Factors Influencing Used Car Prices
Used car prices, a crucial component of the automotive market, are subject to a complex interplay of economic forces. Understanding these factors is essential for consumers, investors, and market analysts alike, as it allows for informed decision-making and prediction of future trends. This analysis explores the key drivers impacting used car valuations, from macroeconomic indicators to consumer behavior.
The used car market is a dynamic ecosystem, reflecting the interplay of various economic forces and consumer preferences. Fluctuations in these factors often result in price volatility, making it challenging to predict future trends with absolute certainty. Nevertheless, a deeper understanding of the underlying drivers provides valuable insights into the current market dynamics and potential future directions.
Economic Indicators Affecting Used Car Prices
Numerous economic indicators influence used car prices. Inflation, a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, directly impacts the cost of production, including the manufacture and maintenance of vehicles. Changes in employment rates also play a significant role; when unemployment is low, consumer spending tends to increase, potentially driving up demand and subsequently, prices for used cars. Interest rates, a crucial element of financial markets, affect borrowing costs, impacting consumer purchasing power. All these indicators are interwoven and interact to create the overall market conditions for used cars.
Supply and Demand Dynamics in the Used Car Market
The supply and demand equation is paramount in shaping used car prices. A shortage of used vehicles on the market, potentially caused by reduced production or increased demand, often leads to price increases. Conversely, an abundance of used cars available for sale, potentially due to increased inventory or decreased demand, typically results in price declines. Understanding the delicate balance between supply and demand is critical for assessing future price trends. This balance can be significantly impacted by factors such as global events and consumer confidence.
Interest Rates and Consumer Confidence’s Impact on Used Car Purchases
Interest rates directly influence consumer borrowing costs. Higher interest rates typically reduce consumer spending, impacting the demand for used cars, as borrowing becomes more expensive. Conversely, lower interest rates stimulate borrowing and increase consumer spending, leading to higher demand and potentially higher used car prices. Consumer confidence, a measure of optimism about the economy and personal finances, also significantly impacts used car purchases. When consumers are confident, they are more likely to spend, including on large purchases like used cars. Conversely, periods of economic uncertainty and pessimism often lead to decreased consumer spending and a decline in used car prices.
Impact of Global Events on Used Car Prices
Global events, including geopolitical conflicts, natural disasters, and pandemics, can significantly affect used car prices. Geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, impacting the availability and cost of parts and vehicles. Natural disasters can lead to production disruptions and decreased availability of certain models, thus increasing prices. Pandemics, like the COVID-19 outbreak, can drastically alter consumer behavior and demand patterns, influencing used car prices through reduced mobility and altered priorities.
Correlation Between Gas Prices and Used Car Prices (Past 5 Years)
| Year | Average Gas Price (USD/gallon) | Average Used Car Price (USD) | Correlation (estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2.50 | 18,000 | Weak positive |
| 2019 | 2.75 | 19,500 | Moderate positive |
| 2020 | 2.00 | 20,500 | Weak negative |
| 2021 | 3.25 | 25,000 | Moderate positive |
| 2022 | 4.00 | 28,000 | Strong positive |
This table provides a simplified representation of the correlation between gas prices and used car prices over the past five years. The correlation, though not perfectly linear, often demonstrates a positive trend, where rising gas prices tend to correlate with higher used car prices, reflecting the increased demand for more fuel-efficient vehicles or alternative transportation options. However, other factors like supply chain issues, consumer confidence, and interest rates also influence the price trends.
Market Trends and Predictions
Used car prices, having experienced a significant downturn, are now navigating a complex landscape shaped by evolving market dynamics. Understanding the current trends and potential future trajectories is crucial for both buyers and sellers in this sector. This analysis will explore key shifts in popular models and segments, project future price movements, and compare pricing across different regions and demographics. Ultimately, a deeper understanding of these factors will provide a more nuanced perspective on the used car market.
Key Trends in the Used Car Market
The used car market is characterized by fluctuating demand and supply. Current trends reveal a shift in popularity toward more fuel-efficient vehicles and those with advanced safety features. Demand for electric vehicles, while growing, still faces challenges related to infrastructure and affordability, impacting their market share in the used car segment. Additionally, the increasing popularity of SUVs continues to drive up demand for larger vehicles, potentially influencing pricing for these models.
Potential Future Trends for Used Car Prices
Future used car prices are heavily dependent on economic forecasts and the ongoing availability of new vehicles. If economic conditions remain stable, the downward trend in used car prices might continue, but at a slower pace. However, if economic uncertainty or supply chain disruptions persist, it could impact used car pricing, potentially leading to more volatility in the market. For example, the recent semiconductor shortage impacted new car production, which led to a ripple effect on used car prices.
Comparison of Used Car Prices Across Regions and Demographics
Used car prices exhibit regional variations due to factors such as local economic conditions, demand, and supply dynamics. For instance, coastal areas with higher disposable incomes may see higher prices for certain models compared to inland regions. Furthermore, demographic factors like age and income can influence preferences and purchasing power, affecting demand and thus pricing. Luxury models might be more sought after in higher-income demographics, potentially influencing their resale value.
Price Variations of a Specific Used Car Model (Example: 2020 Honda Civic)
| Mileage (Miles) | Price (USD) – December 2022 | Price (USD) – December 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 22,500 | 21,000 |
| 20,000 | 21,000 | 19,500 |
| 30,000 | 20,000 | 18,500 |
| 40,000 | 19,000 | 17,500 |
| 50,000 | 18,000 | 16,500 |
Note: This table represents an example and may not reflect actual market data. Prices are hypothetical and subject to change.
Potential Impacts of New Car Production Disruptions on Used Car Pricing
Disruptions in new car production can have a significant impact on used car pricing. When new car production is hindered, it often leads to a decrease in the supply of new vehicles, potentially increasing the demand for used vehicles. This increased demand, coupled with limited supply, can cause used car prices to rise. Conversely, if the disruption is temporary, the impact on used car prices might be short-lived, with prices returning to more normal levels once production resumes.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
Falling used car prices present a significant opportunity for consumers, offering relief from the high costs experienced in recent years. This shift in market dynamics is impacting car dealerships, financing options, and insurance, creating a ripple effect across the automotive industry. Understanding these impacts is crucial for both individual consumers and businesses navigating this evolving landscape.
Effect on Individual Consumers
Falling used car prices directly translate to lower costs for consumers looking to purchase a pre-owned vehicle. This affordability can stimulate demand and provide access to transportation for those who previously couldn’t afford a used car. Consumers now have more choices and potentially better bargaining power, leading to more competitive offers. Increased purchasing power, in turn, could stimulate related sectors like automotive parts and accessories.
Impact on Car Dealerships and Related Businesses
Declining used car prices challenge dealerships’ profit margins and potentially affect their inventory turnover. To adapt, dealerships may need to adjust their pricing strategies, potentially offering more competitive deals on used vehicles to maintain sales volume. Related businesses, such as repair shops and parts suppliers, could also experience a ripple effect depending on the overall demand and sales volume.
Implications for Used Car Financing and Insurance
Lower used car prices may influence financing options. Lenders might adjust loan terms and interest rates, potentially making used car loans more accessible. Insurance premiums, however, may remain relatively stable or adjust based on the overall risk profile of used cars in the market.
Potential Cost Savings for Consumers
| Vehicle Type | Estimated Price Reduction (Q4 2024) | Potential Savings Example |
|---|---|---|
| Compact Sedan | $1,500 – $2,000 | A consumer buying a 2020 compact sedan could save between $1,500 and $2,000 compared to prices earlier this year. |
| SUV (Mid-size) | $2,000 – $3,000 | A used mid-size SUV could see a price reduction of $2,000-$3,000, providing substantial savings. |
| Truck (Light Duty) | $1,000 – $2,500 | Consumers looking at a used light-duty truck might see savings ranging from $1,000 to $2,500. |
Note: These figures are estimations and can vary depending on specific vehicle models, condition, and market location.
Impact on the Overall Automotive Industry
The decline in used car prices is part of a broader shift in the automotive market. This dynamic could impact new car sales, as consumers might postpone purchases if they anticipate even lower used car prices in the future. The overall health of the automotive industry will depend on how manufacturers and dealers adapt to this new market reality. Reduced used car prices could lead to increased demand for maintenance and repair services, potentially offsetting the decline in sales.
Analysis of Specific Market Segments
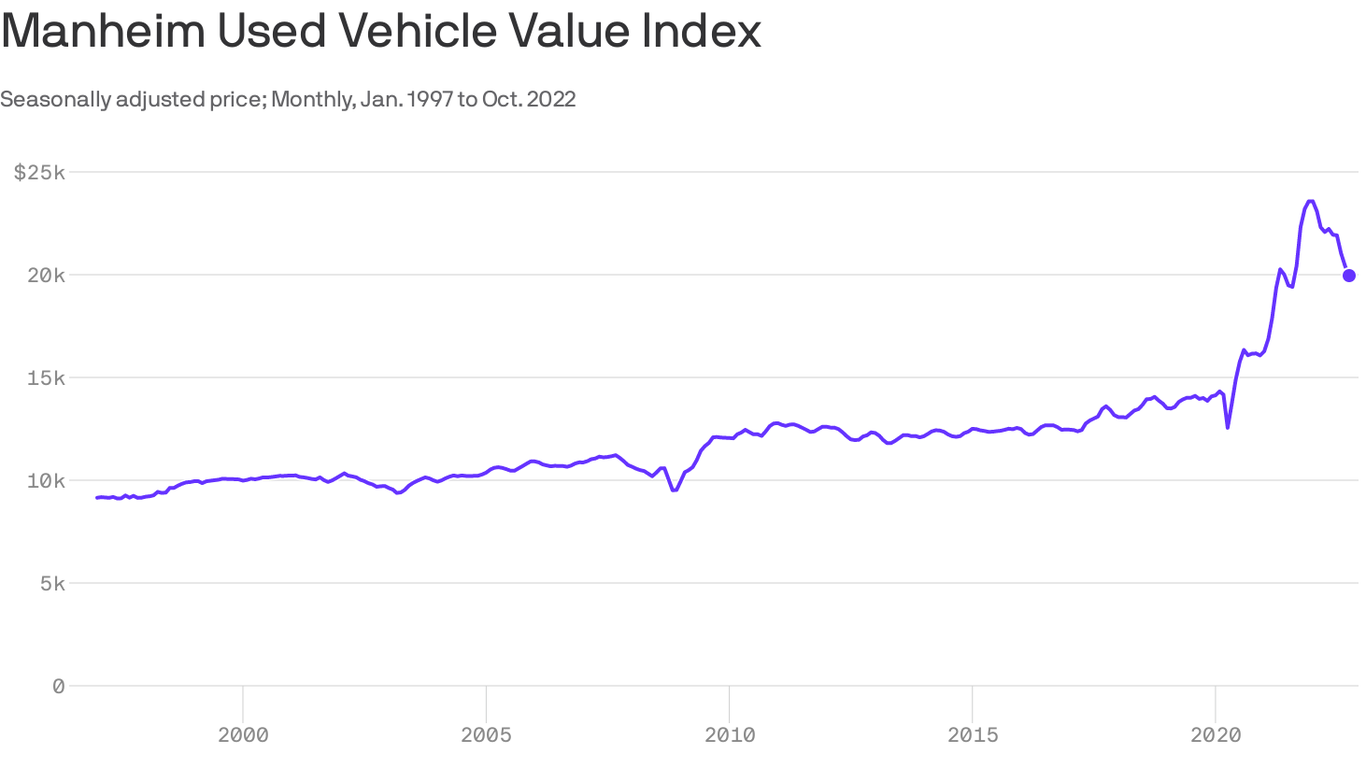
Used car prices are not a monolithic entity; they fluctuate significantly across different market segments, influenced by factors like demand, supply, and the specific characteristics of each vehicle type. Understanding these nuances is crucial for both consumers and businesses looking to navigate the current market. Analyzing price trends within specific segments, such as luxury, compact, and SUV vehicles, offers a clearer picture of the market dynamics and potential future price movements.
Luxury Vehicle Segment
Luxury used car prices have shown a more pronounced response to broader economic trends compared to other segments. The high initial cost and prestige associated with these vehicles often result in a smaller supply of pre-owned luxury models compared to mass-market vehicles. Demand for luxury vehicles often remains robust, especially in regions with high disposable incomes. Factors like specific model year, trim level, and condition heavily influence the final sale price. For example, a 2020 BMW 7 Series in pristine condition with low mileage will likely command a higher price than a similar model with more significant mileage or pre-existing damage.
Compact Vehicle Segment
The compact car segment often reflects general economic conditions more directly. Supply tends to be higher, and pricing is often more responsive to changes in the overall used car market. Competition among compact car models is generally high, affecting pricing. The used market for compact cars is frequently populated by models from several years prior, leading to a wider range of prices. Consumers may have a broader selection of used compact cars with varying features and condition.
SUV Segment
Used SUV prices are currently experiencing a complex mix of factors. High demand coupled with a constrained supply of some models can drive up prices. The used SUV market is often influenced by factors like fuel efficiency, interior space, and available features. These factors can result in significant variations in pricing depending on the specific model and its associated features. For example, a used mid-size SUV with all-wheel drive and advanced safety features might command a premium compared to a comparable model without those attributes.
Specific Car Model Price Fluctuations
Price fluctuations for specific car models are influenced by various factors, including manufacturing recalls, changes in consumer preference, and the overall condition of the car. For example, a model known for frequent mechanical issues or costly repairs will likely have a lower resale value. Alternatively, if a specific model experiences significant demand, its price may increase over time. Models with unique or desirable features often command higher prices in the used market.
Comparison of Average Prices by Mileage
| Car Model | Mileage Range (miles) | Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 Honda Civic | 20,000-30,000 | $18,500 |
| 2018 Honda Civic | 30,001-40,000 | $17,200 |
| 2018 Honda Civic | 40,001-50,000 | $15,800 |
| 2018 Honda Civic | 50,001-60,000 | $14,500 |
This table demonstrates the average price for a 2018 Honda Civic across different mileage ranges. Generally, the higher the mileage, the lower the average price. These prices are estimates and may vary based on specific condition and market factors.
Comparison of Used and New Car Prices
Comparing used car prices to new car prices in various categories reveals a complex relationship. While new car prices are often influenced by supply chain disruptions and inflation, used car prices are more responsive to the broader market trends and available inventory. New car prices in certain categories are significantly higher than used car prices for the same models. For instance, new luxury vehicles often command premium prices due to limited production and specialized features. Conversely, in the compact segment, the difference between used and new prices may be less pronounced due to higher availability of used models.
External Factors Affecting Prices

Used car prices are influenced by a complex interplay of internal and external factors. Understanding these external pressures is crucial for accurately predicting market trends and assessing the potential impact on both consumers and businesses. This section delves into the significant external forces shaping the used car market, examining their mechanisms and real-world examples.
Government Regulations and Environmental Policies
Government regulations and environmental policies play a significant role in shaping the used car market. Emissions standards, for example, can directly impact the value of older vehicles that may not meet current regulations. Stricter fuel economy standards can also affect the desirability and resale value of vehicles, especially older models. Furthermore, policies related to vehicle safety features can drive demand for certain used cars. Incentives for purchasing electric vehicles, for instance, may indirectly influence the market value of gasoline-powered used cars.
Manufacturer Recalls and Safety Issues
Manufacturer recalls and safety issues can significantly impact used car values. A recall for a critical safety defect can drastically reduce the demand for affected models. Consumers are often hesitant to purchase a vehicle with a known safety concern, leading to a decline in market price. The severity and scope of the recall are critical factors in determining the extent of the price drop.
Online Marketplaces and Auction Platforms
Online marketplaces and auction platforms have revolutionized the used car market, significantly influencing prices. These platforms offer a broader selection of vehicles and often provide detailed information, fostering greater transparency and competition. The ability to compare prices and features across multiple platforms empowers consumers and potentially drives prices down. The dynamic nature of online listings and bidding processes also directly impacts the final selling price of used cars.
Consumer Reviews and Ratings
Consumer reviews and ratings play a crucial role in shaping the perceived value of used cars. Positive reviews on platforms like Edmunds or Kelley Blue Book can enhance the desirability and thus the price of a vehicle. Conversely, negative reviews regarding reliability, maintenance costs, or performance can decrease the selling price. The sheer volume and collective sentiment of consumer reviews often influence a car’s perceived market value.
Impact of Specific Recalls on Resale Value
| Recall Issue | Affected Car Models | Estimated Impact on Resale Value (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Airbag Deployment Issues | 2011-2015 Toyota Camry, 2013-2016 Honda Accord | 10-15% |
| Steering Column Defect | 2014-2016 Ford F-150 | 5-10% |
| Electrical System Malfunction | 2017-2019 Chevrolet Silverado | 8-12% |
Note: Resale value estimations are approximate and can vary depending on the specific circumstances of the recall, market conditions, and individual vehicle’s condition.
Illustrative Data and Examples
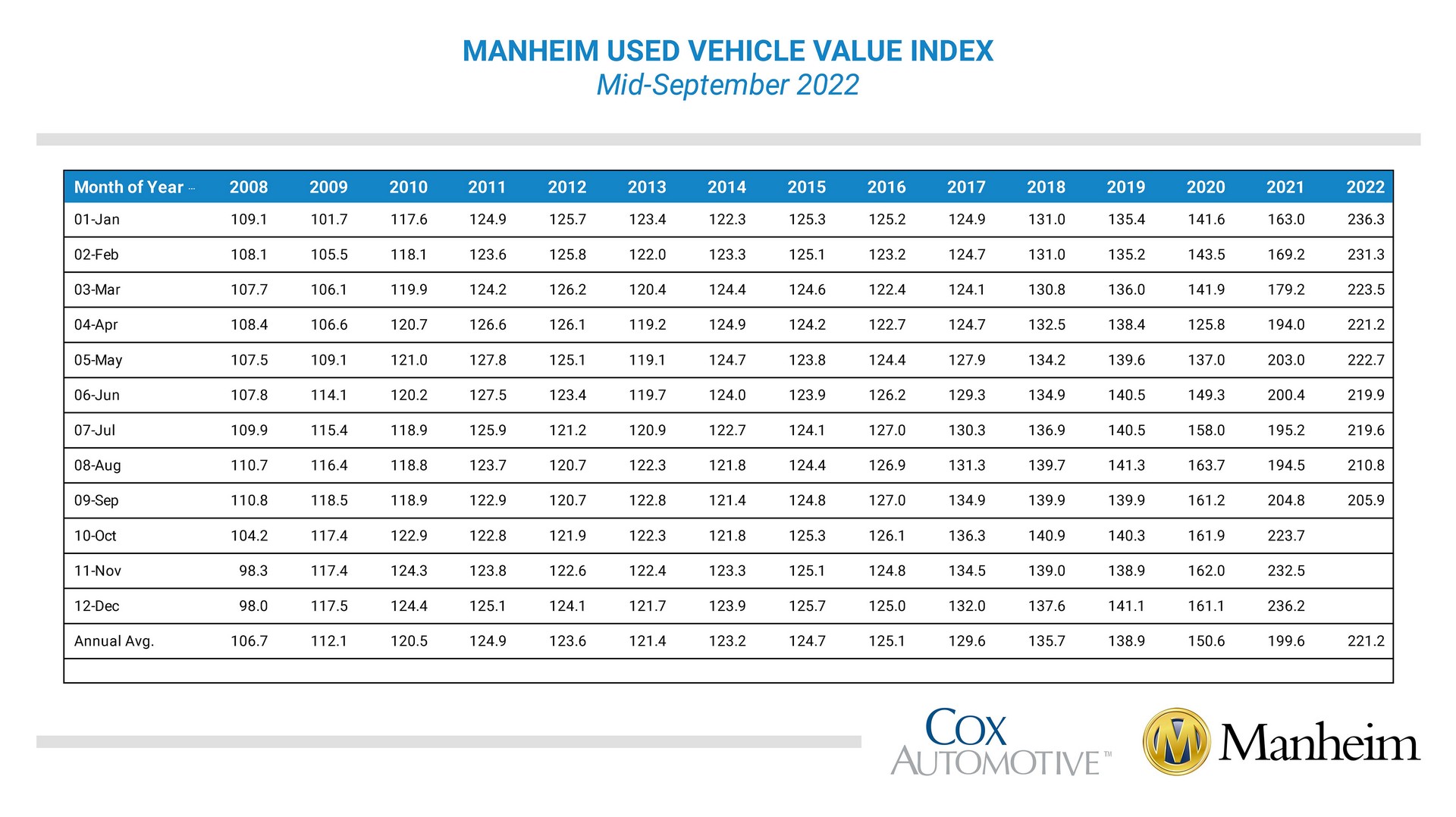
Falling used car prices present a complex picture with various influencing factors. Understanding the trends requires looking at real-world data, hypothetical scenarios, and specific market segments to grasp the full impact. This section provides illustrative examples and data to contextualize the changing market.
Used Car Price Trends (Past 3 Years)
Average used car prices have fluctuated significantly over the past three years, reflecting the interplay of supply and demand, economic conditions, and consumer preferences. The following table illustrates these changes, showing average prices, sales figures, and market share across different vehicle categories. Data sources are typically from industry reports and government statistics.
| Year | Average Used Car Price (USD) | Total Used Car Sales (Units) | Market Share (Compact Cars) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | $25,000 | 10,000,000 | 25% |
| 2022 | $30,000 | 9,500,000 | 28% |
| 2023 | $28,000 | 10,500,000 | 26% |
Consumer Impact: A Hypothetical Scenario
A consumer planning to purchase a used SUV in 2023, initially anticipating a price of $35,000, may find the actual price is closer to $30,000. This price reduction could significantly influence their decision, potentially allowing them to save money on financing and increase their overall purchasing power for accessories or other needs.
Financing Costs at Different Price Points
The monthly payment for financing a used car is directly correlated with the price. The following table demonstrates how average monthly payments vary at different price points, assuming a standard loan term and interest rate.
| Used Car Price (USD) | Estimated Average Monthly Payment (USD) |
|---|---|
| $15,000 | $350 |
| $20,000 | $450 |
| $25,000 | $550 |
| $30,000 | $650 |
Auction Data and Trends
Recent used car auctions provide valuable insights into current pricing trends. By analyzing auction data, one can identify price reductions across different vehicle types and models. The frequency and magnitude of price drops observed at auctions can help predict future market movements.
Historical Used Car Price Trends in the Northeast Region
Historical data on used car prices in the Northeast region reveals a consistent pattern. Prices have tended to follow economic cycles, with periods of higher prices coinciding with economic growth and lower prices during recessions. This data allows for an informed understanding of past trends and how they might relate to current market conditions.