Factors Influencing Used Car Rates
Used car prices are a dynamic reflection of a complex interplay of economic forces. Understanding these forces is crucial for both consumers and sellers navigating the market. From the impact of supply and demand to the subtle influence of manufacturing defects, a multitude of factors converge to determine the final price tag. This analysis delves into the key economic drivers shaping used car values.
Economic Factors Affecting Used Car Prices
The used car market is profoundly influenced by macroeconomic conditions. Inflation, interest rates, and broader economic trends all play a significant role in setting the stage for used car pricing. Fluctuations in these factors directly affect consumer purchasing power and the overall demand for vehicles.
Supply and Demand Dynamics in the Used Car Market
Supply and demand are fundamental economic forces impacting used car prices. A shortage of available vehicles, whether due to decreased production or increased consumer demand, can drive up prices. Conversely, an abundance of used cars on the market often results in lower prices. This interplay of supply and demand is constantly evolving, making used car pricing unpredictable at times.
Inflation and Interest Rates’ Influence on Used Car Rates
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. As inflation rises, the cost of essential goods, including used cars, typically increases. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging consumers from purchasing vehicles, which in turn can affect market prices.
Impact of Manufacturing Defects and Recalls on Used Car Values
Manufacturing defects and recalls can significantly impact the value of a used vehicle. Vehicles with known issues, particularly those subject to recalls, often see a depreciation in value. The perceived risk associated with these issues influences the pricing.
Role of Vehicle Mileage and Condition in Used Car Pricing
Mileage and condition are paramount factors in determining a used car’s value. Vehicles with low mileage and excellent condition tend to command higher prices. Conversely, high mileage and visible signs of wear and tear usually lead to lower prices. This correlation is generally consistent across various models and makes.
Influence of Vehicle Age on Market Value
The age of a vehicle plays a significant role in its market value. Generally, newer vehicles hold their value better than older ones. Depreciation, influenced by technological advancements and model changes, often accelerates with increasing age.
Correlation Between Factors and Used Car Rates
| Factor | Description | Impact on Rate | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mileage | Number of miles driven | Typically negatively impacts rate | 10,000 miles vs. 100,000 miles |
| Condition | Overall state of the vehicle | Higher condition leads to higher rate | Pristine vs. damaged |
| Year | Model year of the vehicle | Newer years generally fetch higher rates | 2023 vs. 2010 |
| Make/Model | Specific brand and model | Some models hold their value better | Toyota Camry vs. a specific sports car |
Used Car Market Trends
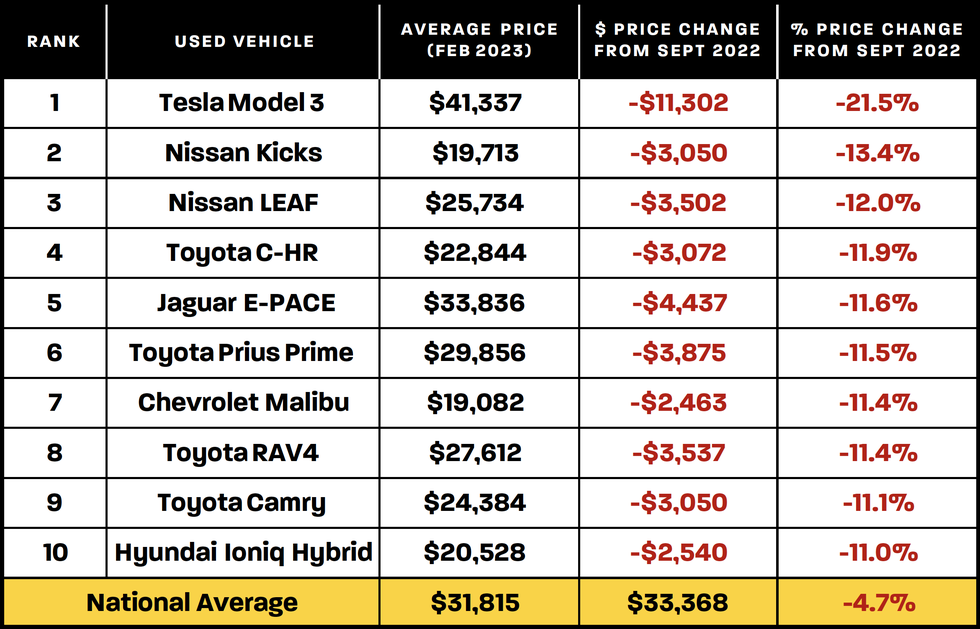
The used car market is a dynamic and complex ecosystem, influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding current trends and long-term projections is crucial for both consumers and businesses involved in the industry. This analysis delves into the current state of the used car market, examining the impact of global events, the relationship between new and used car sales, and regional price variations. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for navigating the fluctuating market and making informed decisions.
Current Trends in the Used Car Market
The used car market is currently experiencing a period of significant change. Increased demand from consumers seeking affordable options is a key driver, pushing prices upward. Simultaneously, supply chain disruptions and inventory shortages are contributing to price volatility, making it difficult to predict future rates. Consumer preferences are also evolving, with shifts in demand for specific models and brands influencing the market’s dynamics.
Long-Term Projections for Used Car Rates
Long-term projections for used car rates are inherently uncertain. While the current upward trend is likely to persist, future fluctuations are inevitable. Factors such as economic conditions, technological advancements, and consumer preferences will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of used car prices. For example, the adoption of electric vehicles might alter consumer demand, potentially impacting the resale value of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Impact of Global Events on the Used Car Market
Global events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, have significantly impacted the used car market. Supply chain disruptions during the pandemic limited the availability of new vehicles, pushing demand toward the used car market. Geopolitical uncertainties can further exacerbate these issues by affecting production and transportation costs, impacting the availability and pricing of used vehicles.
Relationship Between New Car Sales and Used Car Rates
The relationship between new car sales and used car rates is often inverse. When new car sales decline due to economic downturns or supply chain problems, the demand for used cars increases, leading to price escalation. Conversely, robust new car sales can decrease the demand for used vehicles, potentially moderating price increases.
Used Car Prices Across Different Regions
Used car prices vary significantly across different regions. Factors such as local economic conditions, demand, and availability of vehicles all contribute to the discrepancies. For example, regions with high demand and limited inventory may experience substantially higher used car prices compared to regions with lower demand and abundant supply.
Summary of Key Trends in the Used Car Market
| Trend | Description | Region | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Demand | High consumer interest in used cars, driven by affordability and limited new vehicle availability. | Nationwide | Rising prices across the board. |
| Supply Chain Issues | Disruptions in the supply chain impacting vehicle production and availability. | Globally | Price volatility and unpredictable fluctuations. |
| Inventory Shortages | Reduced number of vehicles available for sale in specific regions. | Specific regions | Significant price increases in affected areas. |
| Consumer Preferences | Changes in consumer preferences for specific car models and features. | Nationwide | Fluctuation in prices for specific models. |
Methods for Assessing Used Car Value

Determining the accurate value of a used car is crucial for both buyers and sellers. A precise assessment helps avoid overpaying or underselling, fostering trust and fairness in the transaction. Various methods exist, each with strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to understand the nuances of each approach.
Online Pricing Tools and Resources
Online resources provide a wealth of information for assessing used car values. Websites and mobile applications offer comprehensive databases, enabling comparisons of similar vehicles across various listings. These tools utilize algorithms to analyze data from numerous sources, including dealer inventories, private sales, and auction results. This aggregation allows users to see a broad spectrum of prices for specific models, years, and conditions, facilitating informed decision-making. Key features often include filtering options for specific criteria like mileage, features, and condition, enhancing the precision of the valuation process. For example, Edmunds and Kelley Blue Book (KBB) offer detailed reports with pricing information and comparative analysis.
Dealer Valuation
Dealerships employ experienced professionals to evaluate used cars. Their expertise stems from extensive knowledge of market trends, vehicle maintenance records, and pricing strategies. This specialized understanding allows them to assess a vehicle’s overall condition, factoring in wear and tear, mechanical soundness, and any potential issues. Dealer valuations often serve as a crucial benchmark for negotiating prices, although their assessments may sometimes reflect dealer profit margins. A dealer’s valuation might be higher than an independent appraisal to maximize their profit.
Private Party Negotiations
Private sellers often offer flexibility in pricing negotiations. Direct interaction allows buyers to discuss their needs and concerns, potentially leading to lower prices. However, successful negotiation requires strong bargaining skills and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s value. The ability to ascertain the vehicle’s condition, its market value, and to articulate a fair offer are crucial. For example, a buyer might negotiate a lower price for a vehicle with a minor mechanical issue or higher mileage.
Independent Appraisals
Independent appraisals provide objective evaluations conducted by certified appraisers. These professionals possess specialized training and expertise, enabling them to assess vehicles with neutrality and accuracy. Appraisals consider a broader range of factors beyond the dealer’s perspective, often encompassing detailed inspections and documented evaluations. These appraisals are particularly helpful for insurance claims, estate settlements, or legal disputes. However, independent appraisals are generally more expensive and time-consuming compared to other methods.
Comparison of Valuation Methods
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Marketplaces | Price comparisons from various sources | Broad range of options; readily accessible | Potentially inaccurate listings; inconsistent data quality |
| Dealer Valuation | Professional evaluation by a dealership | Expertise and experience; potentially faster process | May be biased towards dealer profit; limited objectivity |
| Private Party Negotiations | Directly negotiating with sellers | Potential for lower prices; flexibility in terms | Requires negotiation skills; potential for disputes |
| Independent Appraisals | Evaluation by a certified appraiser | Accuracy and objectivity; valuable for legal matters | Costly and time-consuming; less accessibility |
Impact of Different Factors on Used Car Prices

Used car prices are a complex interplay of numerous factors, making it difficult to predict the precise value of a vehicle. Understanding these influences is crucial for both buyers and sellers, enabling informed decisions and a realistic appraisal of market value. The interplay of condition, mileage, location, features, and model-specific characteristics significantly impacts the final sale price.
Vehicle Condition and Mileage
Vehicle condition and mileage are paramount in determining used car pricing. A well-maintained vehicle with low mileage commands a higher price compared to a vehicle with significant wear and tear or a high mileage count. This difference reflects the reduced maintenance and repair costs associated with a vehicle in better condition and lower mileage. Buyers are willing to pay a premium for a vehicle that is likely to require fewer future repairs and replacements.
Impact of Vehicle Features and Options
The features and options available on a used car significantly influence its market value. Higher-end features, such as advanced safety technology, premium sound systems, or upgraded interiors, can increase the asking price. The presence of desirable features often correlates with higher demand from potential buyers, leading to a higher price point.
Impact of Location on Used Car Pricing
Geographic location plays a substantial role in used car pricing. Demand, supply, and local economic conditions influence the price range for used vehicles. Areas with high demand or a limited supply of used vehicles often see higher prices compared to regions with more readily available options.
Regional Variations in Used Car Prices
Used car prices vary significantly across different regions. Economic conditions, local regulations, and cultural preferences contribute to these discrepancies. For example, a particular model of used car might command a higher price in a densely populated metropolitan area with a high demand for vehicles compared to a less populated rural area.
Factors Influencing Specific Model Pricing
Specific car models exhibit unique price trends, influenced by factors such as manufacturing quality, reliability ratings, popularity, and market demand. High demand for a particular model often drives up its price, while models with a reputation for issues might see lower prices. Furthermore, the model’s year of production, the presence of recalled parts, and the car’s specific trim level also affect the price.
Impact of Different Factors on Used Car Prices
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | Overall state of the vehicle (exterior, interior, mechanical) | Better condition, higher price; worse condition, lower price | A pristine, accident-free car vs. a car with significant body damage |
| Mileage | Number of miles driven | Lower mileage, higher price; higher mileage, lower price | A car with 10,000 miles vs. a car with 100,000 miles |
| Location | Region where the car is sold | Higher demand/lower supply, higher price; lower demand/higher supply, lower price | A car sold in a major city vs. a car sold in a rural area |
| Features/Options | Added extras (e.g., navigation, sunroof, leather seats) | More features, potentially higher price; fewer features, potentially lower price | A car with a premium sound system and navigation vs. a basic model |