Overview of Used Car Interest Rates in 2024
Used car interest rates in 2024 are a complex reflection of the interplay between prevailing economic conditions, supply and demand dynamics in the automotive market, and lender policies. While the specific rates vary based on factors like credit score and loan terms, a general trend is emerging. This overview examines the current state, historical trends, and comparison to new car rates.
Current State of Used Car Interest Rates in 2024
Used car interest rates in 2024 show a slight upward trend compared to the historically low rates seen in some previous years. This is largely attributable to a combination of factors, including rising borrowing costs for all types of loans and the persistent demand for used vehicles. Consumers should anticipate rates to potentially fluctuate depending on individual circumstances.
Historical Trends of Used Car Interest Rates (Past 5 Years)
The following table summarizes the general range of used car interest rates over the past five years, offering a concise overview of the historical trends.
| Year | Interest Rate Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2.5% – 5.5% | Interest rates were relatively low, reflecting a period of overall economic stability and moderate demand for used vehicles. |
| 2020 | 3.0% – 6.0% | The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent economic shifts impacted the market, leading to a fluctuating range, with rates trending higher in the latter half of the year. |
| 2021 | 3.5% – 7.0% | Increased demand and supply chain disruptions resulted in higher interest rates and a wider range. |
| 2022 | 4.0% – 8.5% | High inflation and rising interest rates set by central banks impacted all borrowing costs, including those for used cars. |
| 2023 | 4.5% – 7.5% | Interest rates began to stabilize somewhat, but still remained higher than pre-pandemic levels due to lingering economic factors. |
| 2024 (estimated) | 4.8% – 8.0% | Anticipated rates continue to reflect a balance between economic conditions and ongoing demand for used vehicles. |
Comparison of Used Car and New Car Interest Rates in 2024
Interest rates for used cars generally remain higher than those for new cars in 2024. This is a typical pattern; new car financing often benefits from manufacturer incentives and lower risk profiles for lenders. However, the gap between used and new car rates is narrower than it was in previous years. This suggests the increasing competitiveness in the used car market.
Factors Influencing Used Car Interest Rates
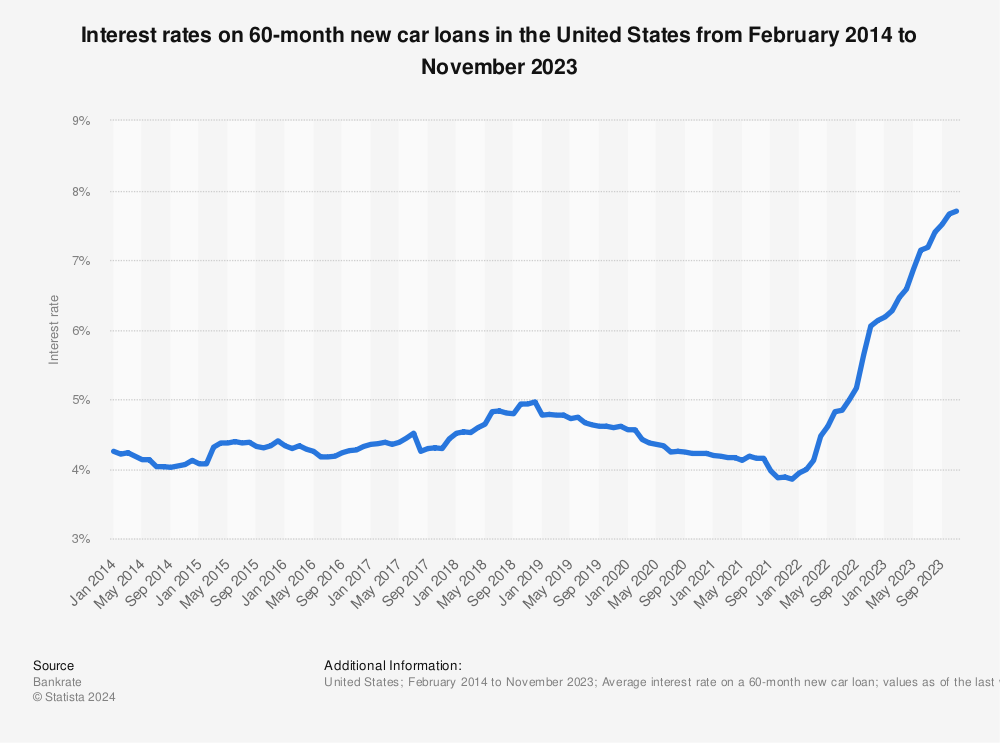
Used car interest rates in 2024 are a complex interplay of various economic and market forces. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers considering financing a used vehicle and for lenders assessing risk. Fluctuations in these factors can significantly impact the overall cost of borrowing, impacting both the buyer and the seller.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions play a pivotal role in shaping used car interest rates. Inflation and recessionary pressures are key indicators that influence borrowing costs. High inflation often leads to higher interest rates across the board as lenders seek to compensate for the eroding purchasing power of money. Conversely, a recessionary environment, characterized by reduced consumer spending and business activity, can sometimes lead to lower interest rates as lenders become more cautious and competitive for loans. For instance, a period of sustained high inflation might necessitate increased interest rates to curb the rising cost of living, while a potential recession might result in lower rates to stimulate economic activity.
Consumer Demand and Supply
The dynamic interplay between consumer demand and the supply of used cars directly impacts interest rates. High demand for used vehicles, often exceeding the available supply, can push up prices, potentially encouraging lenders to increase interest rates to reflect the higher risk associated with lending. Conversely, an oversupply of used cars, potentially due to increased inventory or decreased consumer demand, could lead to lower prices and possibly lower interest rates as lenders perceive less risk. This fluctuation is particularly evident in periods of economic uncertainty or rapid market shifts.
Lending Institutions’ Policies and Practices
Lending institutions, including banks and credit unions, have their own policies and practices that influence used car interest rates. These institutions assess creditworthiness and risk levels for each borrower. Factors like credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, and the borrower’s overall financial history influence the interest rate offered. Stronger credit scores often translate to lower interest rates, while those with less favorable credit profiles may face higher rates. Furthermore, lender-specific risk appetites, and market conditions also influence the interest rates they offer.
Influence of Different Factors on Used Car Interest Rates
| Factor | Influence on Used Car Interest Rates | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Conditions (Inflation/Recession) | Higher inflation often leads to higher interest rates, while recessionary pressures may cause lower rates. | If inflation rises, lenders may raise interest rates to compensate for the decreased value of money. |
| Consumer Demand and Supply | High demand and low supply can drive up interest rates due to increased risk. Conversely, high supply and low demand can lead to lower rates. | A shortage of used cars in a specific market segment may prompt lenders to increase interest rates. |
| Lender Policies/Practices | Lenders’ risk assessment, creditworthiness evaluation, and market conditions influence their lending policies and consequently, the interest rates offered. | A lender with a conservative approach to risk might set higher interest rates than a lender with a more aggressive strategy. |
Types of Used Car Loans and Interest Rates
Used car loans come in various forms, each with its own interest rate structure and terms. Understanding these differences is crucial for consumers seeking the most suitable financing option for their needs. Different loan types cater to diverse financial situations and preferences, impacting the overall cost of borrowing.
Loan Types and Interest Rate Variations
Used car loans are categorized based on various factors, impacting the interest rates. Factors like the borrower’s credit history, the loan term, and the down payment amount significantly influence the interest rate offered. Shopping around and comparing offers from different lenders is essential for securing the best possible rate.
Types of Used Car Loans
Several types of used car loans are available in 2024. Each loan type presents distinct features, influencing the interest rate and repayment terms. Understanding these options empowers consumers to make informed decisions.
- Secured Loans: These loans are secured by the vehicle itself. If the borrower defaults, the lender can repossess the car to recover the outstanding loan amount. Secured loans typically offer lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans, as the lender has recourse to the vehicle as collateral. A common example is a loan where the car is used as collateral.
- Unsecured Loans: These loans are not backed by any collateral. Borrowers with excellent credit histories may qualify for these loans. Unsecured loans typically have higher interest rates compared to secured loans due to the increased risk for the lender. A key distinction is the lack of collateral; the loan is solely based on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
- Retail Loans: Offered directly by dealerships, these loans often have pre-set interest rates. Borrowers may need to meet specific criteria to qualify. The interest rate might be influenced by the dealership’s relationship with the lender. For example, a dealership with a strong partnership with a lending institution might offer favorable rates.
- Bank Loans: Offered by traditional banks, these loans often require a more stringent application process and may come with more detailed terms. Interest rates are often competitive, but the process might be more time-consuming. Consider the loan application process, which could involve credit checks and thorough verification.
- Online Loans: Offered by online lenders, these loans can be processed quickly. Interest rates can vary depending on the borrower’s credit score. They often prioritize speed and convenience over extensive vetting, leading to potential variations in interest rates. The streamlined application process is a major draw.
Loan Terms and Repayment Options
Loan terms vary significantly, influencing the monthly payments and the overall cost of the loan. Different repayment options are also available, affecting the borrower’s budget. These options include fixed-rate and variable-rate loans.
- Loan Terms: Loan terms typically range from 24 to 72 months. Shorter terms lead to higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid. Longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid. For example, a 24-month loan will likely have higher monthly payments than a 60-month loan.
- Repayment Options: Common repayment options include fixed monthly payments, which provide a predictable budget. Some loans offer options for adjusting the monthly payments based on the borrower’s financial situation.
Interest Rate Table
| Loan Type | Typical Interest Rate (Example) | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Secured Loan (e.g., Auto Loan) | 4-8% | Good credit score, stable income |
| Unsecured Loan (e.g., Personal Loan) | 8-12% | Excellent credit score, strong financial history |
| Retail Loan | 5-10% | Meeting dealership’s specific criteria, including credit check |
| Bank Loan | 4-9% | Good credit score, proof of income, debt-to-income ratio |
| Online Loan | 6-11% | Credit check, income verification, minimum credit score requirements |
Note: Interest rates are examples and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
Regional Variations in Used Car Interest Rates

Used car interest rates in the US aren’t uniform across all states. Several factors contribute to these regional differences, impacting both borrowers and lenders. These variations are driven by a complex interplay of local economic conditions, lending practices, and competition among financial institutions.
Regional disparities in used car interest rates can significantly influence affordability and accessibility of vehicle purchases. Understanding these variations allows consumers to make more informed decisions about financing their used car purchases and provides lenders with insight into regional market dynamics.
Factors Contributing to Regional Differences
Regional economic conditions, including employment rates, average income levels, and prevailing interest rates in the broader economy, often influence used car interest rates within a specific state. For example, states with higher unemployment rates might see lenders adjusting interest rates to reflect a potential increase in loan defaults. Additionally, local competition among lending institutions plays a crucial role. In regions with a high concentration of lenders, competition may drive interest rates down to attract customers.
Comparison of Interest Rates in Different Regions
While precise, up-to-the-minute interest rate data is difficult to obtain for every region, historical trends and general observations provide insight. States with stronger economic fundamentals and a higher concentration of lenders often see lower used car interest rates. Conversely, areas with weaker economies or limited lending options may experience higher interest rates.
Regional Used Car Interest Rate Data (Illustrative Example)
| Region | Average Used Car Interest Rate (2023) |
|---|---|
| Northeast (e.g., New York, Massachusetts) | 6.5% – 7.5% |
| Midwest (e.g., Illinois, Ohio) | 6.0% – 7.0% |
| South (e.g., Texas, Florida) | 6.2% – 7.2% |
| West (e.g., California, Washington) | 6.8% – 7.8% |
Note: This table provides illustrative examples only and is not an exhaustive dataset. Actual interest rates can fluctuate based on various factors including the specific lender, the creditworthiness of the borrower, and the vehicle’s condition.
Impact of Used Car Interest Rates on Consumers

Used car interest rates play a significant role in shaping the affordability and accessibility of used vehicles for consumers. Fluctuations in these rates directly influence purchasing decisions, monthly payments, and the overall cost of financing a used car. Understanding these impacts is crucial for consumers navigating the market and making informed choices.
Impact on Purchasing Decisions
Used car interest rates directly influence consumers’ willingness and ability to purchase a vehicle. Higher rates increase the overall cost of borrowing, making used cars less attractive. Conversely, lower rates make financing more accessible, stimulating demand and potentially driving up used car prices. This dynamic interplay between interest rates and consumer purchasing power often leads to market adjustments in both vehicle demand and pricing.
Impact on Monthly Payments and Loan Costs
The monthly payment on a used car loan is directly proportional to the interest rate. Higher interest rates result in substantially higher monthly payments, reducing the affordability of the vehicle for many consumers. Furthermore, the total cost of the loan, including interest, is significantly impacted by the interest rate. A higher interest rate means a higher total cost of the loan over the loan term, potentially exceeding the original purchase price. For example, a $15,000 loan at a 5% interest rate will have a significantly lower monthly payment and total loan cost compared to the same loan at a 10% interest rate.
Impact on Affordability for Different Consumer Segments
The affordability of a used car loan varies significantly based on individual financial situations. Consumers with lower incomes or those with existing debt may find higher interest rates to be an insurmountable barrier. This can disproportionately impact specific demographics and create disparities in access to used vehicles. Consumers with higher credit scores often qualify for lower interest rates, making used car ownership more affordable.
Effect on Market Dynamics
High interest rates typically lead to a decline in used car sales as borrowing becomes more expensive. This can result in a reduction in the overall demand for used vehicles and potentially lead to a stabilization or decline in used car prices. Low interest rates, on the other hand, stimulate demand and may lead to increased competition among sellers. This often leads to price increases.
Comparison of Monthly Payments for Different Loan Amounts and Interest Rates
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate (5%) | Interest Rate (7%) | Interest Rate (9%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | $201.53 | $220.82 | $240.53 |
| $15,000 | $302.29 | $332.64 | $364.00 |
| $20,000 | $403.06 | $444.06 | $486.00 |
| $25,000 | $503.82 | $555.50 | $608.00 |
Note: Monthly payments are calculated for a 60-month loan term. These figures are estimates and actual payments may vary based on individual circumstances and loan terms.
Future Projections for Used Car Interest Rates in 2024
Used car interest rates are a crucial factor for both consumers and the automotive market. Understanding potential future trends is essential for informed financial decisions and strategic planning within the industry. This section provides a forecast for the remainder of 2024, considering expert opinions, economic influences, and anticipated consumer behavior.
Forecasting Used Car Interest Rates for the Remainder of 2024
Interest rate projections for used cars in the latter half of 2024 are contingent on various factors, including the overall economic climate, Federal Reserve policy decisions, and the ongoing demand for used vehicles. Several experts anticipate a gradual decrease in interest rates, driven by a potential easing of inflationary pressures and a subsequent moderation in borrowing costs.
Potential Influence of Future Economic Factors
Several economic indicators will likely impact used car interest rates. A sustained period of moderate inflation, alongside a slowing economy, could encourage the Federal Reserve to lower its benchmark interest rates. This, in turn, would likely translate to lower rates for used car loans. Conversely, if inflation persists at elevated levels or if the economy experiences a significant downturn, the Federal Reserve may maintain or even raise interest rates, potentially leading to higher borrowing costs for used car purchases. Historically, fluctuations in the overall economy have correlated with shifts in used car interest rates.
Potential Changes in Consumer Demand
Consumer demand for used cars is a dynamic variable that can influence interest rates. Factors such as the availability of new vehicles, prevailing economic conditions, and consumer confidence can all impact the level of used car demand. A sustained period of economic uncertainty or a sudden increase in the supply of used cars might lead to a decrease in demand, potentially impacting interest rates. Conversely, a robust economy with limited inventory could increase demand and, consequently, put upward pressure on interest rates.
Projected Used Car Interest Rates (Next 6 Months)
| Month | Projected Interest Rate (Average) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| October 2024 | 5.5% | Anticipated easing of inflationary pressures and potential Fed rate adjustments. |
| November 2024 | 5.25% | Further easing of inflation and a continuing positive economic outlook. |
| December 2024 | 5.0% | Continued downward trend in interest rates, potentially driven by sustained economic stability. |
| January 2025 | 4.75% | Potential for continued easing of interest rates as economic conditions remain stable. |
| February 2025 | 4.5% | Continued moderation in inflation and sustained positive economic trends. |
| March 2025 | 4.25% | Moderate inflation and a possible slight slowdown in economic growth. |
Note: These projections are estimates and are subject to change based on unforeseen economic or market developments.
Tips for Finding the Best Used Car Loan Rates
Securing the best possible used car loan rate requires a strategic approach. Understanding the factors influencing rates and employing effective comparison and negotiation techniques are crucial. This section Artikels practical tips to help consumers navigate the used car loan market and secure favorable terms.
Comparing Loan Offers
Comparing different loan offers is fundamental to securing the best rate. Consumers should not settle for the first offer they receive. Thorough research and comparison are essential for obtaining competitive financing. Different lenders offer varying rates and terms, so comparing multiple options is key to maximizing savings.
- Obtain quotes from multiple lenders. Utilize online loan comparison tools or contact several banks, credit unions, and online lenders directly.
- Analyze the terms of each loan carefully. Examine the interest rate, loan duration, and any associated fees.
- Compare the APR (Annual Percentage Rate) across offers. The APR reflects the true cost of borrowing, encompassing interest and other fees.
- Review loan origination fees. These fees can vary significantly and should be considered when comparing offers.
Negotiating with Lenders
Negotiation is an important aspect of securing a better loan. Consumers should not hesitate to engage in negotiations to secure a more favorable rate.
- Be prepared to negotiate. Have a clear understanding of your credit score and the current market rates.
- Research the prevailing interest rates. Using online resources and contacting multiple lenders can provide insight into current market conditions.
- Present your financial situation to the lender. Demonstrate your ability to repay the loan according to the terms Artikeld in the loan agreement.
- Highlight any positive factors that may strengthen your case, such as a strong credit history, a stable income, or a large down payment.
Working with a Financial Advisor
A financial advisor can provide valuable guidance and support in securing a suitable used car loan. They can help navigate the complexities of the process and ensure consumers are making informed decisions.
- Seek professional advice. A financial advisor can provide tailored recommendations based on individual financial situations.
- Leverage their expertise in loan options. Advisors can help explore different loan options available, including those that might not be readily apparent.
- Benefit from their understanding of market trends. Financial advisors can provide insights into current interest rate trends and inform the decision-making process.
- Gain insights into creditworthiness. A financial advisor can assess creditworthiness and advise on strategies to improve it if necessary.