Used Car Value Assessment Methodology

Used car valuations are crucial for both buyers and sellers, ensuring a fair and transparent transaction. Accurate assessments depend on a robust methodology that considers multiple factors influencing market value. This process goes beyond simply looking at the odometer reading; it delves into the intricate interplay of various factors that determine a vehicle’s worth.
Factors Influencing Used Car Valuations
Used car values are not static; they fluctuate based on a complex interplay of factors. These factors encompass the vehicle’s inherent characteristics, market conditions, and external influences. Understanding these elements is vital for accurate valuations. The condition of the vehicle, including its mechanical integrity, exterior appearance, and interior wear, plays a significant role. Similarly, the model year, the vehicle’s mileage, and the features it offers directly impact its value proposition.
Methods for Assessing Used Car Value
Various methods are employed to assess the value of a used car. These approaches typically combine data analysis with expert judgment. One common method is the comparison approach, which involves analyzing the prices of similar vehicles in the market. Another approach is the cost-to-replace approach, where the value is determined based on the cost of acquiring new or equivalent parts and labor to restore the car to its original condition. Finally, the residual value approach considers the predicted future value of the vehicle. The choice of method depends heavily on the specific vehicle being assessed and the available market data.
Comparison Approach
This method involves comparing the used car to similar vehicles in the market. Key factors include model year, mileage, condition, and features. Databases and online marketplaces provide a wealth of data for this comparison. For example, a 2018 Honda Civic with 50,000 miles and in excellent condition might fetch a higher price than a similar vehicle with 100,000 miles and minor damage. The comparison method provides a strong baseline for estimating value.
Cost-to-Replace Approach
This method assesses the cost of replacing the car’s components and labor to restore it to its original condition. This approach accounts for the car’s current condition and potential repairs. A car requiring extensive repairs will have a lower value than one in excellent condition. It considers the cost of parts, labor, and potential unforeseen issues. This approach is crucial for evaluating vehicles with significant damage or maintenance needs.
Residual Value Approach
This approach anticipates the future value of the vehicle based on its projected depreciation and the prevailing market conditions. This method is particularly useful for evaluating vehicles with long lifespans. For example, a used truck with a strong resale history and anticipated demand will likely have a higher residual value compared to a car with a shorter lifespan and declining market interest. Residual value estimations incorporate factors such as projected mileage, market trends, and the vehicle’s anticipated demand.
Structured Method for Comprehensive Used Car Value Assessment
A structured approach to used car valuation organizes the various factors for a comprehensive evaluation. This process involves systematically collecting data on the vehicle, assessing its condition, and comparing it to similar models in the market. It requires careful consideration of all aspects of the car.
Weighting of Factors in Determining Used Car Value
| Factor | Weighting (Example) |
|---|---|
| Model Year | 30% |
| Mileage | 25% |
| Condition (Exterior & Interior) | 20% |
| Features | 15% |
| Market Demand | 10% |
This table illustrates an example of how different factors might be weighted in determining a used car’s value. The specific weighting will vary based on the make, model, and market conditions. The provided example is not exhaustive and can be adjusted depending on the circumstances.
Edmunds Used Car Valuation Data
Edmunds’ used car valuation data is a crucial resource for consumers seeking accurate and up-to-date information on vehicle values. This data, derived from a sophisticated methodology, is essential for informed purchasing decisions, facilitating negotiations, and understanding market trends. The platform’s valuation process is designed to provide reliable estimates, taking into account a wide array of factors that influence used car prices.
The Edmunds used car valuation process leverages extensive data sets, including real-world transaction data, market research, and expert input to provide highly accurate estimates. This detailed information allows users to make informed decisions about used vehicles. The platform’s analysis encompasses a vast array of vehicle types, models, and years, reflecting the complexities of the modern used car market.
Data Points in Edmunds’ Valuation Process
Edmunds utilizes a variety of data points to generate its valuation estimates. These include but are not limited to: the vehicle’s mileage, condition, trim level, options, and location. The platform also considers external factors like market trends, economic conditions, and supply and demand.
Types of Data Used for Valuation Estimates
Edmunds gathers data from various sources, creating a comprehensive dataset for valuation estimates. This includes dealer transactions, private party sales, auction data, and consumer reports. The platform also uses publicly available data, like government regulatory information, to ensure its valuations reflect the current market.
Historical Trends in Used Car Values
Historical trends in used car values are crucial for understanding market dynamics and making informed decisions. Edmunds tracks these trends, observing factors like the impact of economic downturns or the rise and fall of specific vehicle models. These historical trends provide a framework for interpreting current market conditions. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the used car market experienced significant price fluctuations due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand.
Comparison of Edmunds’ Valuations to Other Sources
The accuracy of Edmunds’ valuations is crucial for consumers. A comparison with other major online sources, such as Kelley Blue Book (KBB) and NADA Guides, can provide insight into the reliability of the platform.
| Valuation Source | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Edmunds | Comprehensive data, detailed vehicle information, expert input. | May not be completely consistent with every other source in all cases. |
| KBB | Widely recognized, frequently updated data. | Potentially less detailed analysis of specific vehicle features. |
| NADA Guides | Industry-standard valuation for professional use. | Access often restricted to industry professionals. |
The table illustrates that each platform has its strengths and weaknesses. While Edmunds often emphasizes detailed vehicle information and comprehensive data, others may offer more readily accessible or industry-specific valuations.
Vehicle Model and Year Consideration in Valuation
Edmunds’ valuation process accounts for variations in vehicle models and years. Different models and years within a specific make and model often have unique features and values. The platform analyzes the impact of these variations on market value. For example, a higher trim level of a specific model year will typically command a higher price compared to a lower trim level of the same model and year. This consideration of trim level is crucial in accurately reflecting the market value of a used car.
Impact of Market Conditions on Valuation
Used car values are dynamic, constantly shifting based on a complex interplay of economic forces, supply and demand, and seasonal trends. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately assessing the worth of a used vehicle. This section delves into the specific ways in which market conditions influence used car pricing, from the broad strokes of economic downturns to the nuances of seasonal fluctuations and the distinct reactions of various car types.
Market conditions exert a significant influence on used car prices. Economic fluctuations, for example, directly affect consumer spending and borrowing power. During periods of economic downturn, consumers often delay major purchases, including vehicles. This decreased demand, coupled with potentially reduced production due to supply chain issues, can lead to a decline in used car values. Conversely, robust economic growth often translates to increased consumer confidence and spending, boosting demand for used cars, thus driving up prices.
Economic Fluctuations and Used Car Prices
Economic downturns frequently result in reduced consumer spending and borrowing power, impacting the demand for vehicles. A significant drop in consumer confidence can lead to a decline in used car prices. Conversely, periods of economic prosperity often see increased consumer spending, leading to higher demand and, consequently, higher used car values. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis saw a substantial decrease in used car prices as consumers cut back on discretionary spending.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The relationship between supply and demand is fundamental in determining used car values. A high supply of used cars relative to demand will typically depress prices. Conversely, low supply and high demand will push prices upwards. This dynamic is further influenced by factors like production levels, import/export restrictions, and the availability of specific models.
Seasonal Variations in Pricing
Seasonal variations can also impact used car prices. The summer months, for example, often see an increase in demand for vehicles as consumers travel more frequently, leading to potentially higher prices. Conversely, the demand for used cars can decrease in the winter months due to adverse weather conditions and potentially lower consumer spending. Inventory levels may also be affected by seasonal trends, influencing supply.
Impact on Specific Market Segments
Different market segments, such as luxury cars and trucks, react differently to market conditions. Luxury cars, often perceived as discretionary purchases, tend to be more sensitive to economic downturns, experiencing sharper price drops during recessions. Trucks, conversely, might hold their value better during economic slowdowns due to their utility and robustness, potentially even experiencing increased demand. Demand for specific models, such as those used for work or specific travel purposes, will also be impacted by seasonal and economic conditions.
Table: Impact of Market Conditions on Used Car Prices
| Market Condition | Impact on Used Car Prices |
|---|---|
| Economic Downturn | Decreased demand, lower prices |
| Economic Prosperity | Increased demand, higher prices |
| High Supply, Low Demand | Lower prices |
| Low Supply, High Demand | Higher prices |
| Summer Months | Increased demand, potentially higher prices |
| Winter Months | Decreased demand, potentially lower prices |
| Luxury Cars | More sensitive to economic downturns |
| Trucks | Often hold value better during slowdowns |
Factors Affecting Used Car Condition
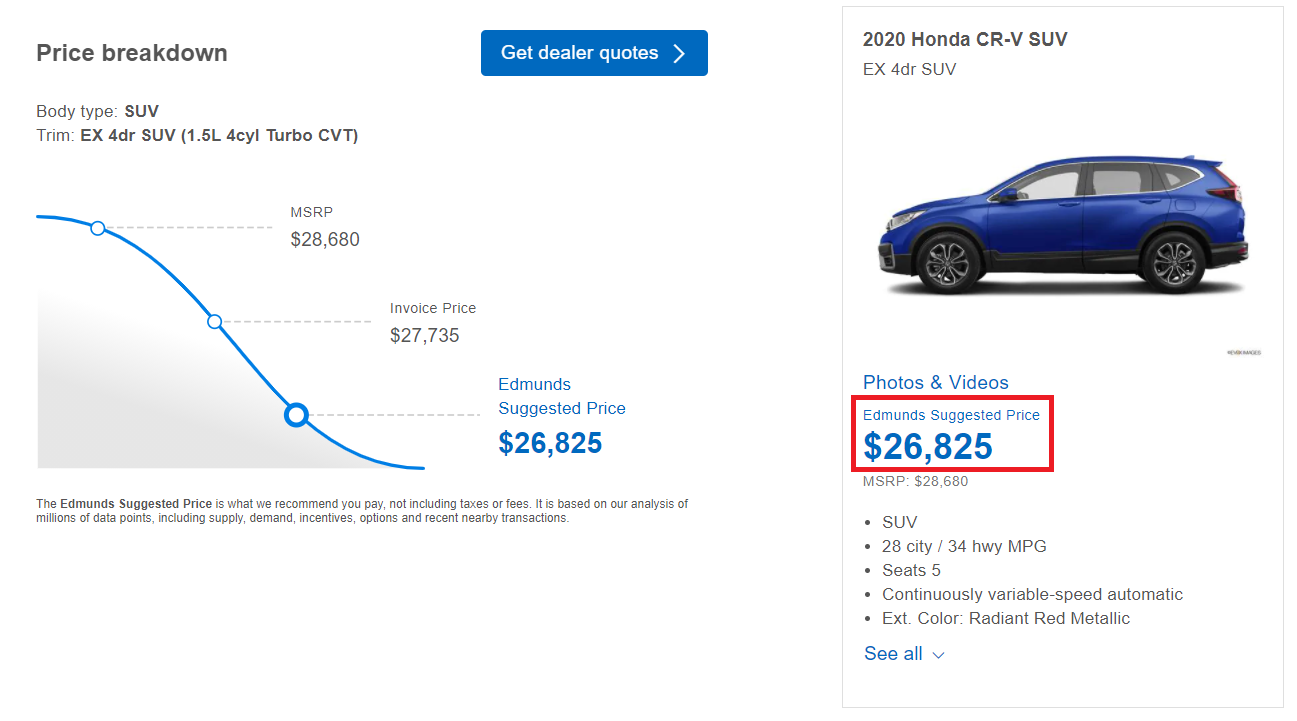
Used car values are significantly impacted by the vehicle’s condition. A well-maintained and undamaged car will command a higher price than one with significant wear and tear or damage history. Understanding these factors is crucial for both buyers and sellers to make informed decisions.
Vehicle condition encompasses a wide range of factors beyond just cosmetic appearance. It includes the extent of any damage, the vehicle’s maintenance history, and the overall wear and tear experienced over its lifetime. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in determining the final selling price.
Importance of Vehicle Condition in Valuation
Vehicle condition is paramount in used car valuation. A pristine, accident-free vehicle with a complete service history will typically fetch a higher price than one with visible damage, a questionable maintenance record, or a history of significant wear and tear. Buyers are willing to pay a premium for vehicles that are likely to require minimal future investment in repairs or maintenance. This translates to a higher return on investment for the buyer.
Effects of Damage Types
Different types of damage affect a used car’s value differently. Accidents, particularly those involving significant structural damage, can drastically reduce a vehicle’s worth. The severity of the damage, the repair quality, and the type of damage (e.g., fender bender vs. frame damage) are key factors. Minor repairs, such as a repairable dent or a repainted fender, might not significantly affect the price, whereas major accident damage with extensive repairs could considerably reduce the value. Even seemingly minor damage, like scratches or faded paint, can impact a car’s perceived condition and thus its value.
Role of Maintenance History
Comprehensive maintenance records are highly valued in used car valuations. A car with a documented service history, including regular oil changes, tire rotations, and other preventative maintenance, often commands a premium. This history suggests the car has been well-cared for, potentially reducing the likelihood of future mechanical issues and costly repairs. A lack of service records or inconsistent maintenance can raise concerns about potential hidden problems, impacting the car’s value negatively.
Correlation Between Vehicle Condition and Price
| Vehicle Condition | Estimated Price Impact |
|---|---|
| Excellent Condition (no damage, complete service history) | High |
| Good Condition (minor damage, complete service history) | Moderate |
| Fair Condition (moderate damage, inconsistent service history) | Low |
| Poor Condition (major damage, incomplete service history) | Very Low |
This table illustrates a general correlation between condition and price. The actual impact can vary based on the specific type and extent of damage, the make and model of the vehicle, and current market conditions.
Impact of Specific Features on Final Value
Specific features, like accident history reports, service records, and repair invoices, significantly influence the final value. A vehicle with a clear accident history report, showing minor damage or no accidents, typically commands a higher price. Conversely, a vehicle with a history of major accidents or undisclosed repairs will have a significantly reduced value. Service records, detailing routine maintenance, can add value by demonstrating the vehicle’s care and reducing the risk of unexpected problems. Repair invoices can provide insight into the extent of repairs performed and their impact on the vehicle’s structural integrity.
Comparative Analysis of Similar Models
Understanding the used car market requires a nuanced approach, especially when comparing similar models. Value assessments aren’t simply about the make and model; factors like trim level, options, mileage, and overall condition play crucial roles. This analysis delves into the intricacies of comparing used car values, highlighting the key differentiators and providing a framework for informed decision-making.
Comparative analysis is vital for buyers seeking the best possible value for their budget. By evaluating models within the same category, one can identify patterns and trends in pricing, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions. It’s crucial to understand the rationale behind variations in pricing for models with ostensibly similar specifications.
Factors Contributing to Value Differences
Differences in used car values for similar models stem from a variety of factors. The presence and quality of added features, as well as the car’s overall condition, significantly impact its market value. Furthermore, the model year, trim level, and specific options available influence the perceived desirability and value.
Impact of Trim Levels and Options
Trim levels and options play a significant role in determining a used car’s value. Higher trim levels often include premium features like upgraded sound systems, advanced safety technologies, and enhanced interior materials. These features can directly affect a car’s desirability and subsequently its value. For example, a higher trim level with leather seats and navigation will typically command a higher price compared to a base model without these options.
Importance of Comparing Used Cars with Similar Mileage, Features, and Years
A crucial aspect of comparative analysis is considering the similarity of the cars being compared. Focusing on models with similar mileage, features, and model years ensures an accurate and meaningful comparison. For instance, a 2020 model with 50,000 miles and leather seats would be compared to other 2020 models with similar mileage and features, rather than older or newer models or those with different equipment levels. This careful selection avoids skewed results.
Illustrative Comparison Table
The table below showcases a hypothetical comparison of used car values for different trims and options of a specific model. This table illustrates the impact of different equipment levels on the used car value.
| Trim Level | Mileage (Miles) | Key Options | Estimated Value ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 50,000 | Standard Features | $20,000 |
| Mid-Range | 45,000 | Leather Seats, Navigation | $22,500 |
| Luxury | 30,000 | Leather Seats, Navigation, Premium Sound System, Heated Seats | $25,000 |
This table is a simplified representation; real-world valuations are affected by market conditions, location, and individual seller negotiation. Note that mileage, condition, and market trends will also influence final pricing.
Geographic Variations in Pricing

Used car values are not uniform across the country. Numerous factors influence pricing, creating significant geographic variations. Understanding these variations is crucial for both buyers and sellers, enabling informed decisions and accurate assessments of market value. Local market dynamics, including supply and demand, play a significant role in shaping prices.
Local market conditions, encompassing factors like economic health and population density, directly impact the price of used cars. High demand in certain areas can drive up prices, while a surplus of vehicles in others can depress them. This disparity extends beyond simply the presence of more or fewer cars; it reflects the complex interplay of economic factors and consumer preferences. For example, areas with robust employment markets and higher incomes often experience higher used car prices.
Impact of Local Market Demand and Supply
Local market dynamics significantly affect used car pricing. Areas with high demand and limited supply often witness premium prices, while regions with an abundance of used vehicles available might experience downward pressure on prices. This principle holds true for specific models and makes, further emphasizing the need for a location-specific assessment of value. This dynamic is influenced by various economic indicators such as employment rates, local income levels, and population density.
Regional Differences in Used Car Pricing Trends
Pricing trends for used cars vary across regions. Coastal areas, often characterized by high housing costs and a concentration of affluent consumers, tend to see higher used car prices. Conversely, rural areas or regions with slower economic growth may experience lower prices. For instance, the demand for certain models of trucks or SUVs might be significantly higher in rural areas due to specific job requirements or transportation needs. This highlights the importance of considering regional characteristics when evaluating used car values.
Geographic Variations in Used Car Prices
The following table showcases the potential geographic variations in used car prices for a hypothetical model: 2020 Honda Civic EX. Prices are estimated and represent potential averages, subject to market fluctuations.
| Region | Estimated Average Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| California | $22,500 |
| Midwest | $20,000 |
| Southeast | $19,000 |
| Northeast | $21,500 |
Note: These are illustrative examples and do not represent definitive data. Actual prices will vary based on individual vehicle condition, mileage, and specific features.
Impact of Local Economic Conditions on Used Car Prices
Local economic conditions directly influence used car prices. Strong employment markets often correlate with higher used car prices due to increased consumer purchasing power. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to decreased demand and lower prices. Areas experiencing rapid population growth might also see increased demand and corresponding price increases. For example, if a region experiences a significant influx of new residents seeking housing and transportation, the demand for used vehicles might surge, leading to higher prices for specific models.
Value Estimation for Specific Vehicle Types
Used car valuations are not uniform across all vehicle types. Factors like design, intended use, and specialized features significantly influence the price. This section delves into the unique valuation considerations for various vehicle types, providing examples and insights into how these variables impact used car values.
Understanding the nuances of specific vehicle types, from SUVs to sports cars, is crucial for accurate assessments. This allows for a more comprehensive and reliable evaluation, accounting for the specific attributes and market demand for each type.
SUV Valuation Considerations
SUVs, with their diverse models and features, exhibit varying valuation criteria. The market often rewards features like spacious interiors, robust cargo space, and advanced safety technologies. Used SUV values are significantly influenced by the vehicle’s overall condition, mileage, and the specific features it offers. For example, an SUV with a powerful engine, four-wheel drive capability, and a premium interior package will typically command a higher price than a comparable, less-equipped model.
Sports Car Valuation Considerations
Sports cars are often valued based on performance, rarity, and collector appeal. Features like horsepower, acceleration, and handling are key determinants. Used sports car values are heavily impacted by the vehicle’s condition, original equipment, and any performance modifications. A meticulously maintained sports car with low mileage and original factory components will usually fetch a higher price than a similar model with significant modifications.
Off-Road Capability Impact on Valuation
Off-road capabilities are a key differentiator for certain vehicle types, particularly SUVs and trucks. The presence of features like four-wheel drive, ground clearance, and specialized suspension systems impacts the value proposition. Used vehicles with robust off-road capabilities are often favored by buyers seeking ruggedness and adaptability. These vehicles frequently command a premium in the market, particularly when in pristine condition and with a proven track record.
Impact of Specialized Features
Specialized features, like performance upgrades, advanced safety systems, and entertainment features, all play a role in determining used car prices. Performance upgrades, such as aftermarket exhaust systems or upgraded suspension components, might increase the value of a sports car or SUV. Advanced safety features, including airbags, electronic stability control, and adaptive cruise control, can boost a vehicle’s perceived safety and reliability, often influencing the price. Entertainment features, such as high-quality sound systems and navigation systems, may add value to a vehicle, especially in higher-end models.
Vehicle Type Value Considerations Table
| Vehicle Type | Key Valuation Considerations | Example Features Impacting Value |
|---|---|---|
| SUVs | Spaciousness, cargo capacity, safety features, off-road capabilities, condition | Four-wheel drive, sunroof, premium interior, advanced safety systems |
| Sports Cars | Performance metrics (horsepower, acceleration), condition, rarity, modifications | High horsepower engine, low mileage, original equipment, aftermarket performance upgrades |
| Trucks | Towing capacity, payload, durability, condition | Heavy-duty suspension, advanced towing packages, off-road features |