Understanding Refinance Rates
Used car refinance rates represent the interest rate charged when a borrower seeks to replace an existing used car loan with a new one, often at a more favorable rate. This process allows for potential savings on monthly payments and overall loan costs. Refinancing can be advantageous if current market conditions or the borrower’s financial situation has improved since the original loan was taken out.
Refinancing is a strategic financial maneuver that can lead to significant cost reductions over the life of the loan. This process is driven by factors such as changes in interest rates, creditworthiness, or the desire for more favorable loan terms. Understanding these factors is crucial to making an informed decision about refinancing.
Factors Influencing Refinance Rates
Various factors play a crucial role in determining used car refinance rates. These factors directly impact the cost and terms of the new loan.
- Credit Score: A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate. Lenders assess creditworthiness to gauge the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. This assessment is crucial for determining the risk associated with extending credit.
- Loan Terms: The loan term, or the length of time it takes to repay the loan, impacts the monthly payment and overall interest paid. Shorter terms typically result in higher monthly payments but lower overall interest. Longer terms, conversely, lead to lower monthly payments but higher overall interest.
- Market Conditions: Fluctuations in prevailing interest rates and the overall economic climate significantly affect used car refinance rates. Periods of low interest rates often result in more attractive refinance options.
Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate Loans
Used car refinance loans can be either fixed-rate or variable-rate. The choice depends on the borrower’s risk tolerance and outlook on future interest rate movements.
- Fixed-Rate Loans: These loans maintain a constant interest rate throughout the loan term. This stability provides predictability in monthly payments, which is attractive to borrowers who prefer consistent financial obligations.
- Variable-Rate Loans: These loans have interest rates that fluctuate based on prevailing market conditions. These loans can offer potentially lower rates initially but may increase over time. Borrowers must be prepared for potential adjustments in their monthly payments.
Comparison with Traditional Loans
Refinancing a used car loan differs from obtaining a traditional used car loan in several aspects. Refinancing leverages existing credit history and assesses the possibility of better rates, while a traditional loan requires a fresh credit evaluation.
- Refinancing involves utilizing an existing loan to secure a new one at potentially more favorable terms. Traditional loans, conversely, require a new application and approval process.
- Refinancing usually targets lower interest rates, often based on improved creditworthiness or market conditions. Traditional loans have interest rates determined by prevailing market conditions and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
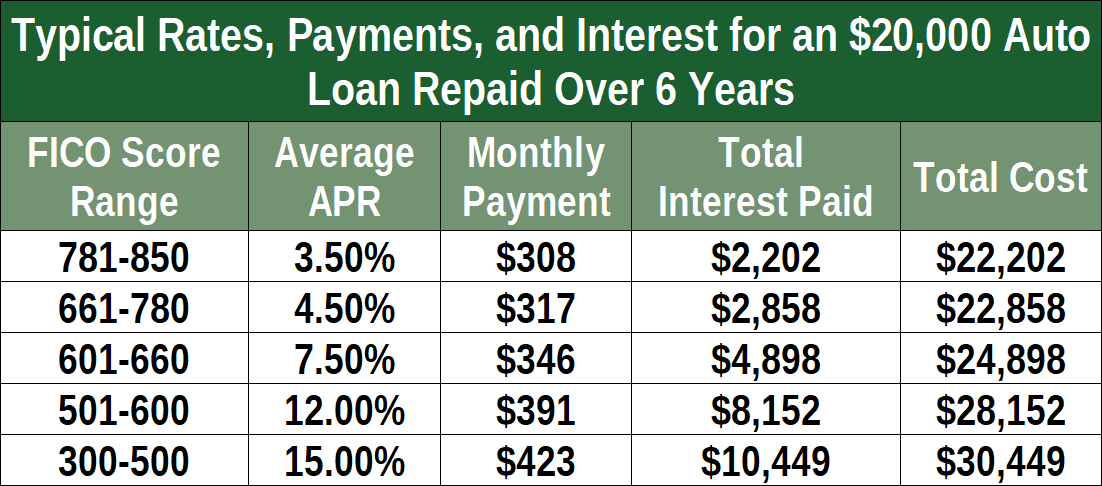
Average Refinance Rates by Credit Score
The following table provides a general overview of average used car refinance rates for different credit scores. These rates are estimates and may vary based on specific lenders and loan terms.
| Credit Score | Average Refinance Rate (estimated) |
|---|---|
| 600-659 | 8-10% |
| 660-719 | 6-8% |
| 720-759 | 5-7% |
| 760+ | 4-6% |
Impact of Market Conditions
Used car refinance rates are dynamic, constantly responding to shifts in the broader economic landscape. Understanding these market forces is crucial for borrowers seeking the most favorable terms. Economic trends, interest rate fluctuations, supply and demand dynamics, and inflationary pressures all play a role in shaping these rates.
Market forces exert significant influence on used car refinance rates, impacting both the availability and cost of financing. Borrowers need to be aware of these factors to make informed decisions and secure the best possible refinance rates.
Economic Trends and Refinance Rates
Economic downturns often lead to a contraction in the overall economy, impacting consumer spending and lending practices. During such periods, banks and lenders may be more cautious, leading to reduced availability of refinance options and potentially higher rates. Conversely, robust economic growth typically fosters a more favorable environment for borrowing, potentially resulting in more competitive refinance rates. This correlation is evident in historical data, showing a strong link between economic performance and used car refinance rates.
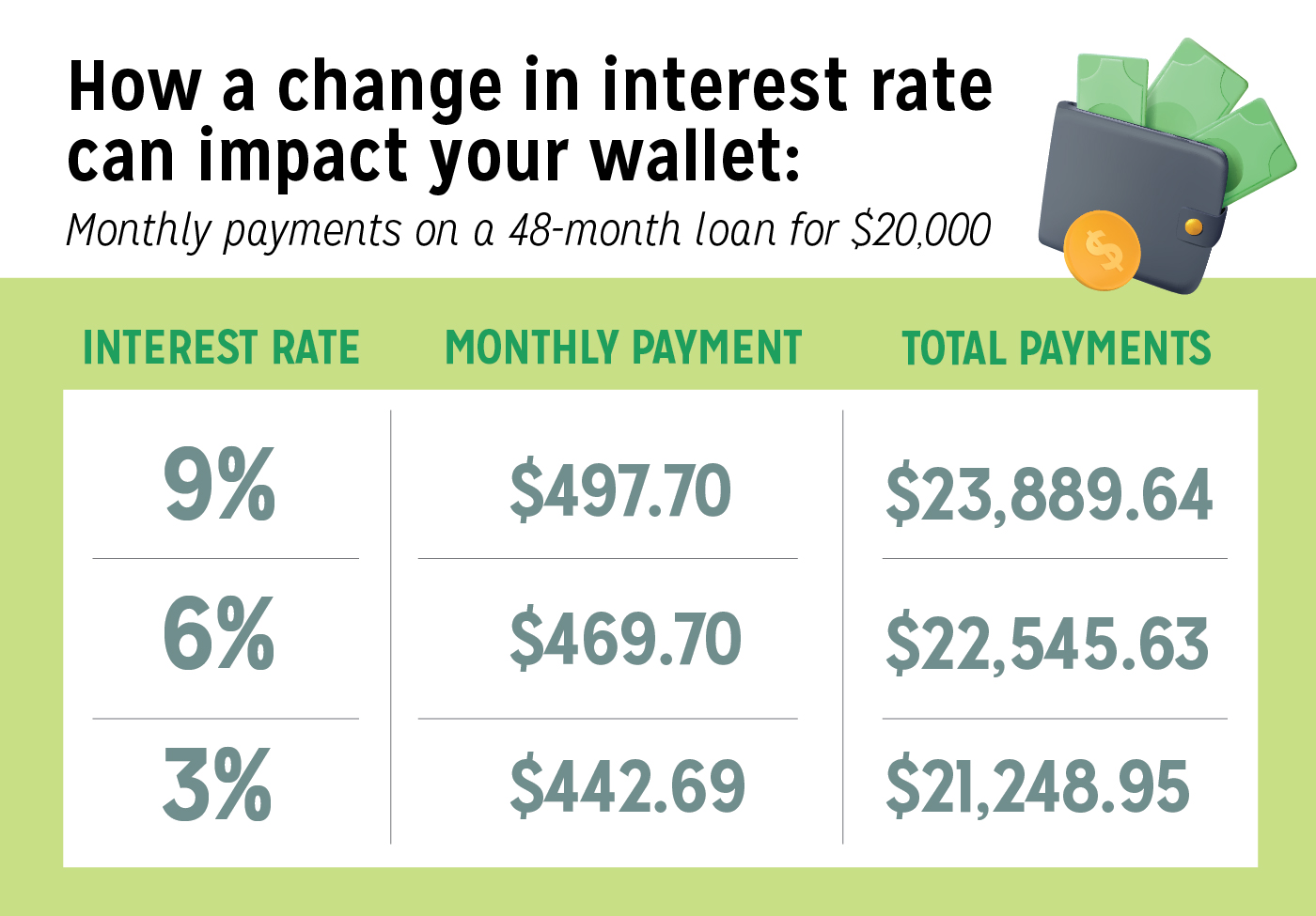
Interest Rate Fluctuations and Their Impact
Changes in the prime interest rate significantly influence the cost of borrowing. A rise in the prime rate usually results in higher used car refinance rates as lenders adjust their pricing models to reflect increased borrowing costs. Conversely, a decrease in the prime rate typically leads to lower refinance rates. This direct relationship underscores the critical role of overall market interest rates in shaping used car refinance rates.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The interplay between supply and demand directly affects used car refinance rates. A shortage of used cars available for refinancing, coupled with high demand, can create upward pressure on rates as lenders capitalize on the scarcity. Conversely, a surplus of used cars may result in more competitive rates, as lenders compete for borrowers. This is reflected in the fluctuating market conditions impacting used car valuations and financing.
Inflation and Refinance Rates
Inflationary pressures can significantly impact refinance rates. As inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases, necessitating higher interest rates to compensate for the erosion of value over time. Lenders, anticipating future inflation, often adjust their interest rates accordingly, reflecting the increased risk associated with lending during periods of high inflation. This dynamic underscores the critical link between inflationary pressures and used car refinance rates.
Correlation Between Interest Rates and Refinance Rates
| Date | Prime Interest Rate (%) | Average Used Car Refinance Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| January 2023 | 4.5 | 6.2 |
| April 2023 | 5.0 | 6.5 |
| July 2023 | 5.5 | 6.8 |
| October 2023 | 5.2 | 6.6 |
The table above illustrates a general correlation between prime interest rates and average used car refinance rates. Note that this is a simplified example; other factors like market conditions and lender-specific policies also influence rates. While a direct, linear relationship isn’t always apparent, a clear trend exists. Higher prime interest rates often correspond with higher used car refinance rates.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Refinancing a used car loan can be a smart financial move, but it’s crucial to weigh the potential advantages against the disadvantages. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision about whether refinancing is the right choice for your specific circumstances. A careful analysis of the current market conditions, loan terms, and personal financial goals is essential before proceeding.
A well-structured approach to understanding the pros and cons of refinancing allows for a clearer picture of the long-term financial implications. Factors such as interest rates, loan terms, and any associated fees play a significant role in determining the overall cost-effectiveness of refinancing.
Advantages of Refinancing
Refinancing a used car loan can offer several advantages, primarily focusing on reducing monthly payments and potentially lowering the overall cost of the loan. A key benefit is the ability to secure a lower interest rate than the existing loan, which can translate into substantial savings over the life of the loan.
Disadvantages of Refinancing
Refinancing isn’t without potential drawbacks. There might be associated fees, such as appraisal fees or closing costs, which can offset some of the savings from a lower interest rate. Furthermore, the refinancing process itself can take time, and during this period, the borrower may continue to accrue interest on the original loan.
Situations Where Refinancing is Beneficial
Refinancing a used car loan can be advantageous in specific situations. For instance, if current interest rates have fallen significantly since the original loan was taken out, refinancing can result in a substantial reduction in monthly payments and overall interest paid. This is especially true if the borrower is facing financial hardship or if their credit score has improved since taking out the original loan. Examples include a borrower who experiences a significant income increase or a significant improvement in their credit score.
Long-Term Costs and Benefits
Comparing the long-term costs and benefits of refinancing versus keeping the original loan is crucial. A thorough analysis needs to consider the current interest rate, potential new interest rates, and any associated fees. For example, a borrower with a high interest rate on their existing loan may find that the savings from refinancing outweigh the costs of the process.
Pros and Cons of Used Car Refinancing
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower monthly payments | Processing fees and closing costs |
| Lower interest rate | Potential for longer processing time |
| Reduced total interest paid | Loss of any potential equity buildup on the original loan |
| Improved financial flexibility | Possible negative impact on credit score if not handled properly |
Finding the Best Rates

Securing the most advantageous used car refinance rate requires a strategic approach. Knowing where to look and how to compare offers is crucial. This section details various resources and methods to identify the best rates tailored to your specific needs.
Identifying Resources for Used Car Refinance Rates
Numerous resources provide access to used car refinance rates. Online marketplaces, dedicated finance websites, and direct lender platforms are common starting points. Banks, credit unions, and online-only lenders often publish their rates on their websites or through their customer service channels. Comparing rates across multiple sources is essential for optimal results.
Comparing Used Car Refinance Rates
Comparing used car refinance rates from different lenders involves careful consideration of various factors. Focus on the interest rate, any associated fees, and the terms of the loan. Lenders may offer different loan durations, which can impact monthly payments and the overall cost of the loan. Understanding the APR (Annual Percentage Rate) is critical, as it factors in all costs associated with the loan. By meticulously comparing these details, you can identify the most favorable rate.
The Role of Online Tools in Finding Refinance Options
Online tools play a significant role in streamlining the used car refinance process. Many websites offer comparative rate calculators, allowing you to input your vehicle details, loan amount, and credit score to instantly see potential rates from multiple lenders. These tools can significantly reduce the time and effort required to identify suitable options. They also facilitate quick comparison shopping, allowing for more informed decisions.
Requesting Quotes from Multiple Lenders
To gain a comprehensive understanding of available used car refinance rates, requesting quotes from multiple lenders is essential. This process typically involves filling out online forms or contacting lenders directly. Provide accurate information about your vehicle, desired loan amount, and creditworthiness. Be prepared to answer any follow-up questions. It’s wise to have your vehicle identification number (VIN) and loan terms in mind to streamline the process.
Comparison of Used Car Refinance Rates from Different Lenders
| Lender | Interest Rate (%) | Loan Term (Years) | Fees | APR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 6.5 | 5 | $200 origination fee | 6.8 |
| Credit Union B | 6.2 | 5 | $150 origination fee | 6.5 |
| Online Lender C | 6.8 | 6 | No origination fee | 7.0 |
| Finance Company D | 7.0 | 7 | $300 origination fee | 7.5 |
Note: This table is a hypothetical example. Actual rates and fees will vary based on individual circumstances and lender policies. Thorough research and personalized consultations are crucial to secure the best possible rates.
Illustrative Scenarios
Refinancing a used car loan can be a smart financial move if done strategically. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as the factors influencing the refinance rate, is crucial for making an informed decision. This section explores various scenarios to illustrate how refinancing might or might not be beneficial.
Scenario 1: Refinancing for Savings
A used car owner with a high-interest rate loan of 12% APR and a remaining balance of $8,000 can potentially save a substantial amount by refinancing. By securing a new loan with a lower interest rate of 7% APR, the borrower could significantly reduce monthly payments and total interest paid over the life of the loan. For example, if the loan term remains the same, the lower monthly payments would lead to significant savings over the long term.
Scenario 2: Refinancing Not Advantageous
A used car owner with a low-interest rate loan of 5% APR and a short remaining loan term might not see significant savings by refinancing. The potential savings from a lower rate may be offset by closing costs or fees associated with the new loan. In this case, the borrower may not realize a tangible benefit from refinancing.
Hypothetical Case Study
Consider a used car loan of $10,000 with a 9% APR and a remaining term of 36 months. The monthly payment is approximately $350. If the borrower refinancesthe loan with a 7% APR and the same term, the monthly payment would be reduced to roughly $320. This represents a monthly savings of $30, resulting in a total interest savings of approximately $360 over the remaining loan term.
Impact of Credit Score on Refinancing Rates
A poor credit score significantly impacts refinance rates. Borrowers with lower credit scores typically face higher interest rates compared to those with excellent credit. For instance, a borrower with a credit score of 600 might qualify for a loan with an interest rate of 12% or higher, whereas a borrower with a score of 750 might qualify for a rate of 8% or lower. This difference in rates can lead to substantially higher monthly payments and total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Impact of Loan Term on Refinancing Rates
A longer loan term generally results in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. A longer term can make refinancing less attractive, as the total interest paid might outweigh the potential savings from a lower interest rate. The borrower needs to consider their financial situation and future needs when choosing a loan term.
Important Considerations
Refinancing a used car loan can save you money, but it’s crucial to approach the process with careful consideration. Jumping into a refinance without understanding the potential pitfalls can lead to unfavorable outcomes. This section highlights key factors to weigh before making a decision.
Thorough research, understanding loan terms, assessing closing costs, and comparing lenders are essential steps to ensure a successful refinance. Ignoring any of these aspects could result in a less favorable outcome than anticipated.
Thorough Research Before Refinancing
Thorough research is paramount before embarking on a refinance. This involves investigating current interest rates, comparing lenders’ offers, and understanding the associated fees. Understanding the current market conditions and interest rate trends allows you to anticipate potential changes and optimize your decision-making process.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
Carefully reviewing loan terms and conditions is critical. Pay close attention to the interest rate, loan duration, and repayment schedule. Comprehending the fine print helps you avoid unexpected surprises and ensures the refinance aligns with your financial goals. Compare the terms offered by different lenders to identify the most suitable option.
Considering Closing Costs
Closing costs are often overlooked but can significantly impact the overall cost of refinancing. These costs can include application fees, appraisal fees, and origination fees. Accurately estimating these costs helps in budgeting and allows for a more informed decision. Understanding how these fees will affect the net savings from refinancing is vital.
Comparing Different Lenders and Their Offers
Comparing multiple lenders is crucial to securing the most favorable refinance rate. Each lender has its own criteria and processes. A comparative analysis of different offers, considering interest rates, fees, and terms, will lead to a more informed decision. Shop around for the best rates and terms available.
Key Factors to Consider When Refinancing a Used Car Loan
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate | The interest rate directly impacts the total cost of the loan. |
| Loan Duration | A shorter loan duration may lead to lower total interest but higher monthly payments. |
| Monthly Payment | Understanding the monthly payment is essential for budgeting and financial planning. |
| Closing Costs | Closing costs can significantly impact the overall cost of refinancing. |
| Fees (Application, Origination, Appraisal) | These fees vary by lender and should be factored into the overall cost. |
| APR (Annual Percentage Rate) | APR reflects the total cost of borrowing, encompassing interest and fees. |
| Lender Reputation | Choosing a reputable lender minimizes the risk of issues during the loan process. |