expanded features can significantly assist users in making well-rounded financial decisions.
Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of used car finance calculators vary considerably. Factors such as the data source used and the underlying algorithms significantly impact the precision of the calculations. Calculators that incorporate real-time data from multiple lenders tend to provide more accurate and reliable estimations compared to those relying on static or outdated information. Furthermore, the calculator’s ability to account for various fees and charges associated with the loan is a critical determinant of accuracy.
Online vs. Offline Calculators
Online calculators generally offer greater accessibility and flexibility. Users can access these tools from any location with an internet connection, enabling quick comparisons of financing options. Offline calculators, typically found in dealerships or financial institutions, often provide personalized consultations. However, online calculators can be more comprehensive in their scope, offering features like real-time interest rate comparisons from multiple lenders, and facilitating the calculation of various loan scenarios.
Comparative Analysis of Calculators
| Calculator | Features | Ease of Use | Accuracy | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculator A | Basic loan calculations, monthly payments | Easy to use, straightforward interface | Average, limited data sources | Free |
| Calculator B | Loan amounts, monthly payments, interest rate comparison (limited), loan term variations | Moderate, requires some understanding of inputs | Good, uses a wider range of data | Free |
| Calculator C | Comprehensive loan calculations, interest rate comparison (multiple lenders), total cost of ownership estimation, loan approval probability estimator | Moderate to difficult, may require more technical knowledge | High, real-time data integration, multiple data sources | Free/Subscription-based |
| Dealership Calculator | Loan calculations, often tied to specific lender offerings | Easy, tailored to dealership environment | Average, potentially biased towards dealership-preferred lenders | Free |
The table above presents a simplified comparison. Real-world experiences may differ based on the specific calculator and its functionalities. Always verify the source of the data and the algorithms used to ensure accuracy. Furthermore, carefully review the terms and conditions of any loan offered through a calculator to understand all associated fees and costs. This comprehensive evaluation will assist you in making informed decisions about financing your used car.
Tips for Using Used Car Finance Calculators Effectively

Maximizing the benefits of used car finance calculators requires a strategic approach. These tools can significantly streamline the financing process, allowing you to compare various options and make informed decisions. Understanding how to use these calculators effectively is crucial for securing the best possible loan terms.
Using a used car finance calculator effectively involves inputting accurate data, meticulously reviewing the results, and strategically comparing multiple offers. By following these tips, you can significantly enhance your chances of securing favorable financing terms.
Inputting Accurate Data for Precise Results
Accurate data entry is paramount for obtaining precise results from a used car finance calculator. Inaccurate information can lead to misleading estimates and potentially less favorable financing terms. Carefully consider the following factors:
- Vehicle Price: Enter the exact price of the used vehicle, including any fees or taxes.
- Down Payment: Input the amount you plan to pay upfront as a down payment. This will directly impact your loan amount and monthly payments.
- Loan Term: Specify the desired loan duration (e.g., 24, 36, or 60 months). Longer terms typically result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs.
- Interest Rate: Input the estimated or quoted interest rate. This is often dependent on creditworthiness and loan terms, so research is key.
- Credit Score: While some calculators don’t directly require credit score input, understanding your credit score’s impact on interest rates is essential. A higher credit score often leads to lower interest rates.
Double-Checking Results and Understanding Loan Terms
Double-checking results is crucial to avoid errors and ensure you understand the loan terms thoroughly. This step involves reviewing the calculated monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of the loan.
- Detailed Loan Summary: Carefully review the summary provided by the calculator. Pay close attention to the total interest amount, monthly payment, and the total cost of borrowing. Verify these figures against your understanding of the loan parameters.
- Comparison to Other Offers: Compare the results from different calculators to ensure consistency. If substantial discrepancies arise, investigate the potential reasons for these differences.
- Understanding Fees: In addition to the interest, some financing options might include additional fees (e.g., origination fees, processing fees). Ensure these are clearly included in the final loan amount.
Strategies for Comparing Multiple Loan Offers
Comparing multiple loan offers is essential for securing the most favorable terms. Using a spreadsheet or a dedicated comparison tool can help you organize and analyze different financing options.
- Creating a Spreadsheet: Create a spreadsheet to organize data from various loan offers. Include details such as interest rate, loan term, monthly payment, and total cost of the loan. This organized approach allows for easy comparison.
- Analyzing Interest Rates and Loan Terms: Compare interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees for different financing options. Identify patterns and trends in the data to discern the best fit.
- Seeking Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor or a loan officer to get professional guidance on comparing multiple offers and understanding the intricacies of each loan.
Illustrative Scenarios and Case Studies
Used car finance calculators are powerful tools for navigating the complexities of auto financing. By applying these calculators to specific situations, you can effectively evaluate different financing options and make informed decisions about your purchase. This section provides illustrative scenarios and case studies to demonstrate the practical application of these calculators.
Applying the Calculator to Varying Credit Scores
Understanding how credit scores influence loan terms is crucial. Different credit scores will result in different interest rates and loan terms. A used car finance calculator can model these scenarios. For example, a buyer with a strong credit score (750+) might qualify for a lower interest rate and a longer loan term compared to a buyer with a lower credit score (650-700). This difference in rates can significantly impact the total cost of the loan. A finance calculator can clearly display the monthly payments and total interest paid under various credit score scenarios.
Exploring Loan Amount Variations
The amount you borrow for a used car significantly affects the loan’s cost and terms. A calculator can project the impact of different loan amounts on monthly payments and the total interest paid. A larger loan amount typically results in higher monthly payments and a greater total interest paid over the loan’s duration. A calculator will clearly show these varying costs.
Case Study: Finding the Best Financing Option
Imagine a customer wanting to purchase a used SUV priced at $25,000. They have a credit score of 720 and wish to finance the entire purchase amount. Using a used car finance calculator, they can explore various loan terms, from 36 months to 72 months, and corresponding interest rates. The calculator will display the monthly payments, total interest, and total loan cost for each option. By comparing the different financing options, the customer can select the one that best aligns with their budget and financial goals.
Step-by-Step Example
A responsive table can effectively demonstrate how a used car finance calculator handles different scenarios. By inputting various loan amounts, loan terms, and interest rates, the user can see the resulting monthly payments.
| Loan Amount | Loan Term (Months) | Interest Rate (%) | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $20,000 | 36 | 6.5 | $650.00 | $1,500.00 |
| $20,000 | 48 | 6.5 | $450.00 | $2,200.00 |
| $25,000 | 48 | 7.0 | $600.00 | $2,800.00 |
This table clearly illustrates the impact of loan amount, loan term, and interest rate on the monthly payment and total interest paid. The user can quickly compare different options and identify the best fit for their specific needs. This kind of detailed analysis is essential for making informed financial decisions.