Understanding Used Car Extended Warranties

Used car extended warranties can provide peace of mind and financial protection, but it’s crucial to understand the nuances before committing. These warranties extend beyond the manufacturer’s original coverage, offering varying levels of protection for pre-owned vehicles. Knowing the types, coverage, and terms is essential for making an informed decision.
Different Types of Extended Warranties
Used car extended warranties come in various forms, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. Powertrain warranties often cover the engine, transmission, and other crucial components. Comprehensive warranties, on the other hand, might encompass a broader range of mechanical and electrical systems. Furthermore, some warranties might include roadside assistance, towing, or even rental car reimbursement. The type of warranty chosen should align with the specific needs and concerns of the car buyer.
Comparison of Warranty Provider Coverage
Different providers offer varying levels of coverage for used cars. Some warranties focus on specific components, like the engine and transmission, while others encompass a broader array of mechanical and electrical systems. The extent of coverage is directly tied to the price paid and the duration of the warranty. It is vital to scrutinize the fine print of each warranty to determine what is and isn’t covered.
Terms and Conditions
Extended warranty contracts typically Artikel specific terms and conditions. These include the duration of the warranty, the specific parts covered, the deductible amount, and the required maintenance procedures. Understanding these terms is crucial to avoid surprises and ensure the warranty works as expected. Exclusions are equally important, as these define what isn’t covered under the warranty.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Many extended warranties have exclusions and limitations. These typically include pre-existing conditions, wear-and-tear, repairs related to accidents, or damage caused by misuse. Furthermore, some providers may exclude certain components, such as the cooling system or the electrical system. Careful review of the warranty documents is paramount to identifying any limitations.
Example Warranty Provider Comparison
| Provider | Coverage | Price | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warranty Company A | Powertrain, basic electronics | $500 | 24 months |
| Warranty Company B | Comprehensive, including interior | $800 | 36 months |
| Warranty Company C | Engine, transmission, and select components | $650 | 30 months |
Note: Prices and coverage are illustrative examples and may vary significantly depending on the specific vehicle, mileage, and provider. Always refer to the official provider’s website for accurate details.
Factors Influencing Warranty Decisions
Purchasing an extended warranty for a used car is a significant financial decision. Buyers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the cost, considering various factors that influence the necessity and value of such a purchase. Understanding these factors empowers informed choices and helps avoid unnecessary expenditures.
Evaluating the need for an extended warranty involves a comprehensive assessment of the vehicle’s condition, potential repair costs, and the buyer’s individual circumstances. The decision isn’t solely based on price; a deep dive into the vehicle’s history, current condition, and potential future repair needs is crucial.
Vehicle History Reports
Accurate vehicle history reports are essential for evaluating the risk of future repairs. These reports often detail previous accidents, maintenance records, and any outstanding recalls. Analyzing this information provides insights into the vehicle’s overall health and potential maintenance needs. A history report that shows consistent and timely maintenance suggests lower risk, while a history of frequent repairs or accidents indicates higher potential costs. This data allows buyers to assess the vehicle’s reliability and anticipate potential future issues.
Mileage and Age
The car’s mileage and age significantly impact the potential for future repairs. Older vehicles, regardless of mileage, often require more frequent maintenance and repairs as components wear out. Similarly, higher mileage usually correlates with increased wear and tear, potentially exposing the vehicle to more repair needs. Predicting repair needs becomes more challenging with vehicles outside typical service intervals. For instance, a 10-year-old car with high mileage may face a higher likelihood of needing major repairs, compared to a 5-year-old car with lower mileage.
Cost Comparison: Repairs vs. Warranty
Comparing the potential cost of repairs to the cost of an extended warranty is crucial for a rational decision. Potential repairs can vary widely in cost, depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and specific components needing attention. Extended warranties, however, offer a predetermined coverage amount for a set period. This structured approach allows for a more direct comparison between potential repair costs and warranty premiums.
Potential Repair Costs vs. Warranty Premiums
The table below illustrates a hypothetical comparison of potential repair costs and warranty premiums for different age/mileage brackets. Note that these figures are estimates and actual costs can vary greatly.
| Age/Mileage Bracket | Estimated Potential Repair Cost | Estimated Warranty Premium |
|---|---|---|
| 3-5 years / 30,000-50,000 miles | $500-$1,500 | $300-$700 |
| 6-8 years / 50,000-80,000 miles | $1,000-$3,000 | $500-$1,200 |
| 9-11 years / 80,000+ miles | $2,000-$5,000+ | $800-$1,800+ |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Extended Warranties
Extended warranties for used cars can be a complex decision, often weighing potential cost savings against the risk of unnecessary spending. Understanding the intricacies of these warranties is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with individual needs and financial circumstances.
Potential Cost Protection
Extended warranties offer the potential to shield buyers from significant repair costs. A breakdown or major component failure during the warranty period can be covered, potentially saving the buyer thousands of dollars. For example, a used car with a known or suspected mechanical issue could benefit from an extended warranty, protecting the buyer from the high expense of a potential repair. This cost protection is particularly valuable for high-value repairs or unexpected issues. However, this protection comes at a cost.
High Premiums and Limited Coverage
Extended warranties often come with premiums that can be substantial. The cost of an extended warranty varies widely depending on the car’s make, model, age, mileage, and the specific coverage offered. It’s crucial to compare quotes from different providers to find the most cost-effective option. Moreover, coverage is often limited. The warranty may exclude certain types of repairs, or have specific mileage or time limits, reducing the scope of protection. For instance, a warranty might exclude routine maintenance or wear-and-tear issues. The limitations of coverage need to be carefully examined.
Unnecessary Spending
The decision to purchase an extended warranty frequently involves assessing the likelihood of incurring significant repair costs within the warranty period. If the car is well-maintained and the buyer is confident in its mechanical condition, the expense of the warranty might be unnecessary. Factors like the car’s age, mileage, and maintenance history should be considered. For example, a well-maintained used car with low mileage and a comprehensive service history might not need an extended warranty. Similarly, an older car with higher mileage might have a higher likelihood of needing costly repairs, potentially justifying the expense of an extended warranty. Buyers must thoroughly evaluate the risks and rewards.
Pros and Cons of Buying an Extended Warranty
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Potential cost savings on major repairs. | High premiums that can be substantial. |
| Peace of mind knowing that significant repairs are covered. | Limited coverage, potentially excluding certain repairs. |
| Protection against unexpected breakdowns. | Risk of unnecessary spending if the car is well-maintained. |
| Potential to avoid large, unforeseen repair costs. | Specific mileage or time limits on coverage. |
| May be a worthwhile investment for high-value repairs. | Comparison shopping is crucial to get the best value. |
Negotiating Extended Warranties

Securing a fair price for an extended warranty on a used car requires strategic negotiation. Understanding the factors influencing warranty pricing and the dealer’s role in the process is crucial. Effective negotiation tactics, coupled with a thorough understanding of the warranty’s terms, can significantly impact the final cost.
Strategies for Fair Pricing
Negotiation for extended warranties involves recognizing the value proposition and considering the potential risks and benefits. Factors like the vehicle’s age, mileage, and overall condition, along with the warranty’s coverage duration, play a critical role. The more comprehensive the coverage, the higher the cost is likely to be. A thorough pre-purchase inspection can reveal potential issues that could impact warranty claims, making it essential to understand the vehicle’s history. Understanding the market value of comparable warranties for similar vehicles is also helpful in establishing a fair price.
Dealer Influence on Warranty Terms
Dealers often have a significant influence on the warranty terms and pricing. They typically offer a range of warranty options, each with different levels of coverage and corresponding costs. Their negotiating position is based on the perceived value of the warranty and the dealer’s profit margin. Acknowledging this influence and being prepared to walk away from an unfavorable deal is crucial in the negotiation process. Knowing the dealer’s profit margin on the warranty is not readily available, but researching comparable deals can offer insight.
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Effective negotiation tactics involve presenting a well-researched case, outlining the vehicle’s condition and the desired coverage. Begin by researching similar warranties in the area and using this as a benchmark. Express your willingness to walk away if the terms aren’t favorable, demonstrating your commitment to getting a fair deal. Be prepared to negotiate the price, coverage duration, and any exclusions within the warranty. Understanding the dealer’s profit margin on warranties is not readily available, but researching comparable deals can offer insight.
Understanding Warranty Terms
Before signing any extended warranty contract, it’s imperative to thoroughly review all terms and conditions. This includes details on covered repairs, exclusions, deductibles, and the claim process. Understanding the warranty’s limitations and exclusions can prevent future disputes. Carefully scrutinize the fine print and seek clarification on any ambiguous language. Be aware of potential limitations on coverage based on factors like vehicle modifications or usage patterns.
Step-by-Step Negotiation Guide
- Research comparable warranties: Gather information on similar warranties offered for vehicles with similar specifications and mileage.
- Assess the vehicle’s condition: Conduct a thorough pre-purchase inspection to understand any potential maintenance or repair needs that might impact warranty claims.
- Develop a negotiation strategy: Based on your research and the vehicle’s condition, determine a realistic price range for the warranty.
- Present a well-researched case: Highlight the value proposition of the warranty, emphasizing its coverage and potential benefits, while presenting your understanding of the market rate for similar warranties.
- Express your willingness to walk away: If the dealer’s offer is significantly above your researched value, be prepared to walk away from the deal. This firmness often leads to more favorable terms.
- Thoroughly review the warranty contract: Before signing, scrutinize every clause, condition, and exclusion. Clarify any ambiguous language and seek clarification on any uncertainties.
- Seek legal counsel if needed: If you have any doubts about the contract’s terms or legal implications, consult with a legal professional.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Purchasing an extended warranty for a used car can be a significant financial decision. Understanding potential pitfalls is crucial to making an informed choice. Carefully scrutinizing the warranty’s terms and conditions can save you from costly surprises down the road.
Misleading advertising and hidden costs are common tactics used to entice buyers. Knowing how to recognize these pitfalls can prevent you from overpaying for a warranty that doesn’t adequately protect your investment. A thorough understanding of coverage and exclusions is vital to avoid unexpected repair bills.
Identifying Misleading Warranty Advertising
Used car extended warranties are often advertised with broad, appealing language. However, these promises can sometimes mask crucial details. Be wary of claims that are too good to be true. Research the specific terms and conditions of the warranty rather than relying solely on advertisements. Compare the advertised benefits to the actual coverage to ensure it aligns with your needs.
Verifying Warranty Coverage and Exclusions
Thorough review of the warranty document is essential. Look for specific details regarding covered repairs, the duration of coverage, and any exclusions. Explicitly stated limitations, like mileage restrictions or exclusions for wear-and-tear items, should be carefully evaluated. Compare the warranty’s terms to similar warranties offered by other providers to get a better sense of the value proposition.
Examples of Warranties with Hidden Costs or Limited Benefits
Some warranties may seem comprehensive at first glance but have hidden costs or limited benefits. A warranty that covers only parts, but not labor, could result in significant out-of-pocket expenses. Similarly, a warranty with a short coverage period or high deductibles may not provide adequate protection. Consider warranties that have a high deductible, which may not be worthwhile. A warranty that doesn’t cover routine maintenance, such as oil changes or tire rotations, may seem like a good deal initially but could lead to unexpected costs.
Common Warranty Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
| Pitfall | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Misleading Advertising | Scrutinize the fine print. Compare advertised benefits with actual coverage details. |
| Hidden Costs | Look for additional charges beyond the base price, such as deductibles, administration fees, or mileage restrictions. |
| Limited Coverage | Verify if the warranty covers repairs for parts, labor, or both. Understand the definition of “mechanical breakdown” and the exclusion of wear and tear. |
| Short Coverage Period | Consider the vehicle’s remaining lifespan and the potential for costly repairs. A shorter coverage period might not provide adequate protection if the vehicle is prone to major repairs. |
| High Deductibles | Compare deductibles to the cost of anticipated repairs. A high deductible might not be worth the investment if the risk of a significant repair is high. |
Alternatives to Extended Warranties
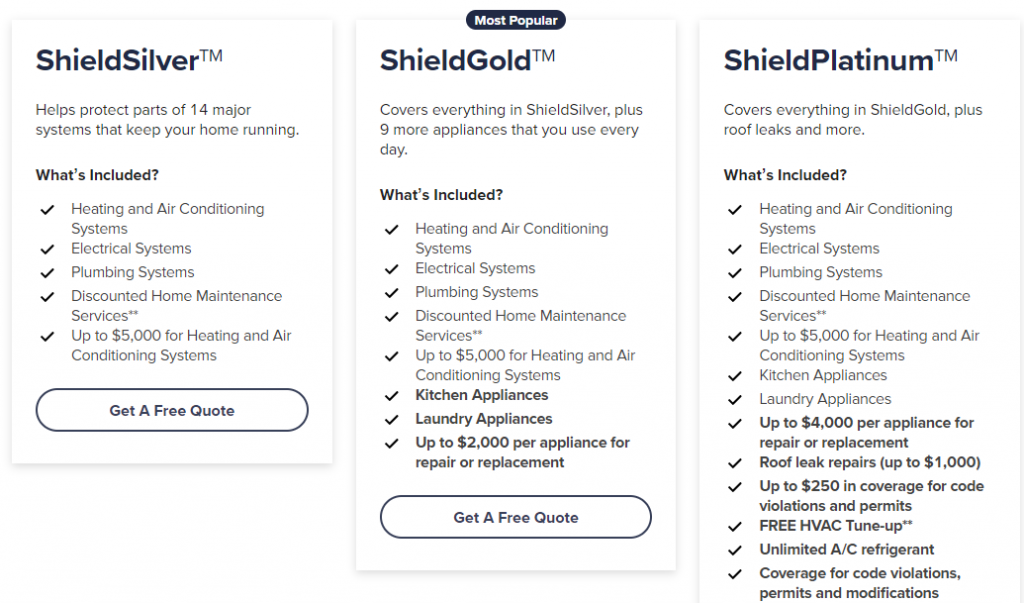
Beyond purchasing an extended warranty, several proactive strategies can effectively mitigate the risk of costly repairs on a used car. These alternative approaches prioritize preventative measures and responsible financial planning, often proving more economical and reliable in the long run.
A comprehensive approach to used car ownership involves more than just the initial purchase. It encompasses a proactive maintenance plan, careful budgeting, and a willingness to address potential issues early. This holistic approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected and expensive repairs, making car ownership a more manageable and predictable experience.
Comprehensive Vehicle Maintenance Plan
A well-structured vehicle maintenance plan is crucial for preventing major repairs. This plan should encompass regular servicing, including oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections of critical components like brakes, tires, and cooling systems. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, or consulting with a trusted mechanic for tailored advice, is vital. Regular inspections and prompt repairs of minor issues can often prevent more significant and expensive problems later.
Budgeting for Potential Repairs
Budgeting for potential repairs is essential. Set aside a specific amount each month to cover routine maintenance and unforeseen mechanical issues. This proactive approach helps avoid financial strain when unexpected repairs arise. This dedicated fund should be separate from general household expenses, ensuring its availability when needed. Consider using a savings account or dedicated vehicle fund to track and maintain these funds. A good rule of thumb is to allocate a percentage of your monthly budget specifically for vehicle maintenance. For example, setting aside 5-10% of your monthly income can provide a cushion against potential repair costs.
Preventive Maintenance Measures
Implementing preventive maintenance measures can significantly reduce the need for costly repairs. These measures include:
- Regularly checking tire pressure and tread depth.
- Inspecting fluid levels (brake fluid, coolant, power steering fluid) regularly.
- Monitoring warning lights and addressing them promptly.
- Conducting visual inspections of the car’s exterior and undercarriage for signs of damage or wear.
- Following a consistent schedule for routine maintenance, like oil changes and filter replacements, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
These proactive steps can help identify and resolve minor issues before they escalate into major, expensive problems.
Comparison of Extended Warranties and Alternative Strategies
The following table highlights a comparison between extended warranties and alternative maintenance strategies:
| Feature | Extended Warranty | Alternative Maintenance Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Upfront premium cost, potential for high premiums | Ongoing, lower-cost expenses spread out over time |
| Control | Limited control over repair choices; often dictated by warranty terms | Complete control over maintenance schedule and repair decisions |
| Coverage | Defined coverage based on warranty terms; potential for exclusions | Comprehensive preventative measures; addressing potential issues proactively |
| Predictability | Potential for unforeseen costs if repair exceeds warranty limits | More predictable costs associated with regular maintenance |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility in repairs or maintenance choices | Flexible schedule and choices in maintenance and repairs |
Understanding Warranty Coverage Details
Decoding the fine print of a used car extended warranty is crucial to avoid unpleasant surprises down the road. Knowing exactly what’s covered and what isn’t empowers you to make an informed decision. This section dives into the specifics of warranty coverage, providing examples and clear explanations.
Various Warranty Coverage Options
Understanding the different coverage options available is key to choosing the right warranty. Extended warranties for used cars often come with a range of options, varying in terms of duration, components covered, and repair costs. Some warranties might focus on specific parts, such as the engine or transmission, while others offer broader coverage. This diversity ensures that buyers can select a plan tailored to their needs and budget.
- Comprehensive Coverage: These warranties typically cover a wide range of mechanical components, including the engine, transmission, electrical systems, and more. The extent of coverage is often Artikeld in the warranty document. A comprehensive warranty is generally more expensive but offers greater peace of mind.
- Limited Coverage: These warranties are often more focused on specific components, such as the engine or powertrain. The cost is generally lower, but the coverage scope is narrower. Understanding which components are included is vital.
- Parts-Only Coverage: This type of warranty typically covers only the cost of replacement parts, not labor. This is often a more budget-friendly option, but it’s crucial to understand that labor costs will still need to be factored in.
Interpreting Warranty Terms
Carefully reviewing the warranty terms and conditions is essential. These documents often contain specific definitions, exclusions, and limitations. Understanding these details helps you avoid misunderstandings later. Pay close attention to the following:
- Exclusions: Warranties frequently exclude certain components, such as cosmetic damage, wear and tear, or damage caused by misuse. Identifying these exclusions helps in managing expectations.
- Deductibles: Many warranties have deductibles, which are the amounts you’ll need to pay out-of-pocket before the warranty kicks in. Knowing the deductible amount is crucial for financial planning.
- Repair Procedures: Some warranties may require specific repair procedures or authorize only certain repair shops. Understanding these restrictions ensures a smooth repair process.
Understanding What’s Covered and Not Covered
A crucial step in evaluating a warranty is to determine what is and isn’t covered. This involves a thorough examination of the warranty document and the associated fine print. Look for explicit statements outlining the coverage details.
- Covered Components: Warranties typically specify the parts or systems they cover, such as the engine, transmission, electrical system, or air conditioning. Understanding these components is vital.
- Exclusions: It’s equally important to identify what’s excluded. Common exclusions include normal wear and tear, damage from accidents, and repairs caused by negligence. Knowing the exclusions allows you to avoid potential disputes later.
Identifying Typically Covered Components
Most used car extended warranties cover critical mechanical components. However, the specific components covered can vary significantly based on the warranty provider and the terms of the agreement.
- Engine and Transmission: These are frequently covered components, especially in comprehensive warranties.
- Electrical System: This includes components like the starter, alternator, and wiring harness.
- Cooling System: Components like the radiator, water pump, and hoses may be included.
- Brakes and Suspension: These are often covered components, but there might be limitations.
Comprehensive Table of Coverage Options
This table provides a general overview of coverage options for used car warranties. Note that specific terms and conditions will vary significantly by provider.
| Coverage Type | Description | Typical Components Covered | Potential Exclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive | Broad coverage of major vehicle systems | Engine, transmission, electrical, cooling, brakes, suspension | Cosmetic damage, wear and tear, misuse |
| Limited | Focuses on specific vehicle systems | Engine, transmission, or powertrain | Exterior components, interior systems |
| Parts-Only | Covers parts, not labor costs | Specific parts (e.g., engine components, transmission parts) | Labor costs, vehicle diagnosis |